Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 6 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Question 1.
Observe the graph (MARCH-2010)
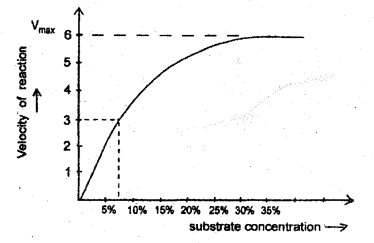
a) What is meant by ‘Vmax’ value?
b) Why is ‘Vmax’ not exceeded by any further rise in the substrate concentration?
c) If a chemical substance closely resembling to that of a substrate is introduced into the reaction system, what will be the consequences ? Substantiate.
Answer:
a) Vmax is the value showing maximum velocity of a reaction.
b) The enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecules. So all enzyme molecules are got saturated and there is no free enzyme molecule to bind with the additional substrate molecule.
c) It will inhibit the activity of the enzyme. This type of inhibition is called competitive inhibition. Due to its close similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substrate-binding site of the enzyme. Consequently, the substrate cannot bind and as a result, the enzyme action declines.
Question 2.
In a 400-metre race competition, Athira won first place. Her friends commented that it is due to her high vital capacity. (MARCH-2010)
a) What do you understand by the tern vital capacity?
b) Suggest ways to improve the vital capacity.
Answer:
a) The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration
b) Regular exercise, Avoid smoking, Yoga.
Question 3.
In a normal person, expiratory reserve volume and residual volume were found to be 1000 ml and 1100 ml respectively. (SAY-2010)
a) Find out his functional residual capacity?
b) How the functional residual capacity differs from the vital capacity?
Answer:
a) ERV+RV i.e 2100ml
b) Functional Residual’Capacity (FRC)
The volume of air that will remain in the lungs after a normal expiration. This includes ERV+RV
Vital Capacity (VC):
The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after forced expiration. This includes ERV, TV and IRV or the maximum volume of air a person can breathe out after a forced inspiration.
Question 4.
The graph given below is oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve. Observe the graph and answer the following questions. (SAY-2011)

a) Identify the P02 where 90% hemoglobin saturation occurs.
b) Write any three factors favorable for the formation of oxyhemoglobin in alveoli.
Answer:
a) 60mm of Hg
b) In the alveoli, there is high pO2, low pC02, lesser H+ concentration, and lower temperature are favorable for the formation of oxyhemoglobin.
Question 5.
Identify the two true statements from the statements given below and rewrite the two false statements correctly. (MARCH-2012)
a) Pneumonia is a chronic disorder due to cigarette smoking.
b) Carbon dioxide combines with hemoglobin to form carbamino hemoglobin.
c) Respiratory rhythm is maintained by the respiratory center in the heart.
d) Alveoli are the primary sites of exchange of gases.
Answer:
True statements b and d
а) Emphysema is a chronic disorder due to Cigarette smoking
c) Respiratory rhythm is maintained by the respiratory center in the medulla.
Question 6.
Observe the figure and answer the questions. (SAY-2012)
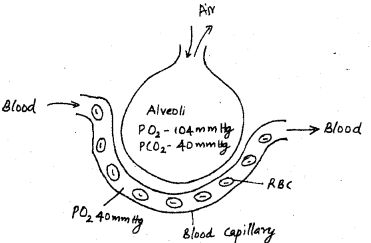
a) What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolar capillary?
b) Name the biological principles involved in the ex-change of gases in the above structure.
c) What happens when partial pressure of oxygen becomes same in the alveoli and alveolar-capillary?
Answer:
a) 40mmHg.
b) Diffusion
c) No gas exchange
Question 7.
Pick out the wrong one and justify your selection. (MARCH-2013)
a) VC = ERV+IRV + TV
b) TLC = VC + RV
c) TV = 500 ml
d) ERV = 3000 ml
Answer:
d-ERV(lt normally comes around 1000-1200 ml)
Question 8.
Observe the diagram and answer the following question: (SAY-2013)
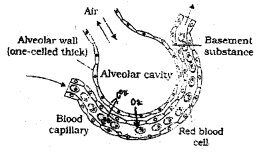
a) Name the biological process involved in the gas exchange shown in the figure.
b) How the oxygen is transported to cells from the alveoli?
Answer:
a) Simple tissues
b) Oxygen bind with haemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin. Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is related to partial pressure of 02. In the alveoli high p02, low pC02, lesser H+ concentration and lower temperature, that helps in the formation of oxyhaemoglobin, whereas in the cells ortissues, Iow p02, high pC02, high H+ concentration and higher temperature are favourable for dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.
Question 9.
Write the functions of parts 1 and 4. Label the parts 2 and 3 in the following figure showing a synapse. (No need to copy the picture) (MARCH-2014)
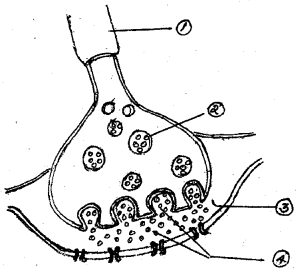
Answer:
1) Transmit impulse away from the neuron
2) Transmit impulses across synaptic cleft(synapse)
3) Synaptic vescicle
4) Synaptic cleft
Question 10.
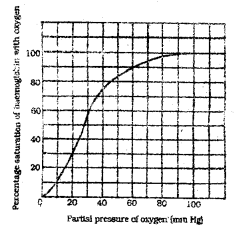
a) What is represented by the above graph? (SAY-2014)
b) Write any three factors which can influence the sigmoid curve of this graph
Answer:
a) Oxygen dissociation curve
b) pCO2, H+ concentration ,pO2 etc.
Question 11.
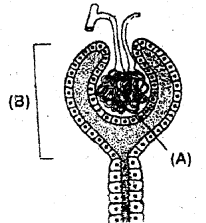
Observe the figure given below and answer the questions. (MARCH-2015)
a) Write the name of the figure.
b) Name the labelled part (A) and (B).
c) Which is the site of formation of ultrafiltrate?
Answer:
a) Nephron
b) A-Glomerulus B-Bowmans capsule
c) Bowmans capsule
Question 12.
Asthma and emphysema are two disorders of the human respiratory system. Mention their causes and symptoms. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Asthma is a difficulty in breathing causing wheezing due to inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles. It occurs due to dust, pollen etc.
Emphysema is a chronic disorder in which alveolar walls are damaged due to which respiratory surface is decreased. One of the major causes of this is cigarette smoking.
Question 13.
Correct the following misconceptions of a student regarding human respiration. (SAY-2015)
a) Vital capacity includes tidal volume, residual volume and dead air.
b) Respiration is controlled by nerve centres located in hypothalamus and cerebrum.
Answer:
a) This includes expiratory reserve volume , inspiratory reserve volume and tidal volume
b) The respiratory rhythm centre of medulla region of the brain responsible for regulation
Question 14.
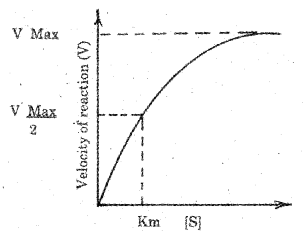
Based on the graph given below, explain the effect of concentration of substrate on enzyme activity. (SAY-2015)
Answer:
With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not increased by further rise in concentration of the substrate because the enzyme molecules are saturated there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules
Question 15.
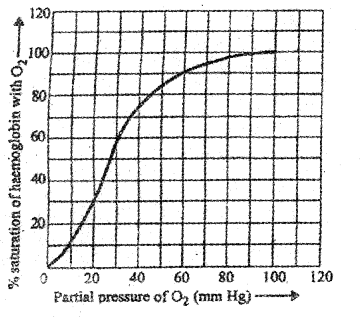
Carefully observe the given Sigmoid curve on the graph and answer the following questions. (MARCH-2016)
a) What does the graph indicates?
b) What are the three factors affecting the Sigmoid pattern of the graph
Answer:
a) oxygen dissociation curve
b) H+ concentration, temperature,C02 and 02
Question 16.
Differentiate the process of inspiration and expiration (MARCH-2017)
| Inspiration | Expiration |
Answer:
| Inspiration | Expiration |
| 1. Diaphragm Contracts | 1. Diaphragm Relaxes |
| 2.Contraction of external Intercostal muscles | 2.Contraction of internal Intercostal muscles |
| 3.Thoracic Volume Increases | 3. Thoracic Volume decreases |
Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer
