Kerala Plus One Political Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Equality
Equality Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Equality?
Answer:
Equality is the situation where everybody gets the same rights. Equality wants all persons to be equal before the law and everybody should be given the same kind of legal protection.
Question 2.
Why does equality matter?
Answer:
Equality means all persons are equal and they should be given equal opportunities, considerations, recognition, and wages. Man fought forages for the equality of people. The concept of Equality originated and grew as a protest against the gross inequalities found in the societies. Only if all persons in the society are given equal opportunities, full individual development will be possible.
Question 3.
Prepare a note on Equality of Opportunities.
Answer:
In the 16th article of the Indian Constitution, the principle of Equality of Opportunities is mentioned. It means equal opportunities should be given to citizens in government services, educational institutions, etc. without any discrimination. All citizens are also given the right to vote on the basis of universal adult franchise. They have the right to contest in the elections and hold public offices. In all these, there are equal opportunities
Question 4.
Prepare a chart showing different types of equality.
Answer:
Lord Bryce talks about 4 kinds of equality. They are Natural Equality, Civil Equality, Political Equality, and Social Equality. Modern thinkers have added another one as a fifth one – Economic Equality. It can be presented as follows.
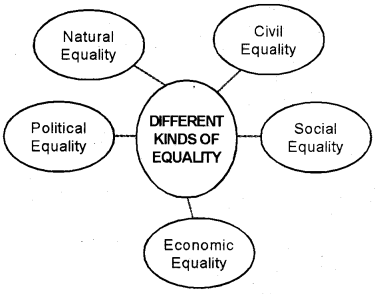
Question 5.
Examine the relations between liberty and equality
Answer:
There is an inseparable relation between liberty and equality. Liberty and equality are like the two sides of a coin. Equality without liberty is meaningless. Here are their relations:
a. Somebody who takes the words in their bare meaning, he may argue that they are contradictory.
b. Full liberty will deny it to many people and thus destroy equality.
c. A certain amount of control on a person’s liberty comes in full equality.
d. The concept of full liberty and full equality can only be a myth.
e. It is in practical situations that liberty and equality are practiced. It is not in an imaginary situation. Only in a stable society, they can be practiced.
f. Liberty on a large scale will ensure that everybody gets it.
g. Equality on a large scale is inevitable for the continued existence of liberty.,
h. Therefore liberty and equality are complementary and not contradictory.
Question 6.
Explain Natural and Economic equalities.
Answer:
Equality is of different kinds. Two of them are Natural Equality and Economic equality. Natural equality is what Nature has given us as a gift. It is our natural right. The three natural equalities are: Freedom to live, freedom to have rights and, freedom to own property. Only in a society where there is economic equality, other forms of equality can have any meaningful existence.
The relation between Natural Equality and Economic equality is shown below: Natural Equality: This idea came up connecting it to natural law. It.saysthat nature created everyone equal. The spokespersons of natural equality say that inequalities are human creations and society should be freed from them. Natural Equality is a mere ideal. Even the concept that nature created all as equals itself is untrue.
Economic equality means the resources of the nation should be enjoyed equally by all. It talks about the eradication of poverty. Although complete equality is impossible, at least a person’s basic needs should be fulfilled. It does not want resources to be monopolized in a few hands. Everyone should have the right to work, to get reasonable wages and also rest. Ideologies like Socialism stress economic equality.
Question 7.
Examine the causes leading towards natural and social inequalities.
Answer:
Lack of circumstances in which a poor man can’t use his voting right properly.
Misuse of voting rights.
Poverty
Inability of the poor to hold high ranks and have authority.
Illiteracy
Unemployment
The rich taking control of the political parties.
Lack of honest media, both print and electronic
Casteism
Question 8.
Complete the following chart:
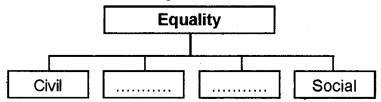
Answer:
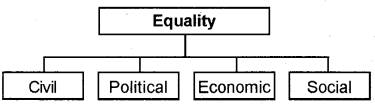
Question 9.
Prepare a seminar report on three different types of equality such as political equality, economic equality and social equality.
Answer:
The Political Science students of Class XI of Kozhikode Government Higher Secondary School conducted a seminar on the topic “Three Different Types of Equality”. The students of the Class were divided into 3 groups and they discussed the relevant portions of the Text. The leaders of each group presented their views
a) Political Equality: To ensure political equality in a society, people should have the opportunities to take part in active politics. Only if they have the right to play their role in the affairs the nation, there will be political equality there. They should have following rights:
i) To participate in the election of the government.
ii) To contest in the elections.
iii) The right to hold public office.
iv) The right to creatively criticize the government through the print and electronic media and through speeches.
The right to criticize the government using any legal medium.
vi) The right to form political parties.
b) Economic Equality: The meaning of Economic Equality is that all citizens must be able to enjoy the nation’s resources equally. This is important for the eradication of poverty. To achieve Economic Equality, the following should be ensured:
i) Make circumstances so that all citizens can earn their livelihood.
ii) All citizens should have enough income to meet their needs.
iii) There should be no gross inequality in wealth in the society.
iv) There should be no economic exploitation of man by man.
The distribution of the means of production and wealth should be controlled, aiming at the welfare of all in the society.
c) Social Equality: This means that all in the society have equal social status. Nobody should have special rights. All should have opportunities to develop their personality. In short, nobody should be given any special consideration in name of caste, religion, race or riches. The Human Rights Declaration by the UN is good for ensuring social equality.
To ensure social equality, equal opportunities should be provided to all. There should no divisions on the basis of caste, religion, race, riches, and gender. There should be Rule of law which ensures that all are equal before the law. Casteism must be abolished completely. The government and the society should do all they can to uplift the marginalized communities and bring them into the mainstream society. Conclusion: After the presentation, a meaningful discussion followed. The teacher added more points. It was a good seminar.
Question 10.
Match column B & C with Column A.
| A | B | C |
| Natural equality | Equal social status | All can enter common public places |
| Civil equality | Bom equal and free | Equality for all |
| Political equality | Equal opportunities to earn and save | Equal pay for equal work |
| Social equality | All have equal rights | All are equal before the law |
| Economic equality | Equal chances to get positions of power | Voting right |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Natural equality | Bom equal and free | Equality for all |
| Civil equality | All have equal rights | All are equal before the faw |
| Political equality | Equal chances to get positions of power | Voting right |
| Social’ equality | Equal social status | All can enter common public places |
| Economic equality | Equal opportunities to earn and save | Equal pay for equal work |
Question 11.
What is the liberal position on equality?
Answer:
a) In a society, the efficient and just means of distributing resources and rewards is competition.
b) Nation should ensure that all are given minimum standard of life and equal opportunities.
c) There will be no inequality when competition is open and free.
d) Political, economic and social opportunities are not mutually connected.
Question 12.
Point out the Marxian position of equality.
Answer:
Marxists refuse to accept the concept of natural equality.
- Most of the social, economic and political inequalities existing in human relations today are historically created. They are therefore not natural.
- Since they are humanly created, they can be solved by human efforts.
- The origin of this inequality comes from the division between mental and physical efforts and from the division between primary producers and the owners of production.
- This division of labor led to the formation of two important classes. One class exploited the other.
- Therefore for the Marxists, the problem of the abolition of inequality is primarily the problem of the abolition of class dominance, exploitation and class distinction.
- Only in a society where there is no class distinction, can there be equality.
- The social control theory of such a society will be not “Each person according to his ability, but each person according to his needs.”
Question 13.
Prepare a chart showing how we can promote equality.
Answer:
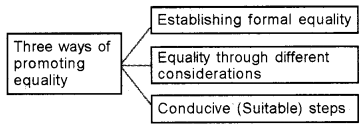
Question 14.
“Political parties are controlled by the rich.” Do you agree with this statement?
Answer:
Yes, I do. The fact that more than 100 members of the Indian Parliament are billionaires justifies this statement.
Question 15.
Match the following:
| A | B | C |
| Lasky | Principles of Social and Political Theory | Civil,political, social,Natural equality |
| Barker | A Grammar of Politics | Political-Legal Equality |
| Lord Bryce | The Modem State | Political Economic Equality |
| Maclver | Modem Democracies | Legal and Social Equality |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Lasky | A Grammar of Politics | Political Economic Equality |
| Barker | Principles of Social and Political Theory | Legal and Social Equality |
| Lord Bryce | Modem Democracies | Civil, political, social, Natural equality |
| Maclver | The Modem State | Political-Legal Equality |
Question 16.
Identify suitable examples for the following:
a) Equal rights
b) Equal opportunities
c) Favorable action
Answer:
a) Right to Vote
b) Opportunity for jobs
c) Reservation
Question 17.
What do you mean absolute equality?
Answer:
Absolute or complete equality is an impossible concept. Man, even by nature, is not equal in physical and mental abilities. There are differences among people in body structure, capabilities, attitudes, likings, etc.
Lasky felt that since people’s needs and capabilities are different, it is impossible to behave with them equally. The needs and capabilities of a mathematician are not the same as a brick-maker. Therefore it is not possible to see or consider them equally.
Question 18.
……….. is the idea that all persons are equal.
Answer:
Equality
Question 19.
From the following find out what constitutes equality:
a) Political equality
b) Social equality
c) Economic equality
d) All of these
Question 20.
It was in the ………… Revolution that the slogan “Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity” was raised.
Answer:
French
Question 21.
……….. inequality is the inequality that results from the differences in abilities and features that come by birth.
Answer:
Natural
Question 22.
What kind of equality is the right to vote?
Answer:
Political equality
