Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals is part of Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals.
Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals
Plus One Structural Organisation in Animals One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which one of the following types of cell is involved in making of the inner walls of large blood vessels?
(a) Cuboidal epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Squamous epithelium
(d) stratified epithelium
Answer:
(c) Squamous epithelium
Question 2.
To which one of the following categories does adipose tissue belong?
(a) Epithelial
(b) Connective
(c) Muscular
(d) Neural
Answer:
(b) Connective
Question 3.
Which one of the following is not a connective tissue?
(a) Bone
(b) Cartilage
(c) Blood
(d) Muscles
Answer:
(d) Muscles
Question 4.
Which one of the following statements is true for cockroach?
(a) The number of ovarioles in each ovary are ten.
(b) The larval stage is called caterpillar
(c) Anal styles are absent in females
(d) They are ureotelic
Answer:
(c) Anal styles are absent in females
Question 5.
Match the following with reference to Cockroach and choose the correct option.
| A. Phallomere | i. Chain of developing ova |
| B. Gonopore | ii. Bundles of sperm |
| C. Spermatophore | iii. Opening of the ejaculatory dust |
| D. Ovarioles | iv. The external genitalia |
(a) A – iii, B – iv, C – ii, D – i
(b) A – iv, B – iii, C – ii, D – i
(c) A – iv, B – ii, C – iii, D – i
(d) A – ii, B – iv, C – iii, D – i
Answer:
(b) A – iv, B – iii, C – ii, D – i
Question 6.
Complete the following sentences:
- The most common species of frog found in India is
- Blood Vascular system of cockroach is
Answer:
- Ranatigrina
- Open
Question 7.
Name the respiratory organs of insects.
Answer:
Trachea
Question 8.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggests a suitable word.
- Dendrons: Dendrites
Axon: _________ - Mast cells: Histamine
Fibroblast: ________
Answer:
- Myelin sheath
- Fibres
Question 9.
- Which among the following is the bone cell _____________.
(Leucocyte, Chondrocyte, Osteocyte, Thrombocyte) - In earthworm, segments 14-16 are covered by a prominent dark band of glandular tissue called __________. (Setae, Clitellum, Typlosol, None of these)
Answer:
- Osteocyte
- Clitellum
Question 10.
‘Neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in our body’. Write the function of neuroglial cells.
Answer:
Neuroglia cells protect and support neurons in our neural system.
Question 11.
From the following segments, find out the segments in which, Clitellum is situated in a mature earthworm.
(a) 12-16
(b) 14 -16
(c) 10-14
(d) 16-18
Answer:
(b) 14 -16
Question 12.
Name the cells present in areolar tissue.
Answer:
Fibroblasts, Macrophages, Mast cells
Question 13.
_____________ make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in our body.
Answer:
Neuroglia
Question 14.
Given below are different types of epithelial tissues. Find out the tissue that are present in the tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys.
Answer:
Cuboidal
Question 15.
Heart is made of
1. Epithelial tissue and Muscular tissue.
2. Muscular tissue and neural tissue.
3. Musculartissue and connective tissue.
4. All the four types of tissues.
Answer:
4. All the four types of tissues.
Question 16.
Write the cellular components of blood.
Answer:
Red blood cells (RBC), White blood cells (WBC) and platelets.
Question 17.
In earthworm, setae are absent in the segments.
(a) First and last
(b) Clitellum only
(c) First, last and clitellum
(d) Peristomium and Clitellum
Answer:
(c) First, last and Clitellum.
Question 18.
Intestine of earthworm contain a special organ which help in absorption. Identify the organ.
Answer:
Typhlosole
Question 19.
Name the structures which help in locomotion in Earthworm.
Answer:
Setae
Question 20.
In cockroach the fertilized eggs are encased in capsule called __________
Answer:
Oothecae
Plus One Structural Organisation in Animals Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Regarding the blood vascular system of frog, some statements are given below. Check whether these are True or False and make corrections if necessary.
- Open type.
- Sinus venosus join the right atrium.
- RBC is non-nucleated.
- Circulation is achieved by the pumping action of the heart.
Answer:
- False – Closed type
- True
- False – RBC is nucleated
- True
Question 2.
You are given two cockroaches and the teacher asked to display the mouthparts of male cockroach.
- How will you identify the male cockroach
- Name the mouthparts of cockroach.
Answer:
- In males styles are present and the abdomen is narrow and V shaped. In females abdomen is broad and anal styles are absent.
- Labrum, mandibles, Hypopharynx, maxilla and Labium.
Question 3.
Give one word for the following.
- Tissue attach one bone to another.
- The structures protect and support neurons in neural system.
Answer:
- Ligaments
- Neuroglial cell
Question 4.
Match the following.
| A | B |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Fallopian tube |
| Squamous epithelium | Ducts of glands |
| Columnar epithelium | alveoli |
| Ciliated epithelium | intestine |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Ducts of glands |
| Squamous epithelium | alveoli |
| Columnar epithelium | intestine |
| Ciliated epithelium | Fallopian tube |
Question 5.
Copy the diagram and label the numbered parts.
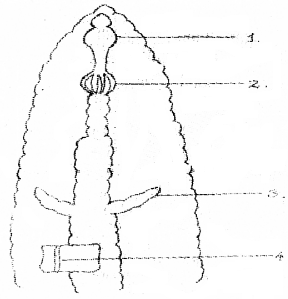
Answer:
- Pharynx
- Gizzard
- Intestinal caecum
- Typhlosole
Question 6.
Observe the diagram
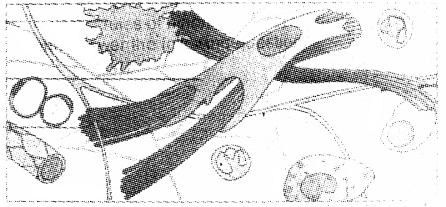
- Name the above connective tissue. Where they found in our body?
- Name any two principle cell found in it.
Answer:
- Areolar connective tissue, present beneath the skin.
- Fibroblast and macrophage
Question 7.
Observe the pool of connective tissues carefully. Classify them under three headings.
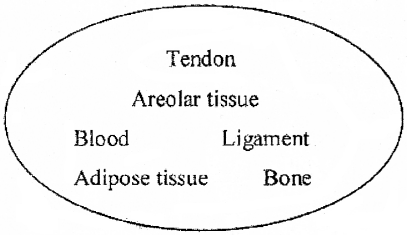
Answer:

Question 8.
Anatomical structures of 3 animals are given below. Identify the 3 animals and arrange the structures into 3 separate groups. (Typhlosole, Malpighian tubules, Blood glands, Cloaca, Phallic gland, Kidney, Collateral Gland)
Answer:
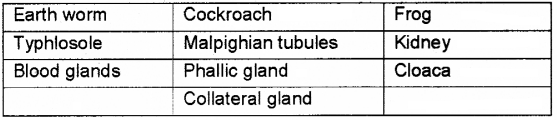
Question 9.
Copy the diagram and label the numbered parts.
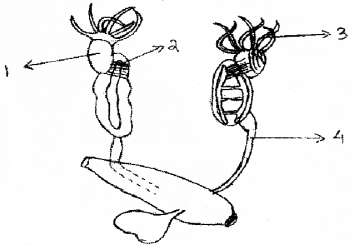
Answer:
- Testis
- Vasa efferentia
- Fat bodies
- Urino genital duct
Question 10.
Match the following.
| Column A | Column B |
| Haemocoelom | Frog |
| Typhlosole | Frog |
| Cloaca | Earthworm |
| Pseudocoelom | Cockroach |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| Haemocoelom | Cockroach |
| Earthworm | Earthworm |
| Cloaca | Frog |
| Pseudocoelom | Ascaris |
Question 11.
Name the labeled parts A, B in the diagram given below
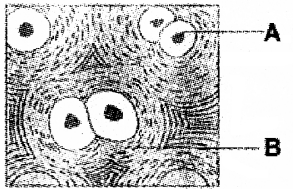
Answer:
A. Chondocyte
B. Collagen fibers
Question 12.
Circulating fluid of cockroach is colourless.
- Name the circulating fluid.
- Name the cell concerned in it.
Answer:
- hemolymph
- hemocytes
Question 13.
Match the following:
| A | B |
| Intestinal mucosa | Skeletal muscle |
| Biceps muscle | Smooth muscle |
| Tendon | Brush bordered columnar epithelium |
| Intestinal muscle | Connective tissue |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Intestinal mucosa | Brush bordered columnar epithelium |
| Biceps muscle | Skeletal muscle |
| Tendon | Connective tissue |
| Intestinal muscle | Smooth muscle |
Question 14.
Give one word for the following.
- Tissue specialised to store fats.
- Tissue contains fibroblasts, macrophages and mast cells.
- Tissue attach skeletal muscles to bones.
Answer:
- Adipose tissue
- Areolar tissue
- Tendons
Question 15.
You are given permanent slides of a bone and cartilage. How will you identify them using a microscope.
Answer:
- Bone: Presence of Haversian system.
Presence of Haversian canal in the centre. - Cartilage: Matrix contain spaces called lacunae.
Lacunae contain chondrocyte.
Question 16.
Frogs maintain ecological balance. As a biological student do you agree with this statement? Why?
Answer:
Frogs maintain ecological balance because they serve as an important link of food chain and food web in the ecosystem.
Question 17.
Ratheesh mounted the mouthparts of cockroach in the following manner. If there is any error, correct it.
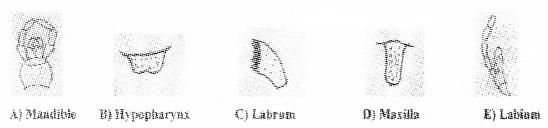
Answer:
A) Labium
B) Labrum
C) Mandibles
D) Hypopharynx
E) Maxilla.
Question 18.
Observe the diagram given below and label the parts
A, B, C, D.
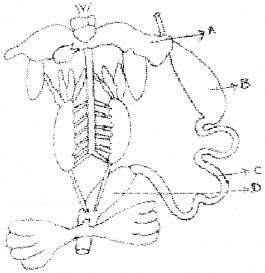
Answer:
A – Liver
B – Stomach
C – Intestine
D – Rectum
Question 19.
While viewing the fallopian tube through CT scan we can find large number of cilia.
- Identify the tissue present in the fallopian tube.
- Mention the function of cilia.
Answer:
- Ciliated epithelium
- Ovum is moved by the help of cilia.
Question 20.
‘An earthworm respires through skin and excretes through nephridia’ Rewrite the above sentence beginning with ‘A cockroach ………………..’ making appropriate
changes.
Answer:
A cockroach respires through trachea and excretes through malpighian tubules.
Question 21.
Match the following
| i | ii |
| Hypopharynx | Food grinding |
| Nephridium | Food absorption |
| Gizzard | Bone cell |
| Typhlosole | Phallomere |
| Osteocyte | Tongue |
| Genitalia | Earthworm |
| Frog |
Answer:
| i | ii |
| Hypopharynx | Tongue |
| Nephridium | Earthworm |
| Gizzard | Food grinding |
| Typhlosole | Food absorption |
| Osteocyte | Bone cell |
| Genitalia | Phallomere |
Question 22.
Identify the diagram and label the part marked A.
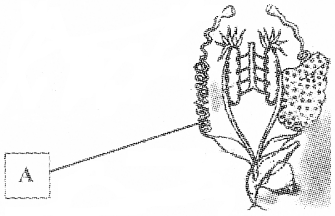
Answer:
Frog female reproductive system Part A is Oviduct
Question 23.
Observe the given diagram.
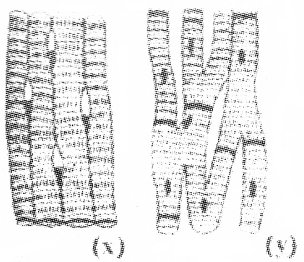
- Identify X and Y.
- Write any two characters of X and Y.
Answer:
- X – Striated muscle
Y – Cardiac muscle - Striated muscle – Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle, striations present Cardiac muscle – Muscles of heart, branched muscle fibres, intercalated disc.
Question 24.
Observe the table given below and fill in the blanks from the list given below:
(Pancreas, Liver, Salivary gland, Tear gland, Adrenal gland, Thyroid gland)

Answer:
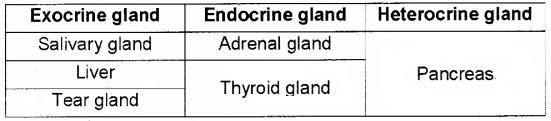
Question 25.
There are some physiological similarities between typhlosole and villi. Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
Both typhlosole and villi are part of intestine of earthworm and human beings respectively. Typhlosole and villi increase the effective area of absorption in the intestine.
Question 26.
Observe the given diagrams.
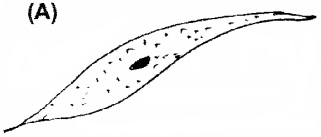
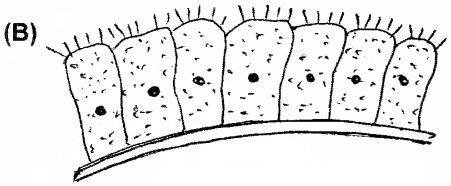
- Identify A and B.
- Write any one function of each.
Answer:
- A – Non-striated muscle (smooth muscle)
B – Ciliated epithelium - A – Found in the wall of internal organs and concerned with the movement of these organs. B – Ciliated epithelium is to move particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium.
Question 27.
Write the significance of
- Blood
- Neuroglia
Answer:
- Blood – The main circulating fluid that help in the transport of various substances.
- Neuroglia – Protect and support neurons. Neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in our body.
Question 28.
Classify the given terms into three columns and give appropriate headings.
Striated, heart muscle, intercalated disc, biceps, visceral organs, no striation.
Answer:

Question 29.
Where do you find the following structures in human body.
- Chondrocytes
- Axon
- Osteocytes
- Plasma
Answer:
- Cartilage
- Neuron
- Bone
- Blood
Question 30.
Write a suitable world for 4th place.
- Muscle to bone – Tendon; Bone to Bone – _____________
- Bone – osteocytes; Cartilage – __________
- Cardiac Muscle – Involuntary; Striated Muscle – __________
- Contractile cell – Muscle; Excitable cell – ______________
Answer:
- Ligament
- Chondrocytes
- Voluntary
- Neuron
Question 31.
Give an account on Nephridia of earthworm.
Answer:
Excretory organs in earthworm is nephridia. There are three types:
1. Septal nephridia: Present on both the sides of intersegmental septa of segments 5 to the last that open into intestine.
2. Integumentary nephridia: attached to lining of the body wall of segment 3 to the last that open on the body surface.
3. Pharyngeal nephridia: present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th, and 6th segments.
Question 32.
Flow chart showing flow of food through the alimentary canal of an earthworm given. Correct the flow chart if there is any mistake.
Mouth→Pharynx → Stomach → intestine → Gizzard → Oesophagus.
Answer:
Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Gizzard → Stomach → Intestine
Question 33.
Match the following.
| Bidder’s canal | Cockroach |
| Labium | Earthworm |
| Typhlosole | Frog |
Answer:
| Bidder’s canal | Frog |
| Labium | Cockroach |
| Typhlosole | Earthworm |
Question 34.
You are given an earthworm for dissection, how will you identify its anterior, posterior, dorsal and ventral sides.
Answer:
The dorsal surface of the body is marked by a dark median mid dorsal line along the longitudinal axis of the body. The ventral surface is distinguished by the presence of genital openings. Anterior end consists of the mouth and the prostomium. The posterior end is slightly rounded.
Question 35.
Blood cell of earthworm lack hemoglobin. But blood of earthworm is red in colour. How do you account for it?
Answer:
Blood cell of earth worm lack hemoglobin. But blood of earthworm is red in colour because hemoglobin is dissolved in blood plasma.
Question 36.
Match the related items from B and C with Column A.
Answer:

Question 37.
Copy and complete the animals on the table and the excretory organs.
| Animals | Excretory organs |
| Earthworm | _______________ |
| ________________ | Malpighian tubules |
| Frog | ________________ |
Answer:
| Animals | Excretory organs |
| Earthworm | Nephridia |
| Coackroach | Malpighian tubules |
| Frog | Kidney |
Question 38.
Identify the animals from the hints given below.
- Invertebrate, Burrowing in moist soil, Nephridia, Genital pore.
- Chordata, Amphibian, Kidney, Cloaca
- Invertebrate, Insecta, Malpighian tubules, gonapophysis.
Answer:
- Earthworm
- Frog
- Cockroach
Question 39.
Identify the statements as True or False.
- First segment of earthworm is Prostomium.
- Peristomium contain mouth.
- Clitellum is on segments 14-16.
- Earthworm has only a single female genital aperture.
Answer:
- False (First segment is peristomium)
- True
- True
- Tare
Question 40.
Earthworm feeds on humus, which contain large amount of humic acid.
- How does the earthworm neutralises the humic acid?
- Name the region of alimentary canal where humic acid is neutralised.
Answer:
- Calciferous gland, present in the stomach, neutralise the humic and present in humus.
- In stomach.
Question 41.
Write a note on typhlosole.
Answer:
The special structure present in the intestine of earthworm between 26-35 segment is called typhlosole. It is an internal median fold of dorsal wall of intestine. Typhlosole increases the effective area of absorption in the intestine.
Question 42.
Blood glands are important in earthworm. Give reason.
Answer:
Blood glands are present on the 4th, 5th and 6th segments of earthworm. They produce blood cells and hemoglobin which is dissolved in blood plasma.
Question 43.
Earthworm is a hermaphrodite animal. Where are its sex organs situated?
Answer:
Two pairs of testes present in the 10th and 11th segments. One pair of ovaries is attached at the inter-segmental septum of the 12th and 13th segment.
Question 44.
Earthworms are known as ‘Friends of farmers’. Give reason.
Answer:
Earthworms are known as ‘friends of farmers’ because they make burrows in the soil and make it porous which helps in respiration and penetration of the developing plant roots. The process of increasing fertility of soil by the earthworm is called vermicomposting. They are also used as bait in the game fishing.
Question 45.
Write the missing word in 4th place.
- Dorsally – Tergites; Ventrally – ……………
- Earthworm – Nephridia; Cockroach – …………….
Answer:
- Stern items
- Malpighian tubules
Question 46.
Cockroach show sexual dimorphism. Write any two morphological differences between male and female cockroaches.
Answer:
- In females, the 7th sternum is boat-shaped and there is presence of a brood pouch.
- In males, there is presence of anal style and genital pore in the 9th segment.
Question 47
While dissecting a cockroach to display its digestive system, a student observed certain thick white tubules. Teacher explained it as part of respiratory system.
- Name the tubules.
- Draw a flow chart showing the flow of air through this system.
Answer:
- Tracheal tubules
- Spiracle → Trachea → Tracheoles → Tissue
Question 48.
- Identify the diagram given below.
- Label the parts a to e.
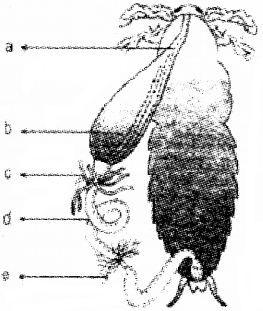
answer:
- Digestive system of cockroach
- parts from a to e
- a – Oesophagus
- b – Crop
- c – Hepatic caeca
- d – Mesentrorr
- e – Malpighian tubules
Question 49.
Blood of cockroach is colourless. Give reason.
Answer:
Blood of cockroach is composed of colourless plasma and hemocytes. No respiratory pigments present in the blood of cockroach. So blood is colourless.
Question 50.
Cockroach is uricotelic animal. Give reason.
Answer:
Cockroach excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of uric acid. So cockroach is known as uricotelic animal.
Question 51.
Name the four structure helps in excretion in cockroaches.
Answer:
- Malpighian tubule
- fat body
- nephrocytes
- urecose gland.
Question 52.
If the head of cockroach is cut off, it will still alive for as long as one week. Give reason.
Answer:
The head of cockroach holds a bit of a nervous system while the rest is situated along the ventral part of its body. So, if the head of cockroach is cut off it will still live for long as one week.
Question 53.
Name the sensory organs of cockroaches.
Answer:
Antennae, Compound eyes, anal cerci, maxillary palps, Labial palps.
Question 54.
Compound eyes are more effective than vertebrate eye. Give reason.
Answer:
Each compound eyes in cockroach consists of about 200 ommatidia. With the help of several ommatidia, a cockroach can receive several images of an object. This kind of vision is known as mosaic vision. Compound eye is more effective than vertebrate eye because it can detect the movement of other animals more easily and efficiently.
Question 55.
Frog show sexual dimorphism. Write the morphological difference present only in male frog.
Answer:
- Presence of vocal sacs
- Presence of copulatory pad on the 1st digit of the forelimb.
Question 56.
Prepare a flow chart showing the flow of food in the alimentary canal of frog. Compare it with alimentary canal of cockroach.
Answer:
1. In frog:
Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → Intestine → Rectus → Cloacal aperture
2. In coackroach:
Mouth → Oesophagus → Crop → Gizzard → Mesentron → ileum → Colon → Rectum → Anus
Question 57.
Cloaca is a common opening of 3 tubes or tracts.
- Name the tracts which opens to cloaca.
- Name the animal which possess cloaca.
Answer:
- Tracts which opens to cloaca
- Alimentary canal
- Urinary canal
- Reproductive tract
- Frog
Question 58.
Name the portal systems found in frog
- Between liver and intestine.
- Between kidney and lower parts of the body.
Answer:
- Hepatic portal system
- Renal portal system
Question 59.
- Frog is ureotelic animal. How?
- Name the different parts of the excretory system- off rog.
Answer:
- Frog excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of urea. So they are called ureotelic animal,
- A pair of kidneys, ureters, cloaca and urinary bladder.
Question 60.
Answer in one word.
- Covering of eyes in frog.
- Number of cranial nerves in frog.
- Membranous covering of Heart of frog.
- Brain of frog is enclosed in a bony structure named ____________
- Larval stage of frog.
Answer:
- Nictitating membrane
- Ten pairs
- Pericardium
- Cranium
- Tadpole
Question 61.
Frogs are beneficial for mankind. Justify.
Answer:
Frogs are beneficial for mankind because they eat insects and protect the crop. Frogs maintain ecological balance because these serve as an important link of food chain and food web in the ecosystem. In some countries the muscular legs of frog are used as food by man.
Plus One Structural Organisation in Animals Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Compare the circulatory system and blood of frog with that of an earthworm.
Answer:
In Frog blood circulatory system is closed type. Frog have a lymphatic system also. Heart is three chambered – two atria and one ventricle. Blood is composed of plasma and cells. The blood cells are RBC, WBC and platelets. RBC’s are nucleated and contain red coloured pigment namely hemoglobin. In earthworm blood circulatory system is closed type.
Blood glands are present on the 4th, 5th and 6th segments. They produce blood cells and hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is dissolved in the plasma. Blood cells are phagocytic in nature.
Question 2.
The mounting of mouthparts of cockroach are given below. If there is any error, correct it.
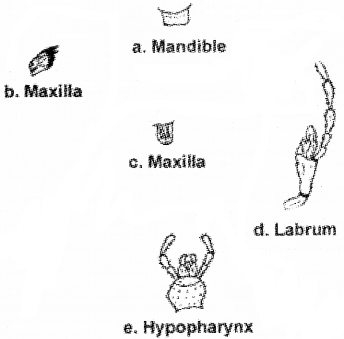
Answer:
a. Labrum
b. Mandible
c. Hypopharynx
d. Maxilla
e. Labium
Question 3.
Answer in one word or one line.
- Give the common name of Periplaneta Americana.
- How many spermathecae are found in earthworm?
- What is the position of a ovaries in cockroach?
- How many segments are present in the abdomen of cockroach.
- Where do you find Malpighian tubules?
- Development through nymphal stage.
Answer:
- Cockroach
- 4 pairs of spermathecae are located 6th – 9th segments.
- 2nd – 6th abdominal segments
- 10 segments
- At the junction of midgut and hindgut.
- Paurometabolous
Question 4.
“All glands in our body do not have ducts of their own.” Do you agree with this statement.
- Justify your answer using example.
- Name three types of cell junctions in the epithelium.
Answer:
- No. There are two types of glands in our body. Exocrine gland and Endocrine gland.
- Exocrine gland – ducted gland
- eg: Salivary gland
- Endocrine gland – ductless gland
- eg: Thyroid gland
- Exocrine gland – ducted gland
- Three types of junctions:
- Tight junction
- Adhering junction
- Gap junction
Question 5.
Observe the following diagram carefully.
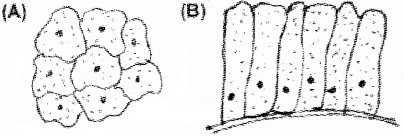
- Identify and compare two diagrams.
- Mention its location and function.
Answer:
- A – squamous epithelium
B – Columnar epithelium - Its locations and functions are
- Both squamous and columnar epithelium are simple epithelium. Squamous epithelium is made up of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. The columnar epithelium is composed of a single layer of tall and slender cells.
- Squamous epithelium is found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved in the functions like forming a diffusion boundary.
Columnar epithelium is found in the lining of stomach and intestine and help in secretion and absorption.
Question 6.
Compare the excretory System in Cockroach and Frog.
Answer:
1. Cockroach:
Excretion is performed by malpighian tubules. They absorb nitrogenous waste products and convert them into uric acid which is excreted out through the hind gut. Therefore, cockroach is called Uricotelic. In addition, the fat body nephrocytes and urecose gland also help in excretion.
2. Frog:
Excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys. Ureter, Urinary bladder and cloaca. Excretory wastes are carried by blood into the kidney where it is separated and excreted. The frog excrete urea and thus a ureotelic animal.
Question 7.
Mention the mode of respiration in a frog while it is
- In water
- On land
- When under aestivation or hibernation.
Answer:
- Gills
- Lungs
- Skin (cutaneous respiration)
Question 8.
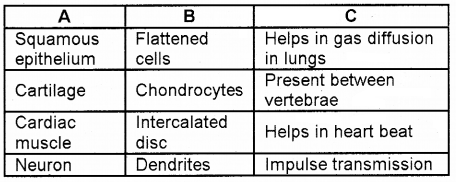
Arrange the columns A, B, and C in the table below and match them properly.
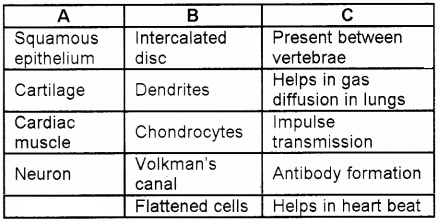
Answer:
Question 9.
Give reasons.
- Simple epithelium functions as lining for the body cavities, ducts, tubes etc. where as compound epithelium is protective in function.
- Cockroach does not possess respiratory pigment.
- Frog in ureotelic where as tadpole is ammonotelic.
Answer:
- Simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells. The compound epithelium consists of two or more cell layers and has protective function.
- Cockroach respiratory organ is trachea. These tracheal tubules carry oxygen from the air to all the parts of their body. So they does not require any respirations pigment.
- Ammonotelism demands an excess of water in the body. Tadpole is aquatic and there is availability of large amount of water. So tadpole is ammonotelic. Whereas Ureotelism requires only a moderate quantity of water. Frog is semiaquatic. So frog is ureotelic.
Plus One Structural Organisation in Animals NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer in one word or one line:
- Give the common name of Periplanata americana.
- How many spermathecae are found in earthworm?
- What is the position of ovaries in cockroach?
- How many segments are present in the abdomen of cockroach?
- Where do you find Malpighian tubules?
Answer:
- Cockroach
- 4 pair of spermathecae are found in earthworm
- 2 large ovaries are found lying laterally in the 2nd to the abdominal segment.
- The abdomen of cockroach consists of 10 segments.
- Malpighian tubules are the main excretory organs of the cockroach.
Question 2.
Answer the following:
- What is the function of nephridia?
- How many types of nephridia are found in earthworm based on their location?
Answer:
- Nephridia is the excretory organ of the earthworm or pheretima.
- There are three types of nephridia in the earthworm:
- septal nephridia, present on both the sides of intersegmental septa of segment 15 to the last that open into intestine,
- integumentary nephridia, attached to lining of the body wall of segment 3 to the last that open on the body surface and pharyngeal nephridia, present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th and the segments.
Question 3.
Distinguish between the following:
- Prostomium and peristomium
- Septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium
Answer:
- Prostomium is the frontmost part of the earth-worm. This is not called a true segment as it doesn’t contain typical organs of an annelida. Peristomium is from where the true segment of the earthworm body starts.
- Septal nephridia, present on both the sides of intersegmental septa of segment 15 to the last that open into intestine.
Pharyngeal nephridia, present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th and 6th segments Both are same structurally and functionally.
Question 4.
What are the cellular components of blood?
Answer:
Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells are the cellular components of the blood.
Question 5.
What are the following and where do you find them in animal body?
- Chondriocytes
- Axons
- Ciliated epithelium
Answer:
- Chondriocytes are cells of cartilage.
- Axons it is the tail like structure of a neuron
- Ciliated epithelium is found in the inner lining of bronchioles, Cilia help trap and clear dust and foreign particles.
Question 6.
Distinguish between
- Simple epithelium and compound epithelium
- Cardiac muscle and striated muscle
- Dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues
- Adipose and blood tissue
- Simple gland and compound gland
Answer:
1. Simple epithelium is composed of one layer of cells, while compound epithelium is composed of more than one layer of cells.
2. Cardiac muscles are present in the cells of heat only. They have contractile property which helps in the pumping action of the heart. Striated muscles are present near articulatory joints. Their role is to facilitate movement of organs like hands and feet.
3. Dense Connective Tissue. Fibres and fibroblasts are compactly packed in the dense connective tissues. Orientation of fibres show a regular or irregular pattern and are called dense regular and dense irregular tissues. In the dense regular connective tissues, collagen fibres are present in rows between may parallel bundles of fibres.
Tendons, which attach skeletal muscles to bones and ligments which attach one bone to another are examples of this tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue has fibroblasts and many fibres (mostly collagen) that are oriented differently. This tissue is present in the skin.
4. Adipose tissue is a type of loose connective tissue located mainly beneath the skin. The cells of this tissue are specialised to store fats. The excess of nutrients which are not used immediately are converted into fats and are stored in this tissue. Blood is a fluid connective tissue. The main function of blood is to transport gases, nutrients and easte products in the body.
5. Simple gland is composed of single cell, while compound gland is composed of multiple cells.
Question 7.
Mark the odd one in each series:
- Areolar tissue, blood, neuron, tendon
- RBC, WBC, platelets, cartilage
- Exocrine, endocrine, salivary gland, ligament
- Maxilla, mandible, labrum, antennae
- Protonema, mesothorax, metathorax, coxa
Answer:
- Neuron is not a connective tissue
- Cartilage is not part of blood
- Ligament is not part of gland
- Antennae is not a masticating part of cockroach
- Protonema is thread like chain of cells, all others are about morphological structure of cockroach.
Plus One Structural Organisation in Animals Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Carotene pigment is found in the cells of
(a) dermis
(b) epidermis
(c) adipose cell
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 2.
The lining of intestine and kidneys in human is
(a) keratinised
(b) brush bordered
(c) ciliated
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) brush bordered
Question 3.
The type of cell junction, which facilitates cell to cell communication is
(a) tight junction
(b) adhering junction
(c) gap junction
(d) desmosomes
(e) brush borders
Answer:
(c) gap junction
Question 4.
Keratinised dead layer of skin is made up of
(a) stratified squamous
(b) simple cuboidal
(c) simple columnar
(d) stratified columnar
Answer:
(a) stratified squamous
Question 5.
Endothelium of blood vessels is made up of
(a) simple cuboidal epithelium
(b) simple squamous epithelium
(c) simple columnar epithelium
(d) simple non-ciliated columnar
Answer:
(b) simple squamous epithelium
Question 6.
In which one of the following preparations are you likely to come across cell junctions most frequently?
(a) Ciliated epithelium
(b) Thrombocyte
(c) Tendon
(d) Hyaline cartilage
Answer:
(a) Ciliated epithelium
Question 7.
Bowman’s glands are located in the
(a) proximal end of uriniferous tubules
(b) anterior pituitary
(c) female reproductive system of cockroach
(d) olfactory epithelium of our nose
Answer:
(d) olfactory epithelium of our nose
Question 8.
Compound squamous epithelium is found in
(a) stomach
(b) intestine
(c) trachea
(d) pharynx
Answer:
(d) pharynx
Question 9.
Find out the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Squamous epithelium – Skin of frog
(b) Columnar epithelium – Peritoneum of body cavity
(c) Ciliated epithelium – Bronchioles
(d) Stratified squamous – Oesophagus epithelium
(e) Glandular epithelium Salivary gland
Answer:
(b) Columnar epithelium – Peritoneum of body cavity
Question 10.
The type of tissue lining the nasal passage, bronchioles and fallopian tubes is
(a) columnar ciliated epithelium
(b) cuboidal epithelium
(c) neurosensory epithelium
(d) germinal epithelium
(e) stratified columnar epithelium
Answer:
(a) columnar ciliated epithelium
Question 11.
The nasal chamber of rabbit has three thin twisted bony plates called conchae. They are lined by
(a) striated cuboidal epithelium
(b) simple cuboidal epithelium
(c) simple squamous epithelium
(d) simple ciliated columnar epithelium
Answer:
(d) simple ciliated columnar epithelium
Question 12.
The cavities of alveoli of lungs are lined by
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) stratified cuboidal epithelium
(d) squamous epithelium
Answer:
(d) squamous epithelium
Question 13.
The type of epithelial cells, which line the inner surface of fallopian tubes, bronchioles and small bronchi, are known as
(a) squamous epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) ciliated epithelium
(d) cubical epithelium
Answer:
(c) ciliated epithelium
Question 14.
Agranulocytes are
(a) lymphocytes and monocytes
(b) eosinophils and basophils
(c) lymphocytes and eosinophils
(d) basophils and monocytes
Answer:
(a) lymphocytes and monocytes
Question 15.
________ acts as a shock absorber to cushion when tibia and femur came together.
(a) Ligament
(b) Cartilage
(c) Tendon
(d) Disc
Answer:
(b) Cartilage
Question 16.
Erythropoiesis starts in
(a) kidney
(b) liver
(c) spleen
(d) red bone marrow
Answer:
(b) liver
Question 17.
Largest single mass of lymphatic tissue in the body is
(a) lung
(b) spleen
(c) liver
(d) kidney
Answer:
(b) spleen
Question 18.
Hypochronic microcytic anaemia and leucopenia are caused by the deficiency of respectively.
(a) pyridoxine and riboflavin
(b) pyridoxine and folacin
(c) biotin and folacin
(d) biotin and cyanocobalamin
Answer:
(b) pyridoxine and folacin
We hope the Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
