Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Neural Control and Coordination
Plus One Neural Control and Coordination One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Resting membrane potential is maintained by
(a) Hormones
(b) Neurotransmitters
(c) Ion pumps
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Ion pumps
Question 2.
The function of our visceral organs is controlled by
(a) Sympathetic and somatic neural system
(b) Sympathetic and parasympathetic neural system
(c) Central and somatic nervous system
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Sympathetic and parasympathetic neural system
Question 3.
Which of the following is not involved in Knee-jerk reflex?
(a) Muscle spindle
(b) Motor neuron
(c) Brain
(d) Interneurons
Answer:
(c) Brain
Question 4.
Mark the vitamin present in Rhodopsin
(a) Vit A
(b) Vit B
(c) Vit C
(d) Vit D
Answer:
(a) Vit A
Question 5.
Human eyeball consists of three layers and it encloses
(a) Lens, iris, optic nerve
(b) Lens, aqueous humor and vitreous humor
(c) Cornea, lens, iris
(d) Cornea, lens, optic nerve
Answer:
(b) Lens, aqueous humor and vitreous humor
Question 6.
Name the structure which connects two cerebral hemisphere
Answer:
Corpus callosum
Question 7.
Name the region of keenest vision in our eye.
Answer:
Fovea or yellow spot
Question 8.
After playing on a giant wheel, we lost our balance. Why?
Answer:
Change in position of Otolith in ear gives mal information to the brain.
Question 9.
Arrange the ear ossicles in order from inner ear to the tympanum.
Incus Stapes Malleus
Answer:
Stapes → Incus → Malleus
Question 10.
Name the receptors respond to irritants such as ammonia, vinegar or hot chilly pepper.
Answer:
Pain receptors
Question 11.
The tissues of eye and ear contain photoreceptors and the auditory receptors. Likewise, some are found as film of liquid coating in the membranes of the receptor cells. Name it.
Answer:
Chemoreceptors
Plus One Neural Control and Coordination Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Light ray → Lens → retina → pupil → cornea → brain → Vitreous chamber → Aqueous chamber → Optic nerve.
Correct the sequence.
Answer:
Light ray → Cornea → Aqueous chamber → Pupil → Lens → Vitreous chamber → Optic nerve → brain.
Question 2.
Classify the following into 3 groups and give appropriate headings.
Thalamus, Corporaquadrigerhina, Pons, hypothalamus, Cerebrum, Medulla Oblongata.
Answer:

Question 3.
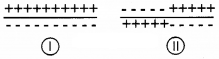
- Identify the above stages of nerve impulse conduction
- Name the ions involved in this process
Answer:
- Identification of the above stages
- I – Resting membrane potential
- II – Action potential
- Na+, K+
Question 4.
Differentiate Blindspot and Yellow spot.
Answer:
1. Blindspot:
The spot at the back of the eye where the optic nerve originates is known as blind spot. Rods and canes are absent here. So the image falling at this spot cannot be carried to the brain.
2. Yellow spot:
Lateral to the blind spot is a depressed area called yellow spot which contains only canes. It is the area of sharpest vision.
Question 5.
‘Sudden death may occur due to the damage of Medulla oblongata’. Why?
Answer:
The medulla oblongata contains several centres which regulate heartbeat, respiration, gastric, secretion, vomiting etc. It carries the nerve fibres which connect spinal cord and cerebrum.
Question 6.
Observe the figure given below.
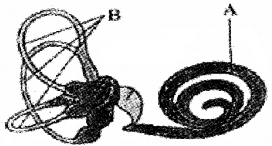
- Identify A & B
- Write the main function of part A.
Answer:
- Identification of A & B
- A – Cochlea
- B – Semicircular canals
- Maintenance of balance of the body and posture.
Question 7.
Where do you find bipolar and multipolar neurons in our body?
Answer:
- Bipolar neuron – Retina of eye
- Multipolar neuron – Cerebral cortex
Question 8.
While playing cricket, the ball hit a boy’s head. He immediately vomited and felt difficulty to breath.
- Identify the part of brain affected.
- Give the function of the affected part.
Answer:
- Medulla oblongata
- The medulla oblongata contains several centres which regulate heartbeat, respiration salivation, vomiting, etc. It carries the nerve fibers which connect the spinal cord and cerebrum.
Question 9.
Nocturnal animals like bats and owls have vision during night. Give reason.
Answer:
Nocturnal animals like owls have only rods in the retina. The rods are sensitive to dim light and enable to see dim light and at night.
Question 10.
Observe the flow diagram of the pathway of a light ray entering the eye.
Lightray → lens retina →pupil → aqueous chamber → vitreous chamber → cornea → optic nerve → brain
- Correct the sequence.
- If the light ray falls on the blindspot, what will happen?
Answer:
- Lightray → cornea → pupil → aqueous chamber → lens → vitreous chamber → retina → optic nerve → brain
- Rods and cones are absent in blind spot and so the image falling at this spot cannot be carried to the brain.
Question 11.
Arrange the following in the order of reception and transmission of the sound wave from the external auditory canal.
Answer:
Cochlear nerve, eardrum, stapes, incus, malleus, cochlea
Eardrum → malleus → incus → stapes → cochlea → cochlear nerve
Question 12.
Observe the given diagram.
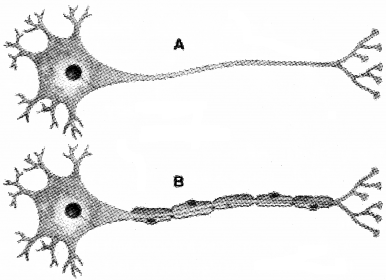
- Write any one difference between A and B.
- Through which neurone the impulse conduction is faster. Justify.
Answer:
- The difference between A and B
- A – non-myelinated neuron
- B – Myelinated neuron
- Impulse conduction is faster through the myelinated neurons.
Question 13.
The given diagram is a part of myelinated nerve fibre.
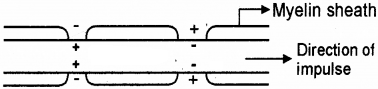
- Identify the part where there is no myelin sheath.
- Name the type of conduction going on in that type of nerve fibre.
Answer:
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Saltatory conduction
Question 14.
Observe the diagram.
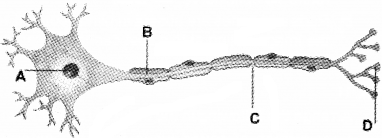
Identify A, B, C and D.
Answer:
- A – Nissl’s granule
- B – Myelin sheath
- C – NodeofRanvier
- D – Synaptic knob
Question 15.
- Identify the picture.
- Write the peculiarity of the picture.
Answer:
- Bipolar neuron
- Bipolar neurons are the neurons with one axon and one dendrite
Question 16.
A patient approaches a doctor with a problem that he was not able to sleep for the last 6 months. The doctor said that it may be due to the defect in the relay centre of his brain and advised him to take sedative pills.
- Which part of brain is described here as ‘relay centre’?
- What are the actions of sedative pills in body?
Answer:
- Thalamus
- Sedative pills work in the Thalamus and prevent the transmission of impulses to cerebrum. Depress brain activity produce feelings of calmness, relaxation, drowsiness and deep sleep.
Question 17.
It is said that the number and pattern of convolutions are associated with the degree of intelligence.
- Is it true?
- If yes, give the scientific reason for it.
Answer:
- True
- More intelligent forms like mammals especially primates have more convolutions than lower forms.
Question 18.
Diagram below represents a neuron at resting membrane potential (RMP).
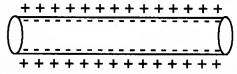
(a) How RMP is maintained?
(b) Draw the changes at the time of depolarization and explain how it happens.
Answer:
(a) RMP is maintained by
1. A resting membrane is poorly permeable to Na+ ions and Cl– ions. But more permeable to K+ ions. The extra cellular fluid has a high concentration of Na+ ion and low concentration of K+ ions. But the intracellular medium has a reverse condition due to the permeability.
2. Sodium-Potassium pump maintain higher concentration of Na+ ions outside the membrane compared to the concentration of Na+ inside
(b)
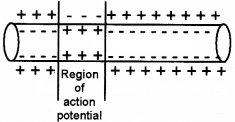
When a neuron is stimulated, there is a momentary reversal of the resting potential. The reversal of polarity is known as depolarisation. When stimulated a resting membrane, sodium pump suddenly stops and sodium ions begin to enter the cells.
The presence of higher concentration of Na+ inside the cell cause the inside membrane +ve and outside become -ve. This condition is called depolarisation.
Question 19.
Copy the diagram and label A, B, C, D.
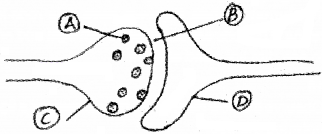
Answer:
- A – Synaptic vesicles
- B – Synaptic cleft
- C – Presynaptic neuron
- D – Postsynaptic neuron
Question 20.
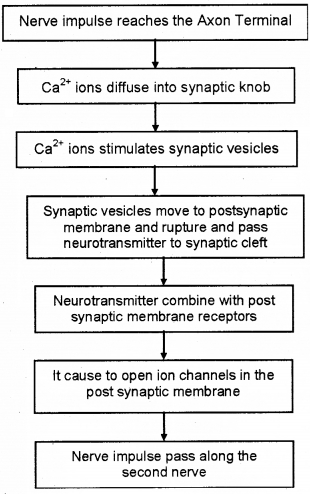
A diagram showing the chemical synaptic transmission is given below. Based on the diagram prepare a flow chart showing the process of synaptic transmission.
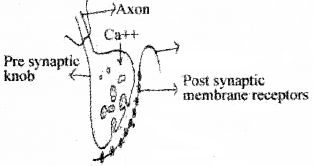
Answer:
Question 21.
While playing cricket the ball hit a boy’s head. He immediately vomited and felt difficulty to breath.
- Identify the part of brain which may be affected by the incident.
- Give functions of this particular part of brain.
Answer:
- Medulla oblongata
- Control heart beat, regulate respiration, control circulation, control digestion, control peristalsis etc.
Question 22.
Observe the schematic representation related to maintaining resting membrane potential of an axon.
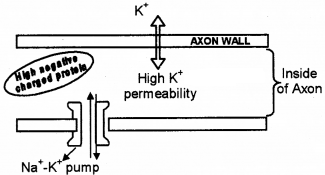
- What are the conditions exhibited in the figure for maintaining resting membrane potential?
- What are the other conditions of resting membrane potential (not exhibited in the diagram)
Answer:
- High permeability of axon wall for K+, Highly negative charge protein in axoplasm, Na+ – K+ pump.
- High K+ concentration inside the axon, High Na+ concentration outside the axon, Low Na+ permeability the axon wall, 3Na+ ions for 2K+ ions.
Question 23.
Observe the portion of Brain and answer the following questions.
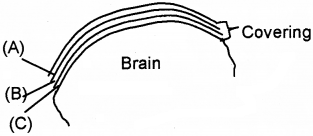
- Name the covering of brain.
- Identify A, B and C.
Answer:
- Meninges
- Identification of A, B, and C
- A – Dura mater
- B – Arachnoid mater
- C – Pia mater
Question 24.
Identify the following figure and label the parts.
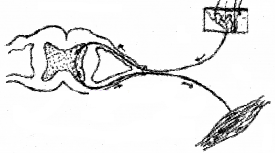
Answer:
Reflex arc
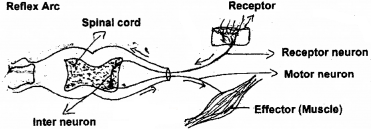
Question 25.
When we step on a thorn, we withdraw our legs suddenly, if we are taking this thorn out, we will not withdraw our legs. Comment on these two statements.
Answer:
1st statement is a reflex action and 2nd statement is a process controlled by Brain.
Question 26.
Observe the picture.
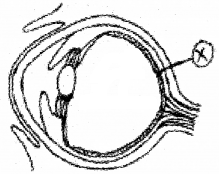
- Identify the part labelled as (x).
- In our retina there are more rod cells than cones. But our vision in darkness is poor. Give scientific explanation to this fact.
Answer:
- Yellow spot or fovea
- Image forms normally on yellow spot. In yellow spot rods are less and cones are more. So low dim light vision.
Question 27.
Find out the relationships and write the suitable word in the IVth place.
- Cornea: Sclera; Yellow spot: _________
- Incus: Middle ear; Cochlea: __________
- Scala vestibuli Perilymph; Scala media: __________
- Rods: Rhodopsin; Cones: ____________
Answer:
- Retina
- Inner ear
- Endolymph
- lodopsin
Question 28.
Arrange the organs according to the mechanism of hearing.
Oval window, Perilymph, Organ of Corti, Ear Ossicles, Pinna, Tectorial membrane, Endolymph, Auditory canal, auditory nerve, brain
Answer:
Pinna → Auditory canal → Ear ossicles → oval window → Perilymph → Endolymph → Organ of Corti → Auditory nerve → Brain
Question 29.
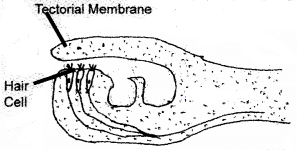
Copy the diagram and mark Tectorial membrane and sensory hair cell.
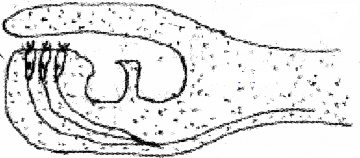
Answer:
Question 30.
Analyse the table and fill in the blanks given in the table with appropriate words.
| Rods | _______________ |
| No ability to detect colour | _______________ |
| ______________ | Cone pigments |
| _______________ | Cone shaped |
| Only one type | ___________________ |
| ___________________ | Photopic vision |
Answer:
| Rods | Cones |
| No ability to detect | Ability to detect |
| colour | colour |
| Rhodopsin | Cone pigments |
| Rod shaped | Cone shaped |
| Only one type | Three type |
| Scotopic | Photopic vision |
Question 31.
In animals like bats and owls photoreceptor cells of the retina have mainly rods.
- What can you infer from this?
- Write down the function of rods and cons.
Answer:
- Rod cells bring about vision in night or dim light vision.
- The function of rods and cons:
- Cones are cone shaped sensory cells of retina that bring about vision in day light and also distinguish colours. There are three types of cone cells for sensing primary colours red, green and blue.
- Rods are rod shaped sensory cells of the retina that bring about vision in night, but cannot distinguish colours.
Question 32.
Ear converts sound waves into neural impulses which are sensed and processed by the brain that enable to recognise sound. Construct a schematic diagram showing the mechanism of hearing the sound of a bell.
Answer:
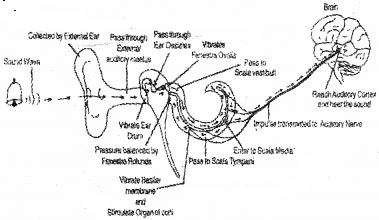
Question 33.
Arrange the structures found in the retina from inside to outside.
Cone cells, optic nerve, Ganglion cells, Bipolar neuron.
Answer:
Optic nerve → ganglion cells → Bipolar neuron → Cone cells
Question 34.
- Name the receptors of smell found as mucous coated thin, yellowish patch of modified pseudo stratified epithelium.
- Where is these receptors located?
Answer:
- Olfactory epithelium
- It is located at the roof of the nasal cavity on either sides of the nasal septum.
Question 35.
The diagram shows a section through a part of the human ear.
- Identify the parts labelled A, B and C.
- Which parts are involved in the equilibrium of the body.
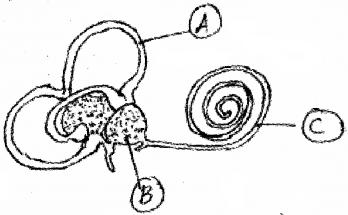
Answer:
- Identification of A, B and C.
- A – Semicircular canal
- B – Vestibule
- C – Cochlea
- Semicircular canal and vestibule.
Question 36.
Why does red flower look black in dim light?
Answer:
Stimulation of cone cells require high intensity of light. In dim light the cone cells are not stimulated. That is why the red flower looks black in dim light.
Question 37.
The taste buds of Humans are located in pockets around the papillae on the surface and sides of the tongue, but some on the surface of the pharynx and the larynx.
- What are the four basic taste senses?
- Find out their location in tongue
Answer:
- sweet, sour, salt, and bitter
- sweet and salty on the front, bitter on the back, and sour on the sides.
Question 38.
The touch receptors are either free dendritic endings or encapsulated dendritic endings present in the skin.
- What are the main functions of receptors of free dendritic endings?
- Name the main receptors of encapsulated dendritic endings. Give its functions.
Answer:
- They respond to pain and temperature
- Meissner’s corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles
- Meissner’s corpuscles:
These are found just beneath the skin epidermis in dermal papillae and abundant in fingertips and soles of the feet. These are light pressure receptors. - Pacinian corpuscles:
These are scattered deep in the dermis and in the subcutaneous tissue of the skin .These are stimulated by deep pressure.
- Meissner’s corpuscles:
Plus One Neural Control and Coordination Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The following steps are involved during synaptic transmission. Rearrange them in correct order.
- Release of neurotransmitter at synaptic cleft.
- Generation of a new potential at post synaptic neuron
- Arrival of impulse at the axon terminal
- Binding of neurotransmitter with specific receptor
- Movement of synaptic vesicle towards the membrane.
Answer:
- Arrival of impulse at the axon terminal
- Movement of synaptic vesicle towards the membrane
- Release of neurotransmitter at synaptic cleft.
- Binding of neurotransmitter with specific receptor.
- Generation of a new potential at post synaptic neuron.
Question 2.
A sharp tap is given at your knee cap with rubber hammer. You suddenly stretch your leg.
- Give name of this response.
- Which nerve centre is involved in this action?
- Construct a flow chart of the pathway of impulses in this action.
Answer:
- Reflex action
- Spinal cord
- Receptors in knee ® Sensory fibres ® Interneuron effector organs response → Motor fibres
Question 3.
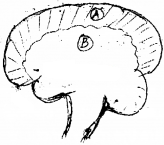
- Identify the organ and label A and B.
- Gait of a drunkard is not normal. Why?
- The death sentence given by the court is always by “hanging” in our country. Why this is preferred to other ways?
Answer:
- Organ-Brain
- A – Gray matter
- B- White matter
- Alcohol effects the cerebellum which control and co-ordinate voluntary muscular action.
- Because death is less painful and fast as atlas pierces the medulla oblongata and it is smashed. Medullar oblongata is the control centre of respiratory and cardiac action. Stoppage of which cause death.
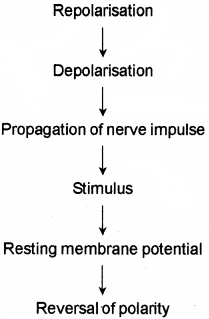
Question 4.
Make necessary correction in the flow chart given.
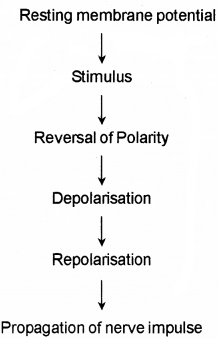
Answer:
Question 5.
Match the following.
| A | B |
| Cerebrum | Respiration, Salivation, Vomiting |
| Cerebellum | Relay centre |
| Medulla oblongata | Seat of mind and intelligence |
| Limbic system | Posture and equilibrium |
| Hypothalamus | Master gland |
| Pituitary | Emotional experiences and expressions. |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Cerebrum | Seat of mind and intelligence |
| Cerebellum | Posture and Equilibrium |
| Medulla oblongata | Respiration, Salivation, Vomiting |
| Limbic system | Relay centre |
| Hypothalamus | Emotional experiences and expressions |
| Pituitary | Master gland |
Question 6.
Suppose you dramatically escaped from a motor accident. Your heart beat and rate of respiration was increased at that moment.
- Name the hormone involved in this change.
- Which part of nervous system control these action?
- Enlist other physiological changes that you may feel at that time.
Answer:
- Adrenalin and Non-adrenaline.
- Medulla oblongata.
- High metabolic rate, High BP, High body temperature, High level of glucose in blood, Pupil diabetes.
Question 7.
Observe the figure below show two ion channels.
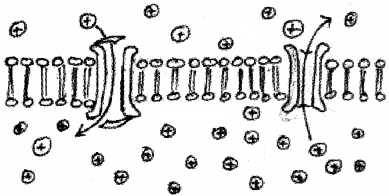
- This pump does not work on part of the axon. Why?
- Which have the ions participated in the process?
- Suggest the use of this process in nerve impulse conduction?
Answer:
- Myelin sheath: Myelin sheath act as insulator for axon and it increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction by saltatory conduction.
- Na+ and K+
- It creates action potential when stimulated by allowing the inward movement of Na+ ions through the Na channel and outward movement of K+ through K+ channel.
Question 8.
Neurons are the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
- Based on the number of axon and dendrites, how the neurons are classified.
- Give examples for each.
- Which neuron receives signal from a sensory organ and transmit the impulse to CNS.
Answer:
- Multipolar, bipolar and unipolar
- Examples
- Multipolar – found in cerebral cortex
- bipolar – found in the retina of eye
- unipolar-found in embryonic state
- afferent neurons or sensory neuron.
Question 9.
Observe the figures a and b.
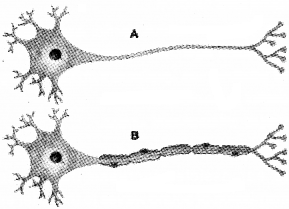
- Mention the structural difference between the two neurons.
- Name the type of impulse transmission through fig B.
- Mention the functional difference between the two neutrons.
Answer:
- Fig a is a non-myelinated neuron and Fig B is a myelinated neuron.
- Saltatory conduction.
- In myelinated impulse transmission is very fast.
Question 10.
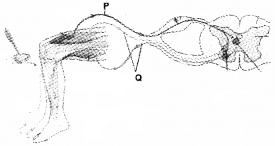
- Identify the diagrammatic representation
- Name P & Q.
- Mention the function of P & Q.
Answer:
- Reflex action (knee jerk reflex)
- Name P & Q
- P – Afferent pathway
- Q – Efferent pathway
- The afferent pathway receives signal from a sensory organ and transmits the impulse into CNS. The efficient pathway carries signals from CNS to the effector.
Question 11.
A diagram of brain is given below.
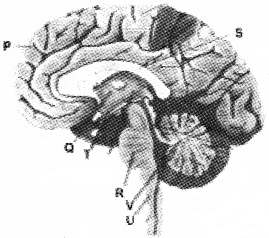
- Identify P Q R S
- Which part is responsible for thinking, memory, and reasoning
- Name the nerve band which connects the two hemispheres of brain.
Answer:
- Identification of P Q R S
- P – Cerebrum
- Q – Thalamus
- R – Pons
- S – Corpus callosum
- Cerebrum
- Corpus callosum
Plus One Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Compare the following:
- Central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral neural system (PNS)
- Resting potential and action potenial
- Choroid and retina
Answer:
1. Central Neural System and Peripheral Neural System:
The CNS includes the brain and the spinal cord and is the site of information processing and control. The PNS comprises of all the nerves of the body associated with the CNS (brain and spinal cord).
2. Resting Potential and Action Potential:
The electrical difference across the resting plasma membrane is called as the resting potential. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane, the membrane at the site becomes freely permeable to Na++.
The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane at the site of stimulus is called the action potential, which is in fact termed as a nerve impulse.
3. Choroid and Retina.
The middle layer, choroid, contains many blood vessels and looks bluish in colour. The choroid layer is thin over the posterior two-third of the eye ball, but it becomes thick in the anterior part to form the ciliary body.
The inner layer is the retina and it contains three layers of cells – from inside to outside – ganglion cells, bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells.
Question 2.
Answer briefly:
- How do you preceivethe colour of an object?
- Which part of our body helps us in maintaining the body balance?
- How does the eye regulate the amount of light that falls on the retina.
Answer:
1. Cones are responsible for color vision. They require brighter light to function than rods require. There are three types of cones, maximally sensitive to long-wavelength, medium-wavelength, and short-wavelength light (often referred to as red, green, and blue, respectively, though the sensitivity peaks are not actually at these colors).
2. The inner ear has three semi-circular canals forming cochlea. Cochlea is responsible for maintaining body balance.
3. The pupil in the eye functions as an aperture. This dilates in case of low light and constricts in case of intense light thereby regulating the amount of light falling on the retina.
Question 3.
The region of the vertebrate eye, where the nerve passes out of the retina is called the
(a) fovea
(b) iris
(c) blind spot
(d) optic chiasma
Answer:
(c) Blind spot
Plus One Neural Control and Coordination Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is not related to the autonomic nervous system?
(a) Peristalsis
(b) Digestion
(c) Excretion
(d) Memory and learning
Answer:
(d) Memory and learning
Question 2.
Comprehension of spoken and written words take place in the region of
(a) association area
(b) motor area
(c) Wernicke’s area
(d) Broca’s area
Answer:
(c) Wernicke’s area
Question 3.
How many laminae are present in the grey matter of spinal cord?
(a) Four
(b) Six
(c) Eight
(d) Ten
Answer:
(d) Ten
Question 4.
Animals possess nerve or nervous systems to respond to their environment. But the single celled Amoeba does not possesses any nerve cell. so, how it come to know whether a particle it encounters is a grain of sand and not its dinner by?
(a) thermotaxis
(b) skin
(c) hormones
(d) chemotaxis
Answer:
(d) chemotaxis
Question 5.
Thermoregulatory centre of human body is associate with
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) hypothalamus
(d) medulla oblongata
Answer:
(c) hypothalamus
Question 6.
Sensation of stomach pain is due to
(a) interoceptors
(b) exteroceptors
(c) proprioceptors
(d) chemotactors
Answer:
(a) interoceptors
Question 7.
Bipolar neurons occur in
(a) vertebrate embryos
(b) retina of eye
(c) brain and spinal cord
(d) skeletal muscles
Answer:
(b) retina of eye
Question 8.
Which foramen is paired in mammalian brain?
(a) Foramen of Luschka
(b) Foramen of Magendie
(c) Foramen of Monro
(d) Inter-ventricular foramen
Answer:
(a) Foramen of Luschka
Question 9.
Which is thickened to form organ of Corti?
(a) Reissner’s membrane
(b) Basilar membrane
(c) Tectorial membrane
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Basilar membrane
Question 10.
Skeletal muscles are controlled by
(a) sympathetic nerves
(b) parasympathetic nerves
(c) somatic nerves
(d) autonomic nerves
Answer:
(c) somatic nerves
Question 11.
Which part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature?
(a) Medulla oblongata
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Hypothalamus
Answer:
(d) Hypothalamus
Question 12.
Alzheimer’s disease in humans is associated with the deficiency of
(a) dopamine
(b) glutamic acid
(c) acetyleholine
(d) Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA)
Answer:
(c) acetyleholine
Question 13.
The posterior part of the retina, which is just opposite to the lens is
(a) cornea
(b) yellow spot
(c) fovea centralis
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(b) yellow spot
Question 14.
In the central nervous system, myelinated fibres form the ______ while the non-myelinated fibre cells form the _________
(a) grey matter, white matter
(b) white matter, grey matter
(c) ependymal cells, neurosecretory cells
(d) neurosecretory cells, ependymal cells
Answer:
(b) white matter, grey matter
Question 15.
The potential difference across the membrane of nerve fibre when it does not shown any physiological activity is called resting potential. It is about
(a) -60mV
(b) -80mV
(c) +60mV
(d) +90mV
(e) -36mV
Answer:
(b) -80mV
Question 16.
Vomiting centre is located in the
(a) stomach and sometimes in duodenum
(b) gastro-intestinal tract
(c) hypothalamus
(d) medulla oblongata
Answer:
(d) medulla oblongata
Question 17.
The function of vagus nerve innervating the heart
(a) initiate the heart beat.
(b) reduce the heart beat
(c) accelerate the heart beat
(d) maintain constant heart heat
Answer:
(b) reduce the heart beat
Question 18.
The size of pupil is controlled by the
(a) ciliary muscles
(b) suspensory
(c) cornea
(d) iris muscles
Answer:
(d) iris muscles
Question 19.
An action potential in the nerve fibre is produced when positive and negative charges on the outside and the inside of the axon membrane are reversed because
(a) more potassium ions enter the axon as compared to sodium ions leaving it
(b) more sodium ions enter the axon as compared to potassium ions leaving it
(c) all potassium ions leave the axon
(d) all sodium ions enter the axon
Answer:
(b) more sodium ions enter the axon as compared to potassium ions leaving it
Question 20.
A 22 years student goes to his ophthalmologist. He has problem in reading books because he is not able to contract his
(a) suspensory ligament
(b) pupil
(c) iris
(d) ciliary muscles
Answer:
(d) ciliary muscles
