Kerala Plus One Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Work, Energy and Power
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find the odd one out and find the relation connecting the remaining quantities. Joule, Calorie, Kilowatt, electron volt.
Answer:
kilowatt, unit of power
1 calorie = 4.2 joule
1 electron volt = 1.6 × 10-19J.
Question 2.
What is the work done by the tension in the string of simple pendulum?
Answer:
Zero
Question 3.
When is the exchange of energy is maximum during an elastic collision?
Answer:
When mass of two colliding bodies are same, there will be maximum exchange of energy.
Question 4.
In atom, an electron is revolving around the nucleus. What is the work done?
Answer:
Work done is zero because work done by centripetal force is zero.
Question 5.
What is the type of collision when macroscopic particles collide?
Answer:
Perfectly inelastic collision.
Question 6.
Name the parameter which is a measure of degree of elasticity of a body.
Answer:
Coefficient of restitution.
Question 7.
What is the source of kinetic energy for falling raindrops?
Answer:
Gravitational potential energy.
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The law of conversation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but can only change from one form into another. A bus and a car, moving with the same kinetic energy are brought to rest by applying an equal retardation force by the breaking systems. Which one will come to rest at a shorter distance? Give the reason behind your answer.
Answer:
Change in K.E. = Force × Displacement
1/2 mv2 = F × S
ie. KE α s
KEcar α Scar _____(1)
KEbus α Sbus ______(2)
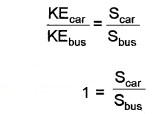
ie. Scar = Sbus
Both will travel equal distance.
Question 2.
A body constrained to move along the Z-axis of a coordinate system is subjected to a constant force \(\bar{F}=(\hat{i}+2 \hat{\jmath}+3 \hat{k}) N\)
- What is the magnitude of force along z-direction?
- What is the work done by this force in moving the body over a distance of 4m along the z-axis?
Answer:
- 3N
- Work done = Force × Displacement = 3 × 4 = 12J.
Question 3.
Match the following
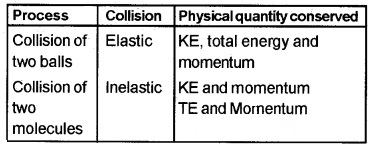
Answer:
Collision of two balls – inelastic – TE and momentum Collision of two molecules – elastic – KE, TE, and momentum.
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A car of mass 1000kg moving with a speed 18mk/h on a horizontal road collides with a horizontally mounted spring of spring constant 6.25 × 103N/m
- What do you mean by Spring constant.
- What is the maximum compression of the spring?
Answer:
1. Spring constant is the force required to stretch the spring by a unit distance.
2. \(\frac{1}{2}\)mv2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx2, 18km/h = 5m/s.
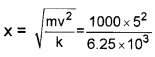
x = 2m.
Question 2.
A man tries to lift a mass 200kg with a force 100N
- Is he doing work? Explain.
- If yes, find the amount of work done If No, find the force required to lift it.
- If it is lifted to 2m in 10 seconds, find his power.
Answer:
- No work is done, as there is no displacement, 100N force is insufficient to raise 200kg.
- Force required to lift 200 kg = 200 × 9.8 = 1960N
- Power = \(\frac{m g h}{t}=\frac{200 \times 9.8 \times 2}{10}\) = 392W.
Question 3.
Two cricket balls are colliding each other.
- Name the collision
- Say whether law of conservation of Kinetic Energy hold good in this case. Why?
- State and prove the other conservation law applicable here.
Answer:
- Inelastic collision
- No, Total KE before collision is not equal to total KE after collision.
- Proof and statement of law of conservation of momentum.
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Two cars A and B travelling with speeds 20m/s and 10m/s respectively applies breaks,.so that A comes to rest in 15 second and B in 7.5s
- From the graph determine which of the two cars travelled further after brakes were applied and by how much distance it travelled?
- Draw the velocity-time graph of A and B in the same graph.
- In the above process the wear and tear of which the car gets affected more?
Answer:
1. The area of velocity time graph gives displacement distance travelled by car A, SA = 1/2 × 20 × 15 = 150 m
distance travelled by the car B, SB = 1/2 × 10 × 7.5 = 37.5.
2.
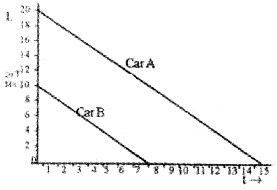
3. Wear and tear gets affected more for car A.
Question 2.
A sphere of mass m is moving with a velocity u and makes a head-on collision with another identical mass which is at rest. It is observed that the stationary mass starts moving with a lesser velocity than u, after the collision.
- Which physical quantity is conserved here?
- Define coefficient of restitution.
- Determine the ratio of the velocities of the two spheres after elastic collision if ‘e’ is the coefficient of restitution.
Answer:
1. conservation of linear momentum.
2. It is defined as the ratio of relative velocity of separation after collision to the relative velocity of approach before collision.
3. Coefficient of restitution,
e = \(\frac{v_{2}-v_{1}}{u_{1}-u_{2}}\)
in this cos u1 = u, u2 = 0, v1 = 0, v2 = u
∴ e = \(\frac{u-0}{u-0}\)
e = 1.
Question 3.
From the table given below
- Draw the force-displacement curve
- Analyse the graph & find the type of force involved
- Estimate the workdone
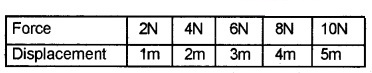
Answer:
1.
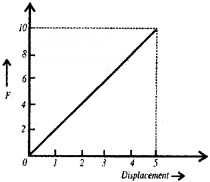
2. Workdone by a variable force.
3. Workdone = Area of the graph
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)bh
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)5 × 10 = 25J.
Question 4.
Raju increased the speed of moving mass ‘50 kg’ from 2 m/s to 4m/s.
- How much force will be required, if velocity change takes place within 0.2 sec?
- How much work is done by Raju?
Answer:
1. F = mass × acceleration
= 50 × \(\frac{(4-2)}{0.2}\)
= 500N.
2. w = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mv2 – \(\frac{1}{2}\)mu2.
=\(\frac{1}{2}\)50 (42 – 22)
= 300 J.
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A car and a truck have the same kinetic energies at a certain instant while they are moving along two parallel roads. (Assume that the truck is heavier than the car)
- Which one will have greater momentum?
- Write the relationship between kinetic energy and linear momentum.
- If the mass of truck is 100 times greater than that of the car, find the ratio between their velocities.
Answer:
1. Kinetic energy, of car, K.Ec = \(\frac{P_{c}^{2}}{2 m_{c}}\)
Kinetic energy of truck,
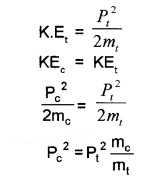
Since mc < mt
Hence Pt > Pc
∴ momentum of truck is greater than car.
2. KE = P2/2m.
3. KEc = KEt
1/2mc Vc2 = 1/2 x mtVt2
But mt = 100mc
\(V_{t}^{2}=\frac{V_{c}^{2}}{100}\)
Velocity of truck, Vt = \(\frac{V_{c}}{10}\)
ratio of velocity, 10Vt = Vc
10:1.
Question 2.
Raju dropped a rubber ball of mass m from a height h to the ground. He observed that the ball rebounds vertically and along the same line to a height h1, which is less than h.
- Is it an elastic or inelastic collision?
- Find the velocity with which it strikes the ground?
- If it is replaced by a solid aluminium ball, then what happens to the height of rebound?
- If the rubber ball is allowed to fall on a spring placed on the ground then what change will Raju notice in the height of rebound?
Answer:
1. Inelastic collision.
2. The velocity with which ball strikes the ground,
v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = 0 + 2g × h
v = \(\sqrt{2 g h}\).
3. Height of rebound decreases.
4. Height of rebound depends on the state of potential energy stored in the spring. If ball falls on a compressed spring, the height of rebound increases due to potential energy given by the spring to bail.
Question 3.
A man tries to lift a mass 200kg with a force 100N.
- Is he doing work? Explain.
- If it is lifted to 2m in 10s, find the power.
- Show that total mechanical energy is conserved fora freely falling body.
Answer:
1. No. Force required to lift the body is 2000N (w = mg = 200 × 10). But the applied force is 100N. Hence there is no displacement due to this applied force.
2. Power P = \(\frac{w}{t}=\frac{m g h}{t}=\frac{200 \times 10 \times 2}{10}\) = 400 watt.
3.
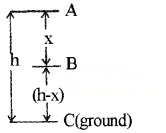
Consider a body of mass ‘m’ at a height h from the ground.
Total energy at point A
Potential energy at A,
PE = mgh
Kinetic energy, KE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) mv2 = 0
(since the body at rest, v = 0).
∴ Total mechanical energy = PE + KE
= mgh + 0 = mgh
Total energy at the point B
The body travels a distance x when it reaches B. The velocity at B, can be found using the formula.
v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = 0 + 2 gx
∴ KE at B, = \(\frac{1}{2}\) mv2
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) m2gx
= mgx
P.E. at B, = mg(h – x)
Total mechanical energy = PE + KE
= mg(h – x) + mgx
= mgh
Total energy at C
Velocity at C can be found using the formula
v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = 0 + 2 gh
∴ KE at C, = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mv2
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)m2gh
= mgh
P.E. at C = 0
Total energy = PE + KE = 0 + mgh = mgh.
Question 4.
An elevator of total mass 1800kg is moving up with a constant speed of 2m/s. A frictional force of 400N acts on this motion.
- The direction of frictional force is______
- Opposite to direction of motion
- In the direction of motion
- What is the work done by gravitational force.
- What is the total work done by the elevator?
Answer:
1. Opposite to direction of motion
2. w = F × V
w = mg × 2
= 1800 × 10 × 2
w = 36000J
3. P = Ptotal × V
= (mg + Ffricti0n) × V
= (1800 × 10 + 4000) × 2
= (18000 + 4000) × 2
P = 44000w.
Question 5.
A stone of mass ‘m’ is to be thrown to a height h
- What is the acceleration of the stone?
- With what minimum velocity should it be thrown.
- At what height does the KE and PE become equal?
- Find the velocity at that height
Answer:
1. –g or –9.8m/s.
2. v = 0, a = -g, S = h
Substitute this values in
V2 = u2 + 2as we get
0 = u2 – 2gh
u = \(\sqrt{2 g h}\)
3. at \(\frac{h}{2}\)., KE and PE are equal.
4. V2 = U2 + 2aS
= U2 – 2g \(\frac{h}{2}\) (u2 = 2gh) = U2 – \(\frac{U^{2}}{2}\),
V2 = \(\frac{U^{2}}{2}\),
V = \(\frac{U}{\sqrt{2}}\).
Question 6.
A toy gun, with a spring compresser 3cm is used to project a stone of mass 50gm to a height of 10m.
- What is the potential energy of spring.
- How much it should be compressed to throw the stone to a height 5m.
- Find out the physical constant associated with the spring.
Answer:
1. PE of the spring = PE of the mass at the height h
= mgh = 0.050 × 9.8 × 10
= 5 × 9.8 = 4.9J
2. \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx12 = mgh1
\(\frac{1}{2}\)kx22 = mgh2
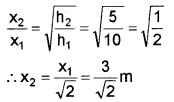
3. physical constant associated with the spring constant
\(\frac{1}{2}\)kx2 = mgh
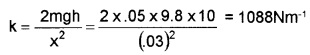
Question 7.
Find the odd one out and find the relation connecting the remaining quantities. Joule, Calorie, Kilowatt, electron volt.
Answer:
kilowatt, unit of power
1 calorie = 4.2 joule
1 electron volt = 1.6 × 10-19J.
Question 8.
Atoy gun, with aspring compressor 3 cm is used to project a stone of mass 50gm to a height of 10m.
- What is the potential energy of spring.
- How much it should be compressed to throw the stone to a height 5m.
- Find out the physical constant associated with the spring.
Answer:
1. PE of the spring = PE of the mass at the height h
= mgh = 0.050 × 9.8 × 10
= 5 × 9.8 = 4.9J
2. \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx12 = mgh1
\(\frac{1}{2}\)kx22 = mgh2
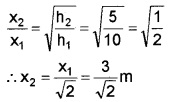
3. physical constant associated with the spring constant
\(\frac{1}{2}\)kx2 = mgh
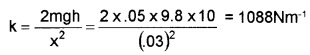
Question 9.
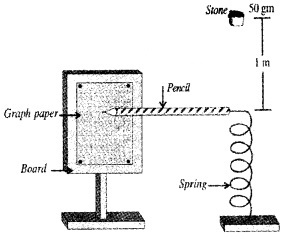
A graph paper is fitted on a board as shown in figure. Near to the graph paper a spring is placed. A pencil is attached to the end of the spring as shown in figure. The pencil is free to move on the graph paper. A stone of mass 50 gm is placed 1m above the spring. [Spring constant k = 98N/m]
- The energy possessed by the stone due to its height is called_______
- If this stone falls on the spring, find the length of mark that produced on the graph paper due to pencil [The change in P E of stone due to compression may be negleted]
- What will happen to the length of mark, if spring having smaller spring constant is used? Justify.
Answer:
1. Potential energy.
2. \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx2 = mgh
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 98 × x2 = 50 × 10-3 × 9.8 × 1
x2 = 100 × 104
x = 10cm.
3. The length of mark will be decreased. Compression of spring depends on spring constant.
Plus One Physics Work, Energy and Power NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative:
- work done by a man in lifting a bucket out of a well by means of a rope tied to the bucket.
- work done by gravitational force in the above case.
- work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined plane.
- work done by an applied force on a body moving on a rough horizontal plane with uniform velocity.
- work done by the resistive force of air on vibrating pendulum in bringing it to rest.
Answer:
- +ve
- -ve
- -ve
- +ve
- -ve
Question 2.
The potential energy function fora particle executing linear simple harmonic motion is given by
V(x) = \(\frac{k x^{2}}{2}\), where k is the force constant of the oscillator, For k = 0.5N nm-1, the graph of V(x) versus x is shown. Show that a particle of total energy 1 J moving under this potential must ‘turn back’ when it reaches x = ± 2m.
Answer:
We know that maximum potential energy = total energy
∴ (\(\frac{1}{2}\)kx2) max = 1 joule or \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 0.5 × (x2)max = 1
or (x2)max = 4 or (x)max = ± 2m.
Question 3.
Choose the correct alternative:
- When a conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body increases/ decreases/remains unaltered.
- Workdone by a body against friction always results in a loss of its kinetic/potential energy.
- The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the external force/sum of the internal forces on the system.
- In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision are the total kinetic energy/total linear momentum/ total energy of the system of two bodies.
Answer:
- decreases
- kinetic energy
- external force
- total linear momentum and also total energy (if the system of two bodies is isolated).
Question 4.
State if each of the following statements is true or false.
- In an elastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved.
- Total energy of a system is always conserved, no matter what internal and external forces on the body are present.
- Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
- In an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is always less than the initial kinetic energy of the system.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- False (true usually but not always).
Question 5.
A rain drop of radius 2mm falls from a height of 500m above the ground. It falls with decreasing acceleration (due to viscous resistance of the air) untill at half its original height, it attains its maximum (terminal) speed, and moves with uniform speed thereafter. What is the work done by the gravitational force on the drop in the first and second half of its journey? What is the work done by the resistive force in the entire journey if its speed on reaching the ground is 10ms-1?
Answer:
r = 2 × 10-3m,
volume = \(\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7}\) (2 × 10-3)3 m3
p = 1000kgm-3,
h = 250m
W= \(\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7}\) × 8 × 10-9 × 1000 × 9.8 × 250J = 0.082J
Data reamains unchanged in the next half.
Question 6.
A bullet of mass 0.012kg and horizontal speed 70ms-1 strikes a block of wood of mass 0.4kg and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block.
Answer:
If V be the velocity of the block after collision, the using law of conservation of momentum, we get
0.012 × 70 + 0 = (0.012 + 0.4)V
or V = \(\frac{0.012 \times 70}{0.412}\) ms-1 = 2.04ms-1
If h be the height through which block rises, then
(M + m) gh = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (M + m)V2
or h = \(\frac{v^{2}}{2 g}\) or
h = \(\frac{2.04 \times 2.04}{2 \times 9.8}\)m = 0.212m = 21.2 cm
Amount of heat produced in the block = loss of K.E.
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 0.012 × 70 × 70 – \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 0.412 × 2.04 × 2.04
= 29.4J – 0.857J = 28.543J.
