Kerala Plus One Political Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Freedom
Freedom Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is freedom?
Answer:
Freedom is the circumstance needed for showing a person’s individuality. In other words, freedom is the lack of control. It is possible to define freedom as the most essential factor for the development of one’s personality.
Question 2.
What is meant by freedom? Is there any relationship between freedom for the individual and freedom for the nation?
Answer:
Freedom means providing an atmosphere where a person has opportunities to develop his individuality. It is when a person can take independent decisions and act independently we say there is freedom. A person should not be controlled by external forces. Freedom also means when persons are able to increase their capabilities and qualities. Society must provide an atmosphere where the Nation, Community, Groups, and individuals can develop properly. Only in a sovereign nation, individuals can get freedom. So for the freedom of individuals freedom of the nation is inevitable.
Question 3.
Prepare a chart showing different types of freedom.
Answer:
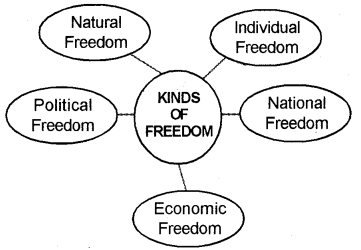
Question 4.
What is the difference between the positive and negative concepts of liberty?
Answer:
Freedom means free from all kinds of control. If this is put into practice, there will be jungle law which is might is right. The strong will dominate the weak and the strongest man will have to be revered by all in the society. Since this negative concept of freedom is not acceptable, the nation has to control freedom. The positive concept of freedom is the removal of obstacles. Negative freedom will lead the nation to an undesirable state. Positive freedom will help in the progress of the nation and the protection of the rights of all individuals.
Question 5.
What is meant by social constraints? Are constraints necessary for enjoying freedom?
Answer:
The members of a society where there are only very limited constraints, the individuals can develop their capacities to the fullest extent. Such a society will be called a free society. The constraints on liberty can be in the forms of external control or dominance. As a result of social evils like casteism also there can be controls for freedom. Serious economic inequality in the society can also bring in such controls.
Why does control become necessary?
- We can’t live in this world without some kind of control.
- There will be differences of opinion among people regarding ideas and concepts.
- There can be a hundred and one reasons for having differences in the society. These differences may lead into open confrontations. People may fight on the roads as they drive.
- There can be quarrels about parking space. There can be fights regarding house or land. There can be differences of opinion even about presenting a drama. Things like this can lead to conflicts, physical violence, and even murder.
- Therefore to settle arguments and control violence, every society needs some kind of control mechanism.
- An ideal society is the one in which people can retain their ideas and by making their own conditions live as they wish.
Question 6.
Construct a table showing the merits and demerits of liberalism.
Answer:
| Merits | Demerits |
| a) Upheld individual freedom. | a) Gave too much importance to individual freedom. |
| b) Took strong measures against Feudalism. | b) Developed close relationship with capitalism, ignoring its defects. |
| c) Supported natural rights. | c) The concept of natural rights is irrelevant. |
| d) Supported secularism, democracy, and reason (logic). | d) Ignored the society. |
| e) Defined the working of a nation. Exposed its shortcomings. | e) The idea that nation is an artificial creation is untrue. Did not see the merits of the nation. |
| f) Studied the dynamics of the markets. | f) Examined markets on the basis of only individual freedom. |
Question 7.
Construct a flow chart showing the safeguards of liberty.
Answer:
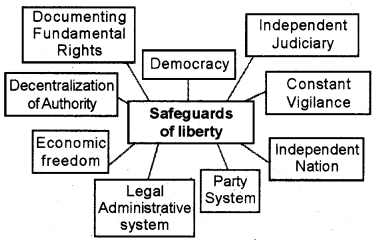
Question 8.
Point out the various sources of constraints.
Answer:
a) Dominance
b) External controls
c) Social and Economic Inequalities
Question 9.
Does the State have any role in upholding the freedom of its citizens? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, there is. The control over the freedom of individuals can be in the form of external control or in the form of authority. These controls can be enforced by the use force. Or they can be brought through government laws. Ruling authorities will have the backing of the use of force. If the government is democratic, people can exercise some control over the rulers. That is why it is said that the most important means of protecting people’s freedom is democratic rule.
Question 10.
What do you mean by freedom of expression? Explain using examples.
Answer:
Freedom of expression means the ability to speak one’s opinion openly without any external pressure and without any fear of external intervention. For example, our ability to speak openly our opinion about the Lok Pal Bill.
Question 11.
Find the odd one out from the lists.
a) Right to vote, Right to Work, Right to Contest in Elections, Right to hold public office.
b) Right to Work, Right to rule, Right to Security, Right to sell things.
Answer:
a) Right to Work
b) Right to sell things.
Question 12.
Twelve different kinds of liberty are given below:
a. Right to Vote,
b. Right to Freedom of Expression,
c. Right to Work,
d. Right to Produce and Sell things,
e. Right to Religion,
f. Right to Contest in Elections,
g. Right to Get Adequate Wages,
h. Right to life,
i. Right to Hold Public Office,
j. Right to Criticise,
k. Right to Assemble,
I. Right to security.
Arrange the above rights under three headings :
i) Citizen Rights,
ii) Economic Rights and
iii) Political Rights.
Answer:
| Citizen Rights | Economic Rights | Political Rights |
| Right to Freedom of Expression | Right to work | Right to Vote |
| Right to Religion | Right to produce and sell things | Right to Contest in Elections |
| Right to life | Right to get adequate wages | Right to hold public office |
| Right to assemble | Right to Security | Right to Criticise |
Question 13.
What do you mean by Harm Principle?
Answer:
The Harm Principle was proposed by J.S. Mill in his famous book “On Liberty”. It says: “The only purpose for which power can be rightfully exercised over any member of a civilized community, against his will, is to prevent harm to others.”
Question 14.
What is the relation between law and liberty?
Answer:
a. The relation between law and liberty is a controversial issue.
b. Some thinkers believe that law & liberty are ideas opposed to each other.
c. The more laws, the less freedom.
d. Enforcing law means curtailing freedom. In Ancient Greece, people with their wrong reasoning maintained this view.
e. The Laissez-faire theory prevalent in the 18th and centuries also held this view.
f. Anarchists tried to do away with government to ensure full freedom to individuals.
g. In opposition to this, law was considered as a condition for freedom.
h. Freedom is what we enjoy when we obey the law of the nation.
i. Excess of laws and harmful laws adversely affect freedom.
Question 15.
‘Liberty is not licensed’. Do you agree with this statement? Explain.
Answer:
1 agree. Liberty is not licensed to do anything one likes without any sort of control. Man is a social creature. When living in a society, some controls are necessary.
Question 16.
Name any four devices to protect liberty.
(Choose any four from the following)
Answer:
a. Democracy
b. Written down Fundamental Rights
c. Independent Judiciary
d. Rule of Law
e. Economic Equality
f. Decentralization of Power
g. Independent and Truthful Media
h. Party System
i. Political Education
j. Right to Equality
k. Constant Vigilance
Question 17.
What do you know about Swaraj? Summarise Gandhiji’s ideas about Swaraj.
Answer:
This is the Indian political concept regarding freedom. ‘Swa’ means self and ‘raj’ meaning rule. Swaraj is a combination of these two words. It means self-rule. However, Gandhiji’s concept of Swaraj had its own meaning. In his book ‘Hind Swaraj’ (1909), he has explained his concept of Swaraj. Gandhiji believed that swaraj means self-control. It is only when we learn to rule ourselves there will be Swaraj.
Swaraj is not mere freedom. It is the freedom to reclaim from institutions that destroy human virtues, a person’s self-esteem, his sense of responsibility and to ensure his fulfillment. Gandhiji believed that in the attainment of Swaraj a person’s individuality and its relations with the community and society play a crucial role.
Question 18.
Prepare a note on liberalism.
Answer:
Liberalism comes from the Latin word ‘liberalism which means a free man. Liberalism was a political theory that became popular in the 19th century and it considered freedom like oxygen to life. It gave great importance to personal freedom. Liberals supported a person’s right to hold fast to his opinions and beliefs and to express them freely.
Modern liberalism gives individual the primary place. This is what makes liberalism different from others. Liberals think that institutions like farrying, group or community do not have any existence of their own. They give greater importance to personal freedom than to values like Equality. They look at political power with suspicion and anxiety. J.S. Mill, T.H. Green and Mahadev Govind Ranade are the protagonists of modern liberalism.
Question 19.
Whose autobiography is “Long Walk to Freedom”?
Answer:
Nelson Mandela’s
Question 20.
Who introduced the ‘Harm’ Principle?
Answer:
John Stuart Mill
Question 21.
Two levels of liberty are ………. and …………
Answer:
Negative, Positive
Question 22.
Complete the table:
| Author/Director | Book/Film |
| Deepa Mehta | |
| Aubrey Menen | |
| Salman Rushdie | |
| Martin Scorsese | |
| Pradeep Dalvi |
Answer:
| Author/Director | Book/ Film |
| Deepa Mehta | Water |
| Aubrey Menen | Ramayana Retold |
| Salman Rushdie | The Satanic Verses |
| Martin Scorsese | The Last Temptation of Christ |
| Pradeep Dalvi | Me Nathuram Godse Boltoy |
