Kerala Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 The Discipline of Computing
Plus One The Discipline of Computing One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which is the base of Mayan’s Number System?
Answer:
Base 20
Question 2.
Greek Number System is known as _________.
Answer:
Ionian number system
Question 3.
Which was the first computer for basic arithmetic calculations?
Answer:
Abacus
Question 4.
Who invented logarithms?
Answer:
John Napier
Question 5.
What is the name of the machine developed by Blaise Pascal?
Answer:
Pascaline
Question 6.
Who was the first programmer in the world?
Answer:
Augusta Ada Lowelace
Question 7.
Computing machines recognizes and operates in ___________ language.
Answer:
Machine
Question 8.
What does EDVAC stand for?
Answer:
Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer. It is designed by Von Neumann.
Question 9.
Give the name for a simple kind of theoretical computing machine.
Answer:
Turing Machine.
Question 10.
The Sumerian number system is also known as _________
Answer:
Sexagesimal
Question 11.
What are the features of Hindu Arabic Number system?
Answer:
The Hindu – Arabic number system had a symbol (0) for zero originated in India 1500 years ago. Its base is 1 0 and it is adopted by many countries.
Question 12.
How is the zero represented in the Babylonian Number System.
Answer:
Blank space
Question 13.
Write the number that is represented in the following Abacus.
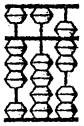
Answer:
- 3 beads of the leftmost rod moved hence it represents 3.
- No beads (0) of the next rod moved hence it represents 0.
- 2 beads of the rightmost rod in the lower part is moved (2+) and one bead is moved in the upper part represents 5.
Hence 2 + 5 = 7
So the answer is 307
Question 14.
Which is the first automatic electromechanical computer?
(a) Pascaline
(b) Abacus
(c) Mark 1
(d) Analytical Engine
Answer:
(c) Mark 1
Question 15.
Find the correct match for each item in column A and B.
| A | B |
| (a) Abacus | (i) Preprogrammed |
| (b) Pascaline | (ii) Computing Machine |
| (c) Jacquard’s Looms | (iii) Punched cards |
| (d) Mark 1 | (iv) Counting frame |
Answer:
| A | B |
| (a) Abacus | (iv) Counting frame |
| (b) Pascaline | (ii) computing machine |
| (c) Jacquard’s Looms | (iii) Punched cards |
| (d) Mark 1 | (i) Pre programmed |
Question 16.
Write the number represented in the abacus given below.
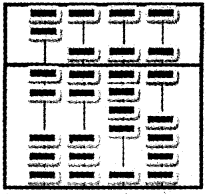
Answer:
- 2 Beads of the left most rod are moved hence it represents 2 – (a)
- 2 Beads of the next rod are moved (2) and one bead is moved in the upper part represents 5. Hence 2 + 5 = 7 – (b)
- 4 Beads of the next rod are moved (4) and one bead is moved in the upper part represents 5. Hence 4 + 5 = 9 – (c)
One bead of the right most rod in the lower part is moved (1) and one bead is moved in the upper part represents 5. Hence 1+5 = 6 – (d)
Join a, b, c and d hence the result is 2796
Question 17.
Who invented a machine to multiply any number by a number between 2 to 9? (1)
(a) Blaise Pascal
(b) John Napier
(c) G.W. Von Leibniz
(d) Joseph Marie Jacquard
Answer:
(c) G.W. Von Leibniz
Question 18.
Order the following technologies according to different generations of a computer (First to Fifth Generation) (1)
- Transistor
- Vacuum Tube
- Artificial intelligence
- Microprocessor
Answer:
- Vacuum tube
- Transistor
- Microprocessor
- Artificial intelligence
Question 19.
The number (158)10 can be represented in Hexadecimal number system as ______________
Answer:
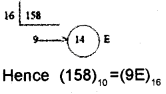
Plus One The Discipline of Computing Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Discuss the impact of the Hindu- Arabic numeral system in the world.
Answer:
It was originated in India around 1500 years ago and was a positional number system with symbol for zero. This greatest contribution is adopted by many of the countries.
Question 2.
Compare the Roman Number System and Mayan’s Number System.
Answer:
The Roman numerals consists of 7 letters such as I, V, X, L, C, D, M and the base is 7.
The Mayans used number system with base 20 because of the sum of the number of fingers and toes is 10 + 10 = 20. This was used for astronomical observations.
Question 3.
A full room sized computer in the first generation now becomes palm sized by the fourth generation. Explain the technological changes that made it possible.
Answer:
Vaccum tubes were used in first generation computers. Hence the size of computer was a size of full room. Instead of vaccum tubes transistors were used in the 2nd generation hence size became smaller. In 3rd generation, Integgted circuits (IC’s) were used. It reduced the size again in 4th generation, microprocessors are used. It reduces the size again and again.
Plus One The Discipline of Computing Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Discuss the developments of the number system from the Egyptian to the Chinese Era.
Answer:
Around 3000 BC Egyptians introduced a number system with base 10. They used unique symbols for 1 to 9, 10 to 90, 100 to 900 and 1000 to 9000. They write from right to left. The next era was of Sumerian/Babylonian number system its base was 60, the largest base also known as sexagesimal system.
They write from left to right. They use blank space for zero. Around 2500 BC Chinese introduced simplest and the most efficient number system. Its base was 10.
Question 2.
Discuss the features of Abacus.
Answer:
In 3000 BC Mesopotamians introduced this and it means calculating board or frame. It is considered as the first computer for basic arithmetical calculations and consists of beads on movable rods divided into two parts.
The Chinese improved the Abacus with seven beads on each wire. A horizontal divider separates the top two beads from the bottom five. The top two beads have a place value of 5 and the below five beads. The beads which are pushed against the horizontal bar represent the number.
Question 3.
Compare the Analytical Engine and Difference Engine of Charles Babbage.
Answer:
The intervention of human beings was eliminated by Charles Babbage in calculations by using Difference engine in 1822. It could perform arithmetic operations and print results automatically.
The Analytical Engine was a proposed mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician Charles Babbage. The Analytical Engine incorporated an arithmetic logic unit, control flow in the form of conditional branching and loops, and integrated memory.
Charles Babbage is considered as the “Father of computer” It is considered as the predecessor of today’s computer. This engine was controlled by programs stored in punched cards. These programs were written by Babbage’s assistant, Augusta Ada King, who was considered as the first programmer in the World.
Question 4.
Bring out the significance of Hollerith’s machine.
Answer:
In 1887, Herman Hollerith an American made first electromechanical punched cards with instructions for input and output. The card contained holes in a particular pattern with special meaning.
The Us Census Bureau had large amount of data to tabulate, that will take nearly 10 years. By this machine this work was completed in one year. In 1896, Hollerith started a company Tabulating Machine Corporation. Now it is called International Business Machines(IBM).
Question 5.
State Moore’s Law and discuss its significance.
Answer:
The number of transistors on IC’s doubles approximately every two years. This law is called Moore’s Law, it is named after Gordon E Moore. It is an observation and not a physical or natural law. He predicted that the trend would continue for at least ten years. It is true and the trend continued for more than half a century.
Question 6.
Discuss the evolution of computer languages.
Answer:
The instructions to the computer are written in different languages. They are Low Level Language (Machine language), Assembly Language (Middle level language) and High Level Language (HLL). In Machine Language 0’s and 1’s are used to write , program. It is very difficult but this is the only language which is understood by the computer. In assembly language mnemohics (codes) are used to write programs.

Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator(EDSAC) built during 1949 was the first to use assembly language. In HLL English like statements are used to write programs. A – 0 programming language developed by Dr. Grace Hopper, in 1952, for UNIVAC-I is the first HLL.
A team lead by John Backus developed FORTRAN @IBM for IBM 704 computer and ‘Lisp’ developed by Tim Hart and Mike Levin at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The other HLLs are C, C++, COBOL, PASCAL, VB, Java, etc. HLL is very easy and can be easily understood by the human being.
Usually programmers prefer HLL to write programs because of its simplicity. But computer understands only machine language. So there is a translation needed. The program which performs this job are language processors.
Question 7.
Discuss the working of Turing Machine.
Answer:
In 1936 Alan Turing introduced a machine, called Turing Machine. A Turing machine is a hypothetical device that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. This tape acts like the memory in a computer. The tape contains cells which starts with blank and may contain 0 or 1. So it is called a 3 Symbol Turing Machine.
The machine can read and write, one cell at a time, using a tape head and move the tape left or right by one cell so that the machine can read and edit the symbol in the neighbouring cells. The action of a Turing machine is determined by
- the current state of the machine
- the symbol in the cell currently being scanned by the head and
- a table of transition rules , which acts as the program.
Question 8.
Explain Turing Test in detail?
Answer:
The Turing test is a test of a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behaviour equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. The test involves a human judge engages in natural language conversations with a human and a machine designed to generate performance indistinguishable from that of a human being.
All participants are separated from one another. If the judge cannot reliably tell the machine from the human, the machine is said to have passed the test. The test does not check the ability to give the correct answer to questions; it checks how closely the answer resembles typical human answers. Turing predicted that by 2000 computer would pass the test.
Question 9.
Following are some facts related to evolution of computers :
(Usage of Transistors, Introduction of Very Large Scale Integrated Circuit, Construction of ENIAC) Categorize these under respective generations and briefly explain each. (3)
Answer:
- Transistor – Second generation
- VLSI – Fourth generation
- ENIAC – First generation
Question 10.
Why is it said “Turing machines are equivalent to modem electronic computers at a certain theoretical level”? (3)
Answer:
In 1887, Herman Hollerith an American made first electromechanical punched cards with instructions for input and output. The card contained holes in a particular pattern with special meaning. The Us Census Bureau had large amount of data to tabulate, that will take nearly 10 years.
By this machine this work was completed in one year. In 1896, Hollerith started a company Tabulating Machine Corporation. Now it is called International Business Machines(IBM).
Question 11.
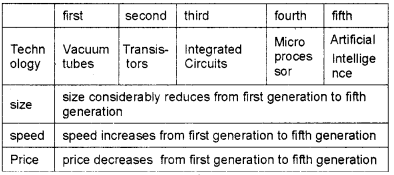
Compare any three features of five generations of computers.
answer:
Plus One The Discipline of Computing Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
List out and explain the various generations of computers.
Answer:
There are five generations of computers from 16th century to till date.
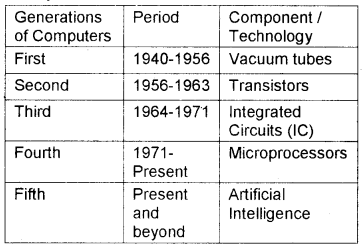
1. First generation computers (1940 – 1956):
Vacuum tubes were used in first-generation computers. The input was based on punched cards and paper tapes and output was displayed on printouts. The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator(ENIAC) belongs to first generation was the first general-purpose programmable electronic computer built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly.
It was 30 – 50 feet long, weight 30 tons, 18,000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 registers, 10,000 capacitors and required 1,50,000 watts of electricity. It requires Air Conditioner. They later developed the first commercially Successful computer, the Universal Automatic Computer(UNIVAC) in 1952.
The mathematician John Von Neumann designed a computer structure that structure is in use nowadays. Von Neumann structure consists of a central processing unit (CPU), Memory unit, Input and Output unit.
The CPU consists of arithmetic logical unit(ALU) and control unit(CU). The instructions are stored in the memory and follows the “Stored Program Concept”. Colossus is the secret code breaking computer developed by a British engineer Tommy Flowers in 1943 to decode German messages.
2. Second generation computers (1956 -1963):
Transistors, instead of Vacuum tubes, were used in 2nd generation computers hence size became smaller, less expensive, less electricity consumption and heat emission and more powerful and faster. A team contained John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley developed this computer at Bell Laboratories.
In this generation onwards the concept of programming language was developed and used magnetic core (primary) memory and magnetic disk(secondary) memory.
These computers used high level languages(high level language means English like statements are used) like FORTRAN (Formula translation) and COBOL(Common Business Oriented Language). The popular computers were IBM 1401 and 1620.
3. Third generation computers (1964 – 1971):
Integrated Circuits(IC’s) were used. IC’s or silicon chips were developed by Jack Kilby, an engineer in Texas Instruments. It reduced the size again and increased the speed and efficiency. The high level language BASIC(Beginners All purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during this period The popular computers were IBM 360 and 370.
Due to its simplicity and cheapness more people were used . The number of transistors on IC’s doubles approximately every two years. This law is called Moore’s Law, it is named after Gordon E Moore. It is an observation and not a physical or natural law.
4. Fourth generation computers (1971 onwards):
Microprocessors are used hence computers are called microcomputers. Microprocessor is a single chip which contains Large Scale of IC’s(LSI) like transistors, capacitors, resistors etc due to this a CPU can place on a single chip. Later LSI were replaced by Very Large Scale Integrated Circuits(VLSI). The popular computers are IBM PC and Apple II.
5. Fifth generation computers (future):
Fifth generation computers are based on Artificial Intelligence(AI). AI is the ability to act as human intelligence like speech recognition, face recognition, robotic vision and movement etc. The most common Al programming language are LISP and Prolog.
Question 2.
Prepare a seminar report on evolution of positional number system.
Answer:
In positional number system, each and every number has a weight. Earlier sticks are used to count items such as animals or objects. Around 3000 BC the Egyptians use number systems with radix 10(base the number of symbols or digits used in the number system) and they write from right to left.
Later Sumerian/Babylonian use number system with largest base 60 and were written from left to right. They use space for zero instead of a symbol,0. In 2500 BC, the Chinese use simple and efficient number system with base 10 very close to number system used in nowadays.
In 500 BC, the Greek number system known as Ionian, it is a decimal number system and used no symbols for zero. The Roman numerals consists of 7 letters such as l, V, X, L, C, D, M.
The Mayans used number system with base 20 because of the sum of the number of fingers and toes is 10 + 10 = 20. It is called vigesimal positional number system. The numerals are made up of three symbols zero (shell shape, with the plastron uppermost), one (a dot) and five (a bar or a horizontal line).
To represent 1 they used one dot, two dots for 2, and so on. The Hindu – Arabic number system had a symbol (0) for zero originated in India 1500 years ago.
Question 3.
Discuss the various computing machines emerged till 1900’s.
Answer:
1. Abacus:
In 3000 BC Mesopotamians introduced this and it means calculating board or frame. It is considered as the first computer for basic arithmetical calculations and consists of beads on movable rods divided into two parts. The Chinese improved the Abacus with seven beads on each wire. Different Abacus are given below.
2. Napier’s bones:
A Mathematician John Napier introduced this in AP 1617.
3. Pascaline:
A French mathematician Blaise Pascal developed this machine that can perform arithmetical operations.
4. Leibniz’s calculator:
In 1673, a German mathematician and Philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Von Leibniz introduced this calculating machine.
5. Jacquard’s loom:
In 1801, Joseph Marie Jacquard invented a mechanical loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex pattern. A stored program in punched cards was used to control the machine with the help of human labour. This punched card concept was adopted by Charles Babbage to control his Analytical engine and later by Hollerith.
6. Difference engine:
The intervention of human beings was eliminated by Charles Babbage in calculations by using Difference engine in 1822. It could perform arithmetic operations and print results automatically.
7. Analytical engine:
In 1833, Charles Babbage introduced this. Charles Babbage is considered as the “Father of computer” It is considered as .the predecessor of today’s computer. This engine was controlled by programs stored in punched cards. These programs were written by Babbage’s assistant, Augusta Ada King, who was considered as the first programmer in the World.
8. Hollerith’s machine:
In 1887, Herman Hollerith an American made first electromechanical punched cards with instructions for input and output. The card contained holes in a particular pattern with special meaning.
The Us Census Bureau had large amount of data to tabulate, which will take nearly 10 years. By this machine this work was completed in one year. In 1896, Hollerith started a company Tabulating Machine Corporation. Now it is called International Business Machines(IBM).
9. Mark -1:
In 1944 Howard Aiken manufactured automatic electromechanical computer in collaboration with engineers at IBM that handled 23 decimal place numbers and can perform addition, subtraction, multiplication and subtraction.
