Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations
Question 1.
Given below is a table which shows the interspecific interaction.’+’ sign indicates beneficial,sign indicates detrimental and ‘0’ indicates neutral. (MARCH-2010)
a) Fill in the blanks.
| Species A | Species B | Interaction |
| – | – | Competiton |
| 0 | – | ……………. |
| + | 0 | …………… |
b) Name the interactions where one species is benefited and the other is detrimental.
Answer:
Amensalism
Commensalism
Question 2.
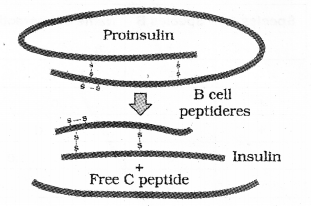
Small bottle labelled with rDNA insulin. (MARCH-2010)
a) Does it a natural insulin ?
b) Identify the major steps involved in this rDNA insulin production.
Answer:
No.
1. Isolation of desired genes.
2. Insertion of desired Genes into plasmids of E. coli.
3. Introduction of plasmids into E coli cells.
4. Culture of E coli cells.
5. After this, a polypeptide chains A and B are separated and connected together by disulphide linkages.
Thus, genetically engineered insulin is prepared
Question 3.
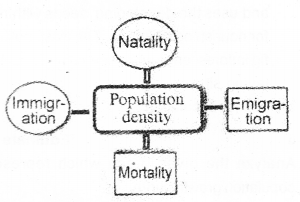
Given below a schematic representation with circles and squares, which shows four factors/processes influence the population density. (MARCH-2010)
Write the positive factors in circles and negative factors in squares.
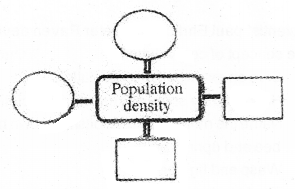
Answer:
Question 4.
Snakes change their body temperature with changes in external temperature, but human beings not. Organism may be classed according to above character with explanation. (MAY-2010)
Answer:
Temperature has a significant role in the kinetics of enzymes and thus influence the metabotic activities and physiological functions. Accordingly organisms can be classified into eurythermal (tolerate wide range of temperature) and Stenothermal (restricted to narrow range of temperature)
Question 5.
Density of a population in a given habitat during a given period, fluctuates due to changes in 4 basic processes – Natality, Mortality, Immigration & Emigration. (MAY-2010)
a) Differentiate Natality and Mortality.
b) Differentiate Immigration and Emigration.
Answer:
a) Mortality is the number of death of a population at a given period and Natality is the number of birth during a given period.
b) Immigration is the number of individuals of the same species that have come into the habitat from elsewhere during the time period. Emigration is the number of individuals of the population who left the habitat and gone elsewhere during the time period.
Question 6.
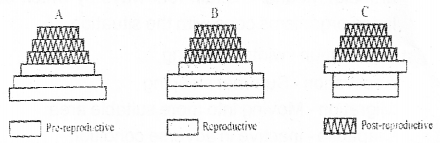
Given above is the bar diagram showing age structure of three different populations. Observe the diagram carefully and answer the following questions. (MARCH-2011)
a) Select the stable population.
b) Compare the nature of population growth in A,B, and C
Answer:
a) ‘B’Stable population
b)
| A | B | C |
| Expanding Positive growth | Stable Zero growth | Declining negative growth |
Question 7.
By observing the relationship of the first, fill in the blanks. (MARCH-2011)
a) Unisexual male flower-Staminate ______
Unisexual female flower ______
b) Organisms tolerating a wide range of temperature – eurythermal
Organisms tolerating a narrow range of temperature ______
Answer:
a) pistillate
b) stenothermal
Question 8.
Population interactions: (MAY-2011)
| Case | Species x | Species y | Species z |
| 1 | + | + | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | – | + |
| 3 | – | + | – |
Where’+’ beneficial interaction detrimental interaction ‘0’ neutral interaction.
Observe the interactions of populations of 3 species as shown in the table. Name the interactions
a) Species x and species y in case 1.
b) Species y and species z in case 2.
c) Species x and species z in case 3.
d) Species y and species z in case 1
Answer:
a) Mutualism
b) Predation/Parasitism
c) Competition
d) Commensalism
Question 9.
Mohammed and his family left to Dubai from Kozhikode on March, 2009. In Kozhikode they are referred as after 2009. How it affects Kozhikode population? (MAY-2011)
Answer:
Emigrants, Decrease the size of population
Question 10.
Inter specific interaction from the interaction of populations of two different species. If we assign + for beneficial, — for detrimental and 0 for neutral interactions, copy and complete the following chart. (MARCH-2012)
| Species A | Species B | Name of interaction |
| …………… | …………………. | Mutualism |
| – | – | ………….. |
| ……………. | …………………. | Commensalism |
| ……………. | ……………………. | Amensalism |
| + | – | ……………… |
Answer:
| Species A | Species B | Name of interaction |
| + | + | |
| Competition | ||
| + | 0 | |
| – | 0 | |
| Parasitism /predation |
Question 11.
Prakash parked his car in bright sunlight for a few hours, with glass windows fully raised. After sometime inside of the car was very hot. (MAY-2012)
a) Name the phenomenon.
b) How can you correlate this phenomenon with global warming?
Answer:
a) Green house effect
b) The green house effect is due to various green house gases, of which the percentage of carbon dioxide is very high. This causes the increase of temperature on earth called Global warming.
Question 12.
Students involved in nature club activity found some interspecific interactions between organisms in a garden area. They made a table of interaction giving’+’ for beneficial interaction,for detrimental and ‘O’ for neutral interaction. (MAY-2012)
| Sno | Species A | Species B |
| i. | + | + |
| ii. | – | – |
| iii. | + | 0 |
| Iv | – | 0 |
a) Give name of interaction in each case.
b) Explain how parasitism differ from predation.
c) Give the significance of species interaction.
Answer:
i – Mutualism
ii – competition
iii – commensalism
iv- amensalism
b) In parasitism, parasite absorb nutrients from the living host In predation, predator kills and eat the prey.
c) Species interaction is beneficial, detrimental or neutral (neither harm nor benefit) to one of the species or both.
Question 13.
Read the statements below and identify the mode of interaction between the species. (MARCH-2013)
a) Tiger eating deer
b) Butterfly feeding pollen
c) Human liver fluke feed on snail
d) Lice on humans
e) Orchid attached to a tree
f) Mycorrhizal association of fungi and roots of higher plants.
g) Sparrow eating seed
h) Egrets foraging close to cattle
Answer:
a) predation
b) mutualism
c) predation or parasitism
d) parasitism
e) commensalism
f) mutualism
g) predation
h) commensalism
Question 14.
In summer we use air conditioners and in winter we use heaters. Here homeostasis is accomplished by artificial means. Explain four ways by which other living organisms cope with the situation. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
Hibernation – winter sleeping
Aestivation – Summer sleeping
Migration – Moving into more suitable area
Diapause – inactive in adverse condition
Question 15.
Many desert plant have adaptations to prevent loss of water from their body. Mention any two adaptations to minimise water loss from plant body. (MAY-2013)
Answer:
a) Many desert plants have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces and have their stomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration.
b) They also have a special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) that enables their stomata to remain closed during daytime.
Question 16.
The size of a population is not static. Which of the following leads to decrease in population? (MAY-2013)
1) Natality and Mortality
2) Mortality and Emigration
3) Mortality and immigration
4) Natality and Immigration
Answer:
Mortality and Emigration
Question 17.
Some type of Orchids live on the branches of Mango trees. The relationship between mango tree and Orchid is an example of. (MAY-2013)
1) Mutualism
2) Predation
3) Commensalism
4) Parasitism
Answer:
Commensalism
Question 18.
The density of population in a given habitat increase or decrease due to different reasons. Name two factors responsible for increase in population in a given area. (MARCH-2014)
Answer:
Natality and Immigration
Question 19.
Observe the diagram:(MAY-2014)
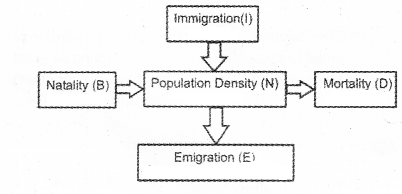
Define the following terms:
a) Natality
b) Mortality
c) Emigration
d) Immigration
Answer:
a) Birth rate or total number of live births per 1,000 of a population in a year.
b) Death rate or total number of death per 1,000 of a population in a year.
c) Emigration- movement of individuals out of the population
d) Immigration- movement of individuals into the population
Question 20.
Response of organisms to abiotic stress involves different methods. Explain any two such responses with suitable examples. (MAY-2014)
Answer:
i) Regulate: Organisms are able to maintain constant body temperature and constant osmotic Concentration. Eg- birds and mammals
ii) Conform: Organisms cannot maintain a constant internal environment.
Eg- Majority (99 percent) of animals and all plants.
Question 21.
Suckerfish and shark live in close association, is a classic example of commensalism. What is commensalism? (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Commensalism -This is the interaction in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
Question 22.
Desert plants like Opuntia are able to grow in extreme conditions. Suggest any two adaptations of this plant. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
1) They have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces
and have their stomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration.
2) They also have a special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) that enables their stomata to remain closed during day time
3) The photosynthetic function is carried out by the flattened stems.
Question 23.
With regard to population growth rate, when responses are limiting the plit is logistic. Verhulst-Pearl Ligstic growth is represented by the equation. (MARCH-2015)
dNdt=rN(K−N)K what,are
a) r
b) K
Answer:
a) r-lntrinsic rate of natural increase or( b-d)
b) k-Carrying capacity
Question 24.
Observe the equation (MAY-2015)
dNdt=rN(K−N)K
a) Which type of growth curve does it represents?
b) What do the following notations represent:
a) N b) r c) K
Answer:
a) Logistic growth
b) N-population of size
b) r- intrinsic rate of natural increase
c) K-Carrying capacity
Question 25.
On earth, life exists even in extreme and harsh conditions. Mention any two major biomes in India. (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
Tropical deciduous forest
Rain forest
Question 26.
a) Population interactions may be beneficial or not. Write any three interactions in detail. (MARCH-2016)
OR
b) Organism are influenced by biotic and abiotic factors. Write an account of any three abiotic environmental factors.
Answer:
a) Mutualism- in this both partners are benefitted eg lichen (+,+)
Commensalism- In this one partner is benefitted other partner is neither benefitted nor harmed (-, +) Competition- In this both partners have detrimental effect or negative effect (-, -)
OR
b) Temperature- it affect the enzyme kinetics of reaction. Enzyme works at optimum temperature
Water- it affect productivity and distribution of plants in aquatic ecosystem.
Light- It influence the photoperiodic flowering of plants
Question 27.
Population growth may be exponential or logistic. Differentiate between them. (MAY-2016)
Answer:
When the resources in the habitat are unlimited, each species has the ability to grow in number. Here the population grows in an exponential or geometric fashion. dN/dt = rN
Limited resources leads to competition between individuals and the ‘fittest’ individual will survive and reproduce. This is called logistic growth
dNdt=rN(K−N)K
Question 28.
Plants are adapted to grow in different habitats. Name any four adaptations of plants in desert habitat. (MAY-2016)
Answer:
Desert plants have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces and stomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration.
They also have CAM pathway in which they open stomata during night and closed during day time.
Question 29.
In a given habitat, the maximum number possible for a species is called _________ of that species in that habitat. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
Carrying capacity (K)
Question 30.
Different types of population interaction has been observed in a population. (MARCH-2017)
Write the types of interaction observed among the following species:
| Species A | Species B | Type of interaction |
| Orchid ophrys | Bees | —————— |
| Cattle | Cattle egret | —————— |
| Sea anemone | Clown fish | ——————- |
| Ticks | Dogs | ——————– |
| Cuscuta | Hedge plant | ——————- |
| Tiger | Deer | ——————– |
OR
B) Organisms other than human beings manage or adapt to stressful conditions by adopting different mechanisms. Explain any three mechanisms adopted by them to maintain the internal environment.
Answer:
A) Mutualism or pseudocopulation Commensalism Commensalism Parasitism Parasitism Predation
OR
B) 1) Conform : About 99% of animals and all plants cannot maintain a constant internal environment according to the external environment. They change their body temperature and osmotic concentration of body fluid when external environment changes.
2) Migrate : Some organisms move away temporarily from the stressful habitat to a more hospitable area and return when stressful period is over.
3) Suspend : Some organisms like bacteria, fungi and lower plants produce thick walled spores to tide over unfavourable conditions.
Some organism avoid the stress by escaping in time by method of hibernation during winter (eg. polar bear) or aestivation to avoid summer related problem (eg: snails and shells).
Question 31.
There are four mechanism by which living organisms other than human beings maintain the constancy of internal environment. Name these processes. (MAY-2017)
Answer:
Organisms maintain internal environment as constant by sweating shivering deposition of fat layer below skin and hairy covering on body surface.
Question 32.
Adaptations are the attributes of the organism that enables it to survive and reproduce in its habitat. Give the adaptations of (MARCH-2014)
a) Cactus plant in desert
b) Kangaroo rat in desert
c) Seals in polar region.
Answer:
a) Desert plants have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces and have theirstomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration
b) kangaroo rat in North American deserts is capable of meeting all its water requirements through its internal fat oxidation
c) In the polar seas aquatic mammals like seals have a thick layer of fat (blubber) below their skin that acts as an insulator and reduces loss of body heat.
