Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Biotechnology and its Applications is part of Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Biotechnology and its Applications.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Botany Chapter wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 |
| Chapter Name | Biotechnology and its Applications |
| Number of Questions Solved | 68 |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Biotechnology and its Applications
Plus Two Botany Biotechnology and its Applications One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Transgenic cotton plant which is resistant to boll worm got the gene from
(a) Bacillus thuringiensis
(b) Spirulina
(c) Dictyostelium
(d) Trichonympha
Answer:
(a) Bacillus thuringiensis
Question 2.
A multinational company outside India tried to sell new varieties of turmeric without proper patent rights. What is such an act referred to?
Answer:
Biopiracy
Question 3.
Name the biological product that obtained from transgenic cow Rosie.
Answer:
Human Alpha Lactalbumin
Question 4.
Name the technique used to prevent the attack of nematode in root of tobacco plants
Answer:
RNA interference
Question 5.
Which is most important method used to correct the genetic defect.
Answer:
Gene therapy
Question 6.
Some times genetically modified organisms will make unpredictable results in future. Which is the organisation of Govt, of India monitor the validity of GM research
Answer:
GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee)
Question 7.
Give an example for organism that possess acidic PH in their stomach?
Answer:
Humans
Question 8.
An important food crop developed by genetic engineering technique solve the problem of it. A deficiency. Name it.
Answer:
Golden rice
Question 9.
The site of production of ADA in the body is:
(a) Bone marrow
(b) lymphocytes
(c) Blood plasma
(d) Monocytes
Answer:
(b) lymphocytes.
Question 10.
In RNAi, genes are silenced using:
(a) ss DNA
(b) ds DNA
(c) ds RNA
(d) ss RNA
Answer:
(c) ds RNA
Question 11.
The first clinical gene therapy was done for the treatment of
(a) AIDS
(b) Cancer
(c) Cystic fibrosis
(d) SCID (Servere Combined Immuno Deficiency resulting form deficiency of ADA)
Answer:
(d) SCID (Servere Combined Immuno Deficiency resulting form deficiency of ADA)
Question 12.
ADA is an enzyme which is deficient in a genetic disorder SCID. What is the full form of ADA?
(a) Adenosine deoxy aminase
(b) Adenosine deaminase
(c) Aspartate deaminase
(d) Arginine deaminase
Answer:
(b) Adenosine deaminase
Question 13.
Siliencing of a gene could be achieved through the use of
(a) Short interfering RNA (RNAi)
(b) Antisense RNA
(c) By both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) By both
Question 14.
Which among the following plants is related with the issues of biopiracy?
(a) Bt cotton
(b) Basmati Rice
(c) Atlas 66
(d) Bt Brinjal
Answer:
(b) Basmati Rice
Question 15.
What is the major disadvantage of insulin taken from slaughtered cattle and pigs?
Answer:
It causes allergy and other types of reactions
Question 16.
Disorder due to ADA deficiency can be over came by…………….
(a) RNA interference
(b) PCR
(c) ELISA
(d) Gene Therapy
Answer:
(b) Gene Therapy
Question 17.
Bacillus thuringiensis produces insecticidal proteins. Why does this protein not kill the Bacillus?
Answer:
Bt toxin exist as inactive protoxins
Question 18.
Very low concentration of DNA of pathogen can be amplified and hence diagnosis becomes easy. Which method is suitable for this method?
Answer:
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Question 19.
Which among the following plants is related with the issues of biopiracy?
(a) Bt cotton
(b) Basmati Rice
(c) Atlas 66
(d) Bt Brinjal
Answer:
(b) Basmati Rice
Question 20.
Crystals of Bt toxin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis do not kill the bacteria themselves because.
(a) Bacteria is resistant to toxin
(b) Toxins only kill animals
(c) Toxin is inactive
(d) Toxin is protein
Answer:
(c) Toxin is inactive
Question 21.
What is the major disadvantage of insulin taken from slaughtered cattle and pigs?
Answer:
It causes allergy and other types of reactions.
Question 22.
RNAi was first introduced in tobacco plants to restrict the infection of a nematode worm………..
Answer:
Meloidegyne incognitia
Question 23.
Manipulation of living organisms by the human race cannot go on any further, without regulations. Which committee in India makes decisions regarding GM research?
Answer:
GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee).
Plus Two Botany Biotechnology and its Applications Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the two uses of PCR technique.
Answer:
- It is used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients.
- It is being used to detect mutations in gene in suspected cancer patients.
Question 2.
Bone marrow transplantation is not permanent cure for ADA deficiency why?
Answer:
Bone marrow transplantation is not permanent cure because the differentiated cells stops the production of ADA after the definite period.
Question 3.
In 1997 American Government got patent for producing a trasgenic plant.
- Name the plant.
- What are the evidences to show that Basmathi rice has been grown in India from centuries?
Answer:
- Basmathi rice.
- There are references of Basmathi rice in ancient texts, folklores, and poetry.
Question 4.
List out the advantages of genetically modified crops.
Answer:
Advantages
- GM crops are more tolerant to abiotic stresses, Reduce post harvest loss
- Increase efficiency of mineral usage
- Increase nutritional value.
- To supply alternate resources in the form of starches, fuels, and pharmaceuticals.
Question 5.
Bacillus thuringiensis produce insecticidal proteins. Called Bt toxins. Explain how Bt toxins works in insects and kill them.
Answer:
Inactive protoxin produced by Bacillus thuringinsis becomes active at the alkaline PH of the insect gut, the activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores that cause cell swelling and lysis.
Question 6.
Bt plants are genetically engineered insect resistant plants.
- What does ‘Bt’ stand for?
- Cite examples for any two ‘cry’ genes which produce Bt toxin.
Answer:
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- Cry I Ac, Cry II Ab.
Question 7.
Serious problems are associated with conventional agriculture.
- Identify the problems
- How is it solved?
Answer:
1. Low crop yield
- Use of expensive agrochemicals.
- The harmful effects of agrochemicals on the environment.
2. These problems can be solved by using genetically modified crops.
Question 8.
Why the crystals of Bt toxin do not kill the bacteria themselves?
Answer:
The toxin is active only at certain alkaline pH inside the gut of the insect. The toxin is inactive inside the bacteria as it exists as protoxin.
Question 9.
Cry genes are of different types.
- Name 3 cry genes.
- Write the uses of proteins produced by these genes?
Answer:
- Cry I Ac, Cry ll Ab, Cry lAb
- Cry IAc& Cry ll Ab – Produces toxic protein to control cotton boll worm Cry lAb – Produce toxic protein to control corn borer.
Question 10.
Insulin in man is normally produced by the (3 cells of the pancreas. But now a days it is commercially produced from bacteria like E.coli and marketed as ‘humulin’.
- Write down the procedure used
- Insulin is not taken from pancreas of slaughtered animals. Why?
Answer:
1. Human insulin was synthesized by American company Eli Lilly by recombinant DNA technology. The 2 DNA sequence coding for A & B polypeptide chain were introduced into E coli. The 2 polypeptide chains are synthesized independently and later linked by disulphide bond to form mature insulin.
2. It causes allergy
Question 11.
Specific genes of nematode are introduced into Tobacco plant through the vector.
- Identify the used vector in above case.
- Explain the role of that introduced gene in the Tobacco plant.
Answer:
- Agrobacterium tumifaciens.
- Offers resistance to the plant by silencing mRNA by the process of RNA interference.
Question 12.
The conventional methods are used for curing ADA deficiency. Identify the conventional methods. Write its demerits.
Answer:
Conventional methods of disease diagnosis like serum and urine analysis are not able to detect low concentration of viruses and other pathogens.
Question 13.
How can PCR detect very low amounts of DNA?
Answer:
PCR is a Polymerase Chain Reaction, which amplifies low amount of DNA making multiple copies of which it helps in the diagnosis of low amount of DNA.
Question 14.
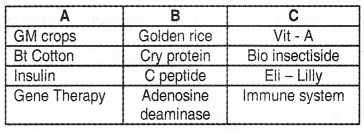
Match the following.
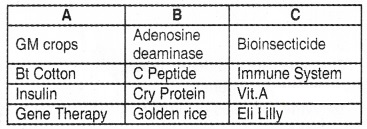
Answer:
Question 15.
Insulin in man is normally produced by Beta cells of pancreas. But now a days it is commercially produced from bacteria like E. coli and marketed as Humulin. Explain how this method is possible.
Answer:
An American company Eli Lilly in 1983 prepared two. DNA sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin and inserted in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Question 16.
One of the applications of biotechnology is the corrective therapy for hereditary diseases.
- Do you agree with this? Which technique is used to achieve this?
- How can this be done?
Answer:
- Yes.Gene therapy
- In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are cultured and functional ADA cDNA is introduced in it. Then, these cells are return back to the patient. These cells can produce adenosine deaminase enzyme.
Question 17.
A nematode is found to be infecting the root of tobacco plant and there by decreasing the yield. Mention a novel technology adopted to check the infestation.
Answer:
The best method used to prevent the attack of nematode is RNA interference (RNAi), It involves silencing of a specific mRNA of nematode.
Question 18.
GM crops prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil. Give reason.
Answer:
GM crops have the ability to resist diseases So the use of chemical pesticide can be decreased. This helps to keep the nitrogen fixing and other useful microbes in the soil as live.
Question 19.
Suppose you have produced a GM plant. Which Govt, organisation will take decisions regarding the validity of your genetic research? Why is such a body necessary?
Answer:
GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee) They take decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing GM- organisms for public services.
Question 20.
Recently you heard a lot about HiNi virus from medias. PCR technique is used for proper diagnosis of the disease by our research institutes. What is the significance of PCR technique in the early diagnosis of H1N1?
Answer:
This technique is used for amplify the viral nucleic acid up to 1 billion copies. This helped in the early diagnosis of diseases.
Question 21.
Name the factors on which behavior of genetically modified organism (GMO) depends.
Answer:
The behavior of GM organism depends on the nature of genes transferred, nature of host plant and animal or bacterium.
Question 22.
What is a DNA probe?
Answer:
DNA probe is a small DNA segment that recognize complementary sequence in DNA molecule and allow identification and isolation of specific DNA sequence from an organism.
Question 23.
Write the two uses of PCR technique.
Answer:
- It is used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients
- It is being used to detect mutations in gene in suspected cancer patients.
Question 24.
How patent is given?
Answer:
Patent is given to
- For producing new product or invention.
- Modified and improved earlier invention.
- Technical know how.
- New designing concept.
Question 25.
Give example of vaccine safety in respect to transgenic animals.
Answer:
Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans. Transgenic mice are being used to test the safety of polio vaccine
Question 26.
Which three options could be thought for increasing food production?
Answer:
- Agro – chemical-based agriculture
- Organic agriculture
- Genetically engineered crop-based agriculture.
Question 27.
What are genetically modified organisms (GMO)?
Answer:
Organisms such as plants, bacteria, fungi, and animals whose genes have been manipulated are known as GMO.
Question 28.
What was the speciality of the milk produced by the transgenic cow Rosie?
Answer:
Contains Human alpha-lactalbumin. Nutritionally more balanced than normal cow milk.
Question 29.
Explain why Bt cotton flowers undergo pollination by butterflies and bees in spite of being insect pest resistance.
Answer:
cotton is genetically engineered to produce a toxin which kills insect pests which eat the plant and cause the damage. Bees and butterflies only forage for nectar in flowers and do not eat any part of the plant so they do not die.
Question 30.
An important food crop developed by genetic engineering technique solve the problem of vitA deficiency.
Answer:
Golden rice is genetically engineered with vitA precursor of carotenoids.
Question 31.
RNA interference takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a metffod of cellular defense. What is RNA interference?
Answer:
It is the silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation or protein synthesis of mRNA.
Question 32.
Pest resistant plants can be developed by genetic engineering. Explain how RNAi is successful in this area?
Answer:
In this process, nematode specific genes are introduced into the host plant through agrobacterium, it produce both sense and antisense RNA, since this two RNAs are complementary to each other, form a dsRNA, RNAi is operated and the nematode can’t produce proteins.
Question 33.
Given below is the diagram showing formation of insulin from pro-insulin. Explain how proinsulin develops to form insulin?
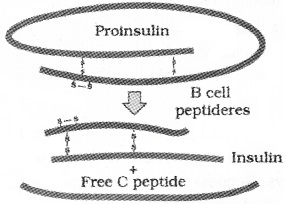
Answer:
Proinsulin is an immature and non functional that contains A, B and C chains, it is matured into insulin by the removal of short c peptide chain.
Question 34.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a four-year-old girl with ADA deficiency.
- Write the steps involved in this method of treatment.
- What is the major disadvantage of this process?
Answer:
1. In this method Lymphocytes taken from the blood of the patient and grown in a culture outside the body, into these, functional ADA cDNA are introduced, after this modified lymphocytes are returned back into the patients body.
2. Since the lymphocytes are not immortal, patient requires periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes.
Question 35.
Given below are two laboratory methods used for molecular diagnosis PCR, ELISA.
- Expand PCR and ELISA
- What is the principle of ELISA
Answer:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay
- Antigen-antibody interaction.
Question 36.
Given below are some biological products, which are produced by transgenic organisms
- a -1 – antitrypsin
- a-lactalbumin
- human insulin
1. Fill in the column given below suitably using the above terms
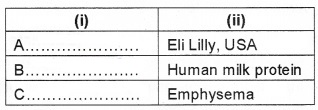
2. ……….is the transgenic cow, which produces human milk protein.
Answer:
1. A = human insulin
B = α lactalbumin
C = α-1-antitrypsin
2. Rosie
Question 37.
Genetically modified plants have been useful in many ways. Suggest some advantages of genetically modified plants in agriculture.
Answer:
- Made crops more tolerant to abiotic stress
- Reduced the use of chemical pesticides
- Reduced post harvest loss
- Increased mineral usage efficiency
Plus Two Botany Biotechnology and its Applications Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Enzyme-Linked Immuno – Sorbent Assay (ELISA) are some of the techniques that serve the purpose of early Diagnosis of disease like AIDS.
- Write the scientific basis of this statement.
- Write the name of pathogen causing AIDS.
Answer:
1. PCR – By amplification of the DNA of virus or bacteria present in the patient helps to identify even the concentration of pathogen is very low in the body of the patient. A single stranded DNA or RNA is tagged with a radio active molecule (probe) is allow to hybridized to its complementary DNA in clone of cells followed by detection using auto radiography .
Thus the mutated gene can be detected as it will not hybridize with the probe. ELISA – Enzyme linked immune sorbent assay is based on the principle of antigen antibody reaction. Infection by pathogen can be detected by the presence of antigen or by detecting antibodies synthesized against the pathogen.
2. HIV-human immuno deficiency virus.
Question 2.
For effective treatment of a disease early diagnosis and understanding its patho physiology is very important. Mention the 3 techniques which are used for the purpose of early diagnosis.
Answer:
PCR-By amplification of the DNA of vims or bacteria present in the patient helps to identify even the concentration of pathogen is very low in the body of the patient.
A single stranded DNA or RNA is tagged with a radio active molecule (probe) is allow to hybridized to its complementary DNA in clone of cells followed by detection using autoradiography. Thus the mutated gene can be detected as it will not hybridize with the probe.
ELISA – Enzyme linked immuno- sorbent assay is based on the principle of antigen-antibody reaction. Infection by pathogen is an antigen it can be detected by the presence of antibodies synthesized against it.
Question 3.
List out the milestones achieved in medicine by the introduction of recombinant DNA technique, citing examples.
Answer:
Recombinant DNA technology have made immense impact in the field of medicine both in diagnosis and therapeutics. Human insulin is produced by E.Coli which is engineered to produce A and B chains of polypeptide.
Gene therapy is curing of disease by delivery of a normal gene into the individual even at the embryo stage. Gene therapy is used to cure Adenosine deaminase deficiency.
Moleculardiagnosis involves PCR (Polymerase chain reaction)and ELISA. In polymerase chain reaction, the genes are amplified it helps to detect viral infection prior to the appearance of symptoms.
Question 4.
Animals that have their DNA manipulated and express foreign gene are called transgenic animals. Write any four characteristics of transgenic animals.
Answer:
1. Transgenic animal can be specifically designed to allow the study of the mechanism of gene expression, its regulation & how they effect the normal function & development.
2. It is also used to study the biological effects of certain gene product & also the biological role of these products in the body.
3. Transgenic animals serve as models for human disease. So that investigation of new treatment for disease is made possible.
Example : Alzheimer’s, cancer, Cystic, fibrosis, etc.
4. Transgenic animal are used produce medicine it is used to treat diseases like Emphysema. The transgenic cow rosie produced human protein enriched milk (alpha- lactalbumin).
5. They are also used for testing the safety of vaccines like polio. It is also used for testing toxicity of drugs.
Question 5.
ADA deficiency is permanently cured by gene therapy.
- Expand ADA.
- Write its normal function in human body.
- If gene for ADA is deleted the person will become susceptible to attack of pathogens and die of ordinary diseases. By analysing the given statement can you explain the role of ADA.
- Can you suggest alternative methods for curing the same disease?
Answer:
- Adenosine deaminase
- It is a crucial enzyme for the immune system to function.
- The patients have non-functioning T- Lymphocytes. So they cannot produce immune responses against invading pathogens.
- Yes. Gene therapy is used for permanent curing of ADA deficiency.
There are two methods for treatment of ADA deficiency.
- by bone-marrow transplantation
- and by enzyme replacement therapy.
Question 6.
Expand
- ELISA
- GEAC
- RNA i
Answer:
- Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay
- Genetic Engineering Approval Committee
- RNA interference
Question 7.
In 1990 first test of human gene therapy was performed in 4-year-old girl ‘De Silva’ with adenosine deaminase deficiency.
- Name the method used to cure the disease
- Explain the procedure of r DNA technology used to recover adenosine deaminase deficiency
- Which is the best cure for this disease?
Answer:
1. Gene therapy.
2. Lymphocytes are taken from patient’s blood it is grown invitro culture. By using retroviral vector functional ADA cDNA (from WBC of normal person) is introduced into vitro cultured lymphocytes These genetically engineered lymphocytes (corrected functional lymphocytes) are reinjected into the patients.
3. If the ADA producing genes are introduced into cells at early embryonic stage it could be a permanent cure.
Question 8.
You have developed a GM plant.
- Which govt, organization will you approach to obtain clearence for its mass production?
- Is such a body is necessary?
- Give two reasons.
Answer:
- GEAC-genetic engineering approval committee
- Yes
- It will make decisions regarding the validity of GM research & the safety of introducing GM organism for public services. It also deals with the patenting problems.
Question 9.
In Tobacco plants pest resistance is achieved by a special technique.
- Name the technique
- Which is the pest killed by this way?
- Explain the method.
Answer:
- RNA interference
- Meloidegyne incognitia(nematode)
- It is the silencing of mRNA done by a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA).
In this technique the pest resistant gene (cDNA) is transferred into host plant by using agrobacterium vector, which become double stranded and silences the mRNA of the pest from expressing inside the host. Thus the plant become resistant to the pest which cannot survive inside the host.
Question 10.
Bacillus thuringienesis is a Bacteria, which produce a toxic insecticidal protein.
- Write down the significance of this bacteria in GMO.
- Insecticidal protein is not harmful to the body of man. Why?
Answer:
1. Bacillus thurungenesis produce a protein Cry protein coded by the cry gene. This protein kill certain insects like lepidopterarns (tobaccobud worm), boll worms, dipterans like mosquitoes.
These genes are isolated from Bacillus thuringenesis and incorporated into several crop plants like cotton. There are specific cry gene for specific toxin and each toxin controls or destroys specific insect.
2. Protein crystals solubilise only in the presence of alkaline pH but stomach of human body contains acidic pH .So it doesn’t make any harmful effect in humans.
Question 11.
Give example of vaccine safety in respect to transgenic animals.
Answer:
Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans. Transgenic mice are being used to test the safety of polio vaccine.
Question 12.
Animals that have their DNA manipulated and express foreign gene are called transgenic animals. Write down the three significance of transgenic animals used as models.
Answer:
1. Normal physiology and development:
To study of how genes are regulated, and how they affect the normal functions of the body and its development.
2. Study of disease:
How genes contribute to the development of disease.
3. Chemical and vaccine safety testing:
Transgenic animals carry genes that sensitive to toxic substances and the effects can be studied.
Question 13.
An early diagonosis of disease can be detected by modern techniques.
- How can PCR detect very low amounts of DNA?
- What is Probe?
Answer:
- PCR is a Polymerase Chain Reaction, which amplifies low amount of DNA making multiple copies of which ft helps in the diagnosis of low amount of DNA.
- It is the single stranded radioactively labelled DNA.
Question 14.
Insecticidal protein crystal are not a solubilized in acidic PH but it is solubilized and become active in alkaline pH. Name the organism possess alkaline PH in their gut?
Answer:
Insects- lepidopterans, coleopterans and depterans.
Question 15.
RNA interference technology is used to prevent transcription process of protein synthesis. Justify the given statement
Answer:
It is used t0 silence the m RNA of nematode by using double-stranded RNA. Here nematode specific genes are introduced into host plant by using agrobacterium vectors, that produce double-stranded RNA and initiated RNA silencing process.
Question 16.
Earlier ADA deficiency can be cured by enzyme replacement therapy or bone marrow transplantation. Write down the procedure used in r-DNA technology to cure the disease.
Answer:
Lymphocytes taken from patients blood it is cultured outside, into this functional ADA cDNA are introduced, then this Lymphocytes are taken back into the patient’s blood. For permanent cure, functional ADA cDNA are introduced into embryonic stage.
Question 17.
Our country is very rich in biodiversity and traditional knowledge. So we have faced many problems related to biopiracy.
- What is biopiracy?
- Give two examples of biopirated plants.
- How can we control biopiracy?
Answer:
- Un authorized use of bioresources and traditional knowledge without compensatory payment
- Basmati rice, turmeric.
- By developing laws and regulations or through patent Bill.
Question 18.
Transgenic animals are those animals whose DNA is manipulated and has an extra or foreign gene to possess and express.
- How can transgenic animals help in testing for vaccine safety.
- Name the enzyme produced by transgenic animal which is used against emphysema.
- For which diseases transgenic models exist?
- Name the first transgenic cow. Write its significance.
Answer:
- Transgenic animals like mice are developed for testing of vaccine before they are used on humans.
- An enzyme a-1-antitrypsin can be obtained from a transgenic animal which is used against emphysema.
- Transgenic model exist for cancer, cystic fibrosis, Alzheimer’s diseases, etc.
- Rosie is the first transgenic cow, was produced human protein enriched milk. The milk contains alpha-lactalbumin in the amount of 2.4 gram per litre and is more nutritionally balanced for
Plus Two Botany Biotechnology and its Applications NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydro carbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Answer:
Oil is lipid synthesized by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol with three molecules of fatty acids. Thus, the oil from the seeds can be removed by preventing the synthesis of either glycerol or the enzyme lipase which catalyses the synthesis of oil. It can be achieved by knocking out the genes coding for the enzyme required for the synthesis of glycerol.
Question 2.
What are cry proteins? Name an organism that produce it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Answer:
- Cry proteins refer to the protein crystals contain¬ing atoxic insecticide.
- It is produced by soil bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis.
- The genes encoding cry proteins called Bt toxin genes were isolated from B. thuringiensis and incorporated into several crop plants such as Bt cotton, Bt corn, etc, to provide resistance against insect pests.
Question 3.
Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Answer:
For making any oral drug or nutritional supplement the action of digestive enzymes has to be taken into account. Most of the antibiotic and vitamin supplements are made in capsule forms to prevent action of HCI in stomach.
For protein preparation the major source is groundnut shells. The protein extracted from the source is predigested so as to make them absorbable by the digestive system.
Question 4.
Find out from internet, what is golden rice?
Answer:
Golden ric is genetically modified and contain Carotene, which is a precursor of Vitamin A.
Question 5.
Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Answer:
No.
Question 6.
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Answer:
Advantage of GM Crops:
- Genetic modification has made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, heat, salt)
- Viral resistance can be introduced.
- Over ripening losses can be reduced eg: Flavr Savr tomato
- Enhanced nutritional value of food eg: Golden rice. Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
Disadvantages of GM Crops:
- Transgenes in crop plants can endanger native species. For example, the gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen might end natural pollinators like honey bees.
- Weeds also become resistant.
- Products of transgene may be allergic or toxic.
- They cause damage to the natural environment.
Question 7.
Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because:
(a) Bacteria are resistant to strain
(b) Toxin is immature
(c) Toxin is inactive
(d) Bacteria encloses toxin a special sac.
Answer:
c) Toxin is inactive
Because Bt toxin is present in the form of protoxin in Bacillus bacterium.
Question 8.
Why does this toxin not kill the Bacillus? How it affects insect?
Answer:
The Bt toxin protein exist as inactive protoxins but once an insect ingest the inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilise the crystals.
The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and create pores that cause cell swell¬ing and lysis and eventually cause death of the insect.
Plus Two Botany Biotechnology and its Applications Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of these is used as vector in gene therapy for SCID?
(a) Arbovirus
(b) Retrovirus
(c) Enterovirus
(d) Parvovirus
Answer:
(b) Retrovirus
Question 2.
Find the incorrect statement.
(a) Gene therapy is a genetic engineering technique used to treat disease at molecular level by replacing defective genes with normal genes.
(b) Calcitonin is a medically useful recombinant product in the treatment of infertility
(c) Bt toxin is biodegradable insecticide obtained from Bacillus
(d) Trichoderma sp.is a biocontrol agent for fungal diseases of plants
Answer:
(b) Calcitonin is a medically useful recombinant product in the treatment of infertility
Question 3.
The technique of DNA fingerprinting was initially developed by
(a) lanWilmut
(b) HarGobindKhurana
(c) Jacque Monod
(d) Alex Jeffreys
Answer:
(d) Alex Jeffreys
Question 4.
Plasmids are suitable vectors for gene cloning because
(a) these are small circular DNA molecules, which can integrate with host chromosomal DNA
(b) these are small circular DNA molecules with their own replication origin site
(c) these can shuttle between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
(d) these often carry antibiotic resistance genes
Answer:
(b) these are small circular DNA molecules with their own replication origin site
Question 5.
Cry II Ab and Cry I Ab Produce toxins that control
(a) cotton bollworms and corn borer respectively
(b) corn borer and cotton bollworms respectively
(c) nematodes and tobacco budworms respectively
(d) corn borer and tobacco budworms respectively
Answer:
(a) cotton bollworms and corn borer respectively
Question 6.
Golden rice was created by transforming rice with two beta-carotene biosynthesis genes, namely.
(a) Psy and Cry 1 genes
(b) LCY-e
(c) CHY-1
(d) CHY-2
Answer:
(a) Psy and Cry 1 genes
Question 7.
Main objective of production / use herbicide resistant GM crops is to
(a) eliminate weeds from the field without the use of manual labour
(b) eliminate weeds from the field without the use of herbicides
(c) encourage eco-friendly herbicides
(d) reduce herbicides accumulation in food articles for health safety
Answer:
(d) reduce herbicides accumulation in food articles for health safety
Question 8.
Biopiracy is related to which of the following?
(a) traditional knowledge
(b) Biomolecules and regarding bioresources
(c) Bioresources
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Bioresources
Question 9.
Genetic engineering has been successfully used for producing
(a) transgenic mice for testing safety of polio vaccine before use in humans
(b) transgenic models for studying new treatments for certain cardiac diseases
(c) transgenic cow-Rosie, which produces high-fat milk for making ghee
(d) animals like bulls for farm work as they have superpower
Answer:
(a) transgenic mice for testing safety of polio vaccine before use in humans
Question 10.
The genetic defect-Adenosine Deaminase deficiency may be cured permanently by
(a) periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes having functional ADA C-DNA
(b) administering adenosine deaminase activators
(c) introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into cells at early embrayonic stages
(d) enzyme replacement therapy
Answer:
(c) introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into cells at early embrayonic stages
Question 11.
RNA interference method involves
(a) Silencing of a specific in RNA due to a complementary ssRNA
(b) Silencing of a specific tRNA due to a complementary dsRNA
(c) Silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary ssRNA
(d) Silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA
Answer:
(d) Silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA
Question 12.
The nematods that infects the roots of tobacco plants and causes a great reduction in yield is
(a) Meloidegyneincognitia
(b) Bacillus thuringiensis
(c) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
(d) Rhizobium meliloti
Answer:
(a) Meloidegyneincognitia
Question 13.
RNAi takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of
(a) Cellular defense
(b) DNA proof reading
(c) Transcription
(d) Translation
Answer:
(a) Cellular defense
Question 14.
The main challenge for production of insulin peptide using rDNA technique was
(a) Getting normal insulin gene
(b) Getting insulin assembled into a mature form
(c) Getting insulin chains formed from bacteria
(d) Getting insulin assembled into proinsulin
Answer:
(b) Getting insulin assembled into a mature form
Question 15.
Bacillus thuriengiensis(Bt) strains have been used as biological control for plants, its application is famous in
(a) cotton
(b) tomatoes
(c) brinjal
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(d) both a and c
Question 16.
Cry endotoxins obtained from Bacillus thuriengensis are effective against
(a) nematode
(b) bollworms
(c) mosquitoes
(d) flies
Answer:
(b) bollworms
Question 17.
Transgenic animal has
(a) foreign DNA
(b) recipient DNA
(c) both a& b
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) both a& b
Question 18.
Genetically engineered cotton plant shows resistance to boll worm insects, but their source of desired gene not induce any adverse effect in bacteria because
(a) cell wall is thick and tough
(b) cell wall is made up of special type of lipids
(c) cytosol does not contain alkaline solution
(d) both b and c.
Answer:
(c) cytosol does not contain alkaline solution
Question 19.
Humulin is prouced in large scale for the specific purpose by
(a) Tissue culture
(b) organ culture
(c) Bio-reactor
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) Bio-reactor
Question 20.
Transgenic food crop which help in solving the problem of night blindness in developing countries is
(a) Bt cotton
(b) golden rice
(c) flvrsavr tomatoes
(d) starlink maize
Answer:
(b) golden rice
Question 21.
In the technique RNA interferance the silencing is done to terminate the function of
(a) hn RNA
(b) m RNA
(c) sn RNA
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) m RNA
Question 22.
If the gene function is disrupted, it corrected by the technique called as
(a) gene slicing
(b) gene splicing
(c) gene therapy
(d) all the above
Answer:
(c) gene therapy
Question 23.
The gene product provides good result as the protein contained in the breast milk is
(a) albumin
(b) alpha lactalbumin
(c) globulin
(d) glutelin
Answer:
(b) alpha lactalbumin
Question 24.
The processed genetically engineered insulin contains
(a) A polypeptide chain
(b) B polypeptide chain
(c) c peptide
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(d) both a and b
We hope Kerala the Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Biotechnology and its Applications help you. If you have any query regarding the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Biotechnology and its Applications, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
