Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter Chapter 9 Hydrogenis part of Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer . Here we have given Plus One Chemistry Previous Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen.
Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen
Question 1.
a) What is heavy water? Mention one use of heavy water. (March – 2009)
b) Explain why hydrogen peroxide is not stored in glass vessels.
c) What is a halogen? What is its use?
Answer:
a) D2O. It is used as moderator in nuclear reactor.
b) H2O2 is highly unstable and it is also explosive.
c) Calogen is Sodium hexametaphosphate. It is used to remove the hardness of water.
Question 2.
Match the following by selecting the items from columns B and C which are most suitable to those in column A.
| A | B | C |
| a) Protium, Tritium | 1) Hard water | i) Fertilizer |
| b) Ca2+, Mq2+ | 2) Heavy Water | ii) Hydrogen |
| c) H2O2 | 3) Isotopes | iii) Moderator in a nuclear reactor |
| d) D2O | 4) Perhydrol | iv) No lather with soap |
| 5) Phenol | v) Antiseptic |
Answer:
| a) Protium, Tritium | Isotopes | Hydrogen |
| b) Ca2+, Mg2+ | Hard water | No lather with soap |
| C) H2O2 | Perhydrol | Antiseptic |
| d) D2O | Heavy water | Moderator in nuclear reactor |
Question 3.
The efficiency of a boiler is found to decrease when boiler scales are formed. (Say – 2010)
a) Which are the possible compounds present in water for scale formation?
b) Write the chemistry of scale formation?
c) Suggest a suitable chemical method to prevent, the scale formation.
Answer:
a) Ca(HCO3)2, Mg(HCO3)2
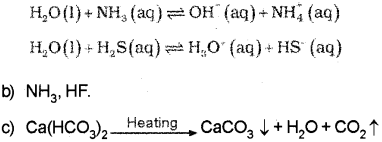
b) On boiling Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3), decomposes to give CaCO3 & MgCO3. These substances are responsible for scale formation.
c) By heating with Na2CO3.
Question 4.
a) Account for the following observations: (March – 2011)
f) The density of ice is lower than that of water.
ii) Haiti water does give ready lather with soap.
b) Justify the position of hydrogen in the periodic table.
Answer:
i) This is due to the presence of hydrogen bond in ice.
ii) This is due to the presence of Ca2+ and mg2+ ions in hard water.
iii) Hydrogen shows similarities with both alkali metals and halogen and hence it is given a seperate position Hi the periodic table.
Similarities with alkali metals
a) Both of them contain one electron in the outer most shell.
b) Both are good reducing agents.
Similarities with halogens
a) Both are diatomic molecules.
b) Both hydrogen and halogens possess lack of one electron than the nearest inert gas.
Question 5.
a) Vegetable oil is converted into vanaspati fat by process. (Say – 2011)
b) D2O is generally called
c) Hydrogen peroxide is an important chemical used in pollution control treatment of domestic and industrial effluents.
i) Write the milecular formula of hydrogen peroxide.
ii) Explain with suitable chemical equation, why hydrogen peroxide is stored in waxlined glass or plastic vessels in dark.
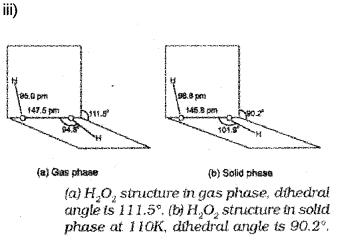
iii) Draw the structure of hydrogen peroxide.
Answer:
a) Hydrogenation
b) Heavy water
c) 1) H2O2
iii) H2O2 decomposes slowly on exposure to light to water and oxygen.
2H2O2(i) → 2H2O(i) + O2(g)
In the presence of metal surfaces or traces of alkali (present in glass containers), the above reaction is catalysed. It is, therefore, stored in wax-lined glass or plastic vessels in dark.
Question 6.
Permanent hardness of water can be removed only by chemical methods. (March – 2012)
a) Write the name of any one salt responsible for the permanent hardness of water.
b) Sodium hexametaphosphate is commercially called
c) How is sodium hexametaphosphate useful in re-moving the permanent hardness of water?
d) Suggest a disadvantage of hard water.
Answer:
a) CaCI2 OR MgSO4
b) Calgon
c) When calgon adding to hard water, Ca or Mg ions present in it react with calgon to form soluble complex salts, ie the Na2+ ions replace Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in hard water. Hence they are not available as free ions to cause hardness.
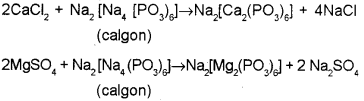
d) 1) Use of hard water in laundry work results in wastage of soap and poor cleaning of the clothes.
2) MaCI2, if present in hard water, undergoes hydrolysis in water releasing Hcl which slowly corrodes the boiler and shortens its life.
Question 7.
a) Hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts. Therefore it does not lather with soap. (Say – 2012)
i) Hard water is harmful for boilers. Why?
ii) How will you remove the hardness from the water by using washing soda?
iii) Which method is more suitable to get pure demineralised water?
b) Hydrogen peroxide is stored in plastic vessels in dark. Why?
Answer:
a) i) If hard water is used in boilers, it will result in the formation of deposits inside the boiler and steam pipes. A deposit consisting of CaCO3 and CaSO4 forms a thick and hard crust called boiler scale. This boiler scale is a bad conductor of heat and hence more fuel is consumed for heating water.
ii) On adding washing soda (Na2CO3) the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions which cause hardness are precipitated as insoluble carbonates and the precipitate can be removed by filtration.
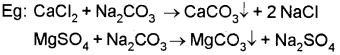
iii) Calgon process
b) H2O2 must be kept in plastic vessel in dark because the rough glass surface causes its decomposition. Also a small amount of phosphoric acid, glycerol or acetanilide is added to H2O2 which retards its decomposition.
Question 8.
About 18% of the total production of dihydrogen is from coal. (March – 2013)
a) What is coal gasification’?
b) How is dihydrogen produced by a ‘water-gas shift reaction’?
c) Write any wo uses of dihydrogen.
Answer:
a) The process of producing ‘Syngas’ (miniature of CO and H2) from coal is called coal gasification.
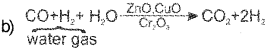
This is called watergas shift reaction.
c) 1) It is used in the manufature of HCI, NH3, CH3OH, Nitric acid etc.
2) It is used in the hydrogenation of oils.
Question 9.
a) Water is an amphoteric substance. Justify. (Say – 2013)
b) Hydrides are binary compounds of hydrogen with other elements. Give one example each for electron-deficient and electron-rich hydride.
Answer:
a) Water can act as acid and a base and therefore is said to have amphoteric nature. It acts as a base towards an acid stronger than itself and as an acid in the presence of base stronger than itself. Thus, it acts as an iacid with NH3 and a base with H2S.
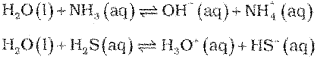
b) Electron deficient hydride : Diborane (B2H6) Electron rich hydride : NH3, HF etc.
Question 10.
a) H2O2 is a bleaching agent. Why?
b) Complete the following reaction.
![]()
c) In a seminar if you are asked to present a paper on hydrogen economy, write any two points you are going to include in your paper.
Answer:
a) The bleaching action of H2O2 is due to the nascent oxygen which it liberates on decomposition.
H2O2 → H2O + [O]
The nascent oxygen oxidises the colouring matter to colourless products.
![]()
c) Hydrogen economy refers to the use of dihydrogen as an alternative source of energy. The basic principle of a hydrogen economy is the transportation and storage of energy in the form of liquid or gaseous dihydrogen. Advantage of a hydrogen economy is that energy is transmitted in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
Question 11.
a) Give one reaction supporting the amphoteric nature of water. (August – 2014)
b) Write the names of any two electron-rich hydrides.
c) Complete the following reaction
Answer:
a) Water n act as acid and a base and therefore is said to have amphoteric nature. acts as a base towards an acid stronger than itself and as an acid in the presence of base stronger than itself. Thus, it acts as an iacid with NH3 and a base with H2S.
Question 12.
a) ‘Syngas’ is a mixture of (March – 2015)
i) CO and H2O
ii) CO and H2
iii) CO2 and H2
iv) CH4 and CO
b) i) A sample of river water does not give lather with soap easily when it is cold, but on heating gives ready lather with soap. Why?
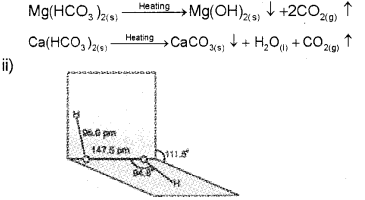
ii) Draw the structure of a hydrogen peroxide molecule.
Answer:
a) ii) CO and H2
b) i) River water has temporary hardness due to the presence of dissolved salts like calcium hydrogen carbonate, Ca(HCO). and/or magnesium hydrogen carbonate, Mg(HCO3)2. On heating, the soluble Mg(HCO3)2, is converted to insoluble Mg(OH3)2, and soluble Ca(HCO)2 is changed to insoluble CaCO3 which are precipitated.
Question 13.
Hydrogen reacts with most of the metals and non-metal Is to form hydrides. (Say – 2015)
a) Elements in which one of the following group/groups of the periodic table do not form hydrides?
i) Groupsl5, 16, 17
ii) Group 13
iii) Groups 7, 8, 9
iv) Group 14
b) Explain the different types of covalent hydrides with suitable examples.
Answer:
a) iii) Groups 7, 8,9
b) There are three types of covalent hydrides.
1) Electron-deficient hydrides: they have too few electrons for writing their conventional Lewis structure, They act as Lewis acids. e.g. Diborane (B2H6)
2) Electron-please hybrids : They have required number of electrons to write their conventional Lewis structures. e.g. Methane (CH4)
3) Electron-rich hydrides : They have excess electrons which are present as lone pairs. They behave as Lewis bases. e.g. ammonia (NH3)
Question 14.
a) Hydrogen peroxide restore the colour of lead paintings. Give a reason. (March – 2016)
b) How does the atomic hydrogen torch function for cutting and welding purpose?
Answer:
a) It is due to the oxidising action of H2O2. It oxidises black lead sulphide (PbS) to white lead sulphate (PbSO4).
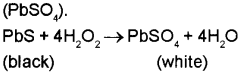
b) In atomic hydrogen torches, atomic hydrogen atoms produced by dissociation of dihydrogen with the help of an electric arc are allowed to recombine on the surface to be welded to generate the temperature of 4000 K. Hence these are used for cutting and welding purposes.
Question 15.
a) Discuss the position of hydrogen in the periodic table. (Say – 2016)
b) Account for the following:
i) H2O2 is a bleaching agent.
ii) Density of ice is lower than that of water.
Answer:
a) Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table. It has one electron in its K shell and has electronic configuration as 1s1. But it is difficult to give a proper place to hydrogen in the periodic table because of its resemblance with halogens as well as alkali metals.
The resemblance with alkali metals:
1) Contains one electron in the valence shell
2) Exhibits +1 oxidation state.
3) Acts as a reducing agent.
4) Forms oxides, halides and sulphides.
Differences from alkali metals:
1) High ionisation enthalpy.
2) H does not exists freely in aqueous solution.
3) Hydrogen halides are different from halides of alkali metals.
The resemblance with halogens:
1) Needs one electron to attain the configuration of nearest noble gas (He).
2) It forms a diatomic molecule (H2).
3) Exhibits-1 oxidation state.
4) Combines with metals and non-metals.
5) High ionisation enthalpy.
The difference from halogens:
1) Less tendency to form hydrides.
2) Absence of unshared electrons.
3) Oxide (H2O) is neutral.
Thus, hydrogen is unique in behaviour and is, best placed separately in the periodic table,
b) i) The bleaching action of H2O2 is due its ability to oxidise the colouring matter.
H2O2 → H2O + [0]
Colouring matter + [O] → Oxidised matter
ii) In ice each H2O molecule is tetrahedrally surrounded by four neighboring H2O molecules with their oxygen atoms occupying the corners of a tetrahedron. There are four hydrogen atoms around each oxygen atom of which two are bonded by covalent bonds whereas the other two are linked through hydrogen bonds. This gives highly ordered three-dimensional structure having large vacant spaces which may be compared to open cage. Due to open cage-like structure, ice has a relatively larger volume for a given mass of liquid water. Consequently, the density of ice is less than water and it floats over water.
Question 16.
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. But in free state it is almost not found in earth’s atmosphere. (March – 2017 )
a) Suggest any three method for the preparation of H2 gas by selecting suitable substance given below.
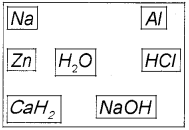
b) Do you expect carbon hydrides of the type CnH2n+2 to act as Lewis acid or base? Why?
Answer:

b) No. This is because CnH2n+2 represents electron’ precise hydrides. These compounds have the required number of electrons to write their conventional Lewis structures. All elements of group 14 form such compounds. They cannot act as Lewis acids due to the absence of electron-deficient orbitals and cannot act as Lewis bases due to the absence of lone pair of electrons.
We hope the Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
