Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation
Question 1.
The blood test report of a patient is given below: (MARCH-2010)

a) Which constituent of his blood is abnormal ?
b) What is the normal function of that constituent ?
Answer:
a) Eosinophil
b) Resist infection / Immunity / Associated with allergic reactions.
Question 2.
Observe the flowchart and answer the questions given on the next page : (MARCH-2010)
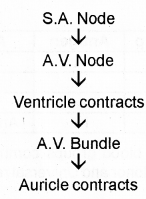
a) Re-draw the flowchart correctly.
b) What will happen if the S.A. node is not working properly?
Answer:
a) SA node → AV node → Auricle contracts → AV bundle → Ventricle contracts
b) SA is the pacemaker of the heart. If it is not working properly cardiac cycle will be obstructed/ cardiac failure/ No normal heartbeat rate.
Question 3.
a) Identify WBC’s marked as a1 b1 c1 and d1 ? (SAY-2010)
b) What is the normal percentage of WBC marked as b ?
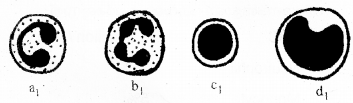
c) Categorise the above WBCs into granulocyte and agranulocyte.
Answer:
a) a1) Eosinophil
b1) Neutrophil
c1) Basophil
d1) Monocyte
b) Neutrophils are the most abundant cells (60-65 per cent) of the total WBCs
c) Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils are different types of granulocytes monocyte is agranulocyte.
Question 4.
Analyse the graph. (SAY-2010)
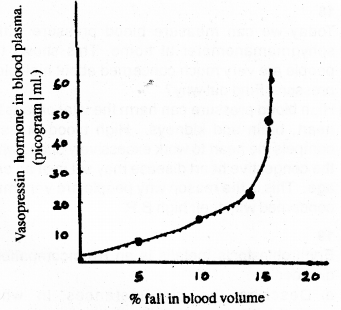
a) What is the relationship between the amount of vasopressin in blood plasma and the blood vol-ume?
b) Suggest a situations in which the vasopressin decreases in the blood.
Answer:
a) If blood volume decreases, the vasopressin hor-mone increases in blood plasma.
b) In cold days, vasopressin decreases in blood it leads to increasing the quantity of urine.
Question 5.
Observe the Graph. (MARCH-2011)
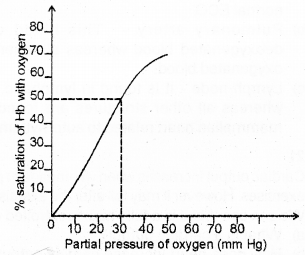
a) Identify the partial pressure of oxygen where 50% of saturation of Hb with oxygen.
b) Mention the factors favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin in alveoli.
Answer:
a) PO2 = 30mm of Hg
b) High p02, low pC02, Law H+ concentration low temperature.
Question 6.
Result of a project study related to the circulatory disorders to an area is given below. (MARCH-2011)
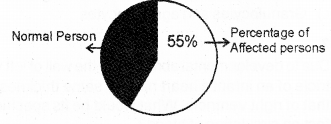
a) What is your observation?
b) Name any one circulatory disorder and its char-acteristics.
c) Suggest two measures to avoid these disorders.
Answer:
a) 55% of persons are affected with cardio vascular disorders.
b) (1) Hypertension – Blood pressure above from the normal
(2) Coronary artery – Affects the blood ves sels disease (CAD) that supply blood to the heart
c) 1) Do regular exercise
2) Avoid fatty diet, smoking, drugs
Question 7.
Identify the wrong statement and rewrite in correct form. (SAY-2011)
a) ‘O’ group is known as universal recipient.
b) AB group blood has no antibodies.
c) Blood normally contains 150000 to 350000 platelets/mm3.
d) Open circulation is present in arthropods and molluscs.
Answer:
(a) O group blood is known as universal donor.
Question 8.
Match the following. (SAY-2011)
| A | B |
| i) Basophil | Phagocytosis |
| ii) Lymphocyte | Inflammatory reaction |
| iii) Neutrophil | Associated with allergic reaction |
| iv) Eosinophil | Secrete antibodies Helps in blood coagulation Oxygen transport |
Answer:
i) basophil — inflammatory reactions
ii) Lymphocyte — Secrete antibodies
iii) Neutrophil — phagocytosis
iv) Eosinophil — associated with allergic reaction
Question 9.
If a person having blood group A is given blood trans-fusion of blood group B by mistake, what will be its effect? (MARCH-2012)
Answer:
Antigen – Antibody reaction takesplace. This results in the agglutination ordestruction of RBCs of Recipients.
Question 10.
The blood pressure of a person is shown as 170/130 mm Hg. What would be his disease? How it affects his body? (SAY-2012)
Answer:
High BP or Hypertension.
It leads to Heart attack or affect the vital organs – Brain or Kidney.
Question 11.
A person with A -ve blood group is injured severely in an accident. His relatives with A +ve and B -ve blood groups were ready to donate blood for him. Infer the consequences if he receives blood from them. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
coagulation of blood occurs
Question 12.
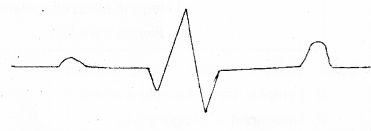
a) Label PQRST in the graph. (MARCH-2013)
b) What does the T wave represent?
Answer:
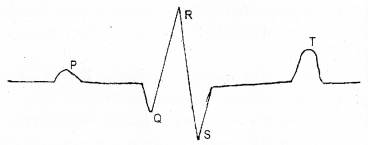
b) T wave represents the relaxation of ventricle
Question 13.
Observe the blood cells and attempt the following questions: (SAY-2013)

a) Which among the above cells least possibly found when you observe a drop of blood?
b) Write one function of any two type.
c) Categorises the WBC based on presence or absence of protein granules.
Answer:
a) Basophils
b) Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin, etc.,and are involved in inflammatory reactions. Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body
c) Granulocytes and agranulocytes
Question 14.
Due to developmental abnormality the wall of left ven-tricle of an infant’s heart has the same thickness as that of right ventricle. What would be its specific ef-fect on circulation of blood? (SAY-2013)
Answer:
It decreases the output blood flow
Question 15.
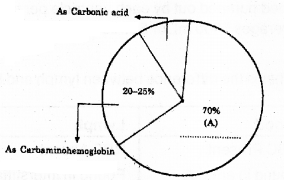
Blood transports C02 from tissues to lungs by various means. Mention any two methods of the same. (MARCH-2014)
Answer:
a) In chemical combination with water present in RBC and plasma
![]()
b) As Carbaminohaemoglobin-
In chemical combination with haemoglobin present in plasma
OR

Question 16.
The sequential events in the heart which are cycli-cally repeated are called the cardiac cycle. (MARCH-2014)
a) What are the phases of the cardiac cycle?
b) Why do we call the human heart as myogenic?
c) What is the rol of SAN (Sinu Atrial Node) on a human heart?
Answer:
a) Atrial systol, ventricular systole and joint diastole
b) Normal activities of the heart are regulated intrinsically, i.e., auto regulated by specialised muscles (nodal tissue), hence the heart is called myogenic.
c) SAN generates an action potential which stimulates both the atria to undergo a simultaneous contraction – the atrial systole. This increases the flow of blood into the ventricles by about 30 percent.
Question 17.
Find the odd one and write the function. (MARCH-2015)
Neutrophil, Erythrocyte, Monocyte, Lymphocyte, Basophil, Eosinophil.
Answer:
Erythrocyte, they helps in the transport of respiratory gases from lungs to tissues and from tissues to lung though blood.
Question 18.
Observe the flowchart and answer the questions given below? (MARCH-2015)
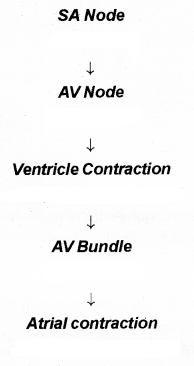
a) Draw the flowchart correctly.
b) What will happen if the SA node is not working properly?
Answer:
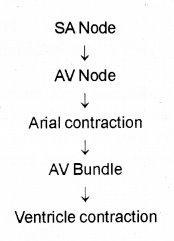
b) Heart beat is not produced
Question 19.
Make a diagrammatic sketch of human double circulation. Label the three associated organs and any one blood vessel. (SAY-2015)
OR
Name the two types of heart valves and mention their functions.
Answer:
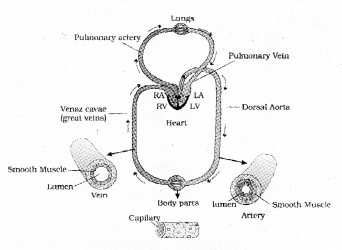
OR
The opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle is guarded by a valve called the tricuspid valve, whereas a bicuspid or mitral valve guards the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
It allows the flow of blood only in one direction, i.e,, from the atria to the ventricles The openings of the right and the left ventricles into the pulmonary artery and the aorta respectively are provided with the semilunar valves.
It allows the flow of blood from ventricles to the pulmonary artery or aorta. These valves prevent any backward flow.
Question 20.
Carbon dioxide transport in the form of bicarbonate ion is picturized below. (MARCH-2016)
Observe the diagram and identify the enzyme.
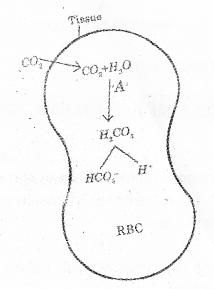
Answer:
A-carbonic anhydrase
Question 21.
The longitudinal section of the human heart showing internal structure is given below. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions. (MARCH-2016)
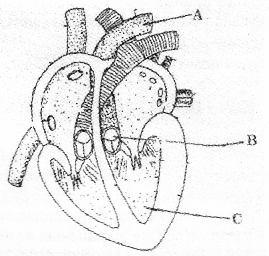
a) Label the parts marked as A, B, C.
b) Draw a flow chart to show double circulation.
OR
“Sinoatrial Node iscalled pace maker of our heart.”
a) Justify the statement.
b) Define cardiac cycle and cardiac output.
Answer:
a) A-aorta B-semilunarvalve C-left ventricle
b)
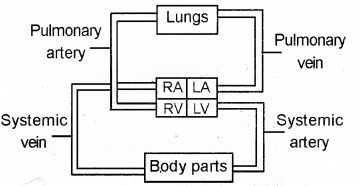
a) SA node initiates, regulate and maintains heart beat
b) Cardiac cycle – sequence of events during the completion of one heart beat (systole and diastole)
Cardiac output-volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute.
Question 22.
Diagramatic representation of C02 transport in man is given. Observe and answer the following. (SAY-2016)
a) Name the method of C02 transport indicated as A
b) Write the name of enzyme involved in the process A.
Answer:
a) Bicarbonates
b) Carbonic anhydrase
Question 23.
a) Fill up A, B, C, D and complete the branching chart given below. (SAY-2016)
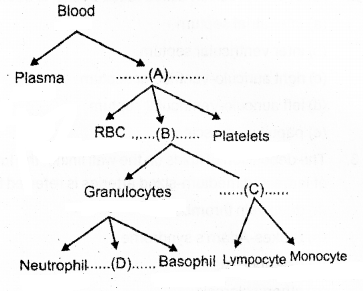
b) Write the function of platelets
OR
In man normal ECG consists of three waves.
a) P-wave
b) QRS complex wave
c) T – wave
What does the above waves mean?
Answer:
a) A – Formed elements/Blood cells
B – WBC/Leucocytes
C-Agranulocytes
D- Eosinophils
b) It helps in blood clotting
OR
a) P wave – Atrial depolarisation
b) QRS – Ventricular depolarisation
c) T – Ventricular repolarisation
Question 24.
a) Select the correct statement regarding the ECG of man. (MARCH-2017)
i) P-wave represents auricular repolarization.
ii) P-wave represents ventricular repolarization.
iii) P-wave represents auriculardepolarization.
iv) P-wave represents ventricular depolarization.
b) Observe the diagram and label A, B, C and D.
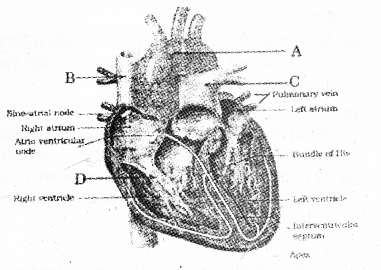
Answer:
a) iii) P-Wave represent auriculardepolarization
b) A – Aorta
B – Venacava
C – Pulmonary Artery
D – Chordae tendineae
Question 25.
Answer the following few words. (MARCH-2014)
a) Significance of pulmonary circulation in man.
b) Function of erythrocytes
c) Pacemaker for a human heart and its significance.
d) Normal blood pressure of human beings and its variation during hypertension.
Answer:
a) Purification of blood by pulmonary circulation and supply of pure blood to tissues by systemic circulation.
b) Transport of 02 from lungs to tissues and 02 from tissues to lungs
c) Initiation of heartbeat or cardiac impulse
d) Normal — 120/80 mm of Hg,
Hypertension —140/90mm of Hg or higher
