Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 9 Locomotion and Movement
Question 1.
Match the following (SAY-2010)
| Type of joints | Examples |
| i) Ball and socket ii) Pivot joint iii) Saddle joint iv) Gliding joint | a) Joints of skull bone b) Between carpels and metacarpels of the thumb c) Between humerus and pectoral girdle d) Between atlas and axis e) Between the carpels |
Answer:
i) Ball and socket – a) between humerus and pectoral girdle
ii) Pivot joint – b) between atlas and axis
iii) Saddle joint – c) between carpal and metacarpal of thumb
iv) Gliding joint – d) between the carpals
Question 2.
Observe the relaxed unit of a muscle given below, (MARCH-2011)
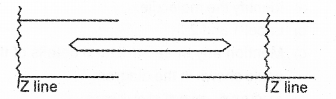
a) Redraw the diagram when the muscle unit is maximally contracted.
b) Repeated activation of the muscle can lead to fatigue. Justify.
Answer:
a)
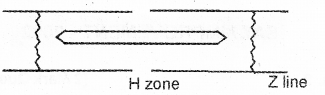
b) Repeated activation of the muscle leading to the accumulation of lactic acid cause fatigue.
Question 3.
Joints are essential for all types of movements involving the bony parts of the body. (SAY-2011)
a) Write any three majortypes of joints in our body.
b) Name the disease caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints.
Answer:
a) Fibrous, cartilaginous and synovial
b) Gout – Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric-acid crystals.
Question 4.
Diagram of a joint is given below: (MARCH-2012)
a) Identify the molecule.
b) Label 1 and 2.
c) Mention any three structural details of the molecule shown in the diagram.
Answer:
a) Hinge joint or synovial joint
b) Fibrous joint, Cartilaginous Joint and synovial Joint
Question 5.
Draw a flow chart showing physiological processes involved in the formation of cross bridge during muscle contraction. (SAY-2012)
Answer:
Neural signal → Acetyl choline produce action potential → Release of ca ions → Increase blood Ca++ level → Ca++ bind with troponin subanit → Remove masking of active site → myosin head bind with actin to form cross bridges.
Question 6.
Observe the structural representation of the muscle given below: (MARCH-2013)
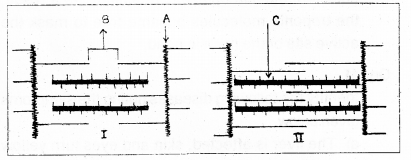
a) Which among this represents the contracted state?
b) Name the parts labelled as A, B and C.
Answer:
a) II
b) A – Z line , B – H zone C – myosin
Question 7.
In your practical class, teacher brought a tray containing the following human bones: (SAY-2013)
Humerus, Patella, Carpals Ulna, Radius, Tibia, Tarsals Femur.
a) Categorize them in to two,
b) Give the criteria of your categorization.
Answer:
a) Pectoral girdle/upper arm — Humerus, carpels, ulna and Radius
Pelvic girdle/lower limb bone patella, tibia, tarsals and femur
b) Pectoral and Pelvic girdle bones help in the articulation of the upper and the lower limbs respectively with the axial skeleton.
Question 8.
Give two examples for each of the following : (MARCH-2014)
a) Synovial joints
b) Muscular proteins
Answer:
Synovial joints — Ball and socket or hinge or gliding joints
Muscular proteins — Actin or myosin orTroponin
Question 9.
The important findings in the case sheet of two patients A and B show that both are suffering from disorders of the skeletal system. (SAY-2014)
a) ‘Patient A’ is suffering from inflammation of joints due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals.
b) ‘Patients B’ shows decreased bone mass and decreased level of oestrogen.
Identify the disorders or diseases of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
Answer:
a) Gout
b) Osteoporosis
Question 10.
Red muscle fibers have greater capacity to do work fora prolonged period, whereas white muscle fibers suffer from fatigue after a short work. Evaluate the statement. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Myoglobin content is high in red muscles . These muscles also contain plenty of mitochondria which can utilise the large amount of oxygen stored in them for ATP production. While white muscles possess very less quantity of myoglobin.
Number of mitochondria are few in them Hence after short work fatigue occurs.
Question 11.
Based on the diagram given below, can you write down the structural changes occuring in sarcometres during muscular contraction? (SAY-2015)
(Hint: Any two changes)
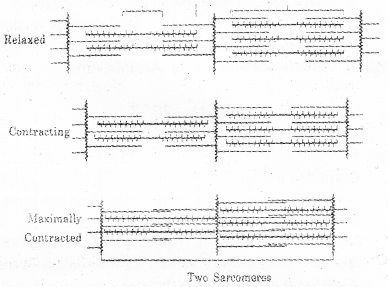
Answer:
During shortening of the muscle the ‘I’ bands get reduced, whereas the ‘A’ bands retain the length.
Question 12.
“A contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker but its volume remains the same.” (MARCH-2016)
a) Which theory explains the process of muscle contraction?
b) Identify two contractile proteins seen in muscle.
Answer:
a) sliding filament theory
b) Actin and Myosin
Question 13.
Name of few bones of appendicular skeleton is given below. (SAY-2016)
Clavicle
Humerus
Tibia
Patella
Scapula
a) Select the bones of pectoral girdle.
b) Name the articulating cavity between femur (thigh bone) and pelvic girdle.
Answer:
a) Clavicle,scapula
b) Acetabulum
Question 14.
Complete the following chart showing structure of myosin flament and its protein based on the hints given in the brackets. (MARCH-2017)
(Light meromyosin, Actin, Trophomyosin, Meromyosin)
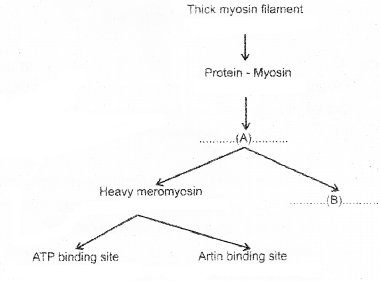
Answer:
A – Meromyosin
B – Light meromyosin
