Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Environmental Issues is part of Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Environmental Issues.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Botany Chapter wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Environmental Issues |
| Number of Questions Solved | 71 |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Environmental Issues
Plus Two Botany Environmental Issues One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
CPCB stand for
(a) Central pollution consistent board
(b) Central particulate collection & analysis board
(c) Central pollution Control Board
(d) Central phenomenon coexisting Board (pollution)
Answer:
(c) Central pollution Control Board
Question 2.
Catalytic converters may contain expensive metals like……….as catalytic in automobiles
(a) Platinum
(b) Palladium
(c) Rhodium
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
The participation of local communities helps to conserve the forest in sustainable manner. Name the recently started project of Govt, of India.
Answer:
In 1980s Government of India has introduced the concept of Joint Forest Management (JFM).
Question 4.
According to the Central Pollution Control Board, particles that are responsible for causing great harm to human health are of diameter:
(a) 2.50 micrometers
(b) 5.00 micrometers
(c) 10.00 micrometers
(d) 7.5 micrometers
Answer:
(a) 2.50 micrometers
Question 5.
Match the items in column I and column II and choose the correct option:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. UV | i) Biomagnification |
| B. Biodegradable Organic matter | ii) Eutrophication |
| C. DDT | iii) Snow blindness |
| D. Phosphates | iv) BOD |
(a) A-ii, B-i, C-iv, D-iii
(b) A-iii, B-ii, C-iv, D-i
(c) A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
(d) A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-i
Answer:
(c) A-iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
Question 6.
Three-mile Island, Chernobyl incidents are typical example for………pollution
(a) Sound
(b) Radioactivity
(c) Water
(d) Physical
Answer:
(b) Radioactivity
Question 7.
Match correctly the following and choose the correct option
| i) EnvironmeriPProtection Act | A. 1974 |
| ii) Air Prevention and Control of Pollution Act | B. 1987 |
| iii) Water Act | C. 1986 |
| iv) Amendment of Air Act to include noise | D. 1981 |
The correct matches is:
(a) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
(b) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
(c) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
(d) i-C, ii-D, iii-B. iv-A
Answer:
(a) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
Question 8.
Catalytic converters are fitted into automobiles to reduce emission of harmful gases. Catalytic converters change unbumt hydrocarbons into:
(a) carbon dioxide and water
(b) carbon mono oxide
(c) methane
(d) carbon dioxide and methane
Answer:
(a) carbon dioxide and water
Question 9.
In the modern world there are different types of substance that may cause pollution. A prominent waste in the modern computer world is “e-waste” The “e-waste” stand for
(a) Eliminated waste
(b) Eroded waste
(c) Electronic waste
(d) Enriched waste
Answer:
(c) Electronic waste
Question 10.
Humans, as well as other animals, have been dumping their wastes into the environment for thousands of years. What is the reason that this appears to be such a problem today?
Answer:
The human population is increasing rapidly, produc-ing more wastes, and a significant amount of the wastes are non-biodegradable.
Question 11.
Air pollution is maximally caused by
(a) Household detergents and pesticides
(b) Automobile exhausts and chemicals from industry
(c) Sewage and pesticides
(d) Sewage and industrial effluents
Answer:
(b) Automobile exhausts and chemicals from industry
Question 12.
Observe the figure given below. Identify the equipment and write its use.
Answer:
Scrubber: A Scrubber can remove gases like sulphur dioxide.
Question 13.
Government of India has instituted an award for individuals or communities from rural areas who have shown extraordinary courage and dedication in protecting wild life. Name that award.
Answer:
Amrita Devi Bishnoi Wildlife Protection Award.
Question 14.
Ecological sanitation is a sustainable system of handling human excreta, using dry composting toilets. Write the advantages of this method.
Answer:
It is Hygienic .efficient, cost effective and human excreta can be recycled into a natural fertilizer.
Question 15.
Choose the correct answer. Substances that cause biomagnification are
(a) Mercury and DDT
(b) Mercury and Phosphorus
(c) DDT and Phosphorus
(d) Phosphorus and nitrogen
Answer:
(a) Mercury and DDT
Question 16.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill in the blank. Green house effect: carbon dioxide; ozone depletion:…………..
Answer:
Chlonofluorocarbons.
Question 17.
Choose the correct statement regarding biomagnification in an aquatic ecosystem.
(a) Decrease in concentration of the toxicant in successive tropic levels.
(b) Higher concentration of toxicant is seen in the first trophic level.
(c) Bird population is least affected.
(d) Causes decline in bird population.
Answer:
(d) Causes decline in bird population.
Question 18.
In 1986 Govt, of India passed Environment Act. Write the purpose of its implementation.
Answer:
To protect and improve the quality of our environment (air, water, and soil).
Question 19.
The participation of local communities helps to conserve the forest in sustainable manner. Name the recently started project of Govt, of India.
Answer:
In 1980s Government of India has introduced the concept of Joint Forest Management (JFM).
Question 20.
Give the term for reradiating of heat radiations by atmosphere dust, water vapours, CO-2 CH-4, O2, etc.
Answer:
Green house effect
Question 21.
How CFCS cause the depletion of Ozone shield?
Answer:
By producing active chlorine which breaks ozone.
Plus Two Botany Environmental Issues Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Expand CPCB – Write its significance.
Answer:
CPCB – Central Pollution Control Board.
CPCB – Aims for controlling particulate matter in the air. According to CPCB the particulate size 2.5 micrometers or less than in diameter (PM 2.5) are responsible for causing greatest harm to human health.
Question 2.
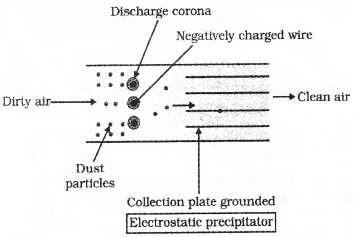
Working condition of electrostatic precipitator is given. By analysing the figure explain the process.

Answer:
At high voltage the electrons produced are attached to dust particles giving them a net negative charge. These charged dust particles are attracted by collecting plates. Then reducing the velocity of air between the plates which help the dust to fall.
Question 3.
Pollutant free Metropolitan cities can be raised by the use of CNG.
- Expand CNG?
- What are the?
Answer:
1. CNG is compressed natural gas.
2. advantages of CNG:
- CNG is better than diesel
- It burns most efficiently
- CNG is cheaper than petrol or diesel
- It cannot be adulterated like petrol or diesel.
Question 4.
Montreal protocol is a procedure signed at Montreal (Canada) in 1987.
- Identify the environmental issue related to this.
- Which is the chemical causing the environmental problem?
Answer:
- Ozone hole
- Chloro fluro carbons release active chlorine atoms which results in degradation of the ozone in the stratosphere.
Question 5.
“Pollutant free Metroes” – Can this be achieved in future?
OR
Pollutant free Metropolitan cities can be raised by the use of CNG. What does CNG implies? Can you suggest the priorities and limitations of CNG?
Answer:
CNG is compressed natural gas. It burns more efficiently than Petrol and diesel, thus brings down the amount of pollutants from automobiles (unburnt hydrocarbons).
CNG is cheaper than petrol or diesel. It cannot be siphoned out by thieves and adultered like petrol or diesel.
The problem in using CNG as fuel is the difficulty of laying down pipelines to deliver CNG through distribution points.
Question 6.
If motor vehicles are equipped with catalytic converter the pollution rate can be reduced.
- Give reason.
- Catalytic converters have its limitations. Mention the limitations.
Answer:
1. Catalytic converters are used in motor vehicles to reduce pollutants. Catalytic converters convert unburnt hydrocarbons into CO2 and water. The catalytic converter uses expensive metals like Platinum, Palladium or rhodium as catalysts.
2. These catalysts are inactivated if leaded petrol is used.
Question 7.
Particulate and gaseous pollutants along with harmless gases are released from the thermal power plants.
- Name any two harmless gases released.
- Name the most widely used device of removing particulate pollutants from the air. Explain how the device is used.
Answer:
1. NO2 & O2.
2. Electrostatic precipitator
It has electrodes which are maintained at several 1000 watts which releases electrons. These electron attach to dust particle giving them a net -ve charge. The collecting plates attract the charged dust particle. The velocity of air between the plates are lowered to allow dust to fall.
Question 8.
Higher BOD could lower the D.O.
- Do you agree with the statement.
- Give reason.
Answer:
1. Yes.
2. Higher BOD lower the D.O. content of water. D.O. is the dissolved 02 content of water. When organic content is increased in water the D.O. is consumed for its oxidation by bacteria which is referred as BOD (Biochemical Oxygen demand) when B.O.D. is greater the D.O. becomes low.
Question 9.
Pesticide DDT was used to control insect such as mosquitoes and agricultural pests. But DDT persisted in the environment and transported from one trophic level to higher trophic levels.
- Name the phenomenon and explain it.
- What happens to the concentration of DDT in each trophic level?
Answer:
1. Biomagnification.
Biomagnification refers to increase in concentration of the toxicant at successive trophic levels.
2. Non biodegradable toxic substance accumulated by an organism cannot be metabolised or excreted and it is passed to the next higher trophic level.
Question 10.
Sewage from common hospitals if disposed to water bodies may cause the outbreak of serious water-borne diseases.
- Mention 2 water-borne diseases.
- Which is the popular method used to remove hospital waste?
Answer:
- Dysentry, typhoid, jaundice, etc.
- Incineration
Question 11.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Catalytic converter | (i) Solid wastes |
| b) Polyblend | (ii) Agrochemicals |
| c) Organic farming | (iii) Plastic wastes |
| d) Sanitary hand fills | (iv) Air pollution |
Answer:
- Catalytic converters – Air pollution
- Polyblend – Plastic wastes
- Organic farming – Agro chemicals
- Sanitary land fills – Solid wastes
Question 12.
Solid waste can create a major problems in metro cities.
- Which is the best way for the safe disposal of the solid waste
- Classify solid waste into 3 groups, which is the alternative remedy for the use of plastic
Answer:
1. Sanitary land fills.
2. The Solid wastes can be categorised into 3 types
- bio degradable
- Recyclable
- non-biodegradable.
The biodegradable waste material can be disposed in deep pits for natural break down. Recycling of material is made easy by the separation done by rag pickers.
Non-biodegradable waste should reduced by using eco-friendly packaging & natural fiber carry bags. State government can play important role by applying laws for reducing the use of plastics.
Question 13.
Integrated organic farming is a zero waste procedure.
- Do you agree with the statement.
- Give reason.
Answer:
1. Yes.
2. Integrated organic farming is a cyclical zero waste procedure, where waste products from one process are cycled and act as nutrients for other processes. This allows the maximum utilization of resources and increases the efficiency of production.
For example if dung is used as manure for the crop, the crop waste can be used to create compost which in turn can be used as fertilizer after generating energy needs of the farm.
Question 14.
Analyse the situation given below and comment on it. “Fertilizers from a paddy field flows to nearby pond.’’
Answer:
Presence of large-amount of nutrients caused by sewage disposal causes excessive growth of planktonic algae which imparts distinct color & decreases quality of water & increases mortality of fishes.
Question 15.
Rag pickers do a great job for our nation. Justify this statement.
Answer:
The Solid wastes can be categories into 3 types
- biodegradable
- Recyclable
- non-biodegradable.
The biodegradable waste material can be disposed in deep pits for natural break down. Recycling of material is made easy by the separation done by rag pickers.
Question 16.
Ecologist argued that organic fertilizers are better for the soil than the chemical fertilizers, (hint – organic fertilizers:- green manures, cattle dung, biofertilizers). Write your opinions.
Answer:
Organic fertilizers are better for the soil as they do not cause pollution of soil and water. Chemical fertilizers which drained into the water bodies will cause eutrophication and algal blooms.
They also cause increase in BOD and lead to the destruction aquatic flora & fauna. Organic fertilizers are cheaper they tend to remain in the soil for long period.
Question 17.
Ahmed khan in Bangalore proved himself a good citizen in using his talents in solving a social issue. Comment on his contribution.
Answer:
Ahamed khan in Bangalore who is a plastic sac manufacturer effectively use poly blend – a fine powder produced from recycled plastic & mixed it with bitumen that is used to lay roads.
By doing so he could enhance the water repellent property of bitumen & which in turn help to road life by three times. It also reduced pollution caused by plasticis. It is an example for the effective way for recycling non biodegradable – plastic.
Question 18.
The concentration of DDT like toxins are higher in man and eagle.
- Name the process.
- Give the reason
Answer:
1. Biomagnification
2. Non bio degradable chemical which accumulate in the body of organism and is passed on to the organisms belonging to the next trophic level. Human beings & Eagle belong to the last trophic level of the food chain. Hence the bio magnification threaten human life.
Question 19.

- Identify the process
- Find out the reason for these.
Answer:
1. Biomagnification.
2. The concentration of DDT is increased at successive trophic levels. It starts at 0.003 ppm in water, it can ultimately can reach 25 ppm in fish-eating birds, through biomagnification.
High concentrations of DDT disturb calcium metabolism in birds, which causes the thinning of eggshell and their premature breaking, causing decrease in bird populations.
Question 20.
Integrated organic farming is a zero waste procedure. Do you agree with the statement. Justify.
Answer:
Yes. Integrated organic farming is a cyclical zero waste procedure, where waste products from one process are cycled and act as nutrients for other processes. This allows the maximum utilization of resources and increases the efficiency of production.
Question 21.
Solid waste can create a major problems in metro cities.
- Which is the best way for the safe disposal of the solid waste
- Classify solid waste into 3 groups, which is the alternative remedy for the use of plastic
Answer:
1. Sanitary land fills
2. The Solid wastes can be categorised into 3 types
- biodegradable
- Recyclable
- non-biodegradable.
Non-biodegradable waste should reduced by using eco-friendly packaging & natural fiber carry bags.
Question 22.
Ahmed khan in Bangalore proved himself a good citizen in using his talents in solving a social issue. Comment on his contribution.
Answer:
- Ahmed Khan in Bangalore has found a solution for problem of accumulating plastic waste.
- Polyblend, a fine powder of recycled modified plastic, is mixed with the bitumen that is used to lay roads.
- Bitumen is a water repellant substance helps to increase road life.
- The raw material for creating Polyblend is any plastic film waste that brought about by rag pickers.
Question 23.
In north- eastern state of India major hectors of Forest land is degraded by a mode of cultivation.
- Name the cultivation method
- Explain the procedure of this cultivation
Answer:
1. Jhum cultivation.
2. In Jhum cultivation or slash & burn cultivation, forest land is converted to agricultural land by cutting and burning trees, ash obtained is used as fertilizer for crop cultivation and other land is used for grazing cattle. The process repeated and it leads to deforestation.
Question 24.
What are Euro II norms?
Answer:
- Sulphur be controlled at 350 ppm in diesel and 150 ppm in the petrol.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are to be contained at 42% of concerned fuel.
Question 25.
It has been recorded that the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere has increased by 0.6°C.
- What has caused this increase?
- Explain its consequences.
Answer:
1. Increase in the level of green house gases causes global warming.
2. Its consequences:
- Polar ice caps and glaciers will melt
- rise in sea level
Question 26.
Air pollution causes serious health problems in men, in industries ECP is a fitted in place of exhaust coming from smokestack to control pollution.
- Which is the device used to control Sulphur Dioxide pollution?
- Name the agency of Government of India monitor air pollution.
Answer:
- Scrubber
- CPCB (Central pollution control board)
Question 27.
Higher concentration of DDT is found in third trophic level than first trophic level
- Name the phenomenon associated with the accumulation of DDT
- Bird population is decreased by the accumulation of DDT. How is it occurs?
Answer:
- biomagnification
- DDT affects the calcium metabolism of birds, causes the thinning of egg shell and premature breaking that it result the reduction in bird population.
Question 28.
Many low lying land become submerged in coming centuries due to the increasing temperature of atmosphere
- Name two greenhouse gases causes global warming
- Write down the measures to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases
Answer:
1. Carbon dioxide and chioro fluoro carbon
2. Measures to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases:
- Cutting down the use of fossil fuels
- Reduce deforestation activities.
Question 29.
Plastic film waste that is used to made modified recycle plastic by Ajmal Khan in collaboration with RV College of Engineering
- Name the product formed after the recycling of film waste
- Name the water repellent substances is mixed with modified a plastic to lay down Road in Bangalore city Corporation
Answer:
- Polyblend
- Bitumen
Question 30.
There is a balance between production and degeneration of ozone in the stratosphere.
- Name the gas that disturbs this balance.
- Explain how this balance is disrupted?
Answer:
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- In stratosphere ,UV rays act on CFCs and release active Cl atoms, that degrades ozone releasing molecular oxygen.
Question 31.
The amount of biodegradable organic matter in sewage water can be estimated by measuring BOD.
- Expand BOD
- Write the impact of the discharge of sewage into a river
Answer:
- BOD – Biochemical Oxygen Demand
- Polluted water contains microorganisms they consume lot of oxygen from water for the biodegradation of organic material that Causes sharp decline in dissolved oxygen.
Question 32.
Radiation by nuclear waste is extremely dangerous to organisms.
- Write any two dangers.
- Write the recommendations for the storage of nuclear waste.
Answer:
- Causes mutation at a very high rate At high doses nuclear radiation is lethal
- Nuclear waste must be stored after sufficient pre-treatment. It must be done in suitable shielded containers buried within the rocks, about 500m deep below the earth’s surface.
Question 33.
There is a balance between production and degeneration of ozone in the stratosphere.
- Name the gas that disturbs this balance.
- Explain how this balance is disrupted?
Answer:
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- In stratosphere, UV rays act on CFCs and release active Cl atoms, which degrades ozone releasing molecular oxygen.
Question 34.
Algal bloom and eutrophication are the two effects of water pollution. Write the differences between the two.
Answer:
1. Algal bloom:
Excessive growth of planktonic algae due to the presence of large amount of nutrients in water.
2. Eutrophication: Natural aging of a lake by nutrient enrichment of its water.
Question 35.
Match the items of column A with B.

Answer:

Question 36.
A number of human activities contribute to deforestation.
- Write any one such activity.
- Write the consequences of deforestation.
Answer:
1. Cutting trees for timber and firewood.
2. consequences of deforestation:
- Increase carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere
- Loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction
- Disturbs hydrologic cycle
- Causes soil erosion
Question 37.
In 1980s the Government of India has introduced JFM to conserve forests.
- Expand JFM.
- Write its significance.
Answer:
- Joint Forest Management.
- Participation by local communities for protecting and managing forest and these communities get benefit of various forest products.
Question 38.
Catalytic converters are fitted into automobiles for reducing emission of poisonous gases into the atmosphere. Write its working in reducing pollution.
Answer:
As the exhaust from the automobiles passes through the catalytic converter, hydrocarbons are converted into harmless carbon dioxide and water. Carbon monoxide is changed into carbon dioxide.
Plus Two Botany Environmental Issues Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
As a part of project work, a group of students collected water samples from different locations. Water samples and its BOD contents are given below.
- Analyse the data given below and find out the sample which is highly polluted.
- Give reason. Expand BOD.
| Sample | BOD |
| A | 20% |
| B | 12% |
| C | 8.5% |
| D | 8% |
Answer:
- Sample. A is highly polluted.
- BOD (Biochemical Oxygen demand).- refers to the amount of O2 that is consumed when organic matter is oxidised by bacteria. If greater the BOD of water, the rate of pollution is high.
Question 2.
Global warming leads to so many hazards in the environment.
- What are the green house gases?
- How does it leads to global warming
- Suggest any three methods to control it.
Answer:
1. Green house gases- CFC, N2O, CH4, CO.
2. In the atmosphere green house gases causes re radiation of infrared radiation & results in the over heating of earth. This is called global warming. Global warming causes changes in the climate Eg. EL Nino effect, Increased melting of polar ice caps rise in sea levels & submerging of coastal areas.
3. Suggest any three methods to control it:
- Cutting down the use of fossil fuel,
- Improving efficiency of energy usage,
- Reducing deforestation, planting trees
Question 3.
Ramu is comparing the graph given in the magazine and recognized that the content of aromatic hydrocarbons, CO, and NOx were decreased from 1997 to 2006 period. Give the reason of your findings.
Answer:
The new auto fuel policy introduced by the government of India is to reduce the sulphur,carbon monoxide and aromatics content in petrol and diesel fuels. The above mentioned things can be put in practice by different engine norms.
- Bharat Stage II (equivalent to Euro-llnorms)
- Euro III emission specifications
- Euro-IV
Question 4.
A factory drains its waste water into the nearby lake. It has caused algal bloom.
- How was the algal bloom caused?
- What would be the consequences?
- Name the phenomenon that caused it?
Answer:
- Nutrients of waste water causes extensive growth of planktonic algae or free floating algae (algal bloom).
- Algae use oxygen .biochemical oxygen demand go high, high fish mortality, deterioration of water quality.
- Eutrophication.
Question 5.
The existence of human beings is under great threat due to the uncontrolled emission of green house gases. Can you suggest any 2 remedial measures to reduce this effect?
Answer:
The emission of green house gases can be reduced by cutting down use of fossil fuel, improving the efficiency of energy usage, reducing deforestation planting trees & slows down the growth of human population.
Question 6.
The balance between the formation and degradation of ozone disrupt due to the overuse of chloro fluoro carbons.
- Name the degraded product of chlorofluorocarbon causes of ozone depletion
- Which is the unit used to measure ozone thickness in stratosphere
- Give two diseases affects men due to ozone depletion
Answer:
1. Active chlorine
2. Dobson (Du)
3. Two diseases affects men due to ozone depletion:
- snow blindness
- cataract
Question 7.
In Kerala, the major source of atmospheric pollution comes from automobile sector.
- Expand CNG
- State some novel practical steps to minimize this type of pollution.
- Which is the govt, agency monitor pollution?
Answer:
1. CNG -Compressed Natural Gas.
2. Air pollution can be controlled by using lead free petrol & by using catalytic converters. The catalytic converters convert unburned hydro carbons into CO2, H2O, CO & nitric oxide are converted to CO2 & N2 gas.
3. CPCB (Central pollution control board).
Question 8.
Ozone balance has been disrupted due to enhancement of ozone degradation by CFC’s.
- Enumerate the role of Cl in O3 depletion.
- Give a note on Montreal protocol.
Answer:
1. Ozone is found in the stratosphere It acts as shield by absorbing UV radiation from the sun. UV rays are injurious to living organisms since DNA & proteins of living organism are affected by UV rays. The refrigerators use CFC.
The CFC’s discharged into the atmosphere it reaches the stratosphere. In stratosphere UV rays act on them releasing chlorine atom. Chlorine degrade ozone and releasing molecular oxygen. As the chlorine atom are not consumed in this reaction they remain in the stratosphere & will have permanent & continuing effect on ozone level.
2. Recognizing the deleterious effects of ozone depletion an international treaty known as Montreal Protocol was signed at Montreal(canada) in 1987 & is effective from 1989. This protocol emphasizes to control the emission of ozone depleting substances.
Question 9.
Night blindness is caused by the deficiency of Vitamin. What is the cause of snow blindness.
Answer:
Due to ozone hole the UVB rays reach the earth and its high dose causes inflamation of cornea called snow blindness, cataract, etc. Such an exposure permanently damage the cornea.
Question 10.
Discuss the role of women and communities in protection and conservation of forests.
Answer:
Amrita devi bishnoi wild life protection award (in the name of lady who sacrificed her life for protecting trees), chipko movement( women belonging to garhwal showed courage by hugging trees to protect them from axe of contractors).
Question 11.
If the ESP is not fitted across the way of exhaust come out from thermal power plant. How does it affect humans.
Answer:
The particulate matter present in exhaust spread the air and causes respiratory problems like asthma, chronic bronchitis, hay fever, etc.
Question 12.
Two years ago, the lake was pure, clean and rich in variety of organisms. While now it is colourless, rich in algae and have a dirty smell. Name the pollutants and the phenomenon.
Answer:
The pollutans are phosphatic and nitrogenous in organic fertilisers. The phenomenon is called eutrophication.
Question 13.
Hundred metre surroundings of hospitals and schools are considered as silent zone. Justify it.
Answer:
It is considered as silent zone because in hospitals sound intensity increases the heart beat altering respiratory patterns of patients etc.but in schools it affects the teaching and learning process.
Question 14.
In 1990, the ozone thickness in a particular area was 190 Du while in 2001 and 2005 it was decreased to 150 Du and 135 Du respectively.
- What is the causes of fall of Du level.
- Which is the good ozone situated and named so?
Answer:
1. Itis due to the increased emission of chlorofluro carbons. It causes the upset of balance between formation and degradation of ozone and results in ozone depletion or thinning of ozone layer.
2. Ozone found in stratosphere filter uv rays coming into the earth.
Question 15.
CO and SO2 are pollutants but they are different from, DDT. BHC etc. Do you agree. Give justifications of your answer.
Answer:
Yes. The former pollutants are gaseous, biodegradable and inorganic but latter are organic and non biodegradable.
Question 16.
What you meant by the auto fuel policy of Govt, of India? Name the latest reformed engine norm.
Answer:
The aim of auto fuel policy is to decrease the emission of sulphur, carbon monoxide and aromatics content in petrol and diesel fuels. Euro-IVnorms- April 1, 2010.
Question 17.
Now a days the acuumulation of plastic waste is the major problem because such wastes are non biodegradable. In some places it is used for beneficial purpose
- Name the mixtures used by Ahmed Khan to lay down roads in Bangalore.
- How was it minimized the accumulation of solid wastes?
Answer:
- Polyblend and bitumen.
- The raw material for creating Polyblend is any plastic film waste. So the accumulation of plastic wastes can be controlled.
Question 18.
Thermal Power plants are inevitable in an industrial and densely populated country like our-what harm they do to the environment? Also mention any precaution that could be taken to save our environment.
Answer:
Hot effluents of thermal power plants are generally released in the nearby water bodies. This causes rise in temperature of such water bodies which causes deoxygenation of water leading to decomposition of organic wastes and killing of aquatic animals. Thermal water pollution can be checked by employing dry or wet cooling towers.
Question 19.
Accumulation of solid waste (e-waste) is the major problem in developed countries.
- What do you mean by e-waste?
- Give its ill effects.
Answer:
- It is formed of irreparable computers and other electronic goods.
- During manual recycling of such waters in the developing countries the workers are exposed to toxic compounds present in them.
Question 20.
It is said that the use of refrigerators cause ozone depletion.
- How is it possible?
- Explain the process of ozone depletion.
- Name any one treaty signed in the international level to control this phenomenon.
Answer:
1. The refrigerators emit CFC (Chloro flora carbon).
2. The CFC’s discharged into the atmosphere reaches the stratosphere. In stratosphere UV rays act on them releasing chlorine atom, chlorine Degrade ozone releasing molecular oxygen. As the chlorine atom are not consumed in this reaction they remain in the stratosphere and have permanent and continuing effect on ozone level.
3. Montreal protocol and Kyoto protocol.
Question 21.
Mention the two major environmental issues of global nature.
Answer:
- Increasing greenhouse effect.
- Depletion of ozone in the stratosphere.
Question 22.
Thermal power plants are inevitable in an industrial and densely populated country like ours. What harm do they do to the environment? Also mention any precaution that could be taken to save our environment.
Answer:
- They release particulate and gaseous air pollutants, hot thermal waste kills organisms sensitive to high temperature, indigenous flora ad fauna lose.
- Use of electrostatic precipitator.
Question 23.
1. On seeing bad state of roads in your locality, as a student, you have recommended to the Municipal corporation to use polyblend.
- What is poly blend? Point out its raw material.
- How will it be advantageous?
2. What are e-wastes? Explain the method of their disposal.
Answer:
1.
- It is a fine powder of recycled modified plastic. This mixture is mixed with bitumen used to lay roads. Raw material – Plastic film waste
- Blends of polyblend and bitumen, when used to lay roads, enhances the bitumen’s water repellent properties and helps to increase road life.
2. Irreparable computers and other electronic goods are known as e-wastes. Burried in landfills or incinerated.
Question 24.
Eutrophication is the main problem in of rivers due to the adding of more and more nitrates and phosphates.
- How does it affect aquatic water body
- What is algal bloom?
- How does it related to D.O. in water bodies.
Answer:
- It change the colour and quality of water and causes the mortality of fish
- Presence of large amounts of nutrients in waters also causes excessive growth of planktonic(free-floating) algae, called an algal bloom
- This results in the decrease of D.O. in water.
Question 25.
DDT content in the water of a lake, that supplies drinking water to the nearby villages, is found to 0.0Q3ppm. The kingfishers of that area are reported to have2ppm DDT.
- Why has the concentration increased in these birds?
- What harm will this cause to bird population?
- Name the Phenomenon.
Answer:
1. Increase in concentration of DDT (non biodegradable) from the water bodies (0.003ppm) to the final consumers like kingfishers (2ppm) is due to increase in cone, of DDT in successive tropic levels (eg. Phytoplankton → Zooplanktons → Fishes → King Fishers) of food chain.
2. It affects ca metabolism and finally premature breaking of egg and declining bird population.
3. Biomagnification.
Question 26.
Observe the figure below.
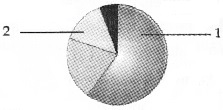
- Identify the greenhouse gases 1,2 and write their percentage of contribution to total global warming.
- Write any four measures to control global warming.
Answer:
1. greenhouse gases 1,2 and write their percentage of contribution to total global warming:
- CO2 – 60%
- CFCs 14%
2. four measures to control global warming:
- Cutting down use of fossil fuel
- Improving efficiency of energy usage
- Reducing deforestation
- Planting trees
Question 27.
Presence of large amounts of nutrients in water cause excessive growth of plankton.
- Name this process.
- Write the dangers caused by this process.
Answer:
1. Algal bloom.
2. Dangers caused by this process:
- Imparts a distinct colour to the water bodies
- Deterioration of the water quality
- Fish mortality
- Toxic to human beings and animals.
Question 28.
Pollutants from man’s activities like effluents from the industries and homes accelerate the aging process of lakes.
- Name this phenomenon.
- Write any four harmful effects of this process.
Answer:
1. Cultural or Accelerated eutrophication.
2. Any four harmful effects of this process:
- Over stimulate the growth of algae
- Cause unpleasant odor
- depletes dissolved oxygen
- Death of fish
Question 29.
CNG is better than diesel. Substantiate this statement writing any four advantage of CNG. Expand CNG.
Answer:
1.
- CNG bums most efficiently
- Cheaper than petrol or diesel
- Cannot be siphoned off by thieves
- cannot be adulterated like petrol or diesel
2. Compressed Natural Gas
Question 30.
Observe the flow chart given below.
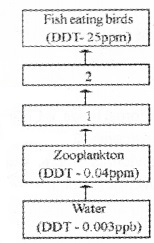
- Fill in the blanks 1 and 2.
- Identify the process illustrated in the flow chart.
Answer:
1.
- Small fish (DDT 0.5 ppm)
- Large fish (DDT 2 ppm)
2. Biomagnification
Question 31.
People in the town of Areata created an integrated waste water treatment within a natural system. Explain the method.
Answer:
The cleaning of waste water is conducted in two stages. In the first stage conventional sedimentation, filtering, and chlorine treatment are given.
Through this step all materials present in water can be removed except dangerous pollutants like dissolved heavy metals.
In the second stage this heavy metal containing water is passed through a series of six connected marshes over 60 hectares of marshland.
In marshy area, plants, algae, fungi, and bacteria were seeded, they can neutralise, absorb and assimilate the pollutants as the water flows through the marshes, after this process water gets purified naturally.
Question 32.
Match the items of column A with B and C.
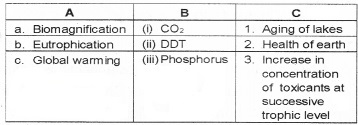
Answer:

Plus Two Botany Environmental Issues NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match the items given in column A and B.
| Column A | Column B |
| a) Catalytic inverter | i) Particulate Matter |
| b) Electrostatic precipitator | ii) carbon monoxide and Nitrogen oxides |
| c) Earmuffs | iii) High noise level |
| d) Landfills | iv) Solid wastes. |
Answer:
(a) – (ii)
(b) – (i)
(c) – (iii)
(d) – (iv)
Question 2.
Write critical notes on following:
- Eutrophication
- Biological magnification
- Ground-water depletion and ways for its replenishment.
Answer:
1. Natural aging of a lake by nutrient enrichment of its water.
2. Biomagnification, also known as bio amplification or biological magnification, is any concentration of a toxin, such as pesticides, in the tissues of tolerant organisms at successively higher levels in a food chain.
3. The level of ground water is falling day by day due to high demand in urban areas as well as in agriculture. Due to over use of surface water, people rely on ground water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use.
About 85% of rural water supply and more than 50% of urban and industrial supply is mined. This results in depletion of ground water.
Ground water can be replenished by-
- Rain water harvesting
- Reduction in consumption and waste.
Question 3.
Why ozone hole forms over Antarctica? How will enhanced ultraviolet radiation affect us?
Answer:
Decline in the thickness of ozone layer over a restricted area is called ozone hole. It was first discovered over Antarctica. Antarctica air is completely isolated from the rest of the world by natural circulation of wind called as Polar Vertex.
CFCs released in the atmosphere slowly enters the stratosphere and wind push them towards the poles. Environmental conditions prevailing in Antarctica during winter months are conductive for the formation of ozone hole.
During winter months, lack of sunlight and low temperature facilitates the formation of ice clouds, which provide the catalytic surface for the reaction of chlorine.
Effect of Ultraviolet Rays
- UV-B radiations are very harmful.Coronea of eye absorbs these radiations and becomes inflamed. This disorder is known as ‘snow blindness’ cataract and leads to diminishing of eye sight.
- UV-B radiations damage skin cells and cause skin cancer.
Question 4.
Discuss the role of women and communities in protection and conservation of forests.
Answer:
Women and tribal communities have played a significant role in protection and conservation of forests. Amritha devi Devi Bishnoi Wild Lide Protection Award, has instituted by government of India for individuals and rural communities for their contribution in protection of wild life.
In 1731, a woman Amritha Devi showed exemplary courage by hugging a tree to prevent its cutting. Her three daughters and hundreds of other Bishnoi followed her. They were killed by soldiers of Jodhpur.
Question 5.
What measures, as ah individual, you would like to reduce environmental pollution?
Answer:
- I will use those articles which are either disposable or can be recycled.
- I would help in tree plantation in my school and surroundings.
- I will minimize the use of fossil fuels.
Plus Two Botany Environmental Issues Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The maximum biological magnification of DDT through food web is seen in.
(a) Bacteria
(b) Algae
(c) Man
(d) Higher plants
Answer:
(c) Man
Question 2.
Eutrophication leads to death of fish due to
(a) Increased O2 content
(b) Increased algae content
(c) Decreased algae content
(d) Decreased O2 content
Answer:
(d) Decreased O2 content
Question 3.
Match the following:-
| A | B |
| 1. The insecticide Act | A. 1968 |
| 2. The water (prevention and control of pollution) Act | B. 1974 |
| 3. The air (prevention and control of pollution)Act | C. 1981 |
| 4. The environment (prevention)Act | D. 1986 |
(a) 1 – d, 2 – c, 3 – b, 4 – a
(b) 1 – a, 2 – d, 3 – c, 4 – b
(c) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c, 4 – d
(d) 1 – c, 2 – d, 3 – a, 4 – b
Answer:
(c) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c, 4 – d
Question 4.
Nitrogen oxides produced from the emission of automobiles and power plants are the source of fine air borne particles which lead to
(a) photochemical smog
(b) dry acid deposition
(c) industrial smog
(d) wet acid deposition
Answer:
(d) wet acid deposition
Question 5.
Drinking of mineral water with very low level of pesticides (about 0.02 ppm) For long periods may
(a) produce immunity against mosquito
(b) cause leukemia (blood cancer) in
(c) cause cancer of the intestine
(d) lead to accumulation of pesticide residues in body fat
Answer:
(d) lead to accumulation of pesticide residues in body fat
Question 6.
The soil pollutants that affect the food chain and food web by killing microorganisms and plants are
(a) nitrogen oxides
(b) pathogens chemical fertilizers
(c) agricultural waste
(d) pesticides
Answer:
(d) pesticides
Question 7.
In a coal-fired power plant, electrostatic precipitators are installed to control emission of
(a) SO
(b) NOX
(c) SPM
(d) CO
Answer:
(c) SPM
Question 8.
Green-house effect is due to the presence of
(a) ozone layer in the atmosphere
(b) moisture layer in the atmosphere
(c) CO2 layer in the atmosphere
(d) infrared light reaching the earth
Answer:
(c) CO2 layer in the atmosphere
Question 9.
Which one of the following pairs pf organisms are exotic species introduced in India?
(a) Ficusreligiosa, Lantana camara
(b) Lantana camara, water hyacinth
(c) water hyacinth, Prosopis cineraria
(d) Nile perch, Ficusreligiosa
Answer:
(b) Lantana camara, water hyacinth
Question 10.
A lake with an inflow of domestic sewage rich in organic waste may result in
(a) drying of the lake very soon due to algal bloom
(b) an increased production of fish due to lot of nutrients
(c) death of fish due to lake of oxygen
(d) increased population of aquatic food web organisms
Answer:
(c) death of fish due to lake of oxygen
Question 11.
A substantial fall in C02 and S02 level has been found in Delhi between 1997 and 2005 due to
(a) use of purified, unleaded petrol
(b) use of purified, unleaded diesel
(c) use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in public transports
(d) use of LiquifiedPetroleam Gas (LPG) in public transports
Answer:
(c) use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in public transports
Question 12.
Electrostatic precipitator is used to remove
(a) CO
(b) particulate matter
(c) lead
(d) secondary pollutant
Answer:
(b) particulate matter
Question 13.
CNG is used to control
(a) water pollution
(b) air pollution
(c) radioactive pollution
(d) thermal pollution
Answer:
(b) air pollution
Question 14.
Major pollutant present in automobile exhaust is
(a) lead
(b) CO
(c) CO2
(d) hydrocarbon
Answer:
(b) CO
Question 15.
If there is no green house gases present in an atmosphere, the average temperature of earth surface is
(a) 100c
(b) 1000 c
(c) 00 c
(d) -150 c
Answer:
(d) -150 c
Question 16.
Deforestation activities and forest fires leads to the rise in global temperature, it is due to
(a) increase in CO level
(b) decrease in CO level
(c) increase in CO2 level
(d) decrease in CO2 level
Answer:
(c) increase in CO2 level
Question 17.
A geing of lake is mainly caused by the accumulation of nutrients such as
(a) N2 & P
(b) N2 & P
(c) P & Ca
(d) Ca & N2
Answer:
(b) N2 & P
Question 18.
Appearance of hole in strato spheric ozone layer is caused by the emission of green gases, it is due to the reaction between
(a) O3 and Cl
(b) O3 and F
(c) O2 and F
(d) O2 and Cl
Answer:
(a) O3 and Cl
Question 19.
The pollutant that seriously affect the marble monuments mainly contains the chemical have the nature is
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) neutral
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) acidic
Question 20.
Chlorinated hydrocarbons enters through one trophic level and its concentration is increased as ppm in successive trophic levels, its nature is
(a) biodegradable
(b) non biodegradable
(c) degradable on combustion
(d) not degradable on combustion
Answer:
(b) non biodegradable
Question 21.
Increase in noise level above particular dB affect the hearing abilities, that is
(a) 20 dB
(b) 60 dB
(c) 80 dB
(d) 150dB
Answer:
(d) 150dB
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Environmental Issues help you. If you have any query regarding the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Environmental Issues, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
