Kerala Plus One Economics Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Economics |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 21/2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions to Candidates :
- There is a ‘cool off time’ of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time of 21/2 hrs.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from 1 to 10. Each carries 1 score. (10 × 1 = 10)
Question 1.
Economic growth without creating employment opportunities.
a) Underemployment
b) Jobless growth
c) Disguised unemployment
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Jobless growth
Question 2.
Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign initiated in China mainly aimed to ………….
a) Capitalization of the country
b) Industrialization of the country
c) The development of service sector
d) The development of human capital
Answer:
b) Industrialization of the country
Question 3.
Karve Committee gives suggestions to promote the working of the following. Find it.
a) Heavy Industries
b) Rural Infrastructure Development
c) The Public Sector Industries
d) Small Scale Industries
Answer:
d) Small Scale Industries
Question 4.
State any two sampling errors.
Answer:
- Selection error
- Non response
Question 5.
Give examples for quantitative and qualitative classification.
Answer:
| Qualitative Classification | Quantitative Classification |
| 1. Nationality | 1. Height |
| 2. Literacy | 2. Weight |
| 3. Religion | 3. Age |
| 4. Gender | 4. Income |
Question 6.
The consumer price index (Base year 2011 = 100) was 125 in January 2018. One rupee coin worth in January 2018 in terms of the base year is ………….
(a) 80 paise
(b) ₹ 1.25
(c) 60 paise
(d) ₹ 2
Answer:
(a) 80 paise
Question 7.
Selling off part of the equity of Public Sector undertakings to the public is known as …………
а) Capital accumulation
b) Investment
c) Disinvestment
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Disinvestment
Question 8.
Calculate the range of 20, 25, 28, 32, 36, 40, 50, 55, 72, 75.
Answer:
Range L – S = 75 – 20 = 55
Question 9.
The basic economic activities include
a) Distribution
b) Production
c) Consumption
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 10.
Find out the relative measure of dispersion.
a) Coefficient of correlation
b) Standard deviation
c) Coefficient of mean deviation
d) Range
Answer:
a) Coefficient of correlation
Answer all questions from 11 to 15, each carries 2 scores. (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 11.
| A | B |
| 1 | 5 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 |
Answer:
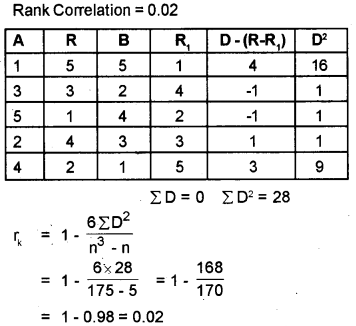
Question 12.
Point out any four important productive activities for the diversification of workforce.
Answer:
- Animal Husbandry
- Fisheries
- Horticulture
- Information Technology and rural development
Question 13.
The average marks of class A(¯XA = 30) is better than class B (¯XB = 25). But teacher says that class B is more consistant and give the standard deviation of A and B as 15 and 10 respectively.
Calculate the coefficient of variation of class A and class B to prove it.
Answer:
CV of A = 50
CV of B = 40
Question 14.
Briefly explain the importance of statistics in economics.
Answer:
The importance of statistics in economics are given below:
- Statistics help to understand an economic problem.
- It helps to present economic facts in a precise and definite form.
- It also helps in condensing the mass of data into numerical measures.
- It is used in finding relationships between different economic variables.
- It predicts by how much an economic variable will change due to the changes in another variable.
- Statistics plays a major role in the formulation plans and policies of the government.
Question 15.
The workers in informal sector have so many limitations compared to the formal sector. Point out any four of them.
Answer:
The workers in informal sector have some limitations.
They are given below:-
- They do not get regular income.
- They do not have any protection from the government.
- Outdated technology are often used.
- Majority of the workers of this sector live in slums.
Answer any six questions from 16 and 22. Each carries three scores. (6 × 3 = 18)
Question 16.
Complete the table.
| Mode of Data Collection | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Personal Interview | ………………… | …………………….. |
| ………………. | ………………… | Cannot be used by the illiterates |
| ……………… | Relatively high response rate | ……………………. |
Answer:
| Mode of Data Collection | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Personal Interview | Response from the respondents will be very high. | It is expensive |
| Mailing Questionnaire | Less Expensive | Cannot be used by the illiterates |
| Telephone Interview | Relatively high response rate | Possibility of influencing respondents |
Question 17.
Categorize the following features of the economics of India, China, Pakistan under three heads.
a) One child norm
b) High fertility rate
c) Economic reforms in 1991
d) High density of population
e) Highest Human Development Index
f) High Infant Mortality Rate
Answer:
| India | China | Pakistan |
| Economic reforms in 1991 | One child norm | High fertility |
| High density of population | Highest Human Development | Infant mortality |
Question 18.
The Stagnation of Indian agriculture during British period was mainly caused by the policies of colonial government. Briefly explain that policies.
Answer:
India’s agriculture sector was stagnant during the colonial rule. The stagnation in agriculture sector was caused mainly because of the following:
- The various systems of land settlement in India.
- The British Government did nothing to improve the condition of agriculture.
- There was immense misery and social tension among the cultivators because of the exploitation by the Zamindars.
- Low level of technology, lack of irrigational facilities and use of negligible amount so fertilizers were also responsible for low production in agriculture.
Question 19.
Calculate the weighted aggregative price index.
| Commodities | Base period Price P0 | Current period Price P1 | Current period Quantity Q1 |
| A | 5 | 10 | 4 |
| B | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| C | 4 | 8 | 10 |
| D | 10 | 15 | 2 |
Answer:
Weighed Aggregative Price Index
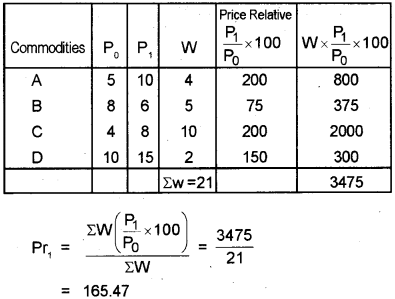
Question 20.
a) Name the foreign trade policy adopted by India during 1950-1990. (1)
b) Identify the policy instruments to protect the domestic industries. (2)
Answer:
a) Foreign trade policy is also known as Export-Import policy. Trade policy can be of two types: The free trade policy and the protective trade policy. Before 1991, India is also protected by inward looking policy only for the purpose of protecting weak industries of India or Indian markets from foreign competition. India is also not interested in exporting and importing of goods and services to foreign countries. The main objectives of this policy was to ensure the countries independent development.
b) Import substitution – It is only for the purpose of protecting domestic industries in India.
Question 21.
As an economic student, teacher asks you to make a project of disguised unemployment. Write the steps to making that project.
Answer:
The steps of project are given below:
- Identifying a problem of study
- Choice of target group
- Bata collection
- Organisation and presentation of data
- Analysis and interpretation
- Conclusion
Question 22.
Write the essential parts of a good statistical table
Answer:
The essential parts of a good statistical table are given below:
- Table Number
- Title
- Column Heading/captions
- Row Headings/stubs
- Body of the table
- Unit of measurement
- Source
- Footnote
Answer any four questions from 23 to 27. Each carries four scores. (4 × 4 = 16)
Question 23.
Analyze the relationship between human capital and economic growth.
Answer:
We know that labour skill of an educated person is more than that of an uneducated person and that the former generates more income than latter. Economic growth means the increase in real National income of a country. The contribution of the educated person to economic growth is more than that of an illiterate person.
Health is also an important factor for economic growth. Thus, both education and health, along with many other factors like on the job training, job market information and migration. Increases an individual’s income generating capacity.
Question 24.
Prepare a frequency distribution from the following data (Exclusive Method).
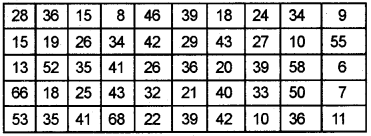
Answer:
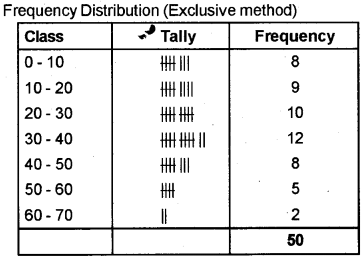
Question 25.
Explain the areas to be addressed for rural development.
Answer:
Rural development is quite a comprehensive term but it essentially means a plan of action for the development of areas which are lagging behind in socio-economic development. It essentially focuses on action for the development of areas that are lagging behind in the overall development of the village economy. Some of the areas which are challenging and need fresh initiatives for development in India include:
- Development of human resources including- literacy, more specifically, female literacy, education and skill development-health, addressing both sanitation and public health
- Land reforms
- Development of the productive resources of each locality
- Infrastructure development like electricity, irrigation, credit, marketing, transport facilities including construction of village roads and feeder roads to nearby highways, facilities for agriculture research and extension, and information dissemination
- Special measures for alleviation of poverty and bringing about significant improvement in the living conditions of the weaker sections of the population emphasizing access to productive employment opportunities.
Question 26.
Identify the challenges faced by the power sector in India.
Answer:
There are many challenges faced by the power sector in India which are given below:
- India’s installed capacity to generate electricity is not sufficient to meet an annual economic growth.
- The loss incurred by the state Electricity Boards in India.
- Private sector power generators and foreign investors are playing their role in this sector.
- Higher power tariffs and power cuts is different parts of the country are strong challenges.
- Thermal power plants are falling shortage of raw materials and coal supplies.
- The current production capacity is quite [ inadequate to meet the requirement of the growing population and economic development.
Question 27.
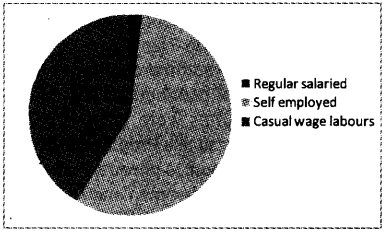
Draw a pie diagram for the following data:
| Regular salaried | 28 |
| Self-employed | 216 |
| Casual wage labours | 156 |
Answer:
| % | Angle at the centre | ||
| Regular salaried Self-employed Casual wage labours | 28 216 39 | 7 54 39 | 25.2 194.4 140.4 |
| 360.0 |
Answer any two questions from 28 to 30. Each carries five scores. (2 × 5 = 10)
Question 28.
Point out the properties and five degrees of correlation coefficient.
Answer:
Properties of correlation coefficient
- ‘r’ has no unit. It is pure number.
- A negative value of T indicates an inverse relation.
- If ‘r’ is positive, the two variables move in the same direction.
- If r = 0, the two variables are uncorrelated.
- If r = 1 or r = -1 the correlation is perfect.
- A high value of r indicates strong linear relation.
- A low value of r indicates a weak linear relation.
- The value of the correlation coefficient lies between -1 and +1.
- The value of r is unaffected by the change of origin and change of scale.
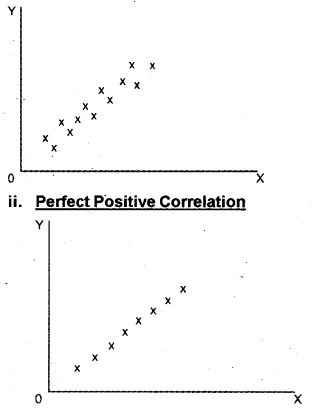
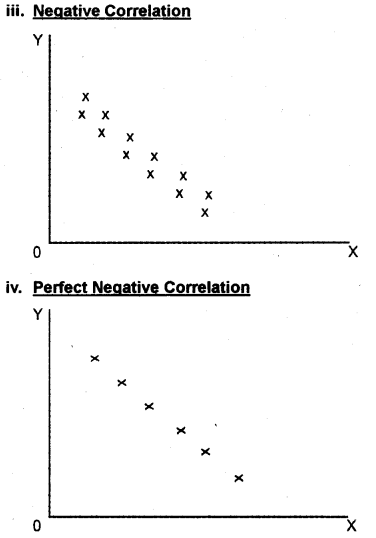
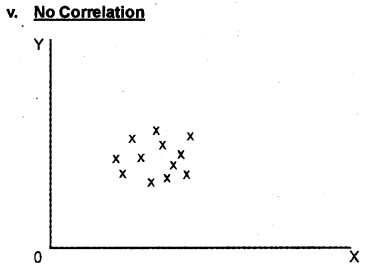
Degrees of correlation Correlation exists on various degree:
Question 29.
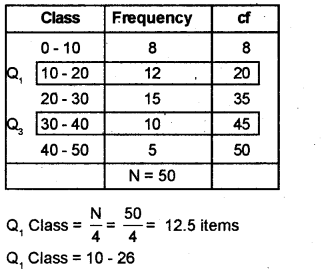
Calculate the quartile deviation for the following data:
| Class | Frequency |
| 0 – 10 | 8 |
| 10 – 20 | 12 |
| 20 – 30 | 15 |
| 30 – 40 | 10 |
| 40 – 50 | 5 |
Answer:
Quartile Deviation:

Question 30.
Critically evaluate the impact of New Economic Policy in Agriculture and Industrial Sector.
Answer:
Yes, Agricultural sector appears to be adversely affected by the reform process. The agricultural sector has not been able to be benefited by the reform process, rather the growth rate has decelerated. Public investment in agriculture sector has been reduced during the reform period. Further the removal of fertilizer subsidy severely affected the mall and marginal farmers.
Due to commencement of WTO a lot of policies have changed which have adversely affected the Indian farmers. Moreover, because of export-oriented policy in agriculture there has been a shift from production for the domestic market towards production for export market focusing on cash crops instead of food grains. This has resulted in the price rise of food grains.
In short India’s agricultural sector is badly affected by the reform process.
New economic policy has affected Indian industrial sector. Industrial production increased several times. However, industrial sector is also badly affected during reform period.
- Reduction in the number of reserved public sector industries. The number of Public Sector industries from 17 to 4.
- Increasing the share of private sector investment.
- Selling the share of public enterprises.
- No insistance on conversion. Now the financial corporation can not insist the industries for conversion of their loans into equity shares.
The government has also made attempts to improve the efficiency of PSUs by giving them autonomy in taking managerial decisions.
Answer any two questions from 31 to 33. Each carries eight scores. (2 × 8 = 16)
Question 31.
“The three diamensional approach of government to reduce poverty helps the Indian citizen to achieve a higher living standard.”
a) Explain the three-dimensional approach to reduce poverty.
b) Critically evaluate them.
Answer:
The benefits of economic development would trickle down to the lower sections of population, faster growth was emphasised as the means to address the problem of poverty. The plans stressed on rapid industrialisation and transformation of agriculture through adoption of green revolution and land reforms. This approach based on trickle down was followed in the 1950s.
An alternative approach was adopted which stressed on providing employment to the poor and supplementing their income in order to pull them out of poverty.
This approach was initiated from the Third Plan. The third approach adopted in India to address the issue of poverty was through provision of minimum basic amenities to the people. The approach was adopted from the Fifth Plan onwards. Under this approach there are some programmes to improve nutritional status of poor households.
Many social security programmes were also launched. The National Social Assistance Programme was initiated by Central Government to provide financial security to elderly people, poor women and widows.
Criticism of poverty alleviation programme:
Poverty alleviation programmes can be able to reduce poverty in India. However implimentation of these programmes have several shortfalls. They are following:
- The benefits of poverty alleviation programmes have been enjoyed mostly by the non-poor.
- In comparison to the magnitude of poverty the amount of resources allocated for these programme is not sufficient.
- These programmes depend mainly on government and bank officials for their implementation since such officials are ill motivated. Inadequate trained, corruption prone and vulnerable to pressure from a variety of local cities, the resources are inefficiently used and wasted.
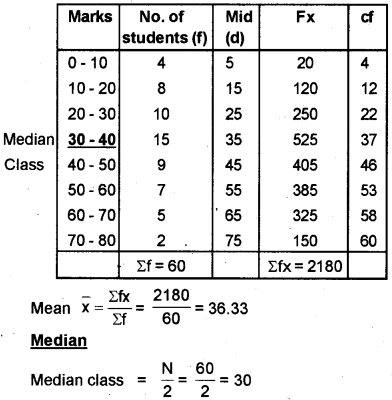
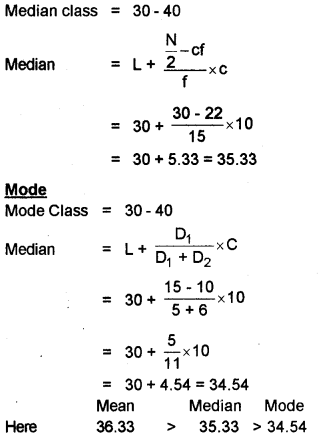
Question 32.
Prove that Arithmetic
Mean > Median > Mode
| Marks | No. of Students |
| 0 – 10 | 4 |
| 10 – 20 | 8 |
| 20 – 30 | 10 |
| 30 – 40 | 15 |
| 40 – 50 | 9 |
| 50 – 60 | 7 |
| 60 – 70 | 5 |
| 70 – 80 | 2 |
Scores – Mean 21/2, Median – 21/2, Mode – 1, Prove -1
Answer:
Question 33.
The developmental activities in India have exerted high pressure on environment.
a) Write the functions of environment.
b) Analyze how the development activities become a burden to the above mentioned functions.
c) Point out any four priority environmental issues identified in India.
Answer:
a) Functions of environment
The functions of environment can be divided into four. They are
- It supplies resources
- It assimilate waste
- It sustain life by providing genetic and biodiversity
- It provides aesthetic service
b. The developmental activities becomes a burden to the environmental function.
As a result of population explosion and industrialisation, production and consumption was on rise. This has made overexploitation of resources a necessity. Resource extraction exceeded their regeneration. This trend of environmental crisis continuous even today.
Global warming ozone depletion, land degradation, air pollution and water pollutions are caused the hindrance of the function of environment. (This explain detail before)
Priority issues of environment problems:
- Depletion of the oceans fisheries.
- Toxic contamination of the sea by industrial runoff.
- Plastic pollution
- Acidification pose great threats to the health of the world’s population.
