Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms is part of Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Botany Chapter wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 |
| Chapter Name | Reproduction in Organisms |
| Number of Questions Solved | 78 |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms
Plus Two Botany Reproduction in Organisms One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Syngamy means:
(a) Fusion of similar spores
(b) Fusion of dissimilar spores
(c) Fusion of cytoplasm
(d) Fusion of gametes
Answer:
(d) Fusion of gametes
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks by observing the relationship of the first.
- Amoeba: Binary fission
Yeast: ………….. - Reptiles: Oviparous
Mammals: ………….
Answer:
- Yeast: Budding
- Mammals: Viviparous
Question 3.
Internal buds of Sponges are:,
(a) Spores
(b) Gemmules
(c) Planula
(d) Blastos
Answer:
(b) Gemmules
Question 4.
In honeybees and lizards, the female gamete undergoes development to form new organism without fertilization. Name this phenomenon.
Answer:
Parthenogenesis
Question 5.
The life span of man is_____years.
(a) 60
(b) 70
(c) 85
(d) 100
Answer:
(d) 100
Question 6.
What is meiocyte?
(a) The cell undergoes meiosis
(b) The cell undergoes mitosis
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) The cell undergoes meiosis
Question 7
All individuals produced are genetically identical
(a) clone
(b) offspring
(c) fission
(d) monoecious
Answer:
(a) clone
Question 8.
Hydra reproduces asexually by
(a) budding
(b) binary fission
(c) Multiple fission
(d) Vegetative propagation
Answer:
(a) budding
Question 9.
Find the propagules of ginger
(a) Runner
(b) Bulbil
(c) Rhizome
(d) Bulb
Answer:
(c) Rhizome
Question 10.
Bulb acts as a propagule in
(a) Onion
(b) Garlic
(c) Agave
(d) Both a and b
Answer:
(d) Both a and b
Question 11.
In some algae_____are motile
(a) male gametes
(b) female gametes
(c) both male and female gametes
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(c) both male and female gametes
Question 12.
A population of genetically identical plants derived from a single parent is called………..
Answer:
Clone
Question 13.
Embryo sac is found in:
(a) Endosperm
(b) Embryo
(c) Ovule
(d) Seed
Answer:
(c) Ovule
Question 14.
Types of asexual reproduction found in Hydra is………
(a) Gemmule formation
(b) Budding
(c) Sporulation
(d) Multiple fission
Answer:
(b) Budding
Question 15.
Observe the relation and fill in the blanks. Syncarpous: the pistils remain united: the pistils remain free.
Answer:
Apocarpous
Question 16.
In honeybees and turkey new organisms are formed through a peculiar phenomenon. Name that phenomenon.
Answer:
Parthenogenesis
Question 17.
Choose the correct answer: Chlamydomonas reproduces asexually through
(a) Gemmules
(b) Conidia
(c) Bud
(d) Zoospores
Answer:
(d) Zoospores
Question 18.
In Marchantia male and female thallus are separate. This condition is called
(a) Dioecious
(b) Hermaphrodite
(c) Monoecious
(d) Bisexual
Answer:
(a) Dioecious
Question 19.
Find the odd one. Bulbil, Bulb, Rhizome, Stem tuber.
Answer:
Bulbil
Question 20.
Identify the correctly matched pair.
(a) Chlamydomonas – conidia
(b) Sponge – Zoospore
(c) Hydra – bud
Answer:
(c) Hydra – bud
Plus Two Botany Reproduction in Organisms Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Sugarcane, Banana, Ginger, and Onion are flowering plants. But these are mostly cultivated by vegetative propagation.
- What is meant by vegetative propagation.
- Can you identify which part of the above plants are used for vegetative propagation.
Answer:
- The regeneration of new plants from the portions of vegetative organs like stem, root, and leaves.
- plants are used for vegetative propagation.
- Sugar cane – stem
- Banana – Rhizome
- Ginger – Rhizome
- Onion – Bulb
Question 2.
Leaves not only produce foods, but also produce young ones. Comment on this statement.
Answer:
In some plants, leaves are organ of vegetative propagation i.e new plants are formed from leaf margins eg-Bryophyllum.
Question 3.
How is pistia and zingiber officinale different in their mode of Asexual reproduction?
Answer:
The above two plants shows vegetative propagation. The vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction The vegetative propagule of pistia is offset (short and thick internode) and zingiber is rhizome (underground stem).
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks by observing the relationship of the first.
- Male and female flowers on the same plant: monoecious
Male and female flowers on different plants: …………. - Fusion of gametes: Syngamy
Offspring from unfertilized female gamete: ……………
Answer:
- Dioecious
- Parthenogenesis
Question 5.
Plant can reproduce both vegetatively and sexually. Name any 4 vegetative propagule.
Answer:
- Eye of potato,
- rhizome of ginger,
- bulbil of agave,
- offset of water hyacinth.
Question 6.
Given below is a diagram showing particular types of reproduction.
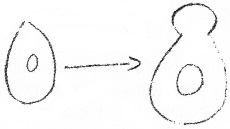
- Name the process of reproduction.
- Briefly explain the process
Answer:
- Budding
- It is the mode of asexual reproduction in which the unicellular organism divides unequally and the buds remain attached to the parent cell. Eg. yeast.
Question 7.
Given below the figures of different types of reproduction present in organisms. Identify and name the type of reproduction.
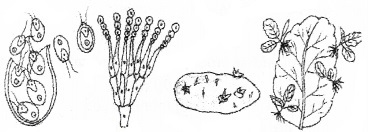
Answer:
- Zoospores in chlamydomanas
- Conidia of penicillium
- Eyes of potato
- Leaf buds of bryophyllum.
Question 8.
Match the following: (Hint: Name of organisms in column A and asexual reproductive structure in Column B)
| A | B |
| 1. Chlamydomonas 2. Penicillium 3. Hydra 4. Sponge | 1. Gemmules 2. Buds 3. Zoospores 4. Conidia |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Chamydomonas 2. Pencillium 3. Hydra 4. Sponge | Zoospores Conidia Buds Gemmules |
Question 9.
In diploid organisms, meiosis and gametogenesis are always interlinked. Justify.
Answer:
In diploid organism, reproductive cells undergoes reduction division – meiosis and produces haploid gametes. Gametogenesis means the process of gamete formation. So meiosis and gametogenesis are always interlinked.
Question 10.
Categorize the following into pre and post-fertilization changes in plants. Gamete transfer, pericarp formation, ovule development, embryogenesis.
Answer:
Pre fertilization-ovule development and gamete transfer. Post fertilization -embryogenesis and pericarp formation.
Question 11.
Events of sexual reproduction is given below.
- Write the events in a sequential order. Fertilization, gamete transfer, zygote, gameto – genesis, embryogenesis.
- Point out the differences between gametogenesis and embryogenesis
Answer:
- Gametogenesis, gamete transfer, fertilization, zygote, embryogenesis.

Question 12.
‘Water-hyacinth’ is commonly called ‘Terror of Bengal’. Give reason.
Answer:
‘Water-hyacinth’ is a highly spreading aquatic weeds, which drains oxygen from the water and leads to the death of fishes.
Question 13.
Bamboo plant and strobilanthus kunthianus (Neela Kurunji) have similarity and dissimilarity in their reproductive and vegetative character. Justify.
Answer:
- Similarity – Both Bamboo and neela kurinji are perennial plants.
- Dissimilarity – Bamboo flowers only once in their life time (in the period of 50-100 years) and die whereas neelakurinji flowers once in 12 years.
Question 14.
Zygote is called as the vital link. Why?
Answer:
Zygote is the product of fertilization, that maintains the continuity of species between organisms of one generation and the next.
Question 15.
Post fertilization changes in flowering plants are given, by observing the given pair complete the others.
(a) Zygote: Embryo
(b) Ovule: ……….
(c) Ovary: ………
(d) Nucellus: Perlsperm
(e) Integument: ……….
(f) PEN: ………..
Answer:
(b) Ovule: Seed
(c) Ovary: Fruit
(e) Integument: seed coat
(d) PEN: Endosperm
Question 16.
Leaves are used not only for photosynthesis but also for reproduction.
- Name the type of reproduction
- Give an example.
Answer:
- Vegetative propagation
- Eg-Broyophyllum
Question 17.
Observe the relationship between first two terms and fill up the blanks.
1. Asexual reproduction – Unparental
Sexual reproduction……………….
2. Zygote: Diploid nucleus: Endosperm: ………….
3. Pea: non albuminous: wheat ………….
Answer:
- biparental
- Triploid nucleus
- albuminous
Question 18.
In yeast and Amoeba the parent cell divides to give rise to two new individual cells. How does the cell division differ in these two organisms?
Answer:
- In yeast, the cell division is unequal and small buds are produced.
- In Amoeba, the cell division is equal and identical daughter cells are produced.
Question 19.
Offsprings formed due to sexual reproduction have better chances of survival. Why?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction combines the characters of two parents and introduces variations which make the offsprings better in environmental adaptation.
Question 20.
Some organism are capable of producing fertilized egg but others are not possible.
- Name the organism producing fertilized egg.
- Why are offspring of oviparous-animals subjected to greater risk as compared to offsprings of viviparous animals.
Answer:
- oviparous animals
- In oviparous orgaisms development of zygote take place outside the body of the female parent while in viviparous organisms development of zygote take place inside the body of female organisms. Hence viviparous type get proper embryonic care and protection.
Question 21.
In one type plant Adventitious buds develops into new leafy shoot by leaf as means of vegetative propagation but in others by rhizome. Give examples for leaf and rhizome used as unit of vegetative propagation.
Answer:
- Leave – bryophyllum
- Rhizome – banana, and Ginger
Question 22.
In certain lower plants, equal and un equal daughter cells are produced by asexual reproduction. Name these Asexual Reproduction with examples
Answer:
In binary fission equal daughter cells are produced. Example bacteria and Paramecium. In budding two unequal daughter cells are produced. Example Yeast and hydra.
Question 23.
In lower plants movement of gametes takes place by water but in seed plants male gametes are non motile. Which part of plant helps the movement of gametes?
Answer:
Pollen tube
Question 24.
Haploid gametes are produced in bryophytes and angiosperms by two types of cell division. Name it
Answer:
- bryophytes-Mitosis
- angiosperms-meiosis
Question 25.
Sexual reproduction is very common in higher plants to produce young ones that shows variation.
- Name the product formed in sexual reproduction is considered as vital link
- Give its significance
Answer:
- product-zygote
- It maintains continuity of species for many generation.
Question 26.
Nature prefer internal fertilization than external fertilisaiton. Do you agree with this statement.
Answer:
Yes, In nature the advanced plants and animals show internal fertilisation.
Question 27.
In fishes gamete fusion takes place in external medium. Give the disadvantage of this method.
Answer:
The offsprings formed through external fertilisation are subjected to the attack of predators.
Question 28.
Animals are categorized into viviparous and oviparous based on the development of the Zygote takes place outside the body or inside. In which of these two types the chances of survival is greater. Why?
Answer:
In oviparous animals like reptiles and birds, the fertilised eggs after the period of incubation young ones hatch out. In viviparous animals, the zygote develops into a young one inside the body of the female organism. After the period of growth, they are delivered out. The chances of survival is greater in viviparous animals.
Question 29.
Mention the characteristic feature and a function of zoospore in some algae.
Answer:
- Zoospores are flagellated, motile aquatic bodies
- On germination give rise to new plants
Question 30.
Name the site of occurrence of syngamy in amphibians and reptiles.
Answer:
- In amphibians syngamy occurs outside the body of organism i.e external.
- In reptile syngamy occur inside the body of the organism i.e internal
Question 31.
What are the three major phases in the life cycle of an organism? Define each phase.
Answer:
Juvenile phase, Reproductive phase, senescent phase
- Juvenile phase-The phase of growth in the organisms before reproductive maturity
- Reproductive phase- In this phase organism attains reproductive maturity
- Senescent phase- The phase between reproductive maturity and death
Question 32.
How does the progeny formed from asexual reproduction differ from those formed by sexual reproduction?
Answer:
The progeny formed from asexual reproduction is the product of single parent and does not have genetic variations.
Question 33.
In yeast and amoeba the parent cell divides and give rise to two new individual cells. How does the cell division differ in these two organisms?
Answer:
In yeast, cell division is unequal and small buds are produced that remain attached to parent cell. In amoeba the cell division is equal and produces identical daughter cells.
Question 34.
Mention the site where syngamy occurs in amphibians and reptiles respectively.
Answer:
In amphibians syngamy occurs outside the body of organisms in the external medium (water). In reptiles syngamy occurs inside the body of an organism.
Question 35.
The turkey usually produces females for several. generations. How is this possible?
Answer:
In a turkey, female gametes undergo development without fertilization. This phenomenon is called parthenogenesis.
Question 36.
Leaves not only produce food but also produce young ones. Substantiate.
Answer:
In few plants the leaves are the means of vegetative propagation in addition to photosynthesis. In such plants, plantlets are formed on the leaves eg- Bryophyllum.
Question 37.
Observe the figures given below, identify and name the organisms and their asexual reproductive structures.
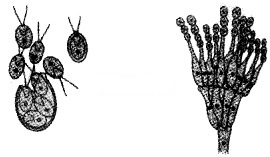
Answer:
Organisms – Asexual reproductive Structures
- Chlamydomonas – Zoospore
- Penicilium – Conidia
Question 38.
The chromosome number in the meiocyte of housefly is 12 and that of its gamete is 6. Write the reason for the change in chromosome number of meiocyte and gamete.
Answer:
Meiocyte is a diploid cell undergo reduction division to form haploid gametes.
Question 39.
In coconut, male and female flowers are separate. Write the technical term for the male and female flowers. Write the condition of the flower.
Answer:
- Female flower – pistillate
- Male flower – staminate
- Condition of the flower – unisexual
Question 40.
Observe the figures given below. Identify the gametes in A and B. Justify your answer.
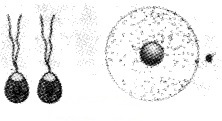
Answer:
- Homogametes
- Heterogametes
In first figure gamates come to fusion have similar structure but in second figure gametes have dissimilar structure.
Question 41.
Match the items of column A with B
| A | B |
| a. Offset | i. Ginger |
| b. Bulb | ii. Agave |
| c. Rhizome | iii. Onion |
| d. Adventitious leaf buds | iv. Water hyacinth |
| v. Bryophyllum |
Answer:

Question 42.
Analyse the table given below and fill in the blanks.
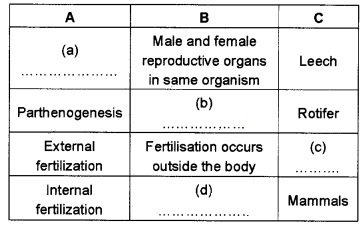
Answer:
- Hermaphrodite or bisexual
- Female gamete develops into new organism without fertilisation
- majority of algae or fishes or amphibians
- Fertilisation occurs inside the body
Question 43.
The chances of survival of young ones is greater in viviparous organisms than oviparous organisms. Justify this statement.
Answer:
In viviparous organisms the zygote develops into young one inside the body of the female organism. So during the course of development proper embryonic care and protection is provided inside the female organism.
Question 44.
In some organisms male and female reproductive organs are seen in the same individual. Name that condition. Give two examples of such organisms.
Answer:
Hermaphrodite Eg.Earthworm, Leech.
Question 45.
Name of certain plants and their vegetative propagules are given below. Make correct pairs using them. Agave, Offset, Ginger, Bulb, Bulbil, Water hyacinth, Potato, Bryophyllum, Rhizome
Answer:
- Agave – Bulbil
- Ginger-Rhizome
- Water hyacinth – offset
- Onion-Bulb
Question 46.
Gametogenesis and gamete transfer are the two prefertilisation events. Write the differences between the two.
Answer:
Gametogenesis – It is the formation of gametes.
Gamete transfer – It is the transfer of male gamete to the female gamete.
Question 47.
Based on the nature of reproduction, organisms are classified as continuous breeders and seasonal breeders. Write the difference between the two.
Answer:
- Continuous breeders – They are reproductively active throughout their reproductive phase.
- Seasonal breeders – They reproduce only during favourable seasons in their reproductive phase.
Question 48.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill in the blanks.
- Hydra: Bud; …….: Gemmule
- Birds: Internal fertilization; …….External fertilization.
Answer:
- Sponge: gemmule
- Algae or fishes or amphibian
Question 49.
Fertilisation in some organisms occur outside the body. Name that kind of fertilization. Write its disadvantage.
Answer:
External fertilization
In this type young ones are subjected to threat of predators. So, it is the disadvantage of external fertilisation.
Question 50.
The offspring formed by asexual reproduction is referred to as clone. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Offsprings formed are morphologically and genetically similar among themselves and to their parents. So such individuals are called clone.
Plus Two Botany Reproduction in Organisms Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
During sexual reproduction-fertilization is an important process. But in most aquatic organisms like fishes, amphibians, etc. external fertilization occur. In most terrestrial organisms internal fertilization is common.
- Point out the differences between external and internal fertilization.
- Write the disadvantages of external fertilization.
Answer:
(a) 1. External Fertilization:
Syngamy occurs in the external medium – water i.e. outside the body of organisms. Eggs and sperms are released outside the female and male parents respectively and move through water before fusion of gametes.
2. Internal Fertilization:
Syngamy occurs inside the body of organisms. Egg is formed inside the female body where they fuse with male gamete that is released by the male parent.
(b) Offsprings formed by external fertilization, are extremely vulnerable to predators threatening their survival up to adulthood.
Question 2.
Write technical terms for the following.
- Morphologically different types of gametes.
- Process of formation of male and female gametes.
- Formation of new organisms without fertilization.
Answer:
- Heterogametes
- Gametogenesis
- Parthenogenesis
Plus Two Botany Reproduction in Organisms NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In bacteria and lower organisms offspring formed are close similar among themselves and to their parents.
- Name offsprings derived through such process
- Write down the 2 characterstics of such offsprings
Answer:
- Clone
- Morphologically and genetically similar
Question 2.
The offsprings formed by a sexual reproduction have better chances of survival. Why?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction combines the characters of two parents and introduces variations which make the offsprings better in environmental adaption.
Question 3.
How does the progeny formed from asexual reproduction differ from those formed by sexual reproduction?
Answer:
The progeny formed from asexual reproduction is the product of single parent and does not have genetic variations.
Question 4.
In some lower and higher plants offsprings are produced shows greater similarity and it occurs mainly through asexual reproduction, in higher plants the process occurs through vegetative propagation.
- What is vegetative propagation?
- Give two suitable examples.
Answer:
1. The process of multiplication, in which parts or fragments of the plant act as reproductive unit or propagule to form new individuals is called vegetative propagation.
2. Examples,
- Buds (eyes) of Potato.
- Rhizome of Ginger.
Question 5.
Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction. Why is vegetative reproduction also considered as a type of asexual reproduction?
Answer:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| 1. It is always uniparental 2. There is no formation and fusion of gametes. 3. Only mitotic cell division takes place. 4. Offsprings are genetically identical to the parent. | 1. It is usually biparental 2. Formation and fusion of gametes take place. 3. It involves both meiosis and mitosis. 4. Offsprings genetically differ from the parent. |
Vegetative reproduction involves single parent and its offsprings are genetically identical hence it is considered as a type of asexual reproduction.
Question 6.
Higher organisms have resorted to sexual reproduction in spite of its complexity. Why?
Answer:
Because sexual reproduction induces genetic variability(adaptations) which make the offsprings better equipped for the struggle of existence.
Question 7.
Some organism are capable of producing fertilized egg but others are not possible.
- Name the organism producing fertilized egg.
- Why are offspring of oviparous animals at a greater risk as compared to offsprings of viviparous animals.
Answer:
- oviparous animals
- In oviparous orgaisms development of zygote take place outside the body of the female parent, (they lay fertilized /unfertilized egg). In viviparous organisms development of zygote develops into a young one inside the body of the female organism.
This offers proper embryonic care and protection and have better chances of survival than young ones of viviparous organisms.
Question 8.
Prefertilisation events events of sexual reproduction in all organisms are gametogenesis and gamete transfer.
- What are the post fertilization events?
- Name the parts of plants such as ovary, ovule and ovary wall develop in post fertilization process.
Answer:
- Zygote formation Embrogenesis
- Ovary-fruit, ovule-seed, ovary wall -pericarp
Plus Two Botany Reproduction in Organisms Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In papaya, the flowers are:
(a) Unisexual
(b) Bisexual
(c) neuter
(d) Flowers are not formed
Answer:
(a) Unisexual
Question 2.
In vegetative propagation, characters of parent plants are:
(a) Changed
(b) Not preserved
(c) preserved
(d) Exchanged
Answer:
(c) preserved
Question 3.
Rhizopus reproduces asexually by:
(a) Conidia
(b) Spores
(c) Gemma
(d) Bulbil
Answer:
(b) Spores
Question 4.
In potato, vegetative propagation takes place by:
(a) Root
(b) Leaf
(c) Grafting
(d) Stem tuber
Answer:
(d) Stem tuber
Question 5.
Vegetatively propagated plants are:
(a) Genetically similar
(b) Genetically dissimilar
(c) Do not bear roots
(d) Do not form buds
Answer:
(a) Genetically similar
Question 6.
Syngamy means:
(a) Fusion of similar spores
(b) Fusion of dissimilar spores
(c) Fusion of cytoplasm
(d) Fusion of gametes
Answer:
(d) Fusion of gametes
Question 7.
In which pair both the plants can be vegetatively propagated by leaf pieces?
(a) Bryophyllum and Kalanchoe
(b) Chrysanthemum and Agave
(c) Agave and Kalanchoe
(d) Asparagus and Bryophyllum
Answer:
(a) Bryophyllum and Kalanchoe
Question 8.
Regeneration of a plant, cell to give rise to new plant is called :
(a) Reproduction
(b) Budding,
(c) Totipotency
(d) Pleuripotency
Answer:
(c) Totipotency
Question 9.
Hydra reproduces asexually through:
(a) iragmettatwn
(b) Budding
(c) binary fission
(d) Sporulation
Answer:
(d) Sporulation
Question 10.
Animals giving birth to young ones are
(a) Oviparous
(b) Ovoviviparous
(c) viviparous
(d) both b and c
Answer:
(c) viviparous
Question 11.
The offspring that are exactly identical to one another as well as identical to their parents are called as
(a) clone
(b) twins
(c) replicates
(d) drones
Answer:
(a) clone
Question 12.
Buds and conidia are asexual reproductive structures of
(a) hydra&rhizopus
(b) rhizopus & penciriium
(c) hydra & pencillium
(d) both a&b
Answer:
(c) hydra & pencillium
Question 13.
Banana is multiplied through
(a) suckers
(b) seeds
(c) rhizome
(d) stolen
Answer:
(c) rhizome
Question 14.
In rotifers, the type of reproduction responsible for the organisms to multiply is
(a) apomixis
(b) parthenogenesis
(c) asexual reproduction
(d) sexual reproduction
Answer:
(b) parthenogenesis
Question 15.
Bulbils are employed for multiplication of
(a) bryophyllum
(b) crocus
(c) Agave
(d) strawberry
Answer:
(c) Agave
Question 16.
During favourable condition Amoeba reproduces by
(a) binary fission
(b) buds
(c) multiple fission
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(a) binary fission
Question 17.
After post-fertilization, the ovary and ovule develops into
(a) pericarp and fruit
(b) fruit and seed
(c) fruit and seed coat
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) fruit and seed
Question 18.
The plants which flower every year after attaining certain maturity are called
(a) monocarpic
(b) polycarpic
(c) perennials
(d) annuals
Answer:
(b) polycarpic
Question 19.
The type of reproduction occurs in ciliated protozoans is
(a) syngamy
(b) conjugation
(c) budding
(d) cross fertilization
Answer:
(b) conjugation
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms help you. If you have any query regarding the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
