Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Biomolecules is part of Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Biomolecules.
Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Biomolecules
Plus One Biomolecules One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Many elements are found in living organisms either free or in the form of compounds. One of the following is not, found in living organisms.
(a) Silicon
(b) Magnesium
(c) Iron
(d) Sodium
Answer:
(a) Silicon
Question 2.
Aminoacids, as the name suggests, have both an amino group and a carboxyl group in their structure. In addition, all naturally occurring amino acids (those which are found in proteins) are called L-aminoacids. From this, can you guess from which compound can the simplest amino acid be made?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Methane
(c) Phenol
(d) Glycine
Answer:
(b) Methane
Question 3.
When we homogenise any tissue in an acid the acid-soluble pool represents
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Cell membrane
(c) Nucleus
(d) Mitochondria
Answer:
(a) Cytoplasm
Question 4.
Many organic substances are negatively charged e.g., acetic acid, while others are positively charged e.g., ammonium ion. An amino acid under certain conditions would have both positive and negative charges simultaneously in the same molecule. Such a form of amino acid is called
(a) Positively charged form
(b) Negatively charged form
(c) Neutral form
(d) Zwitterionic form
Answer:
(d) Zwitterionic form
Question 5.
Sugars are technically balled carbohydrates, referring to the fact that their formulae are only multiple of C(H2O). Hexoses, therefore, have six carbons, twelve hydrogens and six oxygen atoms. Glucose is a hexose.
Choose from among the following another hexose.
(a) Fructose
(b) Erythrose
(c) Ribulose
(d) Ribose
Answer:
(a) Fructose
Question 6.
Fill the gap:
Inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by Malonate is an example for _____________
Answer:
Competitive Inhibition
Question 7.
Name the phospholipid found in cell membrane.
Answer:
Lecithin
Question 8.
The metabolic pathway from glucose to lactic acid which occurs in 10 metabolic steps is called ________________
Answer:
Glycolysis
Question 9.
Energy currency in living systems is _______________
Answer:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Question 10.
Find the off one out.
Rubber, Amino Acids, Drugs, Pigments
Answer:
Amino acids: Amino acids are primary metabolites. All others are secondary metabolites.
Question 11.
Arrange the following Carbo-hydrates in the order of increasing complexity of chemical structure.
Glucose, Oligosaccharides, Lactose, Starch.
Answer:
Glucose → Lactose → Oligosaccharides → Starch
Question 12.
One full turn of the DNA double helix would involve.
(a) 8 steps
(b) 10 steps
(c) 20 steps
(d) 12 steps
Answer:
(b) 10 steps
Question 13.
Match column A with B and C.

Answer:
- Glucose – Glycoside – Carbohydrate
- Aminoacids – Peptide – Protein
- Nucleotide – Phosphor diester – Nucleic acid
Question 14.
A short length of DNA double helix contains 60 Adenine nucleotides and 40 cytosine nucleotides. What will be the total number of nucleotides in it? (60, 120, 80, 200)
Answer:
200
Question 15.
Add suitable word in the gap.
- A protein molecule is a polymers of _____________
- Nucleic acids are polymers of _____________
- DNA has _________ instead of uracil.
- Single stranded structure is found in ___________
Answer:
- Aminoacids
- Nucleotides
- Thymine
- RNA
Question 16.
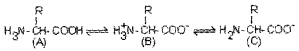
The structure of amino acids in solutions of different PH are given above. Identify the structure ‘B’.
Answer:
Zwitterionic form
Question 17.
![]()
Name the enzyme catalyse this reaction.
Answer:
Carbonic anhydrase
Plus One Biomolecules Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Observe the table and fill the blanks from the brackets.
(Collagen, Cholesterol, chitin, Lecithin)
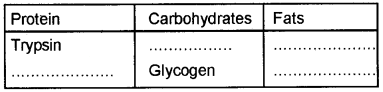
Answer:
Question 2.
Building blocks of proteins are amino acids and that of polysaccharides are monosaccharides. Many polysaccharides are called homopolymers but all proteins are known as heteropolymers.
- Do you agree with the above statement? Give reason.
- Give one example of a homopolymer.
Answer:
- Yes. Many polysaccharides are made up of only one type of monosaccharide. They are known as homopolymers. But all protein contain different type of amino acids. So they all are heteropolymers.
- Cellulose. Cellulose is made up of only one type of monosaccharide ie. glucose.
Question 3.
Classify the following as polypeptide and polysaccharide.
(Insulin, Glycogen, Chitin, Paper)
Answer:
| Polypeptide | Polysaccharide |
| Insulin | Glycogen |
| Chitin | |
| Paper |
Question 4.
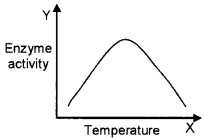
- Observe the graph and comment.
- List out the factors which influence enzyme activity.
Answer:
- Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature called the optimum temperature. Activity declines both below and above the optimum value.
- Temperature, pH, change in substrate concentration, binding of specific chemicals that regulate enzyme activity.
Question 5.
Write the general names of the following.
- Enzymes catalyzing the linking together of two compounds.
- Enzymes that catalyze removed of groups from substrates by mechanism other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds.
Answer:
- Ligases
- Lyases
Question 6.
Find out the differences between DNA and RNA and fill the table given below.
| DNA | RNA |
| ? | Ribonucleotides |
| Deoxyribosugar | ? |
| ? | Single stranded |
| ACTS Present | ? |
Answer:
| DNA | RNA |
| Deoxyribonucleotides | Ribonucleotides |
| Deoxyribosugar | Ribose sugar |
| Double stranded | Single stranded |
| ACTG Present | ACUG Present |
Question 7.
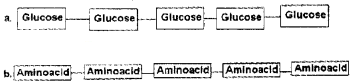
Two polymers are given. In this chain how are monomers linked ?
Answer:
a. Glycosidicbond
b. Peptide bond
Question 8.
The following graph shows the relationship between subtrate concentration and rate of enzymatic reaction.
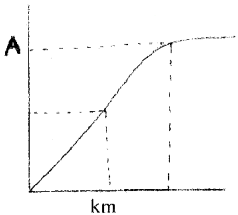
- What is the effect of subtrate concentration on rate of reaction?
- Identify ‘A’.
Answer:
1. With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rise at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity V(max) which is not exceeded by any further rise in concentration of the substrate.
This is because the enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecule and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecule.
2. V(max)
Question 9.
Identify the class of enzyme which catalyse the following reaction.
- S reduced + S’ oxidized → S oxidised + S’ reduced
- S – G + S’→ S + S’ – G
X Y
I I - C – C → X-Y+C
- C-O, C-S, C-N bonds
Answer:
- Oxidoreductase
- Transferase
- Lyases
- Ligases
Question 10.
A portion of DNA double helix is given below. Copy the diagram and make correction if any.
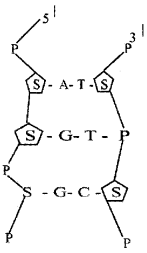
Answer:
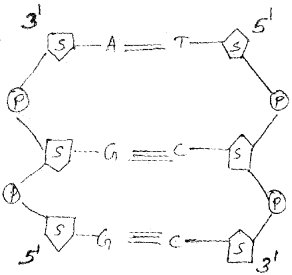
Question 11.
Adenine, Guanine, thymine, Cytosine, Uracil, are the nitrogen bases present in the living organisms. Write their nucleosides and nucleotides.
Answer:
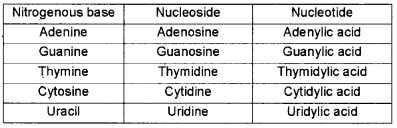
Question 12.
- Prepare a graph showing the action of temperature on enzyme activity.
- What is optimum temperature.
Answer:
1.
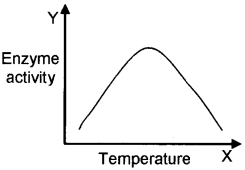
2. Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature called optimum temperature.
Question 13.
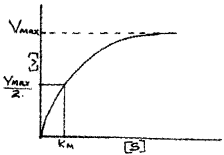
- Identify the given graph
- If we add more substrate after reaching Vmax, What will be the effect in the reaction rate?
Answer:
- Effect of change in concentration of substrate on enzyme activity.
- There is no further increase in the velocity of reaction because there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecule.
Question 14.
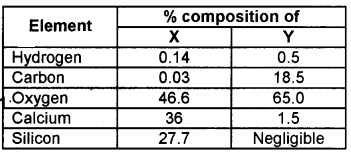
The table shows the percentage composition of different elements of a living matter and a non-living matter represented as X and Y. Identify X and Y.
Answer:
- X – Nonliving matter (Earth’s crust)
- Y – Living matter (human body)
Question 15.
Fatty acids could be saturated or unsaturated. Give an account on it.
Answer:
1. Fatty acids are saturated if they do not have any double bond between the carbons of the molecular chain.
eg: Palmitic acid.
2. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bond between carbon of the molecular chain,
eg: linoleic acid.
Question 16.
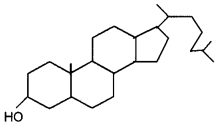
Identify the structure.
Answer:
Cholesterol
Question 17.
General Formula of amino acid is given below.
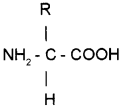
(a) Prepare the amino acids – Glycine and Serine using this formula.
(b) State the influence of pH in the nature of amino acid.
Answer:
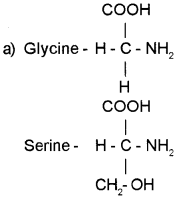
(b) Amino acids are of basic amino acids, acidic amino acids, Neutral amino acids and aromatic amino acids. Hence in solutions of different pH, the structure of amino acids changes.
Question 18.
Chemical structure of an Amino acid is given.
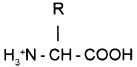
(a) Prepare its Zwitterionic form.
(b) What happens to the Zwitter ion if it is placed in an acidic medium?
Answer:
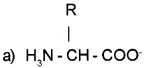
(b) In acidic medium it gains H and become positive charged
Question 19.
Write the missing word.
- Amino acid: Protein, Nucleotide: __________
- Glucose: Monosaccharide, Starch: __________
- Adenine: Thymine, Guanine: ________
- Animals: Glycogen, Plants: _________
Answer:
- Nucleic acid
- Polysaccharide
- Cytosine
- Starch
Question 20.
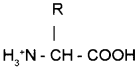
(a) Identify the structure of protein A and B.
(b) Write an example for a protein with a quaternary structure.
Answer:
(a) A) Secondary structure
B) Tertiary structure
(b) Hemoglobin
Question 21.
Proteins carry out many functions in living organisms. List them.
Answer:
- Some protein functions as enzymes.
- Some protein functions as Hormones.
- Some proteins fight infectious organisms.
- Some proteins transport nutrients across the cell membrane.
Question 22.
Give an example forthe following.
- Phospholipids
- Saturated fatty acid
- Nucleoside
- Nucleotide
Answer:
- Lecithin
- Palmitic acid
- Adenosine
- Adenylic acid
Question 23.
B-DNA is the most common DNA. Write the salient features of this DNA.
Answer:
The length of one full turn of a B-DNA molecule is 34A0. The distance between two adjacent nucleotides in a chain is 3.4A0. Thus there are 10 pairs of nucleotides in one full turn of DNA molecule.
Question 24.
Identify the structure.
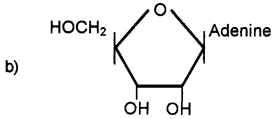
Answer:
(a) Adenine
(b) Adenosine
Question 25.
The given structure showing the molecule give ready energy for biological activities. Identify the structure.
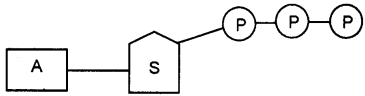
Answer:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Question 26.
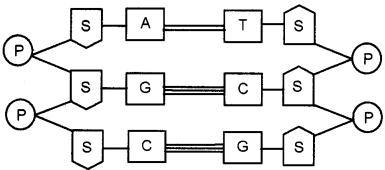
Schematic diagram of DNA is given. Copy the structure and correct it, if there is any mistake.
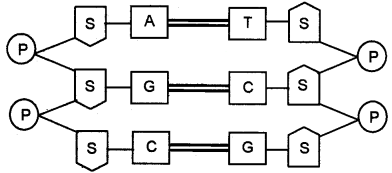
Answer:
Question 27.
Classify the given terms into two columns and give appropriate heading.
rubber, Glucose, amino acids, drugs, gums, spices, cholesterol, Fatty acids.
Answer:
| Primary Metabolism | Secondary Metabolism |
| Glucose | Rubber |
| Amino acids | Drugs |
| Cholesterol | Gums |
| Fatty acids | Spices |
Question 28.
Progress of a chemical reaction and potential energy changes associated with it is plotted as curve.
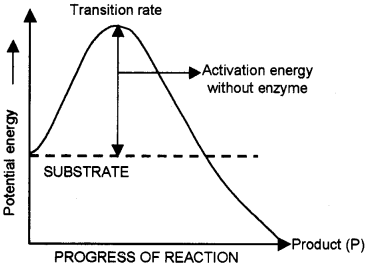
- What happens to the activation energy of the substrate, when enzyme is added to the reaction system?
- Redraw the above graph and also plot another curve showing the progress of the reaction and associated potential energy change, when enzyme is added to the system.
Answer:
1. Activation energy decreases
2.
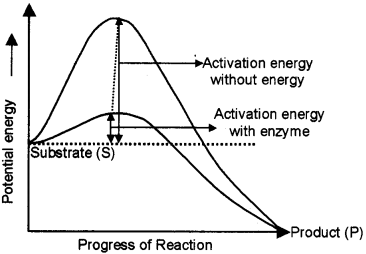
Question 29.
Observe the given graph a and
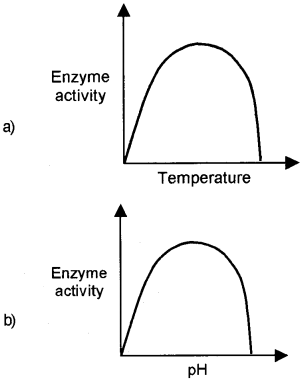
- State how temperature and pH influence enzyme activity.
- Does the substrate concentration influence enzyme activity. If so, how?
Answer:
1. Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature. This is called the optimum temperature. Low temperature or high temperature reduces the enzyme activity. Same as, there is an optimum pH for enzyme activity. Deviation from this pH reduces the enzyme activity.
2. With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction increase at first, as the substrate concentration continues to increase, the increase in the rate of reaction begins to slow down and finally no further rise in velocity occurs. This is because there is no free enzyme molecule to bind additional substrate molecule.
Question 30.
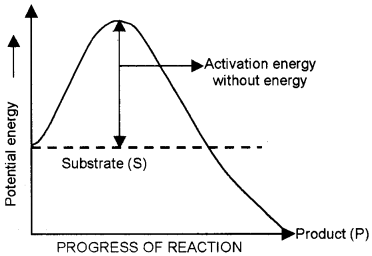
The graph shows the relation between potential energy and progress of reaction. Observe the graph and answer the questions.
- Is this reaction”exothermic or endothermic? Give reason.
- What happen to the amount of enzyme at completion of reaction?
Answer:
- Exothermic. The energy level of substrate is higher than that of product.
- No change to enzyme
Question 31.
Observe the diagram.
- Name the process showing here.
- How is this process would be useful?
Answer:
- Competitive inhibition
- Competitive inhibitor are often used in the control of bacterial pathogen.
Question 32.
Fill in the blank columns with the correct terms/ sentences.
| A | B |
| ………. (1)………….. | Catalyse oxido – reduction between two substrates. |
| Transferase | ……. (1)……….. |
| ………. (2)……….. | Catalyse hydrolysis of ester, glycosidic bond |
| Lyases | ………. (2)…………… |
| ………. (3)………….. | Catalyse inter conversion of optical isomers |
| Ligase | ………. (3)………………….. |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Oxidoreductase | Catalyse oxido – reduction between two substrates. |
| Transferase | Catalyse group transfer between substrates. |
| Hydrolase | Catalyse hydrolysis of ester, glycosidic bond |
| Lyases | Removal of group from a substrate by clearing double bonds. |
| Isomerase | Catalyse inter conversion of optical isomers |
| Ligase | Catalyse linking together of two compounds. |
Plus One Biomolecules Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Structure of a nucleotide pair in DNA is showing below.
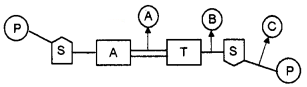
Identify the bonds A, B and C.
Answer:
- A – Hydrogen bond
- B – Glycosidic bond
- C – Ester bond
Question 2.
Give examples.
- Prosthetic group
- Co-enzyme
- Metal ion required for enzyme activity.
Answer:
- Haem is the prosthetic group of enzyme peroxidase.
- NADP and NAD contain Vitamin Niacin.
- Zinc present in carboxypeptidase.
Question 3.
Give one word.
- The nucleic acids that behave like enzymes
- The organic compound tightly bound to the apoenzyme.
- The non-protein organic compound that is not tightly bound to the apoenzyme.
- The protein portion of the enzyme.
Answer:
- Ribosome
- Prosthetic group
- Co-enzyme
- Apoenzyme
Question 4.
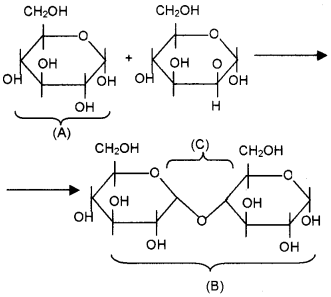
Identify the molecules A and B and name the bond marked C.
Answer:
- A – Glucose
- B – Maltose
- C- Glycosidicbond
Question 5.
Observe the structure.
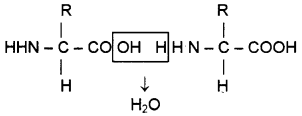
- Identify the bond formed between amino acids.
- How many types of amino acids are present in animal body?
- In nutrition some amino acids are required. Write a note on it.
Answer:
- Peptide bond
- 20 types of amino acids
- Note on amino acids:
- Essential amino acids: The amino acids can not be synthesisecHn the animal body and must be obtained through diet are called essential amino acids.
- Non-essential amino acids: The amino acids which can be synthesised in the body are called non-essential amino acids.
Question 6.
Give name.
- The most abundant protein in animal.
- The most abundant protein in the whole of the biosphere.
- A polymer of fructose.
- Paper made from plant pulp is
- Complex polysaccharide present in the exoskeleton of Arthropods
- Polysaccharide with helical structure
Answer:
- Collagen
- RuBisCo
- Insulin
- Cellulose
- Chitin
- Starch
Question 7.
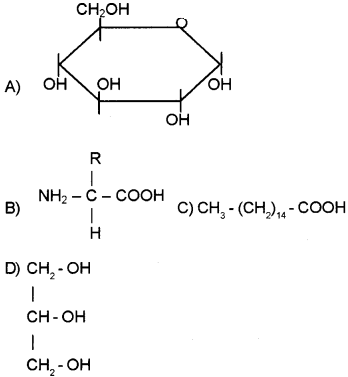
- Identify the structures A, B, C and D.
- Name the molecule formed by the esterification of one ‘D’ molecule and three ‘C’ molecules.
Answer:
- Structures:
- Glucose
- Amino acid (Glycine)
- Fatty acid
- Glycerol
- 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acid Triglyceride
Question 8.
Match column A and B.
| A | B |
| a. Bioluminescence | Fructose |
| b. Inulin | Basic amino acid |
| c. Lysine | Nicotinamide adenine |
| dinucleotide | |
| d. Skelton | Ctenophora |
| e. Nucleoside | Spicules |
| f. Co-enzyme | Thymidine |
Answer:
| A | B |
| a. Bioluminescence | Ctenophora |
| b. Inulin | Fructose |
| c. Lysine | Basic amino acid |
| d. Skelton | Spicules |
| e. Nucleoside | Thymidine |
| f. Co-enzyme | Nicotinamide adenine |
| dinucleotide |
Question 9.
The activity of the enzyme is inhibited by certain chemicals having close resemblance to the substrate in its molecular structure.
- Name the type of inhibition
- Point out a suitable example
- Mention the Significance of this type of inhibition.
Answer:
- Competitive inhibition
- Inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate. Which closely resembles the substrate succinate in structure.
- Competitive inhibition are often used in the control of bacterial pathogen.
Question 10.
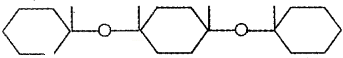
The figure shows the bonding of a biomolecule
- Identify the monomer
- Name the bond between the molecules
- Name the macromolecule formed
Answer:
- Glucose
- Glycosidic bond
- Starch
Plus One Biomolecules NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Answer:
In there is one type of amino acid at both termini then it is homopolymer and it cannot be a pure protein. When there are different types of amino acids on both termini then it is a pure protein as proteins are heteropolymer. This property of protein in because of presence of 21 types of amino acids.
Question 2.
Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics art)
Answer:
- Therapeutic Agents:
- Contraceptive pills: As they are hormones so they are made up of protein.
- Nutritional Supplements: Many brands are available as protein supplements. Example: Protinex.
- Other Uses: Chicken cubes are used in making soups and dishes.
Question 3.
Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Answer:
Triglycerides are formed from a single molecule of glycerol, combined with three fatty acids on each of the OH groups, and make up most of fats digested by humans. Easter bonds from between each fatty acid and the glycerol molecule.
General structure of a triglyceride Chemical formula:
RCOO-CH2CH(-OOCR)CH2-OOCR,
where R, R’, and R” are longer alkyl chains. The three fatty acids RCOOH, RCOOH and RCOOH can be all different, all the same, or only two the same. Chain lengths of the fatty acids in naturally occurring triglycerides can be of varying lengths, but 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common.
Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals are typically composed only of even numbers of carbon atoms due to the way they are biosynthesized from acetyl CoA. Bacteria, however, possess the ability to synthesise odd – and branched-chain fatty acids. Consequently, ruminant animal fat contains odd num¬bered fatty acids, such as 15, due to the action of bacteria in the rumen.
Question 4.
Can you describe What happens when milk is converted into curd or yogurt, from your understanding of proteins?
Answer:
Casein is the predominant phosphoprotein, that accounts for nearly 80% of proteins in cow milk and cheese. Milk-clotting proteases act on the soluble portion of the caseins. K Casein, thus originating an unstable micellar state that results in clot formation. When coagulated with chymosin, casein is sometimes called paracasein.
Casein is not coagulated by heat. It is precipitated by acids and by rennet enzymes, a proteolytic enzyme typically obtained from the stomachs of calves.
Question 5.
Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models)?
Answer:
Following the three-dimensional structure of cellulose can be made using balls and sticks. Similarly, models of other biomolecules can be made.
Question 6.
Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer:
On titrating against a weak base the amino acid ionizes into the following functional groups.
- NH2 (amino group)
- COOH (Carboxyl group)
Question 7.
Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Answer:
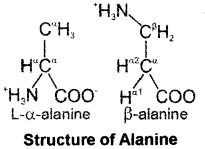
Question 8.
What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
Answer:
Natural gums are polysaccharides of natural origin, capable of causing a large viscosity increase in solution, even at small concentrations. Fevicol is a synthetic glue. These adhesives are a mixture of ingredients (typically polymers) dissolved in a solvent. As the solvent evaporates, the adhesive hardens.
Depending on the chemical composition of the adhesive, they will adhere to different materials to greater or lesser degrees. These adhesives are typically weak and are used for household applications.
Question 9.
Explain the basic structure of a nucleotide.
Answer:
A nucleotide is a building block of nucleic acids. A nucleotide has the following components:
- A heterocyclic compound (base)
- A monosaccharide, and
- Phosphoric acid or phosphate.
Plus One Biomolecules Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Enzyme often has additional parts in their structures that are made up of molecules other than proteins. When this additional chemical part is an organic molecule, it is called
(a) cofactor
(b) coenzyme
(c) substrate
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(a) cofactor
Question 2.
Nucleotides are formed by
(a) sugar and phosphate
(b) purine, pyrimidine and phosphate
(c) purine, pyrimidine, sugar and phosphate
(d) pyrimidine, sugar and phosphate
Answer:
(b) purine, pyrimidine and phosphate
Question 3.
The effectiveness of an enzyme is affected least by
(a) temperature
(b) concentration of the substrate
(c) original activation energy of the system
(d) concentration of the enzyme
Answer:
(c) original activation energy of the system
Question 4.
Which is an organic compound found in most cells?
(a) Glucose
(b) Water
(c) Sodium chloride
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(a) Glucose
Question 5.
Enzymes that catalyse inter-conversion of optical, geometrical, or positional isomers are
(a) ligases
(b) lyases
(c) hydrolases
(d) isomerases
Answer:
(d) isomerases
Question 6.
Which one of the following is wrongly matched?
(a) Fungi – Chitn
(b) Phospholipid – Plasma membrane
(c) Enzyme – Lipopolysacchande
(d) ATP – Nucleotide derivative
Answer:
(c) Enzyme – Lipopolysacchande
Question 7.
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called
(a) coenzyme
(b) holoenzyme
(c) apoenzyme
(d) isoenzyme
Answer:
(a) coenzyme
Question 8.
The ‘Repeating unit of glycogen is
(a) fructose
(b) mannose
(c) glucose
(d) galactose
Answer:
(c) glucose
Question 9.
Feedback inhibition of enzymes is affected by which of the following?
(a) Enzyme
(b) Substrate
(c) End products
(d) Intermediate end products
Answer:
(c) End products
Question 10.
The enzyme, which combines with non-protein part to form a functional enzyme, is known as
(a) coenzyme
(b) holoenzyme
(c) apoenzyme
(d) prosthetic group
Answer:
(b) holoenzyme
Question 11.
Benedict’s reagent test is conducted to confirm the presence of
(a) polysaccharides like starch
(b) lipids
(c) reducing sugars
(d) proteins
Answer:
(c) reducing sugars
Question 12.
Which disaccharide has different linkage?
(a) Maltose
(b) Starch
(c) Sucrose
(d) Lactose
Answer:
(c) Sucrose
Question 13.
Select the wrong statement.
(a) The building blocks of lipids are amino acids
(b) Majority of enzymes contain a non-protein part called the prosthetic group
(c) The thylakoids are arranged one above the other like a stack of coins forming a granum
(d) Crossing over occurs at pachytene stage ofmeiosis-l
Answer:
(a) The building blocks of lipids are amino acids
Question 14.
Which of the following is a disaccharide?
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Galactose
Answer:
(c) Sucrose
Question 15.
Lactose is composed of following components.
(a) glucose and fructose
(b) glucose and glucose
(c) glucose, fructose and galactose
(d) glucose and galactose
Answer:
(d) glucose and galactose
Question 16.
The simple polyhydroxy ketone molecule containing 3-7 carbons is a
(a) disaccharide
(b) monosaccharide
(c) polysaccharide
(d) dipeptide
Answer:
(b) monosaccharide
Question 17.
How many of the twenty-two amino acids are essential for children?
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 7
Answer:
(c) 9
Question 18.
Starch and cellulose are compounds of many units of
(a) glycerol
(b) amino acids
(c) simple sugars
(d) fatty acids
Answer:
(c) simple sugars
We hope the Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Biomolecules help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Biomolecules, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
