Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 9 Locomotion and Movement
Plus One Locomotion and Movement One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Ribs are attached to
(a) Scapula
(b) Sternum
(c) Clavicle
(d) llium
Answer:
(d) llium
Question 2.
What is the type of movable joint present between the atlas and axis?
(a) Pivot
(b) Saddle
(c) Hinge
(d) Gliding
Answer:
(a) Pivot
Question 3.
ATPase of the muscle is located in
(a) Actinin
(b) Troponin
(c) Myosin
(d) Actin
Answer:
(c) Myosin
Question 4.
Macrophages and leucocytes exhibit
(a) Ciliary movement
(b) Flagellar movement
(c) Amoeboid movement
(d) Gliding movement
Answer:
(c) Amoeboid movement
Question 5.
Which one of the following is not a disorder of bone?
(a) Arthritis
(b) Osteoporosis
(c) Rickets
(d) Atherosclerosis
Answer:
(d) Atherosclerosis
Question 6.
Suggest a suitable word for the fourth place
- thin filament : Actin :: Thick filament : ___________
- Pelvic girdle : humerus :: Pelvic girdle : ___________
Answer:
- myosin
- Femur
Question 7.
Copy the paragraph below about the structure of a striated muscle. Choose the words from the following list & fill up the gaps.
Under lightmicroscope, the striated muscle shows ________ (a) band & _______ (b) band. The distance between 2 adjacent Z lines is known as __________ (c).
(sarcomere, lightband, A band, H-zone, M line, darkband)
Answer:
(a) Ligthband
(b) Darkband
(c) Sarcomere
Question 8.
A person is suffering from joint pain. His blood test shown increased amount of Uric acid. What will be the diagnosis?
Answer:
Gout
Question 9.
The infants have 33 vertebrae in the vertebral column. But an adult has only 26 vertebrae. What will happen to the remaining vertebrae.
Answer:
Ulna
Plus One Locomotion and Movement Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The axial skeleton contains 80 bones. Make a table according to where it is seen and number of bones present in each section.
Answer:
| Skull | 29 |
| Vertebral column | 26 |
| Ribs | 24 |
| Sternum | 1 |
| Total | 80 |
Question 2.
One of the following statements is incorrect. Find and correct it.
- The number of cervical vertebrae is seven in all mammals except human beings.
- Thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum together make ribcage.
- Accumulation of uric acid in joints leads to gout.
Answer:
Statement 1 is incorrect. The number of cervical vertebrae is seven in all mammals including human beings.
Question 3.
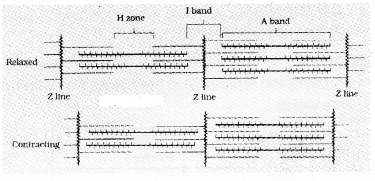
- Name the process shown here, which theory explain this process?
- Draw and complete the process.
Answer:
1. Muscle contraction, Sliding – filament theory
2.
Question 4.
Red muscle fibers have greater capacity to do work for a prolonged period where as white muscles suffer from fatigue after a short time. Give reason.
Answer:
Red muscle fibers are red in colour due to the presence of large amount of myoglobin. Myoglobin is an oxygen storing pigment. These muscle also contain plenty of mitochondria which can utilise the large amount of oxygen stored in them for ATP production.
So red muscle fibers have greater capacity to do work for a prolonged period. White muscle fibers possess very less quantity of myoglobin and mitochondria.
Question 5.
Shoulder joints are not very stable. But they are freely movable. Give reason?
Answer:
Shoulder joints are freely movable joint or synovial joint. In this type of joint there is presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones. Such an arrangement allows considerable movement.
Question 6.
Name the types of joint between the following.
- Atlas/axis
- Between Cranial bones
- Carpal/Meta carpel of thumb
- Between Humerus and pectoral girdle
Answer:
- Pivot joint
- Fibrous joint
- Saddle joint
- Ball and socket joint
Question 7.
Analyse the table & fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
| Radium | Forearm |
| (a) | Femur |
| Atlas | (b) |
| Frontal bone | (c) |
| Humerus | Upper arm |
Answer:
| Radium | Fore arm |
| Thigh bone | Femur |
| Atlas | First vertebrae |
| Frontal bone | Cranium |
| Humerus | Upper arm |
Question 8.
The last two pairs of ribs are called floating ribs.
- What do you meant by the term floating ribs?
- What are true ribs?
Answer:
- Last 2 pairs of ribs are not connected ventrally to the sternum. These ribs are called floating ribs.
- First seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs. Dorsally, they are attached to the thoracic vertebrae and ventrally connected to the sternum with the help of hyaline cartilage.
Question 9.
Some joints in the body are characterized by pressure of a fluid filled cavity between articulating surfaces of two bones. Mention the peculiarity of these types of joint and give examples?
Answer:
This type of joint in called synovial joint or freely movable joint and allows considerable movement.
eg:
- Ball and socket joint (between humerus and pectoral girdle)
- Hinge joint (knee joint)
Question 10.
A muscle cell viewed under a microscope shown the following characters.
- Sarcolemma – Present
- Shape – Cylindrical
- Nucleus – Multinuclear
- Striation – Present
- Identify the muscle cell.
- Calcium ions are necessary for muscle contraction.
Answer:
If a muscle is placed in a solution containing calcium ions. Does the muscle contracts? Substantiate.
Answer:
- Skeletal muscle
- No. For muscle contraction to occur, presence of Ca++ ions intracellularly is needed.
Question 11.
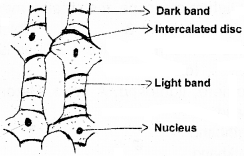
Pictorial representation of tissue is given in a lab diary with only one labelling – intercalated discusing your knowledge about tissue.
- Identify the tissue.
- Draw the structure of tissue and label the parts.
Answer:
1. Cardiac muscle
2.
Question 12.
You can move your hands at your will. But you can’t move your heart at your will. Comment.
Answer:
Muscles of the hand are skeletal muscles and they are voluntary muscle. Muscles of the heart are cardiac muscles and they are involuntary muscles.
Question 13.
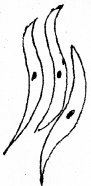
- Identify the muscle cell
- Mention its function.
Answer:
- Non-striated muscle (smooth muscle)
- Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles located in the inner visceral organs like alimentary canal, reproductive tract etc. So they help the transportation of food through digestive tract and gamete through the genital tract.
Question 14.
An investigation was arrived out to find the effect of the temperature on muscle contraction. The results are shown in the graph.
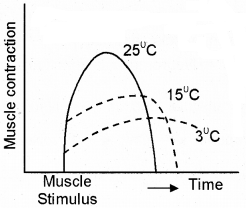
- Describe and suggest an explanation for one effect of temperature on muscle contraction.
- Name the filaments involved in muscle contraction.
Answer:
- When temperature increases muscle contraction increases, but when temperature decreases the extend of muscle contraction decreases, but the time remain in the contracted state increases,
- Actin and myosin
Question 15.
The red colour of the blood is due to the presence of hemoglobin in it. Certain skeletal muscles are red in colour even though they lack hemoglobin. Now explain how the red muscles have that particular colour.
Answer:
Muscle contains a red coloured oxygen storing pigment called myoglobin. Myoglobin content is high in some skeletal muscles which gives a reddish appearance.
Question 16.
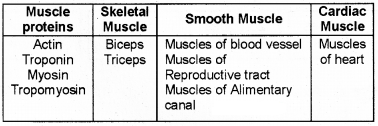
Actin, Troponin, Biceps, Muscles of blood vessels, Muscles of heart, Myosin, Muscles of reproductive tract, Tropomyosin, Muscles of Alimentary canal, Triceps.
Rearrange the terms in four columns on the basis of their similarity and give appropriate headings for each columns.
Answer:
Question 17.
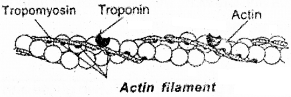
Identify the myofibril and label the parts given below.
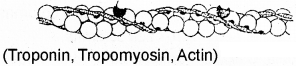
Answer:
Question 18.
Length of A band remains unchanged during muscular contraction. Is this statement true or false? Justify.
Answer:
True. A band or anisotropic band is the region where both thick filaments and thin filaments are present. During muscular contraction, the length of thick filament or thin filament does not change.
Question 19.
Match column I with column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Red muscle | 1. Pelvic girdle |
| 2. Suture | 2. Globular protein |
| 3. Ischium | 3. Immovablejoint |
| 4. Troponin | 4. Mybglobin |
| 5. Sternum |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Red muscle | 4. Mybglobin |
| 2. Suture | 3. Immovable joint |
| 3. Ischium | 1. Pelvic girdle |
| 4. Troponin | 2. Globular protein |
Question 20.
Complete the division of human skeletal system by filling the blanks.
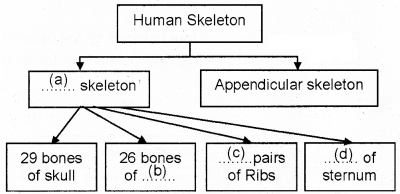
Answer:
(a) Axial
(b) Vertebral column
(c) 12
(d) One
Question 21.
Arrange the following bones into two columns and give proper heading to each columns.
Scapula, Carpals, Femur, Fibula, Tibia, Tarsals, Acetabulum, Metatarsals, Radius, Humerus, Glenoid cavity, Clavicle, Metal Carpals, Phalanges, Patella, Ilium, Ischium, Pubis.
Answer:
| Pectoral girdle and bones of forelimb | Pelvic girdle and Bones of Hind Limb |
| Clavicle | Ilium |
| Scapula | Ischium |
| Humerus | Pelvis |
| Radius | Femur |
| Ulna | Patella |
| Carpals | Tibia |
| Metacarpals | Fibula |
| Phalanges | Metatarsal |
| phalanges |
Question 22.
Your lungs and Heart are well protected in a cage. Which bone contributes to it?
Answer:
In an infant, there are 33 vertebrae in the vertebral column. Five of these bones fuse to form the sacrum and four of other join to become the coccyx. As a result, an adult vertebral column has 26 vertebrae.
Question 23.
There are joints at your shoulders and elbows. But their movement is different. Give reason.
Answer:
- Shoulder joint – Ball and socket joint
- Elbow joint – Hinge joint
Question 24.
What are the different types of movement shown by human cells?
Answer:
Amoeboid, ciliary and muscular, and flagellar movement.
Question 25.
Fill the gaps.
Answer:
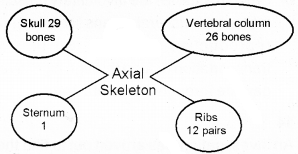
Question 26.
Draw a flow chart showing the flow of stimulus that results in muscle contraction. (Start from Neuromuscular junction)
Answer:
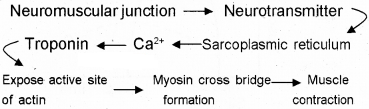
Question 27.
Match the following.
| A | B |
| a. Fixed joint | Shoulder joint |
| b. Ball and socket joints | Wrist and ankle |
| c. Hinge joints | Phalanges of hind limbs |
| d. Pivot joints | Bones of skull |
| e. Gliding joints | Elbow and joints of phalanges |
| f. Ellipsoid joints | Skull and vertebral column. |
Answer:
| A | B |
| a. Fixed joint | Bones of skull |
| b. Ball and socket joints | Shoulder joint |
| c. Hinge joint | Elbow and joints of Phalanges |
| d. Pivot joint | Skull and vertebral column |
| e. Gliding joint | Wrist and ankle |
| f. Ellipsoid joint | Phalanges of hind limbs |
Question 28.
Write the odd one out and give the reason for your answer.
- Fibrous joints, Ball and socket joints, hinge joints, pivot joints
- Humerus, Femur, Radius, Ulna.
Answer:
- Fibrous joints: They are immovable joints of the bones of the skull whereas all others are freely movable joints.
- Femur: It is the thigh bone whereas all other are the bones of the forelimb
Question 29.
Bones of the older people turn brittle and break quickly.
- Name the bone disorder stated above.
- List any two reasons for the above disorder.
Answer:
- Osteoporosis
- reasons for the above disorder
- Imbalance of hormones like thyrocalcitonin, parathyroid, and sex hormones.
- Deficiency of calcium and Vitamin D.
Question 30.
When you ride a bicycle two major joints of your leg should perform properly.
- Name the joints.
- To which type of synovial joints these belong?
Answer:
- Knee joint, Hip Joint
- Hinge joint, Ball and Socket joint
Question 31.
In human body different types of movement shown by some cells.
- Name the type of movement shown by human sperm.
- Which is the part of sperm help this movement?
Answer:
- Flagellar movement
- Whip like movement of the tail and the middle piece of the sperm
Plus One Locomotion and Movement Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
State one difference in each of the following pairs on the basis of what is indicated in brackets.
- Glenoid cavity and acetabulum (location and function)
- Osteoarthritis and Gout (cause)
Answer:
1. Glenoid cavity:
It is a cap like depression in the pectoral girdle to which the head of the humerus fits in.
Acetabulum:
It is a cap like depression present in the pelvic girdle to which head of the femur bone fits in.
2. Osteoarthritis:
It is caused by the degeneration of the articular cartilage.
Gout:
It is caused by accumulation of uric acid crystals.
Question 2.
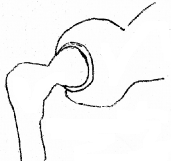
- Observe the diagram and identify the type of joint.
- Where can you find this type of joints in your body?
- Comment on its ability to move.
Answer:
- Ball and socket joint
- Shoulder joints and Hip joints
- In ball and socket joint, one of the bones forms a ball like head while the other forms a cup like socket into which head fits in. It allows the free movement of the bone with the ball like head.
Question 3.
X-ray photography of forelimb of a person is given here. One of the bones found to be fractured. Name the bone with fracture.
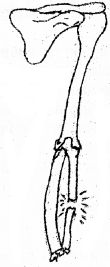
Answer:
a. (i) Across:
1. Hyoid
3. Cranium
4. Pelvic girdle
(ii) Down:
2. Coccyx
5. Ulna
b. Hyoid and cranium
Question 4.
According to colour, muscles are of two types.
- Name the two muscles.
- Why are they called so?
- Give examples.
Answer:
- Red muscle and white muscle.
- Red muscles contain large amount of mitochondria and myoglobin whereas the white muscles contain only less amount of mitochondria and myoglobin.
- Examples
- Red muscles – Extensor muscles on the back.
- White muscles – muscles of the eye ball.
Question 5.
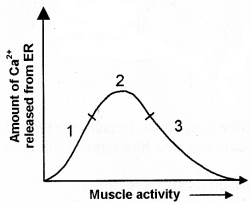
- Observe the above graph and find out the region of graph where muscle show maximum contraction. Justify your answer.
- Name the different types of muscle proteins present in thick and thin filaments.
- Ca2+ is necessary for muscle contraction. Why?
Answer:
1. Region 2 During Muscular contraction amount of Ca2+ released from ER is very high.
2. Thick filament – Muscle protein – myosin
Thin filament – Muscle protein – actin, troponin, tropomyosin.
3. Muscle contraction is regulated by a regulator protein troponin. Troponin mask the active site of actin molecule from myosin head, Action potential reaching a muscle cause the ER to release Ca2+.
This Ca2+ bind with the specific site of troponin. It causes a conformational change by which the active site of actin molecule is exposed and it results in cross bridge activity and muscle contraction.
Question 6.
Will muscle contraction occur in the following conditions. Justify your answer.
- Troponin is removed from the thin filament.
- No ATP is supplied to the muscle.
- All endoplasmic reticulum are removed from muscle cells.
Answer:
- Muscle contraction occur.
- Muscle contraction does not occur. Attachment and detachment of myosin head to actin molecule requires ATP.
- No muscle contraction. Ca2+ necessary for muscular contraction is released from endoplasmic reticulum.
Question 7.
The given statements are about the structure of muscles. Categorise them into a table giving appropriate headings.
- These muscles have striation.
- These are found inside the wall of hollow internal organs.
- These muscles have no striations.
- They are voluntary muscles.
- They are muscles of the arms and legs.
- They are involuntary muscles
Answer:
| Skeletal Muscle | Smooth muscle |
| 1. These muscles have striation | 2. These muscles are found inside the wall of hollow internal organs. |
| 4. They are voluntary muscles. | 3. These muscles have no striation |
| 5. They are muscles of the arms and legs | 6. They are involuntary muscles |
Question 8.
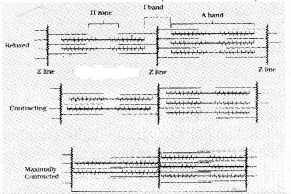
Observe the following diagram.
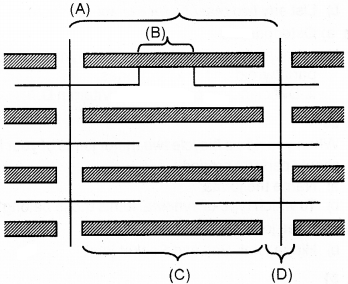
- Identify A, B, C, D.
- What is Sarcomere?
- List out the changes that take place during muscle contraction to ABC and D.
Answer:
- Identification
- A – Sarcomere
- B – Hzone
- C – Aband
- D – Iband
- A sarcomere is a region between two adjacent Z line. It is formed of a complete A band in the middle and halves of two I bands present on either side.
- the changes take place during muscle contraction to ABC and D:
- A – Two Z lines of the sarcomere come close together resulting in the shortening of the sarcomere.
- B – H – Zone completely disappears.
- C – No change in the length of A band
- D – I – band get reduced
Question 9.
Give an example of a synovial joint.
Answer:
- Ball and socket joint (between humerus and pectoral girdle)
- Hinge joint – knee joint
Question 10.
Suppose a person is suffering from calcium deficiency for a prolonged time. How does it affect muscular contraction? (Note: Description necessary)
Answer:
Muscle contraction begins when a nerve impulse reaches at the neuromuscular junction. During this time the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca2+. The Ca2+ binds with the specific site of the troponin of the actin filament.
This causes a conformational change in the troponin molecule and expose the active site on the actin molecule. Myosin filament binds with the active site of actin and there is formation a cross bridge. By the movement of cross bridge contraction occurs.
The contraction is followed by relaxation and it occurs when Ca2+ in pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. As a result, the troponin molecules became free to mask the active site of the myosin head.
Question 11.
Identify the following diseases noting the symptoms given below
- The liver is affected, skin and eyes turn yellow due to the deposit of bile pigments.
- Difficulty in breathing causing wheezing due to the inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles.
- Chronic disorder in which alveolar walls are damaged mainly due to cigarette smoking.
- Auto immune disorder affecting neuro muscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscles.
- Inflammation of joints due to deposition of uric and crystals.
- Age related disorder due to decreased level of estrogen, characterised by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures.
Answer:
- Jaundice
- Asthma
- Emphysema
- Myasthenia gravis
- Gout
- Osteoporosis
Question 12.
Identify the following tissues and write down their location.
- Loose connective tissue which stores fat.
- Dense connective tissue which connect bone to bone.
- A contractile tissue which possess intercalatory disc.
Answer:
- Adipose tissue – beneath the skin
- Ligament – attach one bone to another
- Cardiac muscle – heart
Plus One Locomotion and Movement NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Answer:
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by the sliding filament theory which states that contraction of a muscle fibre takes place by the sliding of the thin filaments over the thick filaments.
Question 2.
Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Answer:
Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal sent by the central nervous system (CNS) via a motor neuron. A motor neuron alongwith the muscle fibres connected to it constitute a motor unit. The junction between a motor neuron and the sarcolemma of the muscle fibre is called the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate.
1. A neural signal reaching this junction releases a neurotransmitter (Acetylcholine) which generates an action potential in the sarcolemma. This spreads through the muscle fibre and causes the release of calcium ions into the sarcoplasm.
2. Increase in Ca2+ level leads to the binding of calcium with a subunit of troponin on actin filaments and thereby remove the masking of active sites for myosin.
3. Utilising the energy from ATP hydrolysis, the myosin head now binds to the exposed active sites on actin to form a cross bridge. This pulls the attached actin filaments towards the centre of ‘A’ band.
4. The 7’ line attached to these actions are also pulled inwards thereby causing a shortening of the sarcomere, i.e., contraction.
5. It is clear from the above steps, that during shortening of the muscle, i.e., contraction, the T bands get reduced, whereas the A’ bands retain the length.
6. The myosin, releasing the ADP and PI goes back to its relaxed state. A new ATP binds and the cross-bridge is broken. The ATP is again hydroysed by the myosin head and the cycle of cross bridge formation and breakage is repeated causing further sliding.
7. The process continues till the Ca2+ ions are pumped back to the sarcoplasmic cisternae resulting in the masking of actin filaments. This causes the return of 7 lines back to their original position, i.e., relaxation.
Question 3.
Write true or false. If false change the statement so that it is true.
- Actin present in thin filament
- H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments
- The human skeleton has 206 bones
- There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
- Sternum is present on the ventral side of the body.
Answer:
- True
- False, H-zone represents thick filaments
- True
- False, There are 12 pairs of ribs in man
- True
Question 4.
Match column I with column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Smooth muscle | (i) Myogobin |
| (b) Tropomyosin | (ii) Thin filament |
| (c) Red muscle | (iii) Sutures |
| (d) Skull | (iv) Involuntary |
Answer:
(a) – (iv)
(b) – (ii)
(c) – (i)
(d) – (iii)
Question 5.
Name the type of joint between the following
- Atlas/axis
- Carpal/metacarpal of the thumb
- Between phalanges
- Femur/acetabulum
- Between carnival bones
- Between public bones in the pelvic girdle
Answer:
- Pivot joint
- Saddle joint
- Gliding joint
- Ball and socket joint
- Fibrous joint
- Cartilaginous
Question 6.
Fill in the blank spaces:
- All mamnals (expect a few) have __________ cervical vertebra.
- The number of phalanges in each limb of human is __________
- Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins namely __________ and _________
- In a muscle fibre Ca2+ is stored in __________
- _______and ________ pairs of ribs are called floating ribs.
- The human cranium is made of _________ bones.
Answer:
- 7
- 14
- tropomyosin, troponin
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
- 11th, 12th
- 8
Plus One Locomotion and Movement Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The muscle band that remains unchanged during contraction and relaxation of the skeletal muscle is
(a) I
(b) H
(c) A
(d) A-line
Answer:
(d) A-line
Question 2.
Intervertebral disc consists of a shock absorber connective tissue known as
(a) hyaline cartilage
(b) elastic cartilage
(c) fibrocartilage
(d) reticulo cartilage
Answer:
(c) fibrocartilage
Question 3.
Common among all mammals is
(a) ventral nerve cord
(b) seven cervical vertebrae
(c) all are carnivores
(d) all are producers
Answer:
(b) seven cervical vertebrae
Question 4.
The lactic acid generated during muscle contraction is converted to glycogen in
(a) muscles
(b) kidney
(c) pancreas
(d) liver
Answer:
(d) liver
Question 5.
Folding and unfolding of actin and myosin leads to amoeboid movement. This is hypothesised by
(a) Allen
(b) Goldacre and Lasch
(c) Berthold
(d) Jennigs
Answer:
(b) Goldacre and Lasch
Question 6.
Muscle fatigue is due to
(a) lactic acid
(b) citric acid
(c) Na
(d) K
Answer:
(a) lactic acid
Question 7.
Which of the following is not syncytial?
(a) Cardiac muscle
(b) Skeletal muscle
(c) Smooth muscle
(d) Interstitial muscle
Answer:
(c) Smooth muscle
Question 8.
Humerus fits into glenoid cavity is example of
(a) ball and socket joint
(b) pivot joint
(c) peg and socket joint
(d) condyloid join
Answer:
(a) ball and socket joint
Question 9.
Human vertebral column is formed by
(a) 21 vertebrae
(b) 30 vertebrae
(c) 26 vertebrae
(d) 33 vertebrae
Answer:
(d) 33 vertebrae
Question 10.
When the body part moves towards the median axis is called
(a) abductor
(b) adductor
(c) supinator
(d) pronator
Answer:
(b) adductor
Question 11.
The thin filaments of a muscle fibre are made up of
(a) actin, troponin, tropomyosin
(b) actin, troponin
(c) niyosin, troponin
(d) actin, tropomyosin
Answer:
(a) actin, troponin, tropomyosin
Question 12.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
(a) Cartilaginous joint Skull bones
(b) Hinge joint – Between vertebrae
(c) Fibrous joint – Between phalanges
(d) Gliding joint – Between zygapophyses of the successive vertebrae
Answer:
(d) Gliding joint – Between zygapophyses of the successive vertebrae
Question 13.
Nucleus purposes is found in
(a) brain
(b) nucleus
(c) intervertebral disc
(d) liver
Answer:
(c) intervertebral disc
Question 14.
Total number of bones found in right upper limb is
(a) 25
(b) 26
(c) 30
(d) 60
Answer:
(c) 30
Question 15.
In a vertebrate, which germ layer forms the skeletor muscles?
(a) Ectoderm
(b)Endoderm
(c) Mesoderm
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(c) Mesoderm
Question 16.
Where did an epidemic bone softening disease itai- itai occurred first in?
(a) South Korea
(b) Japan
(c) China
(d) Burma
Answer:
(b) Japan
Question 17.
Muscle pump is
(a) beating of heart
(b) squeezing effect of muscles upon veins running through them
(c) peristaltic wave that travel along the alimentar canal
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) squeezing effect of muscles upon veins running through them
Question 18.
Slow muscle fibres are found in
(a) eye
(b) leg
(c) stomach
(d) heart
Answer:
(b) leg
Question 19.
The gliding joints are important for gliding movements. One example of such a joint is between the
(a) zygapophyses of adjacent vertebrae
(b) humerous and glenoid cavity
(c) occipital condyle and odontoid process
(d) femur and tibio fibula
Answer:
(a) zygapophyses of adjacent vertebrae
Question 20.
Aqueduct of Sylvius (iter) connects
(a) 1st and 2nd ventricles
(b) 3rd and 4th ventricles
(c) 2nd and 3rd ventricles
(d) 4th and 1st ventricles
Answer:
(b) 3rd and 4th ventricles
Question 21.
Volkmann’s canals occur in
(a) internal ear
(b) liver
(c) cartilage
(d) bone
Answer:
(d) bone
Question 22.
For muscle contraction, in myofibrils the formation, of a protein is essential, such protein discovered by
(a) Jean Hanson
(b) Con and Con
(c) lbert Szent Gyorgyi
(d) Hugh Huxley
Answer:
(c) lbert Szent Gyorgyi
