Kerala Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 Neural Control and Coordination
Question 1.
Complete the given flowchart: (MARCH-2010)
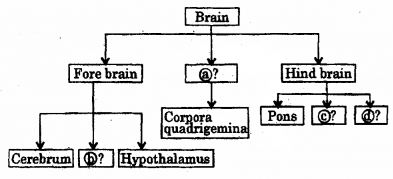
Answer:
a) Midbrain
b) Thalamus
c) Medulla
d) Cerebellum
Question 2.
You may have an experience of sudden withdrawal of body parts when you come in contact with objects that are extremely cold. This response occurs involuntarily without conscious efforts. (MARCH-2010)
a) Name the process behind this.
b) Construct a flowchart showing the pathway of impulses during this process.
Answer:
a) Reflex action
b) Receptor → Sensory neuron → Inter neuron → Motor neuron → effector organ
Question 3.
Observe the diagram: (MARCH-2010)
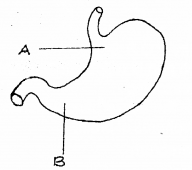
a) Label the parts A and B.
b) Even though concentrated HCI is stored in the stomach, it will not generally damage the stomach wall. Why ?
Answer:
a) A. Cardiac stomach
B. Pyloric stomach
b) Mucus and bicarbonates present in gastric juice protect the stomach wall.
Question 4.
Study the diagram. (SAY-2010)
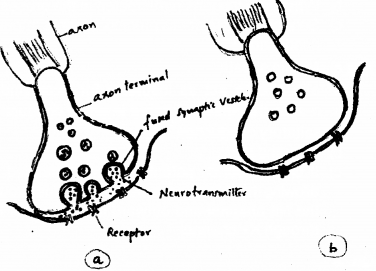
Figure a and b given above are two axon terminals with synapse. Which one is conducting the impulse? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Diagram a, The axon terminals contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters it is not present in diagram b.
Question 5.
Incus, stapes and malleus are the three ear ossicles of the middle ear. Arrange them in the order in which they are present from tympanic membrane to the oval window of the cochlea. (SAY-2010)
Explain their function.
Answer:
Malleus, incus and stapes
The ear ossicles increase the efficiency of transmission of sound waves to the inner ear.
Question 6.
Two types of synapses are given in the diagrams A and B. (SAY-2011)
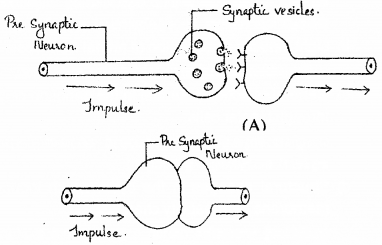 a) Identify A and B.
a) Identify A and B.
b) Impulse transmission in ‘B’ is faster than that of ‘A’. Give reason.
c) Name the chemical substance that helps in the transmission of impulses in ‘A’.
Answer:
a) A chemical synapse B- electrical synapse
b) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along a single axon. Hence impulse transmission across an electrical synapse is always faster than that across a chemical synapse.
c) neurotransmitter
Question 7.
The following diagram shows the characteristics of a phylum. (MARCH-2012)
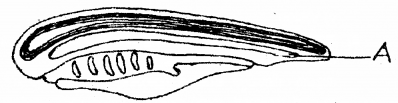
a) Identify the phylum.
b) Label A in the diagram.
c) Mention foursalient features of the phylum.
Answer:
a) Phylum chordata
b) Notochord
c) 1. Presence of Notochord
2. Dorsal hollow nerve chord
3. Pharyngeal gill stits
4. Post anal tail
Question 8.
Analyse the concept may given below and fill the gaps appropriately so as to explain the concept of brain. (SAY-2012)
Answer:
a) Mid brain
b) Hindbrain
c) Inter sensory association
d) Memory & communication
e) Cardiovascular reflex
f) Gastric secretion
Question 9.
Arrange the following processes in nerve impulse con-duction in a sequential order. (MARCH-2013)
a) Bursting of synaptic vesicle
b) Development of action potential
c) Na+-K+ pump starts functioning
d) Stimulus received and influx of Na+ ions
e) Binding of neurotransmitter with postsynaptic membrane
Answer:
f → d → c → b → a → e
Question 10.
Nerve impulse transmission involves. (SAY-2013)
Maintenance of resting potential
Development of action potential
Propagation of action potential
a) Diagrammatically represent the polarised and depolarised state of axon of a neuron.
b) Describe how the resting potential of a neuron is maintained.
c) “Electrical currents fade as they pass along a wire but nerve impulses do not fade as they pass along neurons”. Evaluate the statement and sub-stantiate your answer.
Answer:
a)
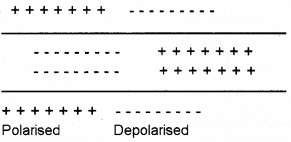
b) These ionic gradients are maintained by the active . transport of ions by the sodium-potassium pump which transports 3 Na+ outwards for 2 K+ into the cell . This helps to maintain the resting potential..
c) Electric current fade due to resistance of conductor. But nerve fibre do not have resistance. So the impulses pass without fade. Myelil sheath also helps to prevent the loss of charges.
Question 11.
Given below are the stages in the generation of optic nerve impulse or action potential on the retina and the role of opsin and retinal in the mechanism of vision. Arrange them in a sequential order. (SAY-2014)
a) Action potential (impulses) are transmitted by the optic nerves to the visual cortex area of the brain.
b) Light induces dissociation of retinal from opsin,
c) Generates action potential in the ganglion cells through bipolar cells.
d) Structural changes in the opsin which induce membrane permeability changes.
e) Potential differences are generated in the photoreceptor cells.
f) Neural impulses are analyzed by visual cortex area of the brain..
Answer:
b → d → e → c → a → f
Question 12.
a) Prepare a pathway of an action by using the following hint. (MARCH-2015)
(Hint – Receptor, Motor neuron, Afferent neuron, Efferent neuron, Intemeuron in the spinal cord, Effector organ.)
b) Give an example of such an action.
OR
Compare rods and cones of the retina based on the following features. ,
i) Shape
ii) Type
iii) Ability to detect colour
iv) Pigments
v) Vision
Answer:
a) Receptor →Afferent neuron → lnter neuron in spinal cord → Motor neuron → Efferent neuron → Effector organ.
b) The stimulus and response forms a reflex arc in the knee jerk reflex
OR
| Rod | Cone | |
| shape | rod shaped | cone shaped |
| Type | one type | Green cone, red cone and blue cone |
| Ability to detect colour | No | Yes |
| Pigments | Rhodopsin | lodopsin |
| Vision | Dim light vision | Colourvision |
Question 13.
Mention the functions of the following structures in human body. (SAY-2015)
(Hint: Any two each)
a) Hypothalamus
b) Axon
Answer:
a) Hypothalamus- Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the pituitary synthesis and release of gonadotrophins. Somatostatin from the hypothalamus inhibits the release of growth hormone from the pituitary
b) Axon – The synaptic knob of axon produce neurotransmitters that helps in impulse transmission
Question 14.
Observe the diagram carefully and answer the following questions. (MARCH-2016)
a) Label the parts marked as A, B, C, D.
b) Identify the photoreceptor cells present in human eye.
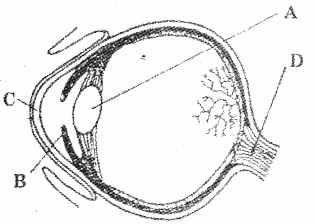
Answer:
a) A-lens, B-lris, c-Cornea. d-Optic nerve
b) Rodes and Cones
Question 15.
Fovea of retina in eye contains…………… (SAY-2016)
a) rod cells only
b) cone cells only
c) both roads and cones
d) rod and cones are absent
Answer:
b) cone cells only
Question 16.
Complete the given table (parts of human brain) (SAY-2016)
| Fore brain | Hind brian |
| Parts | Parts |
| i)Cerebrum | i) Pons |
| ii) Thalamus | ii) ……………………….. |
| iii) …………………….. | iii) Medulla |
a) Which one of the above parts of brain that controls gastric secretions?
Answer:
a) ii – cerebellum
iii – hypothalamus
b) Medulla
Question 17.
Answer the following: (MARCH-2017)
a) Cerebral hemispheres of human brain are connected by
i) association area
ii) corpus callosum
iii) corpora quadrigemina
iv) pons varolii
Observe the diagram and label A, B, C and D.
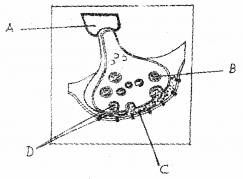
Answer:
a) ii) Corpus callosum
b) A – Axon B – Synaptic vesicle
C – Synaptic cleft D – Neuro Transmitters
