Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Animal Kingdom is part of Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Animal Kingdom.
Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Animal Kingdom
Plus One Animal Kingdom One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
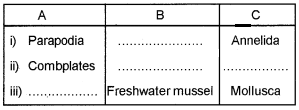
Answer:
i) B – Nereis
ii) B – Ctenoplanna
C – Ctenophora
iii) A – radula
Question 2.
Write any two members of the Phylum Aschelminthes which are found parasitic on Human beings.
Answer:
- Ascaris (Roundworm)
- Wuchereria (Filaria worm)
Question 3.
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with at least some organs/ organ repeated. This characteristic feature is named
(a) Segmentation
(b) Metamerism
(c) Metagenesis
(d) Metamorphosis
Answer:
(b) Metamerism
Question 4.
Given below are types of cells present in some animals. Each one is specialized to perform a single specific function except
(a) Choanocytes
(b) Interstitial cells
(c) Gastrodermal cells
(d) Nematocytes
Answer:
(b) Interstitial cells
Question 5.
Which one of the following sets of animals share a four chambered heart?
(a) Amphibian, Reptiles, Birds
(b) Crocodiles, Birds, Mammals
(c) Crocodiles, Lizards, Turtles
(d) Lizards, Mammals, Birds
Answer:
(b) Crocodiles, Birds, Mammals
Question 6.
Which of the following pairs of animals has non glandular skin.
(a) Snake and Frog
(b) Chameleon and Turtle
(c) Frog and Pigeon
(d) Crocodile and Tiger.
Answer:
(c) Frog and Pigeon
Question 7.
Birds and mammals share one of the following characteristics as a common feature.
(a) Pigmented skin
(b) Alimentary canal with some modification
(c) Viviparity
(d) Warm blooded nature
Answer:
(d) Warm blooded nature
Question 8.
Note the relationship between the first two words and find a suitable word for the fourth place,
- Coelenterata: radial symmetry, platyhelminthes, _______
- Lizard: Poikilothermous, crow, _________
Answer:
- bilaterally symmetrical
- Homoiothermous
Question 9.
- Annelida: Parapodia :: __________ : Comb plates
- _________: Water vascular system :: Coelenterata : cnidoblast
Answer:
- Ctenophora
- Echinodermata
Question 10.
Malpighian tubule is the excretory organ of which phylum?
(a) Phylum porifera
(b) Phylum arthropoda
(c) Phylum Coelenterata
(d) Phylum mollusca
Answer:
(b) Phylum Arthropoda
Question 11.
A chordate animal having flame cells as the excretory organ.
Answer:
Amphioxus
Question 12.
From the pictures given below, find out the poikilothermic animals.

Answer:
B and D are poikilothermic animals.
Question 13.
Segmentation in the body is first observed in which of the following:
(a) Platyhelminthes
(b) Aschelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d) Arthropoda
Answer:
(c) Annelida
Question 14.
Shark has to swim continuously, otherwise, it will sink down. Give reason.
Answer:
Due to absence of air bladder.
Plus One Animal Kingdom Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Arrange the phylum in order.
Arthropoda → Platyhelminthes → Porifera → Ctenophora → Cnidaria → Mollusca → Annelida → Echinodermata → Aschelminthesip
Answer:
- Presence of milk producing mammary gland.
- Presence of hair on skin.
- External ear or pinnae is present.
- Different types of teeth are present in the jaw.
Question 2.
Complete the blanks.
| Character | Phylum |
| a. Body is flat | |
| b. Body has similar segments | |
| c. Body has jointed appendages | |
| d. Body is round |
Answer:
| Character | Phylum |
| a. Body is flat | Platyhelminthes |
| b. Body has similar segments | Annelida |
| c. Body has jointed appendages | Arthropoda |
| d. Body is round | Aschelminthes |
Question 3.
Triploblastic animals are more complex than diploblastic animals. Do you agree with this statement? Justify.
Answer:
Triploblastic animals have more cell layers so they have the possibility of greater degree of cellular specialisation.
Question 4.
All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates. Justify.
Answer:
Notochord is present in all vertebrates but vertebral column is present only in vertebrates and not in all chordates.
Question 5.
Copy and complete the table.
| Chondrichthyes | Osteichthyes |
| a _____________ | Seen in all water forms |
| b. Endoskeleton is cartilage | _____________ |
| c _______________ | Body covered by cycloid scales |
| d ______________ | Mouth is terminal |
Answer:
| Chondrichthyes | Osteichthyes |
| a. Marine form | Seen in all water forms |
| b. Endoskeleton is cartilage | Endoskeleton is bony. |
| c. Body is covered by placoid scale | Body covered by cycloid scales |
| d. Mouth is ventral | Mouth is terminal |
Question 6.
Arrange the phylum in order.
Arthropoda → Platyhelminthes → Porifera → Ctenophora → Cnidaria → Mollusca → Annelida → Echinodermata → Aschelminthes
Answer:
Porifera → Cnidaria → Ctenophora→ Platyhelminthes → Aschelminthes → Annelida → Arthropoda → Mollusca → Echinodermata
Question 7.
Categorise and classify the following organisms and arrange them in a table with separate columns and provide appropriate headings.
Exocoetus, Physalia, Ascaris, Apis, Locusta, Corvus, Pita, Hydra, Sepia, Ancylostoma.
Answer:
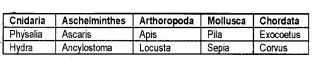
Question 8.
- Identify the phylum which exhibit metagenesis or alternation of generation.
- What is meant by alternation of generation?
Answer:
- Cnidaria
- Alternation of sexual and asexual forms of organism: ie., Polyp asexually produce medusa, medusa sexually product polyp.
Question 9.
Name the following.
- Phylum in which flatworms are included
- Excretory organs of Annelids.
- Largest phylum.
- An oviparous mammal.
Answer:
- Platyhelminthes
- Nephridia
- Arthropoda
- Platypus
Question 10.
Apis, Prawn, Locust, Spider
Following animals have different habit and habitat. But they have many common characters.
- Mention the common characters.
- Identify their phylum.
Answer:
- Joint footed animals
- Metameric segmentation
- Chitinous exoskeleton
- Arthropoda
Question 11.
A list of animals are given below. Arrange them according to increase in complexity of organization. Scorpion, Earthworm, Liver fluke, Pigeon, Seaanemon, Sycon, Elephant, Anabas.
Answer:
Sycon, Seaanemon, Liver fluke, Earthworm, Scor¬pion, Anabas, Pegeon, Elephant.
Question 12.
Nithin is Studying in Std. XI. He collected some specimens during the field trip conducted by the Science Club of his School. Help Nithin to Classify the Animal in respective Phylum.
Prawn, Slug worm, Butterfly, Pila, Grass Hopper, Crab
Answer:
| Arthropoda | Mollusca |
| Prawn | Slugworm |
| Butterfly | Pila |
| Grass hopper | |
| Crab |
Question 13.
During a field trip Raju has collected some organisms with the following characters. Help him to identify the phyla of those organisms.
- Metamerically segmented body.
- Body covered with calcareous shell.
- Dorso-ventrally flattened leaf like body.
- Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
Answer:
- Annelida
- Mollusca
- Platyhelminthes
- Arthropoda
Question 14.
Categorise the following fishes into Osteichthyes and Chondrichthyes?
- Exocoetus
- Trygon
Answer:
- Exocoetus – Oesteichthyes
- Trygon – Chondrichthyes
Question 15.
Arrange the following terms in two columns correctly. Malpighian tubules, radula, metamerism, Bioluminescence, choanocytes, nematocytes, Phylum-coelenterate, phylum-Arthropoda, phylum- ctnophora, phylum-Mollusca, Phylum-Porifera.
Answer:
| Malpighian | Phylum – Arthropoda |
| Radula | Phylum – Mollusca |
| Metamerism | Phylum – Annelida |
| Bioluminescence | Phylum – Ctenophora |
| Choanocytes | Phylum – Porifera |
| Nematocytes | Phylum – Coelenterata |
Question 16.
Match the following
| Bidders canal | Earthworm |
| Typhlosole | Catla |
| Air bladder | Shark |
| Placoid scale | frog |
Answer:
| Bidders canal | frog |
| Typhlosole | Earthworm |
| Air bladder | Catla |
| Placoid scale | Shark |
Question 17.
Observe the given organisms
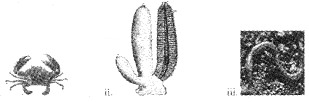
- Place these animals in proper phylum.
- Segmentation in the body is first observed in which of the above phylum?
Answer:
- i) Arthropoda,
ii) Porifera,
ii) Annelida - Annelida
Question 18.
Observe the table given below and fill the blank columns A, B, C and from the animals given in brackets. (Ascaris, Starfish, Fasciola, Earthworm)

Answer:

Question 19.
1. Identify the animal given below.
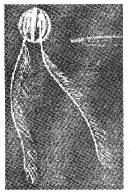
2. Write one well marked property of the above animal.
Answer:
- Pleurobrachia
- Bioluminescence is well marked property of pleurobrachia
Question 20.
Representatives of some vertebrate classes are introducing themselves. Write down the name of the class in which they belong.
- My gills are covered by operculum. I have bony endoskeleton.
- I give birth to young ones. My body is covered by hair.
- My skin is glandular? Have trilocular heart.
- I live only in marine water. My endoskeleton is made up of cartilage.
Answer:
- Osteichthyes
- Mammalia
- Amphibia
- Chondrichthyes
Question 21.
During classroom discussion a student said that sponges are more complex than cnidarians. Do you agree with him. Justify.
Answer:
NO. Sponges are asymmetrical and body is formed of loose aggregate of cells. Cells are not organised to from tissues and organs. Cnidarians are radially symmetrical and tissue grade of organisation. So cnidarians are more complex than sponges.
Question 22.
Due to the absence of air bladder, fishes belonging to the class Chondrichthyes have to swim constantly. How important is the presence of air bladder in these fishes?
Answer:
Due to the absence of air bladder in chondrichthyes, they have to swim constantly to avoid sinking. If air bladder is present which regulates buoyancy.
Question 23.
Match the column A, B &C in the table given below:
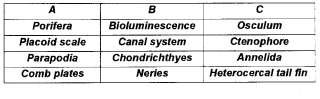
Answer:
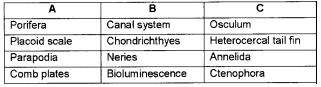
Question 24.
Identify the phylum whose larvae are bilaterally symmetrical, but adults are radially symmetrical.
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
- Echinodermata
Mention two salient features of the phylum.
Answer:
4. Echinodermata
Salient features Presence of Echinodermata:
- Water vascular system
- Spiny bodies, Endoskeleton of Calcareous ossicles
Question 25.
Write the name of phylum.
- Diploblastic, tissue grade of organisation, radially symmetrical, polymorphic animals.
- Soft bodied, Unsegmented, Bilaterally symmetrical animals with open type circulation.
- Triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, true coelomic animals with metamerism, closed circulation.
- Triploblastic, chitinous exoskeleton and open circulation.
Answer:
- Cnidaria
- Mollusca
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
Question 26.
Observe the table given below and fill the blank columns a, b, c, and d from the animals given in brackets.
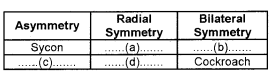
(Hydra, Shark, Spongilla, Obelia)
Answer:
(a) Hydra/Obelia
(b) Shark
(c) Spongilla
(d) Hydra/Obelia
Question 27.
Copy and complete the table.
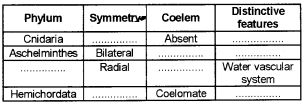
Answer:
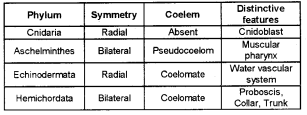
Question 28.
You are provided with two fishes Catla (Bony fish) and Shark (Cartilagenous fish). Prepare a table showing difference in:
(a) Position of mouth
(b) Air bladder
(c) Scales
(d) Fertilization
Answer:
| Calta (Bony fish) | Shark (Cartilaginous fish) |
| (a) Mouth is terminal | Mouth is ventral |
| (b) Air bladder present | Air bladder absent |
| (c) Cycloid scales | Placoid scales |
| (d) External Fertilization | Internal Fertilization |
Question 29.
Prepare a list of some animals that are found parasitic on human beings.
Answer:
Tapeworm (Taenia), Ascaris (Roundworm), Wuchereria (Filaria worm), Ancylostoma(Hookworm)
Question 30.

- Identify the 2 forms of Cnidarians.
- Mention any 2 difference between them.
Answer:
- A – polyp
B – medusa - Polyp: Asexual, sessile, mouth upwards Medusa: Sexual, Free swimming, Mouth downwards
Plus One Animal Kingdom Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the given organisms and arrange them in the order of their phylum.
Limulus, Corvus, Spongilla, Ascaris, Physalia, Nereis, Catla, Sepia, Echinus, Taenia, Pleurobrachia, Tiger, Viper, Toad.
Answer:
| Non chordata | Chordata |
| Limulus – Arthropoda | Corvus |
| Spongilla – Porifera | Catla |
| Ascaris – Aschelminthes | Tiger |
| Physalia – Cnidaria | Viper |
| Nereis-Annelida | Toad |
| Sepia – Mollusca | |
| Echinus – Echinodermata | |
| Taenia – Platyhelminthes | |
| Pleurobrachia – Ctenophora |
Question 2.
Match the following.
| (a) Operculum | i. Ctenophora |
| (b) Parapodia | ii. Mollusca |
| (c) Scales | iii. Porifera |
| (d) Comb plates | iv. Reptilia |
| (e) Radula | v. Annelida |
| (f) Hairs | vi. Cyclostomata |
| (g) Choanocytes | vii. Mammalia |
| (h) Gill slits | viii. Osteichthyes |
Answer:
| (a) Operculum | viii. Osteichthyes |
| (b) Parapodia | v. Annelida |
| (c) Scales | iv. Reptilia |
| (d) Comb plates | i. Ctenophora |
| (e) Radula | ii. Mollusca |
| (f) Hairs | vii. Mammalia |
| (g) Choanocytes | iii. Porifera |
| (h) Gill slits | vi. Cyclostomata |
Question 3.
Observe the diagram

- Identify the phylum of this hypothetical organism.
- List out the features that helps in identifying it.
- Write about the fate of notochord in Urochordata, Cephalochordata and Chordata.
Answer:
- Chordata
- Notochord, Dorsal nerve cord, Pharyngeal gill slits, Post anal tail
- In Urochordatarfiotochond is present only in larval tail. In Cephalochondata, notochord extends from head to tail region is persistent throughout their life. In vertebrata, the notochord is replaced by a cartilagenous or bony vertebral column in the adults.
Question 4.
Select the following items into their appropriate phylum.
Radula, Parapodia, Comb plate, Nephridia, Choanocytes, Flame cells.
Answer:
- Radula – Mollusca
- Parapodia – Annelida
- Comb plate – Ctenophora
- Nephridia – Annelida
- Choanocytes – Porifera
- Flame cells – Platyhelminthes
Question 5.
(a) Fill and complete the chart given below.
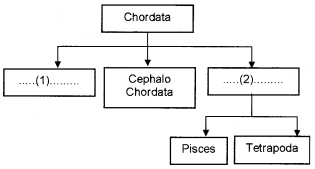
(b) Write any two fundamental characters of the phylum chordata.
(c) Classify Tetrapoda into classes:
Answer:
Male accessory ducts store and transport the sperms from testis to the outside through urethra. Male accessory glands secrete seminal Plasma, Which is rich in fructose, citrate, prostaglandins and certain enzymes. The secretion of cowper’s glands lubricate the penis.
Question 6.
Write down the functions of the following (any two) structures and assign their phyla.
- Radula
- Flame cells
- Parapodia
Answer:
- Radula: File like rasping organ for feeding.
Phylum: Mollusca - Flame cells: Osmoregulation and excretion
Phylum: Platyhelminthes - Parapodia: help in swimming
Phylum: Annelida
Question 7.
1. Identify the organism A and B.
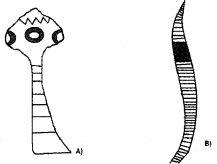
2. Which features of these organism enable you to identify them?
Answer:
- A-Tapeworm
B – Earthworm - Features of these organism:
- Tapeworm: Scolex is present, suckers and hooks are present. No true segmentation.
- Earthworm: True segmentation, Absence of Scolex, hook and suckers, Clitellum is present.
Question 8.
- Which of the following animals exhibit metagenesis? (Ascaris Obelia Earthworm Crab)
- To which phylum does it belong?
- Write any two features of the phylum.
Answer:
- Obelia
- Cnidaria
- Two features of the phylum:
- Presence of Cnidoblasts
- Cnidarians exhibit two basic forms called polyp and medusa.
Question 9.
Pick out the appropriate one from the term given within bracket and put against the corresponding phylum.
- Porifera
- Coelenterata
- Platyhelminthes
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
- Echinodermata
- Chordata
(Hirudin, Flame cell, Choanocytes, Cnidoblast, Jointed legs, Radula, Notochord and Dermal Ossicles)
Answer:
- Porifera – Choanocytes
- Coelenterata – Cnidoblast
- Platyhelminthes – Flame cells
- Annelida – Hirudin
- Arthropoda – Jointed legs
- Mollusca – Radula
- Echinodermata -Dermal ossicles
- Chordata – Notochord
Question 10.

- Identify the organism (A) and (B) and which class do they belong?
- On which basis do you classify these animals?
(Hint: Write any 2 Identifying characters)
Answer:
- Organism in (A) and (B)
- A – Bony fish – Osteichthyes
- B – Cartilagenous fish – Chondrichthyes
2.
| Osteichthyes | Chondrichthyes |
| Mouth is terminal | Mouth is ventral |
| Operculum is present | Operculum absent |
Question 11.
From a fish market, you got a fish, on a close watching you friend says it is a cartilaginous fish.
- Which characters helped him to identify it as a cartilaginous fish, (any four characters.)
- Name the class it belongs.
Answer:
- Characters:
- a – Gillslits are separate and without operculum
- b – Placoidscale
- c – Mouth is located ventrally
- d – heterocercal caudal fin
- Chondrichthyes
Question 12.
Presence or absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification.
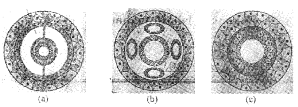
- Identify the different types of body cavities.
- Give examples to each
Answer:
- Different types of Body Cavities:
- a – Coelomate
- b – Pseudocoelomate
- c – Acoelomate
- Examples:
- Coelomate – Chordates
- Pseudocoelomate – Aschelminthes
- Acoelomate – Platyhelminthes
Question 13.
From the following general characters find out corresponding/Class with an Example
- Exclusively marine, triploblastic, spines on the skin, radially symmetrical in the adult and bilaterally symmetrical in the larval stage.
- Marine, they migrate towards freshwater for spawning, then their larvae return to ocean after metamorphosis.
- Triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, coelomate and metamerically segmented animals.
Answer:
- Echinodermata
- eg: Starfish
- Class – Cyclostomata
- eg: Petromyzon
- Annelida
- eg: Earthworm
Question 14.
Arrange the following points in a two-column table and give suitable heading for each column.
- Notochord present
- Post anal tail absent
- Pharynx Perforated by gill slits
- Notochord absent
- Posts anal tail present
- Gill slits are absent
Answer:
| Chordata | Non Chordata |
| Notochord present | Post anal tail present |
| Pharynx perforated by gill slits | Notochord absent |
| Post anal tail present | Gill slits absent |
Question 15.
Observe the figure and answer the questions.

- Identify the structure.
- Name the phylum which possess this structure.
- How this structure help the organism?
Answer:
- Cnidoblastornematocyst
- Cnidaria
- Capture of Prey
- Defense organ.
Question 16.
Note the relationship between first two words and suggest suitable words for the 4th place.
- Planaria: Flartfe cells: Earthworm: _________
- Jaw present: Gnathostomata:: Jaw absent: ___________
Answer:
- Nephridia
- Agnatha
Question 17.
Give reasons for the following.
- Respiratory and circulatory system are absent in parasitic platyhelminthes and Aschelminthes.
- Arthropods are the most successful invertebrate.
- Body of endoparasites are covered with cuticle.
Answer:
- Parasitic Plalyhelminthes and Aschelminthes lives in anaerobic condition. So respiratory and circulatory systems are absent in these parasitic forms.
- Arthropods are most successful, because of the presence of unique chitinous cuticle.
- In these parasites, the cuticle helps in escaping from the action of digestive enzymes.
Question 18.
Arthropodes are organisms with chitinous exoskeleton. Suppose exoskeleton is absent in arthropods. List the difficulties arthropodes has to face.
Answer:
- Their body will be dried up due to evaporation
- They couldn’t escape from predators.
- They couldn’t live in all environments.
Question 19.
Suppose during your field visit for collection from a rocky seashore you have got some live specimens such as sea urchin, sea cucumber, sea anemone. Is it possible to keep them on an aquarium in your school. Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
No. It is not possible.
Marine animals cannot live on freshwater because it leads to endosmosis and death occurs.
Question 20.
- Why nematocysts are more concentrated on the oral end and tentacles of cnidarians?
- What are the difficulties that coelenterate have to face if nematocysts were absent in body.
Answer:
- Nematocysts are concerned with defence and offence. Tentacles are usually used for defence, offence and food collection. Hence nematocysts are more concentrated in the oral end.
- The major difficulties cnidarians has to face in the absence of nematocysts are for food collection and escaping from enemies.
Question 21.
- Which of the following show the body cavity of earthworm?
- Identify the names of germlayers ‘a’ and ’b’.
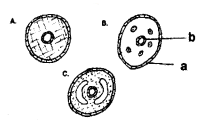
Answer:
- Figure C is the body cavity of earthworm. Because it is a true coelom
- The names of germlayers
- a-ectoderm
- b-endQderm
Question 22.
Identify the characters listed below and put (✓) mark on appropriate places
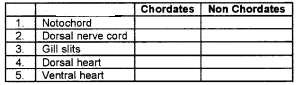
Answer:

Question 23.
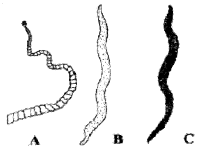
- Identify the organisms.
- Which feature of these organisms enable you to identify them?
Answer:
- The organisms:
- A-Tape worm
- B – Ascaris
- C – Earthworm
- Features:
- Tapeworm – Body is dorso-ventrally flattened and segmented.
- Ascaris – Body is cylindrical and vermiform
- Earthworm – Body is divided into similar segments and clitellum is present.
Question 24.
During a classroom discussion a student said that sponges are more complex than cnidarians. Do you agree with him. Jusftfy.
Answer:
1. Sponges: Cellular grade of organisation and cell aggregate body plan.
2. Cnidarians: Tissue level of organisation and blind sac body plan. So Cnidarians are more complex than sponges.
Question 25.
While comparing the digestive system of a roundworm and flatworm, a boy noted some differences. List out the differences.
Answer:
1. Flatworms: Digestive system incomplete, has only a single opening, ingestion and egestion occurs through the same opening.
2. Round worm: Complete digestive system, it has both mouth and anus. A muscular pharynx is also present in their digestive system.
Question 26.
- Identify the invertebrate whose mouth is on ventral or lower side and anus is on dorsal or upper side.
- Mention the phylum.
- Comment on its General characters.
Answer:
- Starfish
- Echinodermata
- Its General characters are:
- Water vascular system
- Tube feet
- Coelomate
- Spiny body
Question 27.
Match the following.
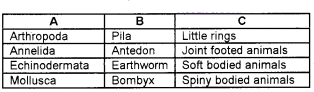
Answer:
- Arthropoda – Bombyx – Joint footed animals
- Annelida – Earthworm – Little rings
- Echinodermata – Antedon – Spiny bodies animals
- Mollusca – Pila – Soft bodies animals
Question 28.
Animals showing metameric segmentation are included under annelida. Body of tapeworm has numerous segments, but the animal is not included under annelida. How will you account for it?
Answer:
Tapeworm show false segmentation. In true segmentation number of segments is fixed and age of the segments are all same.
Question 29.
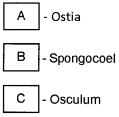
Complete the given flow chart showing the flow of water through canal system in sponges.
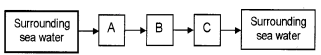
Answer:
Question 30.
Mention a single word for the following.
- Sexes are not separate.
- Body wall with three layers.
- File like rasping organs in Mollusca.
- Segmentation of animal body.
- The property of a living organism to emit light.
- Alternation of generation in Cnidarians.
Answer:
- Hermaphrodite
- Triploblastic
- Radula
- Metamerism
- Bioluminescence
- Metagenesis
Question 31.
The birds are well adapted for flying.
- Write the general characters of Aves.
- Give some of the flight adaptations seen in birds.
Answer:
- General characters of Aves:
- Presence of feathers
- Presence of beak
- Forelimbs are modified into wings.
- Warm blooded
- Respiration by lungs with air sacs.
- Oviparous
- Flight adaptations:
- Forelimbs are modified into wings
- Long bones are hollow with air cavities (Pneumatic)
- Air sacs connected to lungs supplement respiration
- Constant body temperature
Plus One Animal Kingdom NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the difference between direct and indirect development?
Answer:
1. Direct Development:
In direct development the young animal resembles an adult. There is no intermediate stage.
2. Indirect Development:
In indirect development there is intermediate stage, like larval stage. For example, frog before being developed into adult passthrough a tadpole stage. This is the case of indirect development.
Question 2.
What are the peculiar features that you find in parasitic platyhelminthes?
Answer:
In parasitic platyhelminthes hooks and suckers are present. Suckers help the parasite, in sucking the blood from the host.
Question 3.
What are the reasons that you can think of for the arthropods to constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom?
Answer:
Arthropods are the first phylum to have well developed systems to carry out different activities. There is distinct system for respiration, locomotion and reproduction. Their survival capacity is great because of elaborate system. This has helped them survive in diverse conditions. They can live in water, on land and in air.
This can be one of the reasons why arthropods are the largest group among the animal kingdom. Another reason is their early development compared to animals of higher phylum.
Question 4.
Water vascular system is the characteristic of which group of the following:
(a) Porifera
(b) Ctenophora
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Chordata
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Question 5.
“All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates”. Justify the statement.
Answer:
All chordates have notochord present in some stage of life.
The difference between vertebrates and nonvertebrates is as follows:
In vertebrates the notochord is present in the embryonic stage. This is replaced by a vertebral column during the adult stages.
Question 6.
How important is the presence of air bladder in Pisces?
Answer:
Presence of air-bladder in Pisces helps in buoyancy. This means that members of pisces don’t have to keep on swimming to remain floating.
Question 7.
What are the modifications that are observed in birds that help them fly?
Answer:
Following modification in birds help them fly:
- Pneumatic or hollow bones make for a light weight skeleton.
- Fore limbs are modified into wings to assist in flight.
- Excertion of urine and faeces is through single opening facilitating weight reduction.
- Aerodynamic body helps in flying.
Question 8.
Could the number of eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother be equal? Why?
Answer:
Usually number of eggs produced by oviparous mothers is greater than number of young ones produced by viviparous mothers. The main reason for this is the need of resources required for development of the embryo.
In oviparous the major part of development of the embryo takes place outside the uterus. This makes lesser burden on the mother.
On the other hand in viviparous animals the development takes place inside the uterus so lesser number of young ones can be successfully incubated. Moreover, once eggs are outside they are at risk of getting eaten by some predator because of their immobility, so need of more eggs is there to ensure continuity of progeny.
Plus One Animal Kingdom Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Calcareous skeleton is found in
(a) echinoderms
(b) some sponges
(c) mollusca
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 2.
Which cannot be the character of cnidaria
(a) musculoepithelial cells
(b) gastrovascular cavity
(c) nerve cells and process
(d) organ grade organization
Answer:
(d) organ grade organization
Question 3.
A non-matching set in the following is
(a) sepia – cuttle fish
(b) octopus – devilfish
(c) limulus – king crab
(d) ancylostoma – pinworm
Answer:
(d) ancylostoma – pinworm
Question 4.
A character common to Echinoderms and chordates
(a) marine
(b) benthonic
(c) deuterostome
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) deuterostome
Question 5.
Largest animal in the world that feed on smallest plankton is the
(a) dolphin
(b) killer whale
(c) blue whale
(d) sea cow
Answer:
(c) blue whale
Question 6.
Which is common to amphibian, reptelia and fishes
(a) nucleated RBC
(b) dermal scales
(c) poikelothermic condition
(d) both a and d
Answer:
(d) both a and d
Question 7.
Which of the following has pseudocoelomate tube within a tube body plan
(a) hydra
(b) planaria
(c) ascaris
(d) pheretima
Answer:
(c) ascaris
Question 8.
Ink gland associated with alimentary canal is found in
(a) sepia
(b) earthworm
(c) starfish
(d) cockroach
Answer:
(a) sepia
Question 9.
Which is common to all tetrapods
(a) epidermal scales
(b) red coloured blood
(c) 12 pairs of cranial nerve
(d) ureotelism
Answer:
(b) red coloured blood
Question 10.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of phylum annelida?
(a) closed circulatory system
(b) segmentation
(c) pseudocoelom
(d) ventral nerve cord
Answer:
(c) pseudocoelom
Question 11.
Respiratory pigment of mollusc is
(a) haemocyanin
(b) haemoglobin
(c) haemoerythrin
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(a) haemocyanin
Question 12.
Select the character that can be attributed to chondrithytes
(a) persistened notochord
(b) placoid scales
(c) poikelothermic body
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 13.
The central cavity of sponge is called
(a) spongocoel
(b) coelocentron
(c) canal system
(d) spongilla
Answer:
(c) canal system
Question 14.
Flame cell are excretory organ of
(a) hydra
(b) cockroach
(c) planaria
(d) frog
Answer:
(c) planaria
Question 15.
Pneumatic skeleton is a feature of
(a) amphibians
(b) reptiles
(c) fishes
(d) birds
Answer:
(d) birds
Question 16.
The number of gills present in osteichthyes is
(a) 2 pairs
(b) 6-15 pairs
(c) 5 pairs
(d) 4 pairs
Answer:
(d) 4 pairs
We hope the Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Animal Kingdom help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Animal Kingdom, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
