Kerala Plus One Chemistry Improvement Question Paper Say 2017 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 60
General Instructions to Candidates:
- There is a ‘cool off time’ of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with questions and to plan your answers.
- Read the instructions carefully.
- Read questions carefully before answering.
- Calculations, figures and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Question numbers 1 – 7 carry one score each. Answer all the questions. (7 × 1 = 7)
Question 1.
Give the equation showing relation between empirical formula and molecular formula of a compound.
Answer:
Molecular formula = Empirical formula × n
where n = 1, 2,3…
Question 2.
Which of the following transition of electron in the hydrogen atom will emit maximum energy?
i) n5 → n4
ii) n4 → n3
iii) n3 → n2
iv) same in all transition
Answer:
iii) n3 → n2
Question 3.
The geometry and type of hybridisation of central atom in BF3 are
i) linear, SP
ii) tetrahedral, SP3
iii) trigonal planar, SP2
iv) Pyramidal, SP3
Answer:
iii) trigonal planar, SP2
Question 4.
Arrange the following elements in the increasing order of first ionisation energy: Li, Be, B
Answer:
Li < B < Be
Question 5.
The compressibility factor of an ideal gas is …………
Answer:
1
Question 6.
What is the molecular formula of Buck ministers fullerene?
Answer:
C60
Question 7.
Ozone layer depletion in Antarctica is due to the formation of the compound
i) acrolein
ii) formaldehyde
iii) SO2 and SO3
iv) chlorine nitrate
Answer:
iv) chlorine nitrate
Question numbers 8 – 20 carry two scores each. Answer any ten. (10 × 2 = 20)
Question 8.
In the two oxides of carbon, the mass ratio of oxygen is 1.33 : 2.66. Identify the law illustrated by the above ratio and state the law.
Answer:
Law of Multiple Proportions.
The law states that if two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Question 9.
Using s, p, d notation describe the orbitals with following set of quantum number
a) n = 4, I = 1
b) n = 3, I = 2
Answer:
a) 4p
b) 3d
Question 10.
A set of molecules are given below:
NaCl, O2, KCl, BF3, PCl5
a) Classify the molecules into ionic and covalent compounds.
b) Classify the above molecules into those obeying octet rule and those not obeying octet rule.
Answer:
a) Ionic compounds – NaCl, KCl
Covalent compounds – O2, BF3, PCI5
b) Obeying octet rule – NaCl, O2, KCl
Not obeying octet rule – BF3, PCI5
Question 11.
Identify the extensive and intensive properties from the following:
density, internal energy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity
Answer:
Extensive properties – internal energy, heat capacity
Intensive properties – density, molar heat capacity
Question 12.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1) Exothermic reaction | a) Reversible reaction |
| 2) Isothermal process | b) qv |
| 3) If a process carried out at constant volume then ΔV= | c) ΔH<0 |
| 4) A process carried out infinitesimally slow steps | d) dT = 0 |
Answer:
1) Exothermic reaction – c) ΔH < 0
2) Isothermal process – d) dT = 0
3) If a process is carried out at constant volume then ΔU = – b) qv
4) A process carried out in infinitesimally slow steps – a) Reversible reaction
Question 13.
Derive the relation between Kp and Kc of a gaseous reversible reaction.
Answer:
Consider a general gaseous reversible reaction,
aA(g) + bB(g) ⇌ cC(g) + dD(g)
The equilibrium constant in terms of molar concentration is given by,
Kc=[C]∘[D]d[ A]a[B]bKc=[C]∘[D]d[ A]a[B]b
For reactions involving gases it is more convenient to express the equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure.
The equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure is given by,
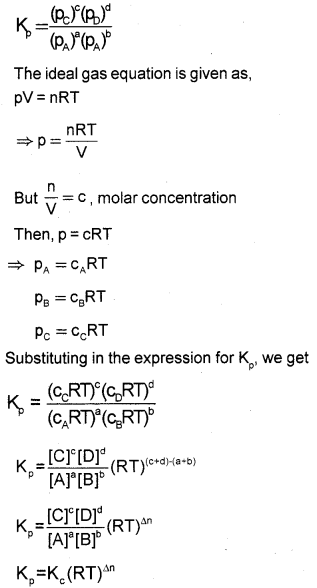
where Δn = (number of moles of gaseous products) – (number of moles of gaseous reactants) in the balanced chemical equation.
Question 14.
a) What is Buffer solution?
b) Flow a basic buffer can be prepared?
Answer:
a) The solutions which resist change in pH on dilution or with the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali are called Buffer solutions.
b) A basic buffer can be prepared from weak bases and their salts with strong acids. For example, a mixture of NH4OH and NH4Cl acts as a buffer around a pH 9.25.
Question 15.
Briefly explain the bonding in diborane.
Answer:
In diborane the four terminal hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane. Above and below this plane, there are two bridging hydrogen atoms. Each boron atom uses sp3 hybrid orbitals for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrid orbitals on each boron atom, one is without an electron. The four terminal B-H bonds are regular two centre-two-electron bonds while the two bridge (B-H-B) bonds are three centre-two electron bonds also referred to as banana bonds.
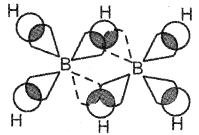
Question 16.
Nitrogen, sulphur, halogen and phosphorous present in an organic compound are detected by Lassaigne’s test. Explain Lassaigne’s test for detecting nitrogen?
Answer:
The given organic compound is fused with metallic sodium in a fusion tube and the fused mass is extracted by boiling with distilled water to get sodium fusion extract. This is boiled with iron(II) sulphate and then acidified with conc.H2SO4. Then NaCN present in the extract first reacts with iron(II) sulphate and forms sodium hexacyanoferrate(II). On heating with conc.H2SO4 some iron(II) ions are oxidised to iron(III) ions which react with sodium hexacyanoferrate(II) to produce iron (III) hexacyanoferrate(II) which is Prussian blue in colour. The formation of Prussian blue colour confirms the presence of nitrogen in the organic compound.
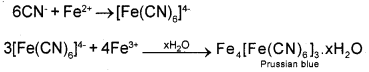
Question 17.
Write Van der Waals equation for one mole gas and also write the physical significance of Van der Waals constants.
Answer:
The van der Waals’ equation for one mole of a real gas is given by
(p+aV2)(V−b)=RT(p+aV2)(V−b)=RT
p = pressure
V = volume of the gas
R = universal gas constant
T = temperature in kelvin
a & b = van der Waals’ constants the value of which depend on the characteristic of a gas.
Significance of ‘a’: It is a measure of magnitude of intermolecular attractive forces within the gas and is independent of temperature and pressure. Larger the value of ‘a’, larger will be the intermolecular attraction among the gas molecules.
Question 18.
Complete the reaction
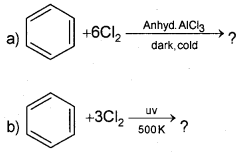
Answer:
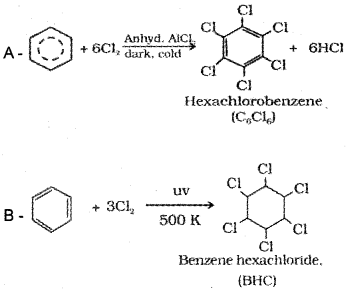
Question 19.
Predict the products formed by addition reaction of HBr to but-1-ene in the presence of peroxide and in the absence of peroxide.
Answer:
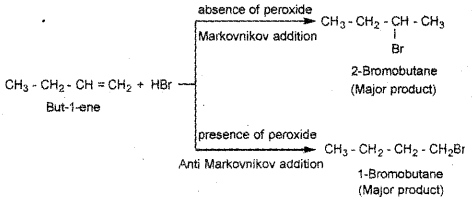
Question 20.
Give any two importance of green chemistry in day-to-day life.
Answer:
1. Dry cleaning of clothes – The process in dry cleaning using the carsinogenic solvent tetrachloroethene is replaced by a process, whereliquified CO2. with a suitable detergent is used which result in less harm to ground water.
2. H2O2 is used for the purpose of bleaching clothes in the process of laundary, which gives better results and makes use of lesser amount of water.
3. Bleaching of paper – Instead of chlorine gas, H2O2 with a suitable catalyst is used.
4. Synthesis of chemicals – Ethanal is commercially prepared by one step oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium with an yield of 90%.
![]()
Question numbers 21 – 29 carry three score each. Answer any seven. (7 × 3 = 21)
Question 21.
Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following.
a) 14 g of Nitrogen (N2).
b) 14 mole atom Nitrogen (N2).
c) 14 U of Nitrogen (N2)
Answer:
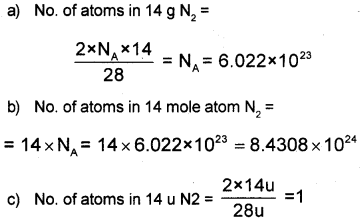
Question 22.
a) Identify the position of the elements in the periodic table having outer electronic configuration
i) ns2np4 with n = 3
ii) (n – 1) d2ns2 with n = 4.
b) “Removal of electron from an atom become easier on moving down the group.” Give reason.
Answer:
a) i) Period – 3, Group – 16 (Sulphur)
ii) Period – 4, Group – 4 (Titanium)
b) On moving down a group in the periodic table the effective nuclear charge experienced by a valence electron in an atom will be less than the actual charge on the nucleus because of shielding or screening of the valence electron from the nucleus by the intervening core electrons. The increase in shielding outweighs the increasing nuclear charge and the removal of the outermost electron requires less energy down a group.
Question 23.
a) Write the two postulates of Kinetic molecular theory of gases responsible for deviation of real gases from ideal behaviour.
b) What is Boyle point?
Answer:
a) i) Gases consist of large number of identical particles that are so small and so far apart on the average that the actual volume of the molecules is negligible in comparison to the empty space between them.
ii) There is no force of attraction between the particles of a gas at ordinary temperature and pressure.
b) Boyle point of a gas is the temperature at which a real gas obeys ideal gas law over an appreciable range of pressure.
Question 24.
a) Derive the equation for Gibb’s energy change (ΔG) in terms of ΔH and ΔS.
b) Write any two condition for which AG becomes negative according to Gibb’s equation.
Answer:
a) The Gibbs energy, G is given by
G = H – TS
But H = U + PV
G = U + PV – TS
The Gibbs energy change (ΔG) during the process can be expressed as
ΔG = ΔU + Δ(PV) – Δ(TS)
ΔG = ΔU+ PΔV + VΔP – TΔS – SΔT
At constant temperature and pressure, ΔT = &
ΔP = 0
ΔG = ΔU + PΔV – TΔS
But, ΔU + PΔV = ΔH
∴ ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
b) i) When ΔH = -ve and ΔS= +ve is ΔG is – ve at all temperatures.
ii) When both ΔH and ΔS are -ve A G is -ve at low temperatures i.e. when TΔS < ΔH.
iii) When both ΔH and ΔS are +ve ΔG is -ve at high temperatures i.e. when TΔS > ΔH.
Question 25.
Decomposition of PCI5 can be represented as
![]()
ΔH = 124.0 KJ mol-1
Describe the effect of the following on the above equilibrium?
a) addition of PCI5
b) increase in pressure
c) increase in temperature
Answer:
a) When PCI5 is added, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, system tries to decrease its concentration by increasing the rate of forward reaction.
b) On increasing pressure, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in the number of moles of gaseous species. Here the number of moles of the gaseous species decreases in the backward reaction. Hence, on increasing pressure the rate of backward reaction increases.
c) According to Le Chateliers’ principle, on increasing temperature the rate of endothermic reaction increases. Here the forward reaction is endothermic. Hence, on increasing temperature the rate of forward reaction increases.
Question 26.
Explain the following reactions.
a) CO is heated with ZnO.
b) Boric acid is added to water.
c) BF3 with NaH
Answer:
a) When CO is heated with ZnO, Zn and CO2 are formed.
![]()
b) When boric acid is added to water it accepts electrons of hydroxyl ions of water to form [B(OH)4]- and hydronium ions.
B(OH)3 + 2HOH → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+
c) When BF3 is heated with NaH at 450 K, diborane and sodium fluoride are formed.
![]()
Question 27.
Balance the following redox reaction using oxidation number or ion-electron method:
![]()
Answer:

Balancing H atoms:
MnO4–(aq) + 4H+(aq) → MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l)
As the reaction occurs in basic medium, 4OH- ions are added on both sides.
MnO4 –(aq) + 2H2O(l) → MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 4OH–(aq)
Replacing the H+ and OH- ions with water the resultant equation is:
MnO4–(aq) + 2H2O(l) → MnO2(s) + 4OH–(aq)
Step 5: Balancing the charges of the two half reactions by adding required number of electrons:
2l–(aq) → l2(s) + 2e–
MnO4–(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 3e– → MnO2(s) + 4OH–(aq)
Equating the number of electrons:
6l–(aq) → 3l2(S) + 6e–
2MnO4–(aq) + 4H2O(l) + 6e → 2MnO2(s) + 8OH–(aq)
Step 6: Add to half reactions to obtain the net reaction after cancelling electrons on both sides:
6l–(aq) + 2MnO4–(aq) + 4H2O(l) → 3l2(S) + 2MnO2(s) + 8OH–(aq)
(Or using oxidation number method.)
Question 28.
What causes the temporary and permanent hardness of water? Give one method to remove permanent hardness?
Answer:
Temporary hardness of water is caused by the presence of dissolved bicarbonates of Mg and Ca.
Permanent hardness of water is caused by the presence of soluble salts of magnesium and calcium in the form of chlorides and sulphates.
Permanent hardness can be removed by treatment with washing soda. Washing soda reacts with soluble chlorides and sulphates of magnesiumm and calcium to form insoluble carbonates.
MCl2 + Na2CO3 → MCO3↓ + 2NaCl
MSO4 + Na2CO3 → MCO3↓ + Na2SO4
(Or any other suitable method).
Question 29.
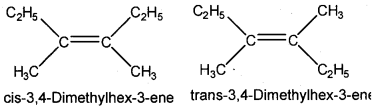
Analyse the given compound.
C2H5C(CH3) = C(CH3)C2H5
a) Write the IUPAC name of the compound.
b) Draw the structures of the geometrical isomers possible for the compound.
Answer:
a) 3, 4-Dimethylhex-3-ene
b)
Question numbers 30 – 33 carry four score each. Write any three. (3 × 4 = 12)
Question 30.
a) Write the Schrodinger wave equation and explain the terms.
b) Draw the boundary surface diagrams of any four 3d orbitals.
Answer:
a) For a system such as an atom or a molecule whose energy does not change with time the Schrodinger equation is written as
ˆH^HΨ = EΨ
where
ˆH^H is a mathematical operator called Hamiltonian
E = total energy of the system which takes into account the kinetic energies of all the sub-atomic particles, attractive potential between the electrons and nuclei and repulsive potential among the electrons and nuclei individually Ψ is the amplitude of the electron wave called the wave function.
b)
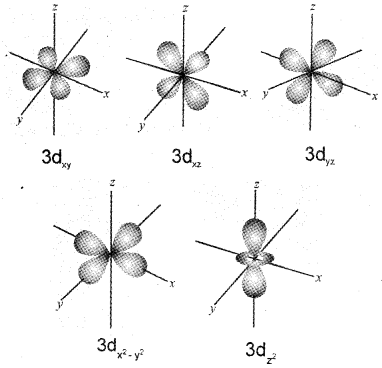
Question 31.
Compare the relative stability of the following species and indicate their magnetic properties based on molecular orbital theory.
O−2O−2 and O+2O+2
Answer:
According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, the electronic configurations of O−2O−2 and O+2O+2 are:
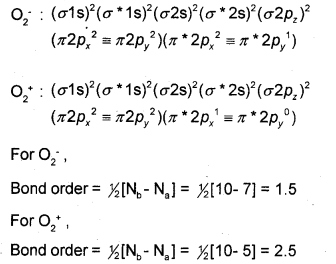
As bond order increases stability increases. Thus, O+2O+2 with higher value of bond order is more stable than O−2O−2.
In both O−2O−2 and O+2O+2 one orbital each is singly occupied with one unpaired electron. Hence, both the species are paramagnetic.
Question 32.
By passing Cl2 gas through a solution, gets bleaching powder
a) Write the balanced chemical equation for above reaction.
b) What happens if CO2 gas is passed instead of Cl2 and write the balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
a) When Cl2 gas is passed through milk of lime, calcium hypochlorite is formed, a constituent of bleaching powder.
![]()
b) When CO2 gas is passed through lime water it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Question 33.
a) Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
(CH3)3C+,(CH3)2CH+,CH3CH2CH2+
Justify your answer.
b) Write the principle involved in the distillation of organic compound under reduced pressure? Give an example.
Answer:
a) (CH3)3C+ is the most stable among the given carbocations.
Alkyl groups directly attached to the positively charged carbon stabilise the carbocations due to inductive and hyperconjugation effects. Due to the presence of three – CH3 groups directly attached to the positively charged carbon, (CH3)3C+ has maximum +l effect and hyper conjugation which results in maximum dispersal of charge and hence maximum stability.
Thus, stability increases in the order:
CH3CH2CH2+ < (CH3)2CH+ < (CH3)3C+
b) This method is used to purify liquids having very high boiling points and those, which decompose at or below their boiling points. Such liquids are made to boil at a temperature lower than their normal boiling points by reducing their pressure on their surface.
For example, glycerol can be separated from spent-lye in soap industry by using this technique.
