Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation is part of Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation.
Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation
Plus One Body Fluids and Circulation One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the double walled membrane of the human heart. (Cuticle, Pleura, Pericardium, Sarcolemma)
Answer:
Pericardium
Question 2.
Which metal is responsible for blood clotting?
(a) Iron
(b) Calcium
(c) Copper
(d) Magnesium
Answer:
(b) Calcium
Question 3.
In a case sheet, doctor denoted a patients BP as 140/90. What does it show?
Answer:
Hypertension
Question 4.
Mark the pair of substances among the following which is essential for coagulation of blood.
(a) Heparin and calcium ions
(b) Calcium ions and platelet factors
(c) Oxalates and citrates
(d) Platelet factors and heparin
Answer:
(b) Calcium ions and platelet factors
Question 5.
Which one of the following type of cells lack nucleus?
(a) RBC
(b) Neutrophils
(c) Eosinosphils
(d) Monocytes
Answer:
(a) RBC
Question 6.
ECG depicts the depolarisation and repolarisation processes during the cardiac cycle. In the ECG of a normal healthy individual one of the following waves is not represented.
(a) Depolarisation of atria
(b) Repolarisation of atria
(c) Depolarisation of ventricles
(d) Repolarisation of ventricles
Answer:
(b) Repolarisation of atria
Question 7.
Which one of the following blood cells is involved in antibody production?
(a) B-Lymphocytes
(b) T-Lymphocytes
(c) RBC
(d) Neutrophils
Answer:
(a) B-Lymphocytes
Question 8.
The cells involved in inflammatory reactions are
(a) Basophils
(b) Neutrophils
(c) Eosinophils
(d) Lymphocytes
Answer:
(a) Basophils
Question 9.
Name the incompatibility observed between the Rh-ve blood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus.
Answer:
Erythroblastosis foetalis
Question 10.
Tricuspid valve is present in between _______ and _________?
(a) Right auricle and right ventricle
(b) Left auricle and left ventricle
(c) Right auricle and left auricle
(d) Right ventricle and left ventricle
Answer:
(a) Right auricle and right ventricle
Question 11.
Rhythmic heartbeat is maintained by a highly specialized excitatory and conductive system. The correct sequence of events will be
(a) AV node → Bundle of His → S A node → Purkinje fibers
(b) Purkinje fibers → AV node → S A node → Bundle of His
(c) A V node → S A node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers
(d) S A node → A V node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers
Answer:
(d) S A node → A V node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers
Question 12.
The normal cardiogram of man is shown below.
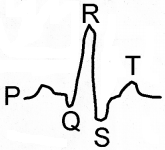
In the diagram, QRS wave has largest amplitude, which represents ventricular depolarization. What condition is obtained if QRS wave is enlarged?
Answer:
Myocardial infarction or cardiac arrest.
Plus One Body Fluids and Circulation Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The diagrammatic figure given below represents two types of blood circulations.
- Identify the A and B
- Write hepatic portal system
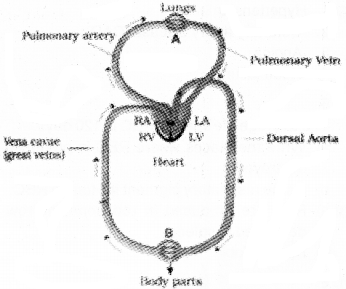
Answer:
- A – Pulmonary circulation B – Systemic circulation
- Hepatic portal system is a portal system which carries blood from intestine to liver.
Question 2.
Doctor advised administering Anti Rh antibodies to Seetha immediately after the first delivery. Justify this statement.
Answer:
If the mother’s blood group is Rh- and foetus blood group is Rh+, there is chance for the condition of erythroblastosis foetalis. This can be avoided by administering Anti-Rh antibodies to the mother immediately afterthe delivery of the first child.
Question 3.
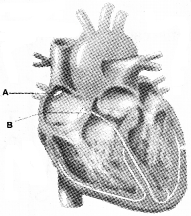
- Identify A & B
- Mention the role of A in the myogenic property of Heart.
Answer:
1. A – SA node B – AV node
2. In myogenic heart cardiac impulse in originated from SA node. So the SA node is called pacemaker. The rate of heart beat in determined by the rate of discharge of cardiac impulse from SA node.
Question 4.
Silicosis, T.B., Pneumonia, asbestosis are the diseases affecting respiratory system. Name four diseases affecting circulatory system.
Answer:
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Angina
- Heart failure
Question 5.
The average life span of RBC is 120 days.
- Write the places where RBC is produced and destroyed?
- Name respiratory pigment in Human RBC.
Answer:
- RBS are produced in red bone marrow and destroyed in spleen
- Haemoglobin
Question 6.
The stroke volume of a normal person is 70ml/min. Find out his cardiac output?
(Hint: Cardiac output = stroke volume × No. of heartbeats/min.)
Answer:
HP No.of heartbeats/min = 72
Stroke volume = 70
Cardiac output = 70 × 72 = 5040 ml
Question 7.
Suppose your friend is suffering from obesity, diabetes and hypertension, etc. What are type of food materials would you suggest?
Answer:
Fried items and bakery items must not be used. Sugar and sugary materials should be avoided. Fiber-rich vegetarian food is recommended.
Question 8.
Study the table. Correct the mistakes to match column A, B & C.
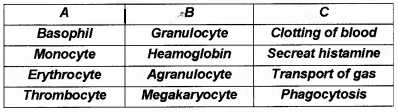
Answer:
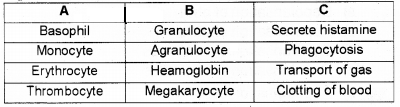
Question 9.
Copy the diagram and fill (a) and (b).
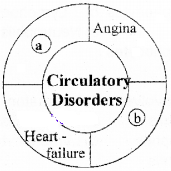
Answer:
(a) Hypertension
(b) Coronary Artery Disease.
Question 10.
Complete the table.

Answer:

Question 11.
Observe the diagram.
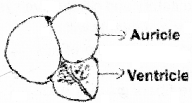
- Which step of cardiac cycle is shown here?
- Which sound is produced during the step and how is it produced?
Answer:
- Ventricular systole
- The ‘lub’ sound. This is produced by the closing of AV valve in orderto prevent backward flow of blood to auricle.
Question 12.
Some of the features of the body fluids are listed below. Analyse the features and categorise them into two groups.
- Transparent fluid found in tissue space.
- Extracellular fluid of the blood.
- Contains 91% water, 7% proteins and 1% inorganic and organic substances.
- Absorbs the digested fats and lipids and transports in the form of chylomicrons.
Answer:
| Plasma | Lymph |
| 2. Extra cellular fluid of blood | 1. Transparent fluid found in tissue space |
| 3. Contains 91% water, 7% proteins and 1% inorganic and organic substances | 4. Absorbs the digested fats and lipids and transports in the form chylomicrons |
Question 13.
‘Bundle of His’ is divided into finer branches known as Purkinje Tissue. Impulses are conducted rapidly along these fibres at 5 m/s and spread from these to all parts of the chambers.
- What is the function of Purkinje Tissue?
- Which are the chambers mentioned in the paragraph?
Answer:
- Conduction of impulse from the Bundle of His and rapidly transfers to the wall of the ventricles,
- Right and Left ventricles
Question 14.
“All veins carry deoxygenated blood and all arteries carry oxygenated blood.”
- Do you agree?
- Justify your answer.
Answer:
1. Statement is incorrect.
2. Arteries are the blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. Veins are the blood vessels which carry blood towards the heart. All arteries carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery.
All veins carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein. Pulmonary artery carry deoxygenated blood towards the lungs and pulmonary vein carry oxygenated blood toward heart.
Question 15.
Using the terms given, prepare a flow chart incorrect order.
Right auricle, aorta, left ventricle, left auricle, superior vena cava, capillaries, lungs, right ventricle, pulmonary vein, pulmonary artery.
Answer:
Right Auricle → Right ventricle → Pulmonary artery → Lungs → Pulmonary vein → Left Auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Capillaries → Superior vena cava → Right Auricle.
Question 16.
Complete the table using ‘open’ or ‘close’.
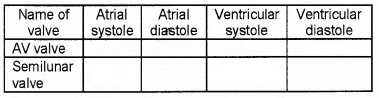
Answer:
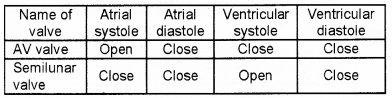
Question 17.
The human blood vascular system is diagrammatically represented below.
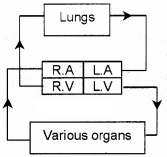
- What is the significance of Pulmonary circulation in the cardiac cycle?
- Why circulation in human considering as double circulation?
Answer:
1. The to and fro circulation between the lungs and heart is known as Pulmonary circulation. The purpose of pulmonary circulation is oxygenation of blood.
2. In human circulation is double circulation, it involves Pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Right half receives and pumps the deoxygenated blood while the left half the oxygenated blood.
Question 18.
You know when you cut your finger or hurt yourself, your wound does not continue to bleed for long time. Usually blood stops flowing after some time. State how?
Answer:
When blood oozes out of a cut, it set into gel within a few minutes. This is known as coagulation. The mechanism of blood coagulation is as follows.
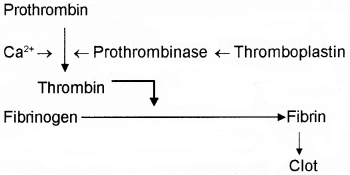
Question 19.
Copy the table and fill in the gap with appropriate words.
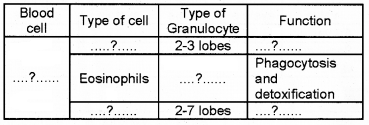
Answer:
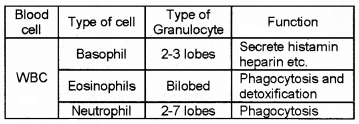
Question 20.
Study the diagrammatic representation :
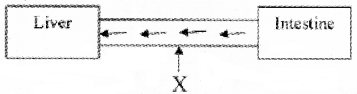
- ‘X’ marked in the figure is a blood vessel. Name the blood vessel.
- Give the importance of circulation between these two organs.
Answer:
- hepatic portal vein
- hepatic portal vein carries nutrients from intestine to liver.
Question 21.
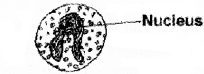
Heparin is a substance which prevents clotting of blood. Histamine is an anti-inflammatory substance.
- Mention the leucocytes that secretes the above said substances.
- Draw and label its nucleus.
Answer:
1. Basophil
2.
Plus One Body Fluids and Circulation Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill up the blanks with appropriate words.
- Thrombocytes are produced from _________
- Pace maker of the heart is _________
- The nervous band that connects the two cerebral hemispheres is _________
Answer:
- Megakaryocytes
- Sinoatrial node (SAN)
- Corpus callosum
Question 2.
The given figure shows a Systole.
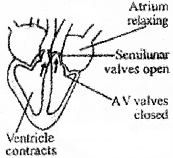
- Identify the Systole in the figure?
- How long does it lasts?
- What happens to the bicuspid and tricuspid valves during this systole?
Answer:
- Ventricular systole
- 0.25 seconds
- Closed
Question 3.
Draw a Schematic diagram showing the circulation of blood in man, starting from left ventricle of heart and ending in the right auricle.
- Name the type of circulation.
- Mention the significance of this circulation.
Answer:
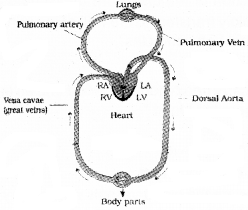
- Systemic circulation
- The systemic circulation provides nutrients, O2 and other essential substances to the tissues and takes CO2 and other harmful substances away for elimination.
Question 4.
A unique vascular connection exists between the digestive tract and liver.
- Name the vascular connection.
- Name the vascular connection found in frog between kidney and lower parts of body.
- What is CAD?
Answer:
- Hepatic portal system
- Renal portal system
- CAD – Coronary Artery Disease
Question 5.
Complete the table using the terms given in bracket. (Lymphocyte, granulocyte, eosinophil, basophil, plasma, leucocyte)
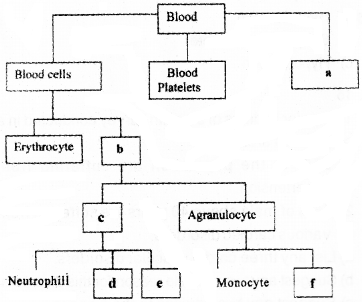
Answer:
- a – Plasma
- b – leucocyte
- c – granulocyte
- d – basophil
- e – Eosinophil
- f – lymphocyte
Question 6.
Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions.
- Identify the type of circulation.
- Prepare a flow chart showing the above circulation.
- Write the purpose of this circulation.
Answer:
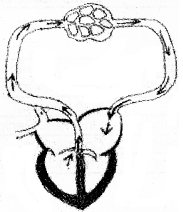
- Pulmonary circulation
- Right, ventricle → Pulmonary artery → lungs → Pulmonary vein → Left auricle
- Oxygenation of blood
Question 7.
Leukocytes are the soldiers of the body. Justify?
Answer:
Leukocytes provides defence mechanism to the body against infection. For example Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body.
Basophils secrete histamine, heparin etc. and are involved in inflammatory reactions. Eosinophils resist infections and are also associated with allergic reactions. Lymphocytes are responsible for immune responses of the body.
Question 8.
Listed below are some of the features of open and closed circulatory system. Arrange them into two categories.
- Usually low-pressure system
- Found in vertebrates
- Blood returns to heart rapidly
- High pressure system
- Blood returns to heart slowly
- Found in Arthopods
Answer:
| Open circulation | Closed circulation |
| 1. Usually low pressure system | 4. High pressure system |
| 5. Blood returns to heart slowly | 3. Blood returns to heart rapidly |
| 6. Found in Arthropods | 2. Found in vertebrates |
Question 9.
The heart of fish is said to be a venous heart, whether your heart is a venous one or not? Justify.
Answer:
The heart of fish is a venous heart, because it is a 2 chambered heart, and only deoxygenated blood flows through the heart chambers.
Human heart is a four-chambered heart and carries both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. So human heart is not a venous heart.
Question 10.
Observe the diagram.
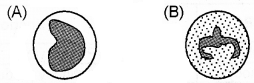
- Identify the blood cell A and B.
- How can they differentiate?
- What are their function?
Answer:
- The blood cells A and B
- A – Monocyte
- B – Neutrophil
- They can be differentiated in two ways
- Monocyte – Agranulocyte, Horseshoe shaped nucleus
- Neutrophil – Granulocyte, multilobed nucleus
- Their functions
- Monocyte – They protect the body by engulfing the pathogen (Phagocytosis)
- Neutrophil – Phagocytic cells
Question 11.
During a clinical check-up, doctor diagnosed that the patient’s heart murmurs.
- What are murmurs?
- Why does a heart murmur?
- The heart sound ‘dub’ is caused by the closure of AV valve. Do you agree with this statement?
Answer:
1. Due to the abnormalities in chambers or valves of the heart, some abnormal sounds may be audible in addition to normal heart sound. These are called murmurs.
2. Heart may murmur due to valvular damage.
3. The statement is incorrect because ‘dub’ is caused by the sudden closure of semilunar valve.
Question 12.
Observe the diagram and answer the following
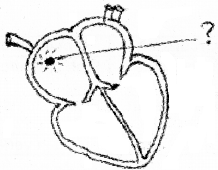
- Name the area labelled here.
- What is the importance of this area?
- Name the area associated with this.
- Draw a flow chart showing conducting system of heart.
Answer:
- Sino-atrial node (SAN)
- Cardiac impulse originates from SAN.
- AV node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibres.
- SAN → AVN → Bundle of His→ Purkinje fibres → Ventricle.
Question 13.
Match the following.
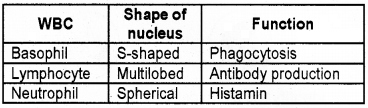
Answer:
Question 14.
A person’s blood pressure is found to be about 140/ 100mm Hg.
- What is the condition the person is suffering?
- How do you measure BP?
- Blood pressure is 100/60mm Hg. How you interpret it?
Answer:
- Hypertension
- Sphygmomanometer
- Hypotension
Question 15.
The major findings of a health survey conducted in a corporation area are
- 25% of the population are suffering from hypertension.
- 15% of male above 40 years are suffering from various cardiac disorders.
1. List any three cardiovascular disorders.
2. Suggest any two possible reasons for these disorders.
3. Suggest any two advices to the disease.
Answer:
- Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Cardiac arrest
- Two possible reason for cardiovascular disorders:
- Regular intake of fatty food
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Advices to the disease:
- Avoid fatty food
- Do regular exercise
Question 16.
Match Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Eosinophils | Coagulation |
| (b) RBC | Universal Recipient |
| (c) AB Group | Resist infections |
| (d) Platelets | Contraction of Heart |
| (e) Systole | Gas transport |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Eosinophils | Resist infections |
| (b) RBC | Gas transport |
| (c) AB Group | Universal Recipient |
| (d) Platelets | Coagulation |
| (e) Systole | Contraction of Heart |
Question 17.
Select the correct statement from the following:
- A monocyte is a granulocyte.
- Frog has 4 chambered heart.
- Blood is a tissue.
- The respiratory organs of insects are gills.
Answer:
- Blood is a tissue. (Monocyte is an agranulocyte Frog has 3 chambered heart Respiratory organs of insects are trachea)
Question 18.
Today we can measure blood pressure with a sphygmomanometer at home. This shows that people are very much concerned about high blood pressure. Find out why?
Answer:
High blood pressure can harm vital organs like the heart, brain, and kidneys. High blood pressure compels the heart to work excessively due to which congestive heart disease may set in at an early age. This is the reason why people are very much concerned with their high B.P.
Question 19.
Erythroblastosis foetalis is an Rh incompatibility disorder.
- Describe the circumstances in which erythroblastosis foetalis might arise.
- How is the problem usually averted?
Answer:
1. If the first child of an Rh- woman is Rh+, she develops anti-Rh antibodies in her blood. During subsequent pregnancies, if the foetus is Rh+ and Rh antibodies enter the fetal blood from the mother blood causing agglutination resulting in erythroblastosis foetalis.
2. This problem can be avoided by administering anti-Rh antibodies to the mother immediately after the delivery of the first child.
Question 20.
Write the odd one out and give the reason for your answer.
- P wave, QRS wave, T wave, beta wave.
- Renal artery, Pulmonary artery, Hepatic artery, Coronary artery.
- SA node, lymph node, AV node, Purkinje fibres
Answer:
- Beta wave: These are the waves of normal EEG, whereas all others are the components of a normal ECG.
- Pulmonary artery: This blood carries deoxygenated blood whereas all others carry oxygenated blood.
- Lymph node: It is found in the lymphatic system whereas all other structures are found in the mammalian heart related to auto rhythmicity.
Question 21.
Cardiac output increases when we engage in physical exercises. However, it may fall after the exercise stops. We can see that it is a full heart controlled event.
- What is cardiac output?
- How does the heart increase cardiac output during exercise?
Answer:
- Cardiac output is the volume of the blood ejected by. each ventricle into the arterial system per minute,
- In response to the sensory impulses and the adrenal medullary hormone, the excitability of the pacemaker is increased and thereby heart rate is increased during exercise. This in turn increases the heart rate.
Question 22.
Copy and complete the table on blood group, antigen and antibody.
1.
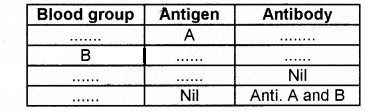
2. Name the blood groups commonly known as Universal donor and Universal recipient.
Answer:
1.
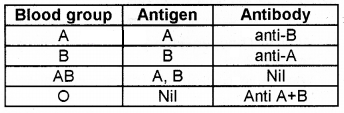
2. The blood groups are commonly known as Universal donors and Universal recipients.
- Universal donor: ‘O’ group.
- Universal recipient: ‘AB’ group.
Plus One Body Fluids and Circulation NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the importance of plasma proteins?
Answer:
Fibrinogen, globulins and albumins are the major proteins. Fibrinogens are needed for clotting or coagulation of blood. Globulins primarily are involved in defense mechanisms of the body and the albumins help in osmotic balance.
Question 2.
Match Column I with Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Eosinophils | (i) Coagulation |
| (b) RBC | (ii) Universal Recipient |
| (c) AB Group | (iii) Resist Infections |
| (d) Platelets | (iv) Contraction of Heart |
| (e) Systole | (v) Gas transport |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Eosinophils | (iii) Resist Infections |
| (b) RBC | (v) Gas transport |
| (c) AB Group | (ii) Universal Recipient |
| (d) Platelets | (i) Coagulation |
| (e) Systole | (iv) Contraction of Heart |
Question 3.
Why do we consider blood as a connective tissue?
Answer:
Blood is considered a connective tissue for two basic reasons:
- embryologically, it has the same origin (mesodermal) as do the other connective tissue types and
- Blood connects the body systems together bringing the needed oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other signaling molecules, and removing the wastes.
Question 4.
The sino-atrial node is called the pacemaker of our heart. Why?
Answer:
The sino-atrial node is a bundle of nerves which initiates the conduction of the heartbeat. So, this is also called the pacemaker of our heart.
Question 5.
What is the significance of the atrioventricular node and atrioventricular bundle in the functioning of heart?
Answer:
AV Node and atrioventricular bundles are responsible for conduction of cardiac beat cycle to further parts of heart.
Question 6.
Define a cardiac cycle and cardiac output.
Answer:
Cardiac Cycle. The rhythmic contraction and dilatation of different parts of heart in one beat is called cardiac cycle. Cardiac Output. The heart beats 72 times per minute, i.e., that many cardiac cycles are performed per minute. From this it could be deduced that the duration of a cardiac cycle is 0.8 seconds.
During a cardiac cycle, each ventricle pumps out approximately 70mL of blood which is called the stroke volume. The stroke volume multiplied by the heart rate (no. of beats per min.) gives the cardiac output. Therefore, the cardiac output can be defined as the volume of blood pumped out by each ventricle per minute and averages 5000 mL or 5 litres in a healthy individual.
Question 7.
What is the difference between lymph and blood?
Answer:
| Blood | Lymph |
| RBC Present | RBC Absent |
| Found in arteries, veins and capillaries | Found in interstitial space |
| Can transport gases | Cannot transport gases |
Plus One Body Fluids and Circulation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In higher vertebrates, SA – node helps in
(a) conduction of blood
(b) initiation of heartbeat
(c) opening of tricuspid valve
(d) opening of bicuspid valve
Answer:
(b) initiation of heartbeat
Question 2.
An oval depression called fossa ovalis, is seen on
(a) inter atrial septum
(b) inter ventricular septum
(c) right auriculo-ventricular septum
(d) left auriculo-ventricular septum
(e) papullary muscles
Answer:
(a) interatrial septum
Question 3.
The deposition of lipids on the wall lining, the lumen of large and medium-sized arteries is referred to as
(a) deep vein thrombosis
(b) Stokes-Adam’s syndrome
(c) osteoporosis
(d) atherosclerosis
Answer:
(d) atherosclerosis
Question 4.
Which of the following are located in tunica media of human blood vessels?
(a) Collagen fibres and smooth muscle
(b) Squamous epithelium and striated muscle
(c) white fibres and smooth muscle
(d) Yellow fibres and smooth muscle
Answer:
(d) Yellow fibres and smooth muscle
Question 5.
The important function of lymph is to
(a) transport oxygen to the brain
(b) transport carbon dioxide to the lungs
(c) return RBCstothe lymph nodes
(d) return interstitial fluid to the blood
Answer:
(d) return interstitial fluid to the blood
Question 6.
Cardiac output is determined by
(a) heart rate
(b) stroke volume
(c) blood flow
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 7.
Which of the following matches correctly?
(a) Inferior vena cava – Receives deoxygenated blood from the head and body
(b) Superior vena – Receives deoxygenated blood from the lower body and organs
(c) pulmonary artery – carries deoxygenated blood to lungs
(d) hepatic artery – carries deoxygenated blood to the gut
Answer:
(c) pulmonary artery – carries deoxygenated blood to lungs
Question 8.
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be grafted at the site made up of
(a) atrioventricular bundle
(b) Purkinje system
(c) sinuatrial node
(d) atrioventricular node
Answer:
(c) sinuatrial node
Question 9.
Generally, an artificial pacemaker consists of one battery made up of
(a) nickel
(b) dry cadmium
(c) photosensitive material
(d) lithium
Answer:
(d) lithium
Question 10.
which type of white blood cells are concerned with the release of histamine and the natural anticoagulant heparin?
(a) Neutrophils
(b) Basophils
(c) Eosinophils
(d) Monocytes
Answer:
(b) Basophils
Question 11.
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to
(a) pushing open of the venous valves
(b) suction pull
(c) stimulation of the sino-auricular node
(d) pressure difference between the caval and atrium
Answer:
(d) pressure difference between the caval and atrium
Question 12.
which one of the following has an open circulator system?
(a) Pheretima
(b) Periplaneta
(c) Hirudinaria
(d) Octopus
Answer:
(b) Periplaneta
Question 13.
in higher vertebrates, SA – node helps in
(a) conduction of blood
(b) initiation of heartbeat
(c) opening of tricuspid valve
(d) opening of bicuspid valve
Answer:
(b) initiation of heartbeat
Question 14.
The opening of auricles and ventricles on the right side is guarded by
(a) tricuspid valve
(b) bicuspid valve
(c) semilunar valve
(d) Eustachian tube
Answer:
(a) tricuspid valve
Question 15.
Which of the following sequences is truly a systemic circulation pathway?
(a) Right ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Tissues Pulmonary veins → Left auricle
(b) Right auricle → Left ventricle → Aorta → Tissues → Veins → Right auricle
(c) Left auricle → Left ventricle → Pulmonary aorta + Tissues → Right auricle
(d) Left auricle → Left ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Arteries → Tissues → Veins → Right atrium
Answer:
(d) Left auricle → Left ventricle → Pulmonary aorta → Arteries → Tissues → Veins → Right atrium
Question 16.
Open circulatory system is present in
I. Arthropods
II. Annelids
III. Chordates
IV. Molluscs
(a) III only
(b) III and II
(c) I and IV
(d) IV only
Answer:
(c) I and IV
Question 17.
The artery, which supplies blood to the pericardium is
(a) brachial artery
(b) pulmonary vein
(c) vertebral artery
(d) coronary artery
Answer:
(d) coronary artery
Question 18.
In diastole, heart is filled by
(a) mixed blood
(b) venous blood
(c) oxygenated blood
(d) deoxygenated blood
Answer:
(d) deoxygenated blood
Question 19.
You are required to draw blood from patient and to keep it in a test tube for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma. You are also provided with the following four types of test tubes. Which of them will you not use for the purpose?
(a) Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate
(b) Chilled test tube
(c) Test tube containing heparin
(d) Test tube containing sodium oxalate
Answer:
(c) Test tube containing heparin
We hope the Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
