Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production is part of Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Botany Chapter wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| Number of Questions Solved | 82 |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Plus Two Botany Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Hisardale is a
(a) Good quality apple produced in Punjab
(b) Good quality sheep in Assam
(c) Good quality horse developed in Punjab by crossing Marino ewes and Bikaneri rams
(d) New breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing Marino rams and Bikaneri ewes
Answer:
(d)
Question 2.
During the period 1960-2000, wheat production increased from 11 million tones to 75 million tones while rice production went up from 35 million tones to 89.5 million tones. This was due to the development of varieties of wheat & rice possess the character
(a) Small
(b) Dwarf
(c) Semi-dwarf
(d) Long
Answer:
(c) Semi-dwarf
Question 3.
Give examples of some micro organisms that are used as SCP.
Answer:
Spirulina,
Methylophilus
Question 4.
Due to inbreeding depression fertility and productivity of animals are lost. Which is the best method used to overcome these?
Answer:
Outcrossing
Question 5.
Which part of the plant best suited for making virus free plantlet by in-vitro culture.
Answer:
Meristem
Question 6.
Find the odd one among the following. Sonalika, Jaya & Ratna, Prabhat Kranti, Kalyan Sona.
Answer:
Parbhani kranti
Question 7.
Hisaradale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by cross-breeding. Name its parents.
Answer:
Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams
Question 8.
Sonalika and Kalyan Sona are varieties of
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Millet
(d) Tobacco
Answer:
Nonalika and Kalyan Sona are varieties of wheat.
Question 9.
Which one of the following is not a fungal disease?
(a) Rust of wheat
(b) SmutofBajra
(c) Black rot of crucifers
(d) Red rot of sugarcane
Answer:
Black rot of crucifers is a bacterial disease
Question 10.
To isolate proteoplast, one needs
(a) Pectinase
(b) Cellulase
(c) Both pectinase and cellulas
(d) Chitinase
Answer:
(c) Both pectinase and cellulas
Question 11.
Which one of the following is a marine fish?
(a) Rohu
(b) Hilsa
(c) Catla
(d) Common Carp
Answer:
(b) Hilsa
Question 12.
Which one of the following products of apiculture is used in cosmetics and polishes?
(a) Honey
(b) Oil
(c) Wax
(d) Royal jelly
Answer:
(c)
Wax is a product of apiculture used in cosmetics and polishes.
Question 13.
More than 70 per cent of livestock population is in
(a) Denmark
(b) India
(c) China
(d) India and China
Answer:
(d)
More than 70% of the world livestock population is in India and China.
Question 14.
Male and female animals of two different related species are mated. In some cases, the progeny may combine the desirable features of both the parents. Name the type of hybridization?
Answer:
Interspecific hybridisation
Question 15.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill in the blanks
- IR-8: Rice
- Atlas 66: …………
Answer:
Wheat
Question 16.
Name the disease resistant variety of wheat developed against Hill bunt disease.
Answer:
Himgiri
Question 17.
Fill in the blank……..is a wheat variety with high protein content and used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat.
Answer:
Atlas 66
Question 18.
Fill in the blank The part of plant used for virus free culture is……………..
Answer:
Meristem or shoot tip
Question 19.
For successful bee-keeping
(a) Knowledge of the nature and habits of bees, selection of suitable location for keeping the beehives
(b) Catching and hiving of Swarms(group of bees)
(c) Management of beehived during different season
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 20.
The main steps in breeding a new genetic variety of a crop are
- Evaluation and selection of parents
- Cross hybridization among the selected Parents
- Collection of variability
- Testing, release and commercialization of new cultivars
- selection and testing of superior recombinants
(a) 1,2,3,4,5
(b) 1,4,5,2,3
(c) 3,1,2,5,4
(d) 3,2,5,1,4
Answer:
(c) 3,1,2,5,4
Question 21.
What is the common to following fishes Hilsa, Sardines, Mackerel, Pomfrets
(a) They are not edible
(b) Economically not viable
(c) Marine in nature
(d) All are fresh water fishes
Answer:
(c) Marine in nature
Question 22.
Give the term for the process of rearing honey bees.
Answer:
Apiculture
Question 23.
Name the varieties of cauliflowers which is resistant to black rot and curl blight black rot.
Answer:
Pusa shubhra and pusa snowball.
Question 24.
Mention the strategy used to increase homozygosity in cattle for desired traits.
Answer:
Inbreeding
Question 25.
Which part of the plant best suited for making virus free plantlet by in-vitro culture.
Answer:
Meristem
Question 26.
Find the odd one among the following and justify. Sonalika, Jaya & Ratna, Prabhat Kranti, Kalyan Sona.
Answer:
Parbhani kranti
Question 27.
When a farmer cultivated Bananas in a feild, most of banana plants were infected by virus. Can you suggest any method for propagation of virus free Banana plants.
Answer:
Meristem culture or shoot tip culture.
Question 28.
Define inbreeding depression. What is its danger?
Answer:
Continuous – Inbreeding without selection leads to loss of fertility & productivity.
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks using appropriate words: Interspecific hybrid produced by the cross between
![]()
Answer:
Mule
Question 30.
Fill in the blank________virus created a scare in the country and drastically affected egg and chicken consumption.
Answer:
Bird Flu Virus
Question 31.
Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab through
(a) Out crossing
(b) Outbreeding
(c) Crossing breeding
(d) Interspecific hybridisation
Answer:
(c) Crossing breeding
Question 32.
Male and female animals of two different related species are mated. In some cases, the progeny may combine the desirable features of both the parents. Name the type of hybridization?
Answer:
Interspecific hybridisation
Question 33.
______is the common species of honeybee in India.
Answer:
Apis indica
Question 34.
Carefully read the statements given below related to the steps in plant breeding. Choose the correct sequence.
- Testing and commercialization of new variety
- Evaluation and selection of parents
- Selecting and testing superior recombinants
- Cross hybridization among the selected parents
- Collection of variability
(a) 5,2,4,3,1
(b) 1,4,3,5,2
(c) 2,3,4,5,1
(d) 4,5,3,2,1
Answer:
(a) 5,2,4,3,1
Question 35.
Name the disease resistant variety of wheat developed against Hill bunt disease.
Answer:
Himgiri
Question 36.
Fill in the blank. Plants produced through micropropagation are genetically identical to the orginal plant from which they were grown are known as________
Answer:
Somaclones.
Question 37.
Fill in the blank_______is a wheat variety with high protein content and used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat.
Answer:
Atlass 66
Plus Two Botany Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Plant breeders mostly use apical buds as explants in rapid propagation of sugarcane and banana. Write its significance.
Answer:
The apical bud is a meristem which is free of vims. By using these meristem as ‘explants’ in tissue culture large number of virus free – healthy plants can be obtained within a short period.
Question 2.
Following are the steps in MOET programme for herd improvement in which a cow has been Administered hormones with FSH life activities. Arrange steps in their correct sequence.
(a) Transferred to a surrogate mother
(b) It is either mated with elite bull or artificially Inseminated
(c) Fertilized egg at 32 cell stage are recovered non surgically
(d) It produces 6 to 8 eggs instead of one egg which they normally yield per cycle.
Answer:
(d) It produces 6- 8 egg cells instead of one egg per cycle.
(b) It is either mated with elite bull or artificially inseminated.
(c) Fertilised eggs at 32 celled stage are recovered non surgically.
(a) Transferred to a surrogate mother.
Question 3.
Name any four hybrid varieties of crop plants which have been developed in India.
Answer:
Jaya & Ratna variety of rice Sonalika & Kalyansona variety wheat, Pusa A4 variety of bhindi, Pusasadabahar variety of chilly.
Question 4.
Micro organisms are used to make proteins to meet the demand of food for increasing populations.
- Name an alternate source of proteins for animal and human nutrition.
- Is this protein harmful to the environment. Justify.
Answer:
1. SCP – Single Cell Protein eg: Spirulina.
2. In this process microbs are grown on an industrial scale as a source of good protein. Spirulina can be grown easily on materials like waste water from potato processing plant (containing starch), straw, Molases, The product is rich in protein, minerals, fat, carbohydrates & vitamin. This process reduces environmental pollution.
Question 5.
Nature of explants influence the quality of plants formed using tissue culture.
- What is meant by explants?
- Can you evaluate the above given statements?
Answer:
- Any part of the plant used for micropropagation in vitro is called explants.
- Meristems (apical and axillary) are free of virus. By using meristems as explants in tissue culture virus free healthy plants can be produced in large number within short duration.
Question 6.
Name any four hybrid varieties of crop.
Answer:
- Himgiri – Wheat
- Pusaswarnim – Brassica
- Pusashubhra – Cauliflower
- Pusakomal – Cow pea
Question 7.
When the farmercultivated Bananas in his field, most of the banana plants were infected by virus. Can you suggest any method for the propagation of healthy virus free banana plants?
Answer:
Although the plant is infected with virus, the meristem (apical bud) is free of virus. Hence remove the meritstjem and grow it into in-vitro to obtain virus free plants. Thus large number of healthy plants can be produced within short period by the method of micropropagation.
Question 8.
The idea of tissue culture originated from the concept of totipotency.
- What is meant by it?
- Name the chemical substance present in nutrient medium used as carbon source
Answer:
- The inherent capacity of a cell to give rise to a whole plant is called tolipotency.
- Sucrose
Question 9.
Biofortification is the most practical approach to improve the health of people
- What is biofortification
- Give four examples of biofortified crops released by IARI, New Delhi.
Answer:
1. It is the breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals, higher protein and healthier fats.
2. four examples of biofortified crops released by IARI, New Delhi:
- vitamin A-enriched carrots, spinach, pumpkin;
- vitamin C enriched bitter gourd, bathua, ustard,tomato;
- Iron and calcium enriched spinach and bathua;
- Protein enriched beans – broad, lablab, French and garden peas
Question 10.
Inbreeding strategy follows mating of superior male and superior female. Write down the criteria for selection of superior in the case of cattle.
Answer:
Superior males i.e the bull which gives rise to superior progeny and superior females i.e cow or buffalo that produces more milk per lactation.
Question 11.
Nature of explants influence the quality of plants formed using tissue culture
- What are expfSnts?
- Evaluate the above statement.
Answer:
1. Any part of a plant taken out (Egstem, leaf, root etc.) and grown in a test tube, under sterile conditions in special nutrient media.
2. It is a special mode of asexual reproduction in which all new plants formed are qualitatively and qualitatively similar to the parent(maintaining the desirable characters).
Question 12.
Beekeeping is the old age cottage industry that is very significant commercially
- Name the useful products obtained
- Why does a beekeeper keep beehives in crop fields during flowering period?
Answer:
1. Honey and Bee wax.
2. a beekeeper keep beehives in crop fields during flowering period:
- To increase the chances of pollination
- To increase the yield of honey.
Question 13.
- Mention the property that enables the explants to regenerate into a new plant
- A banana, herb is virus infected. Describe the method that will help in obtaining healthy banana plant form diseased plant.
Answer:
- Totipotency
- Extract the Meristem (apical and axillary) and grow it in vitro to obtain vims free banana plants.
Question 14.
Honey collection improves when beehives are kept in crop fields during flowering seasons. Explain.
Answer:
Bees are the pollination of many crops. Keeping beehives in crop fields during flowering period increases pollination and improve the honey yield. It is beneficial both for crop yield and honey yield.
Question 15.
Jersey is an important breed of cattle
- Define breed
- Differentiate between inbreeding and outbreeding
Answer:
1. A group of animals related by descent and similar in most characters like general appearance, feature, size, configuration etc. are called a breed.
2. Inbreeding – The mating of more closely related individuals within the same breed for 4-6 generations.
3. Out breeding – Breeding of the unrelated animals of the same breed but have no common ancestors for 4 – 6 generations.
Question 16.
What is the major advantage of producing plant by micro propagation?
Answer:
Micropropagation is a tissue culture technique which enables us to get unlimited number of plants in a limited space and short time.
Question 17.
When inbreeding depression becomes a problem, how can we overcome the issue?
Answer:
Firstly select animals from inbreed population and mate them with unrelated superior animals of the same breed (Outcrossing)). This helps to restore fertility and yield.
Question 18.
Match the following column A column B
| A | B |
| 1. Inbreeding | a) Cross between two different related species |
| 2. Interspecific hybridization | b) Mating of animals within the same breed but having no common ancestors |
| 3. Outcrossing | c) Superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed |
| 4. Crossbreeding | d) Breeding between the animals of same breed |
Answer:
1(d), 2(a), 3(b), 4(c)
Question 19.
To improve the chances of successful production of hybrids, MOET is employed.
- Expand MOET
- Explain the steps involved in MOET
Answer:
1. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology
2. steps involved in MOET
- A cow is administered with FSH hormones, it induce follicular maturation and super ovulation.
- They produce 6-8 egg instead of one egg per cycle.
- Cow is mated with elite bull or artificially inseminated.
- Zygote at 8-32 cells are recovered non surgically and transferred to surrogate mother.
- The genetic mother is available for another round of super ovulation.
Question 20.
Give one example each of variety developed against white rust and bacterial blight.
Answer:
- White rust – Pusa Swarnim
- Bacterial blight – Pusa Komal
Question 21.
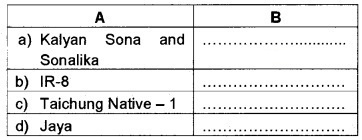
Observe the statements given below:
- High yielding disease resistant wheat
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in Taiwan
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in India
- Semi-dwarf variety rice developed in Philippines Fill up column B using the above statements.

Answer:
- High yielding disease resistant wheat
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in Philippines
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in Taiwan
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in India.
Question 22.
Observe the table and fill a, b, c and d.
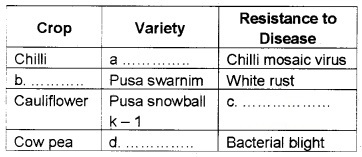
Answer:
(a) Pusa sadabahar
(b) Brassica
(c) Black rot/curl blight black rot
(d) Pusa komal
Question 23.
Construct a table with column-A Crop, and Column – B Variety using the hints given below. Hints – Wheat, Brassica, Cow pea, Cauliflower, PusaSwamim, PusaShubhra, Himgiri, PusaKomal
Answer:
| Crop | Variety |
| Wheat | Himgiri |
| Brassica | Pusa Swarnim |
| Cowpea | Pusa Komal |
| Cauliflower | Pusa Shubhra |
Question 24.
- In mung bean, two varieties are developed through mutation breeding for disease resistance. Name the disease for which the varieties are produced.
- Name two agents that induce mutation.
Answer:
- Resistance against yellow mosaic virus
- Resistance to powdery mildew chemicals, gamma radiation.
Question 25.
Parbhanikranthi is a resistant variety of bhindi.
- Which disease this breed is resistant to?
- Name the scientific name of parbhani kranthi.
Answer:
- Yellow mosaic virus
- Abelmoschus esculentus
Question 26.
Observe the terms given below. Arrange then in the order of crop, variety, and insect pests in three columns. Pusa Gaurav, Aphids, Shoot and fruit borer, Brassica, PusaSem 3, Okra, PusaSawani, Pusa A-4
Answer:
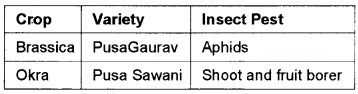
Question 27.
The most practical means to improve public health is biofortification.
- What do you mean by biofortification.
- List out its main objectives.
Answer:
1. It is the Breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins, minerals, higher protiens and healtheir fats
2. objectives:
- protein content and quality
- oil content and quality.
- vitamin content
- micronutrient and mineral content
Question 28.
- Indian agricultural institute, New Delhi developed vegetables with enriched vitamin and minerals.
- Write two examples of vitamin A, iron and calcium enriched vegetables.
Answer:
- Vitamin A enriched-Carrot, pumpkin
- Iron and calcium enriched Spinach and bathua.
Question 29.
Explant, totipotency, micropropagation are terms very commonly used in tissue culture. Explain each terms.
Answer:
1. Explant: Any plant part taken for tissue culture
2. Totipotency: Capacity to generate whole plant from any cell
3. MicroPropaaation: Propagation of thousands of plants through tissue culture.
Question 30.
Pomato is a somatic hybrid. How this is developed?
Answer:
It is developed through following steps
- Isolation of single cell each from potato and tomato.
- Digestion of the cell wall using enzymes.
- Isolate the protoplast.
- Fuse to get hybrid protoplast. This can be grown to form a new plant.
Question 31.
Distinguish between the following. Apiculture and Pisciculture.
Answer:
Apiculture or Bee keeping is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey. Pisciculture aims to increase the production of fishes.
Question 32.
Name two semi-dwarf rice and wheat varieties developed in India.
Answer:
- Semi-dwarf rice – Java & Ratna
- Semi-dwarf wheat – Sonalika & Kalyansona.
Question 33.
In some animals productivity is lost due to continuous inbreeding process
- Name the breeding strategy is used to overcome productivity loss
- Name the breading technique used to produce heterozygous offsprings
Answer:
- Outcrossing
- Cross breeding
Question 34.
Healthy plants are obtained from diseased plants by an important tissue culture technique.
- Name it.
- Which is the nutritive substance used as carbon source?
Answer:
- Meristem culture
- Sucrose
Question 35.
In 2000 hybrid Maize with higher levels of amino acid developed by plant breeding method
- Name the strategy used
- Give an example for protein-rich variety developed
Answer:
- biofortification
- Atlas 66
Question 36.
In 1960 the grain production of our country has increased due to the introduction of semi dwarf rice and wheat varieties.
- Name the world renowned scientist has worked behind the Green Revolution program
- Give an example for two rice varieties developed in India
Answer:
- Norman E Borlaug
- Jaya and Ratna
Question 37.
In Ayurvedic medicine and honey is very important to treat many diseases
- Which is the most common species of bees used?
- What are the significance of Apiculture?
Answer:
- Apis indica
- It helps to increase Honey yield, pollination efficiency and crop yield.
Question 38.
Name any five hybrid varieties of crop plants which have been developed in India
Answer:
The five hybrid varieties of crop plants which have been developed in India are:
Crop Plant Hybrid Variety
- Wheat – Sonalika and Kalian sona
- Rice – Jaya and Ratna
- Cauliflower – Pusa shubra and Pusa snowball K-1
- Cowpea – Pusa komal
- Mustard – Pusaswarnim
Question 39.
What is the major advantage of producing plants by micropropagation?
Answer:
Micropropagation is a method of producing new plants in a short duration using plant tissue culture. Some major advantages of micropropagation are as follows:
- Micropropagation helps in the propagation of a large number of plants in a short span of time.
- The plants produced are identical to the mother plant.
Question 40.
How is a somatic hybrid different from a hybrid?
Answer:
Isolated protoplasts from two different varieties of plants can be fused to get hybrid protoplasts, which can be further grown to form a new hybrid plant that is called somatic hybrid.
Question 41.
What is emasculation? Why and when is it done
Answer:
Removal of anther from a bisexual flower is called emasculation. It is used to avoid self-pollination and is used in artificial hybridisation programme. It is done before the dehiscence of anther.
Question 42.
Plants raised through tissue cultures are clones of the ‘parent’ plant. Discuss the utility of these plants.
Answer:
Plant raised through tissue cultures are clones of the parent plant that means they are genetically identical to the original plant. They are utilised for maintaining a desirable trait of parent.
Question 43.
- The shift from grain to meat diets creates more demands for cereals. Why?
- A250 kg cow produces 200g of protein per day but 250g of Methylophillus methylotrophus can produce 25 tonnes of protein. Name this emerging area of research. Explain its benefits.
Answer:
1. It takes 3-10 kg of grain to produce 1 kg of meat using animal farming. That is why cereals demand increases.
2. Spirulina can be easily grown on starch, molasses etc. and can make food which is rich in proteins, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins. This could be a good alternative for dealing with the problem of malnutrition.
Question 44.
Observe the statements given below:
- High yielding disease resistant wheat
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in Taiwan
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in India
- Semi-dwarf variety rice developed in Philippines
Fill up column- B using the above statements.
Answer:
- High yielding disease resistarit wheat
- Semi -dwarf variety of rice developed in Philippines
- Semi-dwarf variety of rice developed in Taiwan
- Semi -dwarf variety of rice developed in India
Question 45.
Observe the table and fill a, b, c and d.
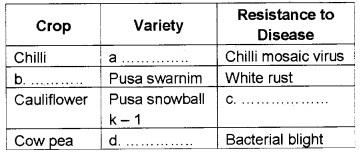
Answer:
(a) Pusa sadabahar
(b) Brassica
(c) Black rot/curl blight black rot
(d) Pusa komal
Question 46.
parbhani kranthi is a resistant variety of bhindi.
- Which disease this breed is resistant to?
- Name the scientific name of parbhani kranthi.
Answer:
- Yellow mosaic vims
- Abelmoschus esculentus
Plus Two Botany Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Poultry Farm Management of chicken, ducks, turkey and geese for food or their eggs
- What are the important points to remember on poultry farming.
- Name the causative organism of bird flu.
Answer:
1. poultry farming:
- Maintain disease free condition in farm.
- Provide proper feed and water.
2. Virus (H5 N1)
Question 2.
Your neighbor owned a diary farm. For better diary farm management what advise can you give for him?
Answer:
Dairy farm management includes processes and systems that increase yield and improve quality of milk.
It includes selection of good breeds having high yielding potential, resistance to diseases they have to be housed well, should have adequate water, maintained disease free, feeding should be in a scientific manner(in the quality and quantity of fodder), maintaining cleanliness and hygiene during milking, storage and transport of the milk and its products, and require regular visit of a veterinary doctor.
Question 3.
Pusagaura, pusaA-4, Himagiri, pusacomal are some hybrid varieties developed through plant breeding. Sumesh get this information from a magazine. But he did not know the steps of plant breeding through which these varieties are produced. Can you help him?
Answer:
The main steps of plant breeding are
- Collection of variability
- Evaluation and selection of parents:
- Cross hybridisation among the selected parents:
- Selection and testing of superior recombinants:
- Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars.
Question 4.
Match the following.
| a. Mutagen | Homozygosity |
| b. Crossbreeding | Ethylmethylsulphonate |
| c. Inbreeding | G.Haberlandt |
| d. Plant tissue culture | Hisardale |
| e. Biofortification | Methylophilusmethylotropus |
| f. Single cell protein | Nutrition quality |
Answer:
| a. Mutagen | Ethyl methyl sulphonate |
| b. Cross breeding | Hisardale |
| c. Inbreeding | Homozygosity |
| d. Plant tissue culture | Haberlandt |
| e. Biofortification | Nutrion quality |
| f. Single cell protein | Methylophilusmethylotrophus |
Question 5.
Breeding technique that help to improve cattle population in India, some breeds are good in milk yielding and disease resistance
- What is cross breeding?
- What advantage does it confer?
- Give one example.
Answer:
1. Cross breeding is the mating between animals of different breeds. It involves mating of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed.
2. This method allows the desirable qualities of two different breeds to be combined. Thus the hybrid progeny will have desirable traits of both the breeds.
3. Eg-Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams.
Question 6.
Plant breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant species in order to create desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give better yields and disease resistance. Write’the major steps in breeding a new variety of crop.
Answer:
The steps involved in plant breeding are:
1. Collection of variability:
Collection and preservation of different wild varieties, species and relatives of cultivated species and evaluation of their characteristics.
2. Evaluation and selection of parents:
Evaluation of germplasm helps to identify plants with desirable characters and are selected as parents for hybridization.
3. Cross hybridisation among the selected plants:
The two parents selected are artificially hybridized and producing hybrid with desirable character.
4. Seletion and testing of superior recombinants:
The hybrids obtained are tested for superior character and are self pollinated for several generations till they reach a state of uniformity.
5. Testing release and commercialisation of new cultivars:
The selected lines are evaluated and the performance are recorded and is compared to the best available local cultivar and released as a new variety.
Question 7.
It is suggested to supply Atlas-66 variety of Wheat grains to the malnutrient communities.
- Name the technology used to produce Atlas 66?
- Explain it
- Give four examples of biofortified crops released by IARI, New Delhi.
Answer:
1. Biofortification.
2. It is the breeding of crop with higher level of vitamin& Minerals or higher protein & healthier fats. It is the most practical means to improve public health.
3. IARI, New Delhi, released vitamin enriched carrots, Spinach, pumkin vitamin c enriched bitter gourd, mustard,tomato& calcium enriched spinach & protein enriched beans – Broad lablab, French beans & garden peas.
Question 8.
Somatic hybridization technique is used to raise hybrid plants with combined characters of two different plants.
- How is it achieved?
- Give an example
- What are soma clones?
Answer:
1. Protoplast can’ijeHsolated from cells by digesting their walls using enzymes. Somatic hybridization is the fusion of isolated protoplasts from two different varieties of plants having desirable characters.
The fusion results in the formation of hybrid protoplast. These protoplast are further grown into a new plant. The plants obtained are called somatic hybrids.
2. Pomato
3. Plants got during micro propagation (tissue culture) are genetically identical to the original plant from where they are grown.
Question 9.
Inbreeding increases homozygosity and causes inbreeding depression.
- What you meant by inbreeding depression.
- Name the progenies obtained through this process with selection.
Answer:
1. Inbreeding is the mating of more closely related individuals of the same breed. Continued inbreeding leads to increasing homozygozity and ultimately results in the reduction of fertility and productivity.
2. Purelines.
Question 10.
‘Apiculture’ has become an established income-generating industry ______
- What is Apiculture?
- Which is the most commonly used species?
- What are the matters one should know before starting apiculture?
Answer:
1. Apiculture is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey.
2. The commonly used species of honeybee is Apis indica.
3. The following points are considered for successful bee keeping.
- Knowledge of the nature and habits of bees.
- Selection of suitable location for keeping the bee hives.
- Catching and hiving of swarms(group of bees).
- Management of bee hives during different seasons.
Question 11.
To improve changes of successful production of hybrids other means are also used. MOET is one such programme.
- What is MOET?
- Write down the steps used for herd improvement.
Answer:
1. MOET is multiple ovulation embryo transfer technology. It is the controlled breeding method. It is done to improve the chances of successful production of hybrids.
2. steps used for herd improvement:
- Cow is given hormones with FSH-like activity
- To induce follicular maturation and super ovulation
- It produce 6-8 eggs/cycle.
- This animal is then mated with an elite bull or artificially inseminated.
- The fertilised eggs at 8-32 cells stages, are removed and transferred to surrogate mother.
Question 12.
Pusa-gaurav, pusa A-4, Himagiri, pusa comal are some hybrid varieties developed through plant breeding. Sumesh get this information from a magazine. But he did not know the steps of plant breeding.
- Write down the steps of plant breeding
- Name the revolution that leads to the food production in World.
Answer:
1. The main steps of plant breeding are
- Collection of variability
- Evaluation and selection of parents
- Cross hybridisation among the selected parents
- Selection and testing of superior recombinants
- Testing, release and commercialisation of new cultivars
2. Green revolution
Question 13.
Bee-keeping is the maintenance of hives honey bees for the production of honey. Illustrate the important steps for successful bee keeping.
Answer:
- Knowledge of the nature and habit of
- Selection of suitable location for keeping the beehives.
- Catching and hiving of swarms.
- Management of beehives during different seasons
- Handling and collection of honey and bee wax.
Question 14.
Breeding between animals of the same breed is called inbreeding. Write the steps of inbreeding.
Answer:
- Identifies superior male and female of the same breed.
- Mate them in pairs.
- Identifies the superior male and female of the progeny for further mating.
- Select the best breed.
Question 15.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of inbreeding.
Answer:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Increase homozygpsity | Expose harmful recessive genes |
| Evolve pure line | Continued inbreeding reduces fertility |
| Accumulation of desirable gene and elimination of less desirable gene | Inbreeding depression |
Question 16.
Why does a beekeeper keep beehives in crop fields during the flowering periods?
Answer:
Bees are available during flowering periods, as they feed on the pollen and nectar of flowers.
- It increases pollination efficiency and crop yield.
- It also improves honey yield.
Question 17.
Raju is working in an Agricultural Research station and is directed to provide large number of plants like banana, orchids, haploid varieties of water melon and two medicinal plants whose leaves and roots are used as medicines.
- Write the most suitable method that Raju can adopt.
- Give any two advantages of this method.
Answer:
1. Micro propagation
It is the tissue culture method used to produce large no. of plants within a short period.
2. advantages of this method:
- The plants are genetically identical to the original plant from which they grown (soma clones).
- The plants must be virus free as meristems are used as explants.
Plus Two Botany Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
If your family owned a dairy farm. What measures would you undertake to improve the quality and quantity of milk production?
Answer:
To improve the quality and quantity of milk production the following steps are to be taken.
- Selection of good breeds having high yielding potential and disease resistance.
- The cattle should be housed well with adequate water and maintained disease free.
- The feeding of cattle should be in scientific manner – giving emphasis on quality and quantity of fodder.
- Cleanliness and hygiene (both of cattle and handlers) should be given paramount importance to milking, storage and transport of milk.
Question 2.
Name any five hybrid varieties of crop.
Answer:
- Himgiri – Wheat
- Pusaswarnim – Brassica
- Pusashubhra – Cauliflower
- Pusakomal – Cow pea
- PusaSadabahar-Chilli
Question 3.
Name the methods employed in a animal breeding. According to you which of the method is best. Why?
Answer:
The methods employed in animal breeding are:
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding such as out crossing, cross breeding and interspecific hybridization.
- Controlled breeding such as artificial insemination and multiple ovulation embryo transfer technique.
Artificial insemination method of controlled breeding is best because it ensures good quality progeny and it is economic also.
Question 4.
What is apiculture? How is it important is our lives?
Answer:
Apiculture:
Rearing of honey bees for the commercial production of honey and bee wax. Apiculture is a low cost investment and highly profitable. It provides honey, wax and act as pollinator of many crops.
Question 5.
Discuss the role of fishery in enhancement of food production.
Answer:
A large section of the Indian population uses fish and many other aquatic animals such as crabs, lobsters, prawns etc. as food. The fish serve as a chief source of protein, has very little fat, carries a good amount of minerals, vitamins and iodine. Thus fisheries plays significant role in enhancement of food production.
Question 6.
Explain what is meant by biofortification.
Answer:
Biofortification:
Breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher protein and healthier fats is called biofortification. The biofortification is done with improvement of public health as the primary goal.
Question 7.
Which part of the plant is best suited for making virus-free plants and why?
Answer:
The apical and axillary meristem are the best suited parts of plant for the production of virus-free plants. These parts are generally free from virus due to the absence of vascular tissue through which vims are transported.
Question 8.
What is the major advantage of producing plant by micro propagation?
Answer:
Micropropagation is a tissue culture technique which enables us to get unlimited number of plants in a limited space and short time.
Question 9.
Find out what the various components of the medium used for propagation of an explant in vitro are?
Answer:
The major components of the medium are water, inorganic salts, sucrose (source of carbon and energy), vitamins, amino acids, and growth hormones like auxins, cytokinins etc.
- Other compounds like casein, coconut milk, yeast extract etc. may be added for specific purposes.
- If required a gelling agent agar is added to the liquid medium for its solidification.
Question 10.
Name any five hybrid varieties of crop plants which have been developed in India.
Answer:
- Wheat – Himgiri
- Rice – Jaya, Ratna
- Brassica – PusaSwarnim
- Cow pea – Pusa Comal
- Chilli – PusaSadabahar
Plus Two Botany Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Hybrid vigour is mostly due to
(a) superiority of all the genes
(b) homozygosity of pure characters
(c) heterozygosity
(d) mixing of recessive characters only
Answer:
(c) heterozygosity
Question 2.
Breeding of crops which high levels of minerals, vitamins and proteins is called
(a) Somatic hybridisation
(b) Biofortification
(c) Biomagnification
(d) Micropropagation
Answer:
(c) Biomagnification
Question 3.
Disease resistant crop is obtained by
(a) crossing with new varieties
(b) crossing with wild varieties
(c) injecting with organic compounds
(d) crossing with recessive varieties
Answer:
(b) crossing with wild varieties
Question 4.
In maize, hybrid vigour is exploited by
(a) bombarding the seeds with DNA
(b) crossing of two superior desirable parental lines
(c) harvesting seeds from the most productive plants
(d) inducing mutations
Answer:
(b) crossing of two superior desirable parental lines
Question 5.
Wonder wheat is new wheat variety developed by
(a) Mexico’s international Wheat and Maize Improvement Centre
(b) Indian National Botanical Research Institute
(c) Australian Crop Improvement Centre
(d) African Crop Improvement Centre
Answer:
(a) Mexico’s international Wheat and Maize Improvement Centre
Question 6.
The terminator gene technology causes
(a) failure of seed setting after one generation
(b) breakage of seed dormancy
(c) early flowering in plants
(d) death of microorganisms in soil
Answer:
(a) failure of seed setting after one generation
Question 7.
Study the following columns.
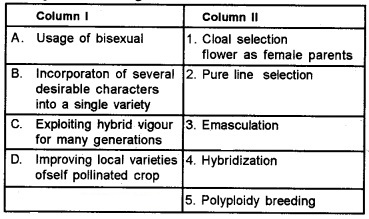

Answer:
(c) 3 4 1 2
Question 8.
The high yielding hybrid crop varieties to exploit hybrid vigour, the farmers need to purchase fresh hybrid seed every year because.
(a) hybridvigour is not long-standing due to inbreeding depression
(b) they are not allowed to grow their own seed
(c) it is always associated with increased heterozygosity
(d) always associated with increased homozygosity
Answer:
(c) it is always associated with increased heterozygosity
Question 9.
In crop improvement programme, haploids are of great importance because they
(a) grow better under adverse conditions
(b) are useful in the study of meiosis
(c) requires only abgut half the amount of chemical fertilizers compared to diploids
(d) give homozygous lines
Answer:
(d) give homozygous lines
Question 10.
Match the following columns and choose the correct option.
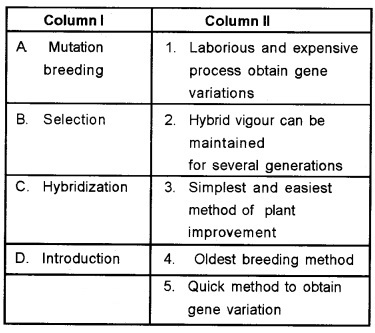

Answer:
(b) 1 2 4 5
Question 11.
Three crops that contribute maximum to global food grain production are
(a) Wheat, rice and maize
(b) Wheat, maize and sorghum
(c) rice, maize and Sorghum
(d) Wheat, rice and barley
Answer:
(a) Wheat, rice and maize
Question 12.
India’s wheat yield revolution in the 1960s was possible primarily due to
(a) hybrid seeds
(b) increased chlorophyll content
(c) mutations resulting in plant height reduction
(d) quantitative trait mutations
Answer:
(c) mutations resulting in plant height reduction
Question 13.
Mule is a product of
(a) breeding
(b) inter generic hybridisation
(c) hybridization
(d) interspecific hybridisation
Answer:
(d) interspecific hybridisation
Question 14.
Protoplasts of two different species are fused in
(a) micro-propagation
(b) somatic hybridisation
(c) clonal propagation
(d) organography
Answer:
(b) somatic hybridisation
Question 15.
Removal of anthers of some flowers during plant breeding is
(a) emasculation
(b) anthesis
(c) pollination
(d) for collection of pollen
Answer:
(a) emasculation
Question 16.
The type of hormone used for MOET is
(a) insulin
(b) LH
(c) FSH
(d) LTH
Answer:
(c) FSH
17. The species of insect very common in apiculture is
(a) Apisindica
(b) Apisdorsata
(c) Both a & b
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) Apisindica
Question 18.
The industry mainly responsible for the catching, rearing and selling of fish and its products come under
(a) Pisciculture
(b) Aquaculture
(c) Silviculture
(d) Apiculture
Answer:
(a) Pisciculture
Question 19.
Which method is used to overcome inbreeding depression
(a) Intra specific hybridization
(b) self pollination
(c) outbreeding
(d) intra varietal hybridization
Answer:
(c) outbreeding
Question 20.
Bird flu is caused by
(a) H1N1
(b) H5N1
(c) H3N1
(d) H2N1
Answer:
(b) H5N1
Question 21.
Disease free plants are produced by
(a) somatic hybridization
(b) meristem culture
(c) protoplast culture
(d) embryo culture
Answer:
(b) meristem culture
Question 22.
Atlas 66 is the variety of
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c) maize
(d) sorghum
Answer:
(a) wheat
Question 23.
Somaclones shows
(a) similarity with parents
(b) dissimilarity with parents
(c) similarity among offsprings but not with parents
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) similarity with parents
Question 24.
Green revolution mainly aims for growing
(a) disease resistance variety
(b) semi dwarf variety
(c) self fertilizing variety
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) semi dwarf variety
Question 25.
Hisardale is the superior breed of sheep developed by
(a) cross breeding
(b) genetic engineering
(c) somatic hybridization
(d) inbreeding
Answer:
(a) cross breeding
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production help you. If you have any query regarding the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
