Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 4 Biomolecules
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks marked as a, b, c and d. (SAY-2010)
| Base | Nucleoside | Nucleotide |
| Adenine | Adenosine | Adenylic acid |
| Guanine | ….a…… | Guanylic acid |
| …b…. | Cytidine | Cytidilic acid |
| Thymine | ….c…… | ….. d…… |
Answer:
a — guanosine
b — cytosine
c — thymidine
d — Thymidilicacid
Question 2.
Non-protein constituents called cofactors are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytic activity. (MARCH-2011)
a) Name the protein portion of the enzyme,
b) What happens to the catalytic activity when the cofactor is removed from the enzyme?
c) Mention any two kinds of cofactors with examples.
Answer:
a) Apo enzyme
b) catalytic activity decreases
c) 1) Prosthetic group. Eg: Hearn
2) Co-enzyme, Eg: NAD, NADP.
Question 3.
The breakdown of biomacromolecules in the duodenum is mentioned below. Fill the blank boxes with correct terms. (SAY-2011)
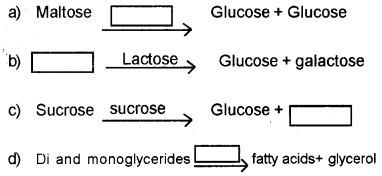
Answer:
a) Maltase
b) Lactose
c) Fructose
d) Lipase
Question 4.
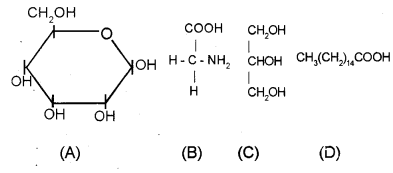
a) Identify A to D. (SAY-2011)
b) Name the compound obtained by the fusion of one ‘C’ and three ‘D’.
Answer:
A — Glucose
B — Aminoacid
C — Glycerol
D — Fatty acid (palmitic acid)
b) Triglyceride
Question 5.
Carbohydrate: Sugars: : (SAY-2012)
Proteins: ……………..
Answer:
Amino acids or Peptides.
Question 6.
Prepare an equation for a chemical reaction using the following components. (SAY-2012)
Carbonic anhydrase, carbonic acid, water, carbon dioxide.
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
Analyse the graph showing the activity of salivary amylase (SAY-2012)
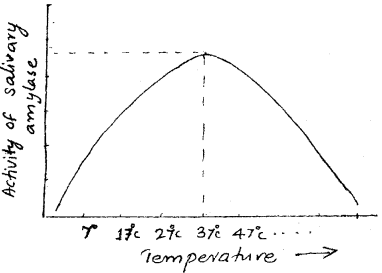
a) Which is the optimum temperature for salivary amylase obtained from the graph.
b) Why the activity declines below the optimum value?
Answer:
a) 37°C
b) Low temperature makes the enzyme inactive.
Question 8.
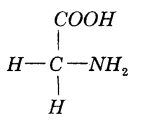
a) Identify this compound. (MARCH-2013)
b) Name the bond produced when another biomolecule of the same category combines with this.
c) If a number of such molecules are bonded together, what will be the resultant molecule?
Answer:
a) Glycine – amino acid
b) peptide bond
c) polypeptide or protein
Question 9.
Observe the following representation and fill up the blanks appropriately. (SAY-2013)
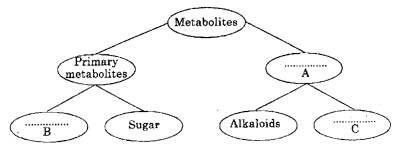
Answer:
a) Secondary metabolite
b) Amino acids
c) Flavonoids
Question 10.
Observe the graph showing the activity of an enzyme influenced by pH. (SAY-2013)
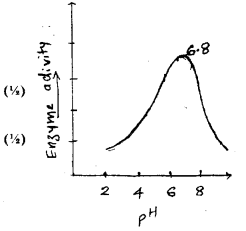
a) Name the possible enzyme involved in this reaction.
b) Where is its site of action?
c) Mention any other factor which affects this enzyme activity that results in a similar pattern of graph.
d) Name another similar enzyme acting on the same substrate.
Answer:
a) Salivary amylase
b) buccal cavity
c) Temperature and substrate concentration
d) Pancreatic amylase
Question 11.
Observe the graph ad answer the following : (SAY-2013)
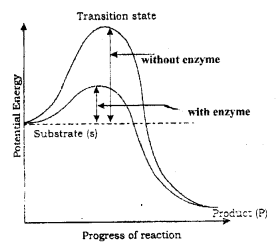
a) Find out the role of the enzyme.
b) Mention any two factors that influence the activity of an enzyme and state their influence.
Answer:
a) Enzyme lower the activation energy and reaction proceeds at rate faster than that of uncatalysed reaction.
b) Enzyme shows highest activity at optimum temperature and PH.
Question 12.
Name the chemical bonds formed between the following : (MARCH-2014)
a) Amino acids in a protein molecule
b) Sugar and phosphate in nucleic acids.
Answer:
a) Peptide bond
b) Phospho diester or Ester bond
Question 13.
Distinguish between cofactor and coenzyme with an example for each. (MARCH-2014)
Answer:
Co-factor — Inorganic or metallic ions which form non protein part of an enzyme Eg- Zinc in carboxy pep-tidase
Coenzyme — Non protein organic part of enzyme Eg – FAD/NAD
Question 14.
a) Why are proteins heteropolymers? (SAY-2014)
b) Identify the protein from the given list of biomacromolecules and write its function. (Cellulose, Starch, Antibody, Inulin)
c) Identify the type of protein structures of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
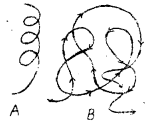
OR
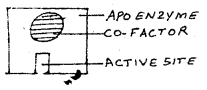
Symbolic representation of a functional enzyme is given below.
a) Write one difference between a co-factor and an Apoenzyme.
b) Name the different types of co-factors.
c) What is the co-factor for the enzyme, Carbox- ypeptidase?
Answer:
a) Because it is made up of different aminoacids antibody- act against foreign bodies coming into the body
b) A -secondary structure B-Tertiary structure
OR
a) Co-factor—non protein part of an enzyme
Apoenzyme -Protein part of enzyme
b) Three kinds of cofactors are identified: prosthetic
groups, co-enzymes and metal ions
c) zinc is a cofactor for the proteolytic enzyme
carboxypeptidase
Question 15.
Select the wrongly matched pair from the following: (MARCH-2017)
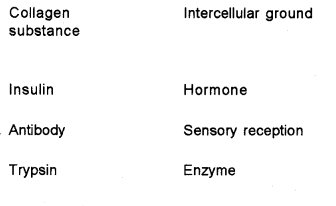
Answer:
Antibody – sensory reception
Question 16.
Identify protein stuctures. (A) and (b) from the following figure. (MARCH-2015)
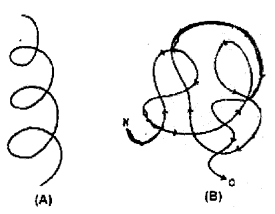
Answer:
a) Secondary structure
b) Tertiary structure
Question 17.
Analyze the graph showing the activity of an enzyme, influenced by temperature (MARCH-2015)
a) What is meant by optimum temperature?
b) Why does the enzyme activity decline at too high temperatures?
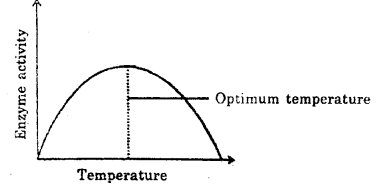
Answer:
a) Enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature called the optimum temperature, b) Low temperature preserves the enzyme in a temporarily inactive state whereas high temperature destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
Question 18.
Complete the following sequence with appropriate words. (SAY-2015)
Amino acids: ……………. (a) ………… bond: Proteins
……… (b) ………. : Glycosidic bond: Polysaccharides
Answer:
a) peptide bond
b) glucose
Question 19.
Metabolites are organic compounds constantly utilized in various metabolic activities in the cells. (MARCH-2016)
a) What are the two types of metabolites in cells?
b) Given an example for each type of metabolite.
Answer:
a) primarymetabolites and secondary metabolites
b) primarymetabolites-lipid,protein,carbohydrate etc secondary metabolites-alkalloids, terpenoides etc.
Question 20.
Enzymes are biocatalysts which regulate various biochemical reactions. (SAY-2016)
Illustrate the following reactions.
E + S → ES → E + P
E + S → ES → E + P
Answer:
Enzyme combines with substrate and forms enzyme substrate complex.
Enzyme substrate complex dissociates and forms enzyme and products.
Question 21.
Identify the given biomolecule that comes under the fat. (SAY-2016)
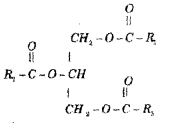
Answer:
Triglyceride
Question 22.
a) Name the biomacromolecule (polymer) in which the peptide bond is present. (SAY-2016)
b) Name the bond present between the phosphate and the hydroxyl group of sugar in nucleic acids.
Answer:
a) Protein b) phosphodiester bond
Question 23.
Identify the given biomoledules. (MARCH-2017)
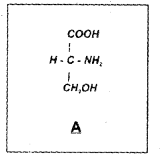
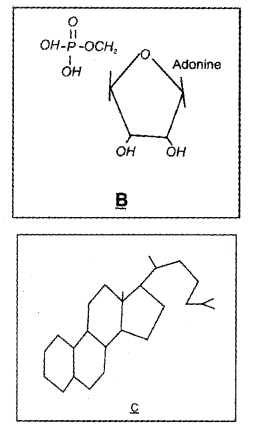
Answer:
A) Amino acid
B) Adenylic acid
C) Cholesterol
