Kerala Plus One Zoology Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Zoology |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time: 1 Hour
Cool off time : 10 Minutes
Maximum : 30 Scores
General Instructions to candidates:
- There is a ‘cool off time’ of 10 minutes each for Botany and Zoology in addition to the writing time of 1 hour each. Further there is a ‘5 minutes’ ‘preparatory time’ at the end of the Botany Examination and before the commencement of the Zoology Examination.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read the instructions carefully.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- Calculations, figures and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from question numbers 1 to 3. Each carry 1 score. (3 × 1 = 3)
Question 1.
Binomial nomenclature was proposed by ………..
Answer:
Carolus Linneaus
Question 2.
Tendons and Ligaments are example of ……….. tissue
a) Areolar
b) Adipose
c) Dense regular
d) Dense irregular
Answer:
c) Dense regular
Question 3.
……….. is the most abundant protein in the animal world.
Answer:
Collagen
Answer any nine questions from 4 to 14. Each carries two scores. (9 × 2 = 18)
Question 4.
“All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates’’. Do you agree with this statement? Substantiate.
Answer:
Yes,
The notochord is replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult.
Question 5.
Distinguish between:
a) Tidal volume and Residual volume
b) Vital capacity and Total lung capacity
Answer:
a) Residual Volume (RV):
Volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. This averages 1100 mL to 1200 mL.
Tidal Volume (TV): Volume of air inspired or expired during a normal respiration. It is approx 500 mL
b) Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration.
Total Lung Capacity: Total volume of air accommodated in the lungs at the end of a forced inspiration.
Question 6.
Observe the figure of the organism given below

a) Identify the organism
b) Name the calss in which it belongs
c) Mention any two salient features fo the class
Answer:
a) Hippocampus
b) Osteichthyes
c) 1. They have four pairs of gills which are covered by an operculum on each side.
2. Air bladder is present which regulates buoyancy
Question 7.
a) Name the following:
i) The carbohydrate splitting enzyme present in human saliva.
ii) The antibacterial enzyme present in human saliva
b) In which region of the alimentary canal does the following reactions occur?
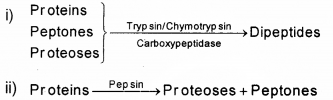
Answer:
a) 1. Salivary amylase
2. Lysosyme
b) 1. Intestine
2. Stomach
Question 8.
a) Person with ‘AB’ blood group is called ‘universal recepient’. Give a reason.
b) List out any two disorders of human criculatory system.
Answer:
a) Persons with ‘AB’ group can accept blood from persons with AB as well as the other groups of blood.
Therefore, such persons are called ‘universal recipients’.
b) 1. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Hypertension is the term for blood pressure that is higher than normal (120/80).
2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Coronary Artery Disease, often referred to as atherosclerosis, affects the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle.
Question 9.
Complete the flowchart given below.
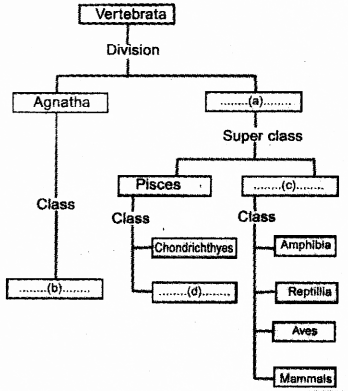
Answer:
a) Gnathostomata
b) Cyclostomata
c) Tetrapoda
d) Osteichthyes
Question 10.
a) Give one word for the following:
i) Presence of Glucose in Urine
ii) Presence of Ketone bodies in Urine
b) Which human disorder is having the above mentioned two symptoms?
Answer:
a) 1.Glycosuria
2. Ketonuria
b) Diabetes mellitus
Question 11.
Observe the figures given below.
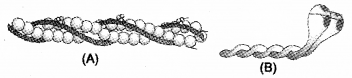
a) Identify figure ‘A’ and ‘B’.
b) Name the subunits of ‘A’ and ‘B’
Answer:
a) 1. Actin
2. Myosin
b) Each actin (thin) filament is made of two ‘F’ (filamentous) actins helically wound to each other. Each ‘F’ actin is a polymer of monomeric ‘G’ (Globular) begins.
Myosin consists of monomeric proteins called Meromyosins.
Each meromyosin has two important parts, a globular head with a short arm and a tail, the former being called the heavy meromyosin (HMM) and the latter, the light meromyosin (LMM).
Question 12.
Note the relationship in the first pair and then complete the second pair.
a) Insulin : Hypglycemic hormone
………. : Hyperglycemic hormone
b) Over secretion of Growth hormone : Gigantism
Low secretion of Growth hormone : ………..
Answer:
a) glucagon
b) dwarfism
Question 13.
Observe the diagram A and B given below.
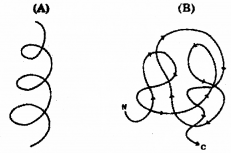
What is ‘A’ and ‘B’?
b) Mention the other two levels of protein structure.
Answer:
a) A – Secondary structure of protein
B – tertiary structure of proteins
b) primary structure of proteins and quarternary structure of proteins
Question 14.
Classify the following animals on the basis of the mode of nitrogenous waste excretion in the table given below.
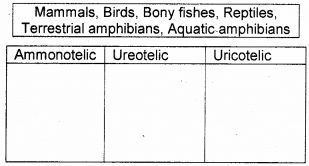
Answer:
| Amonotelic | Ureotelic | Urecotelic |
| Bony fishes | mammals | reptiles |
| Aquatic amphibians | Terrestrial amphibians | Birds |
Answer any three questions from 15 to 18. Each carries three scores. (3 × 3 = 9)
Question 15.
Find the odd one from each group. Justify your answer.
a) Star fish, Devil fish, Dog fish, Jelly fish
b) Flying fish, Angel fish, Saw fish, Fighting fish
c) Sea lily, Sea cucumber, Sea hare, Sea urchin
Answer:
a) Dog fish – belongs to chordates while others are non chordates
b) Saw fish – belongs to chodricthyes while others are Osteichthyes
c) Sea hare – belongs to phylum mollusca while others are phylum Echinodermata
Question 16.
Prepare a flow chart showing the parts of human brain, by using the details given below.

Answer:
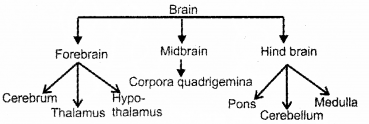
Question 17.
Diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG is given below.
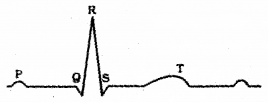
a) Expand ECG
b) What does the ‘P’, ‘T’ waves denote?
c) Mention the clinical significance of ECG.
Answer:
a) ECG – electrocardiogram
b) P wave – atrial depolarization
T wave – ventricular repolarisation
c) It helps in the diagnosis of heart diseases
Question 18.
Match column ‘A’ with those in columns ‘B’ and ‘C’.
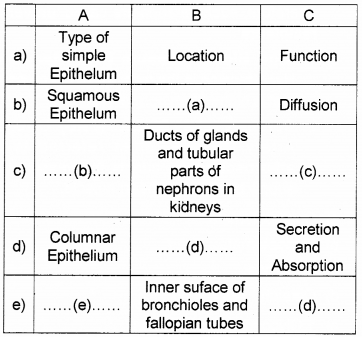
Answer:
a) found in the wall of blood vessels
b) cuboidal epithelium
c) secretion/absorption
d) lining of stomach or intestine
e) ciliated epithelium
f) movement/transport
