Kerala Plus One Economics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 7 Employment – Growth, Informalisation and Related Issues
Question 1.
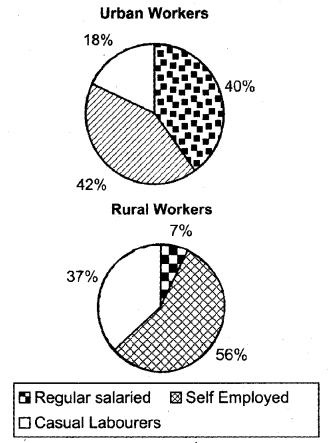
What inference can be made from the above pie diagrams? (March 2009)
Answer:
- In both rural and urban areas, self-employed workers are more.
- Regular salaried persons are high in urban areas compared to those in rural areas.
- In rural areas, casual labourers are 37% whereas in urban areas they consist of only 18%.
Question 2.
In India, workers are employed in the formal sector and informal sector. Is it necessary to generate employment in the formal sector rather than in the informal sector? Give reasons. (Say 2009)
Answer:
Yes. It is necessary to generate employment in the formal sector.
The reasons are:
- Acceptance of labour laws
- Social security benefits
- Formation of trade unions
- Minimum wage fixation High level of monitory gains.
Question 3.
Mr.Pradeep is a shop owner specializing in shoes and bags. Identify the name of employment. (Say 2009)
Answer:
Self-employment
Question 4.
The population of a country is 85 crones. Among them, 65 crores are workers. Find out the worker population ratio of that country. (March 2010)
Answer:

Question 5.
Pradeep is the owner of a textile shop in the city. Madhu is a loading worker in a wholesale vegetable shop. Distinguish between the types of employment mentioned here. (March 2011)
Answer:
Self-employed workers and casual wage labor are mentioned here. Workers who own and operate an enterprise to earn their livelihood are known as self-employed. On the other hand, the workers are called casual wage labourers.
Question 6.
True or False. (March 2012)
Disguised unemployment prevails in the Indian farm sector.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
Distinguish between formal sector workers and informal sector workers. (March 2012)
Answer:
All the public sector establishments and those private sector establishments which employ 10 hired workers or more are called formal sector establishments and those who work in such establishments are formal sector workers. All other enterprises and workers working in those enterprises form the informal sector.
There are several benefits enjoyed by the workers in the formal sector. Some of them are:
- Those who are working in the formal sector enjoy social security benefits.
- They earn more than those in the informal sector.
Question 8.
In India worker-population ratio is low in urban areas compared to rural areas. What is meant by this worker-population ratio? (Say 2012)
Answer:
Worker population ratio is defined as the number of persons employed per thousand persons.
WPR = No. of employed persons/Total population × 100
Worker Population Ratio is an indicator used for analyzing the employment situation in the country. This is also useful in knowing the proportion of the population that is actively contributing to the production of goods and services in the economy.
Question 9.
Give a suitable term for the given idea. (March 2013)
“Moving of workers from self-employment to casual wage work.”
Answer:
Casualisation of labour
Question 10.
It is a known fact that the farm sector in India is over-crowded. An increasing labour force needs to find alternative employment opportunities. Suggest some alternative livelihood options. (Say 2013)
Answer:
- Self-employment
- Industrial jobs
- Computer-related works
Question 11.
Study the following table and comment on the worker-population ratio in India. (Say 2013)
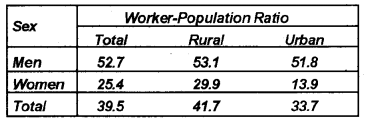
Answer:
- Worker – population ratio is higher in rural areas compared to urban areas.
- Worker – population ratio among women is very low.
- Regional differences in worker – population ratio among male are very less.
Question 12.
Distinguish between formal sector workers and informal sector workers. (March 2014)
Answer:
All the public sector establishments and those private sector establishments which employ 10 hired workers or more are called formal sector establishments and those who work in such establishments are formal sector workers. All other enterprises and workers working in these enterprises form the informal sector. Thus, informal sector includes millions of farmers, agricultural labourers, owners of small enterprises, and people working in those enterprises as also the self-employed who do not have any hired workers.
Question 13.
Aysha is an educated, unemployed youth seeking employment in the formal sector. Suggest the merits of formal sector employment. (Say 2014)
Answer:
Formal sector is the sector which encompasses all jobs with normal hours and regular wages and is recognized as income sources on which income taxes must be paid. Opposite of informal sector.
Benefits
- Enjoys social security benefits
- Gets more earning
- Limited hours of work
- Has trade union participation
Question 14.
Look at the following examples. Categorize them into formal sector workers and informal sector workers. (March 2015)
- A teacher taking classes in a school.
- A head load worker carrying a bag of cement on his back in a market.
- A doctor in a hospital treating a patient.
- A daily wage labourer working under a contractor.
- A handloom weaver working in her house.
- Nurse in a government hospital.
Answer:
- Formal sector
- Informal sector
- Formal sector
- Informal sector
- Informal sector
- Formal sector
Question 15.
Write the name of the wage employment programme started in India in 2005. Explain the achievements of that scheme in employment generation taking your village as an example. (Say 2015)
Answer:
MNREGP: This programme creator employment opportunities in villages for a minimum period of 100 days in a year. Unemployed women in villages are especially gained the benefits of this scheme.
Question 16.
Give one word. (Say 2015)
The process of moving from self-employment and regular salaried employment to casual wage work.
Answer:
Casualisation of the workforce.
Question 17.
Distinguish between formal sector workers and informal sector workers. (March 2016)
Answer:
All the public sector establishments and those private sector establishments which employ 10 hired workers or more are called formal sector establishments and those who work in such establishments are formal sector workers. All other enterprises and workers working in those enterprises form the informal sector.
There are several benefits enjoyed by the workers in the formal sector. Some of them are:
- Those who are working in the formal sector enjoy social security benefits.
- They earn more than those in the informal sector.
Question 18.
Classify the following jobs into organized and unorganized sectors. (Say 2016)
[Agricultural labourer, school teachers, street vendor, head load worker, business executive, railway ticket examiner, cart puller, software engineer]
Answer:
Organised sector
- School Teacher
- Business Executive
- Railway Ticket Examiner
- Software Engineer
Unorganised sector
- Agricultural labourer
- Street vendor
- Head load worker
- Cart puller
Question 19.
Worker population ratio is _________ (March 2017)
a) Population/Worker
b) Worker/Population
c) Population/Worker × 100
d) Worker/Population × 100
Answer:
d) Worker/Population × 100
Question 20.
Which one of the following statements is NOT TRUE about the employment sector in India? (March 2017)
a) 93% of workers are in the informal sector.
b) 50% of the workers are self-employed.
c) Disguised and seasonal unemployment exists in the Indian farm sector.
d) During 1972-2010 there was a movement of workers from casual wage to self-employment.
Answer:
d) During 1972-2010 there .was a movement of workers from casual wage to self-employment.
