Kerala Plus One Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 13 Kinetic Theory
Question 1.
Two vessels of the same size are at the same temperature. One of them contains 1 kg of hydrogen (molecular weight 2) and the other contains 1 kg of nitrogen (molecular weight 28). (MARCH-2010)
a) Which of the vessels contains more molecules?
b) In which vessel is the average molecular speed greater? How many times greater?
c) Which of the vessels is at higher pressure? Why?
Answer:
a) Hydrogen vessel
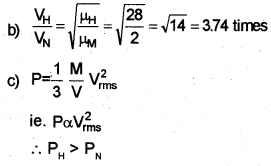
Question 2.
a) According to the kinetic theory of gases, the molecules of a gas are identical and in random motion. The collisions made by these molecules on the walls of the container exert pressure on the walls. (MARCH-2011)
Deduce an expression for the pressure of an ideal gas and also find at what temperature the r.m.s. speed of hydrogen is double its value at STP.
b) For a gas γ = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) and R is the universal gas constant, find the values of Cp and Cv.
Answer:
a)
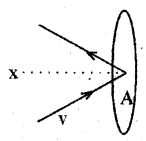
Consider molecules of gas in a container. The molecules are moving in random directions with a velocity V. The velocity V can be resolved along x, y and z directions as Vx, Vy, and Vz respectively. If we assume a molecule hits the area A of a container with velocity Vx and rebounds back with -Vx. The change in momentum imparted to the area A by the molecule = 2mVx
The molecules cover a distance Vx t along the x-direction in a time t. All the molecules within the volume AVxt will collide with the area in a time t. If ‘n’ is the number of molecules per unit volume, the total number of molecules hitting the area A,
N = A Vx t n.
But on average, only half of those molecules will be hitting the area, and the remaining molecules will be moving away from the area. Hence the momentum imparted to the area in a time t
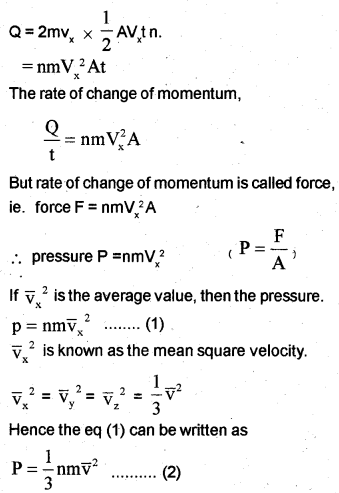
But nm = ρ, the density of gas

b)
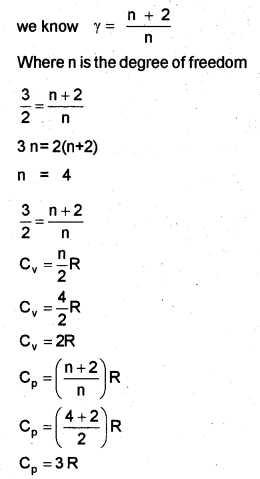
Question 3.
Three moles of an ideal gas kept at a constant temperature of 300 K are compressed from the volume of 10 litres to 5 litres. (MAY-2012)
Answer:
At constant temperature, P ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\). Explain it briefly on the basis of Kinetic theory of Gases.
When volume is reduced, the number of molecules per unit volume increases. So a large number of molecules collide with walls of vessel per second increases. As a result, large momentum (per second) is transferred to wall. When momentum increases, the force and pressure acting on the wall increases.
Question 4.
Kinetic theory of gases is based on the molecular picture of matter. (MARCH-2013)
a) Write any two postulates of kinetic theory of gases.
b) Write short notes on :
i) Equipartition of energy
ii) Mean free path
Answer:
a) The kinetic theory of gases has been developed by Clausius, Maxwell, Boltzmann and others. The theory is based on the following postulates.
1) The gas is a collection of a large number of molecules. The molecules are perfectly elastic hard spheres.
2) The size of a molecule is negligible compared with the distance between the molecules.
3) The molecules are always in random motion
4) During their motion, the molecules collide with each other and with the walls of the containing vessel.
5) There is no force of attraction or repulsion between molecules.
b) i) The total kinetic energy of a molecule is equally divided among the different degrees of freedom.
The average energy per degree of freedom
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) KBT
ii) The molecules in a gas have a finite size. So they collide with other molecules during their motion.
The average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions is called mean free path.
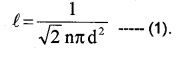
Question 5.
A gas is made up of hydrogen and oxygen molecules. (MAY-2013)
a) Which molecule moves faster?
b) Find the ratio of the velocities of hydrogen and oxygen molecules.
Answer:
a) Vrms ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ √M }\)
Hydrogen moves faster than oxygen because mass of hydrogen is smaller than oxygen.
b)
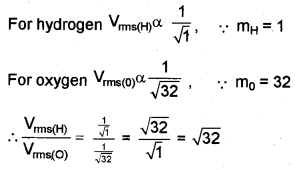
Question 6.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, gas molecules are always in random motion. (MARCH-2014)
a) State the law of equipartition of energy.
b) What do you mean by ‘mean free path? Give an equation for the mean free path.
Answer:
a) The total kinetic energy of a molecule is equally divided among the different degrees of freedom,
b) The molecules in a gas have a finite size. So they collide with other molecules during their motion.
The average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions is called mean free path.
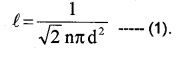
Question 7.
a) Write the ideal gas equation. (MAY-2014)
b) Write any four postulates of the kinetic theory of gases.
Answer:
a) PV = nRT
b) The kinetic theory of gases has been developed by Clausius, Maxwell, Boltzmann and others. The theory is based on the following postulates.
1) The gas is a collection of a large number of molecules. The molecules are perfectly elastic hard spheres.
2) The size of a molecule is negligible compared with the distance between the molecules.
3) The molecules are always in random motion
4) During their motion, the molecules collide with each other and with the walls of the containing vessel.
5) There is no force of attraction or repulsion between molecules.
Question 8.
No real gas is truly ideal” (MARCH-2015)
a) When does a real gas approach ideal gas behaviour?
b) Define the law of equipartition of energy.
Answer:
a) At high temperature and at low pressure.
b) Law of equipartition energy.
The total kinetic energy of a molecule is equally divided among the different degrees of freedom.
Question 9.
Mention two conditions under which the real gases obey the ideal gas equation. (MAY-2015)
Answer:
Real gases obey the ideal gas equation at high temperature and low pressure.
Question 10.
Write four postulates of kinetic theory of gases. (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
a) The kinetic theory of gases has been developed by Clausius, Maxwell, Boltzmann and others. The theory is based on the following postulates.
1) The gas is a collection of a large number of molecules. The molecules are perfectly elastic hard spheres.
2) The size of a molecule is negligible compared with the distance between the molecules.
3) The molecules are always in random motion
4) During their motion, the molecules collide with each other and with the walls of the containing vessel.
5) There is no force of attraction or repulsion between molecules.
Question 11.
What do you understand by the term, mean free path of molecules? Name the factors on which it depends. (MAY-2016)
Answer:
The mean free path is the average distance covered by a molecule between two successive collisions.
\(\ell=\frac{1}{n \pi d^{2}}\)
The mean free path depends inversely on number density and size of the molecule.
Question 12.
Estimate the average thermal energy of helium atom (MARCH-2017)
at a temperature of 27°C.
[Boltzmann constant is 1.38 x 10-23J/k.]
Answer:
Average thermal energy, E = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) kBT
kB = 1.38 x 10-23J/k
T = 27°C
= 300 k
E = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) x 1.38 x 10-23 x 300
= 6.21 x 10-25J
