Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions is part of Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer . Here we have given Plus One Chemistry Previous Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions.
Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks. (March – 2009)
a) The oxidation state of Cl in HCI04 is …………
b) A reducing agent is a substance which ………… electrons in a chemical reaction.
c) Among the elements Flurine and Iodine, ………… exhibit both positive and negative oxidation states.
Answer:
a) HCIO4
1 + x + Δx- 2 = 0
1+ x – 8 = 0
x – 7 = 0
x = 7
b) donates
c) Iodine
Question 2.
Chemical reactions which involve oxidation and reduction are called redox reactions. The unbalanced equation in the ionic form of a redox reaction is shown below. (March – 2010)
a) Identify the oxidizing agent in this reaction.
b) Name the species getting oxidized in the above reaction.
c) Balance the above equation by the oxidation number method.
![]()
Answer:
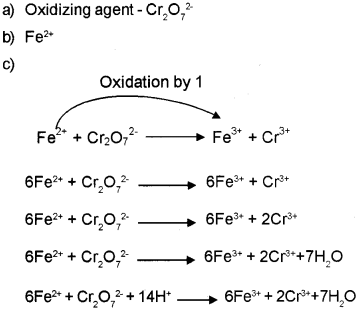
Question 3.
A farmer prepared 1% solution of copper sulphate using iron rod as the stirrer for preparing Bordeaux mixture. Next day he notices that the blue color almost disappeared and the iron get coated with reddish brown material. (Say – 2010)
a) What is the reddish brown material deposited on the iron rod?
b) Account forthe color change of the solution.
c) Justify that the above phenomenon is a redox reaction.
Answer:
a) Copper is the reddish brown material deposited on the iron rod.
b) Due to salvated electrons.
c) Oxidation potential of Fe is greater than that of copper.
Question 4.
Balance the following equation by the half reaction method. (March – 2012)
![]()
Answer:
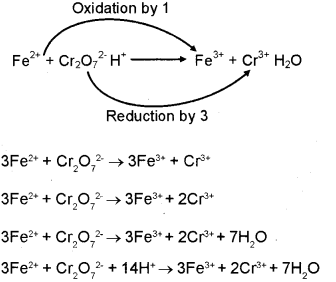
Question 5.
The chemical reactions taking place in electro chemical cells are redox reactions. A Daniel cell is represented below. (Say – 2011)
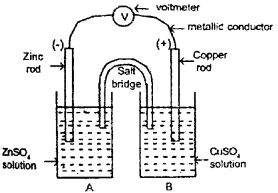
a) Asthe reaction proceeds in this cell one of the metal rod gets dissolved in its solution and the other metal get deposited from the solution to the metal rod. Which metal is getting deposited?
b) Identify the metal which is acting as the oxidizing agent in this reaction.
c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction taking place at compartment A.
Answer:
a) Cu is deposited on the copper rod from the solution.
b) Cu2+(aq) is the oxidising agent.
c) Zn(a) → Z2+(aq) + 2e-
Question 6.
In redox reactions, oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. (Say – 2011)
a) How are oxidation and reduction related to the oxidation number?
b) During a group discussion, one of your friends argues that thermal decomposition of KCIO3 is a redox reaction while that of CaCO3 is not a redox reaction. Give your opinion and substantiate.
Answer:
a) Oxidation is a chemical process in which there is an increase in the oxidation number of an element and reduction is a chemical process in which there is a decrease in the oxidation number of an element.
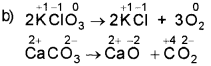
Both reactions are not a redox reaction. In both reaction there is no change in oxidation state ie no loss or gain of electorns.
Question 7.
a) Using stock notation, represent the following compounds. FeO and MnO2. (Say – 2012)
b) Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously. Write any two redox reactions.
Answer:
a) FeO → Fe(ll) O – Iron (II) oxide
MnO2 Mn(IV) O2 → Manganese (IV) oxide
b) 1) H2O2 → H2O + 1/2 O2
2) H2O + F2 → HF + HOF are Redox reactions.
Question 8.
Competitive electron transfer reactions are utilized in the construction of Galvanic cells. (March – 2013)
a) Write the redox reaction involved when metallic cobalt is placed in a nickel sulphate solution. (Note : Only the ionic reaction is expected).
b) In the reaction Pb + PbO2(s) + 2H2 SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2 O(i) identify the following:
i) Substance oxidied
ii) Substance reduced
iii) Oxidizing agent
iv) Reducting agent?
Answer:
a) Co + Ni2+ → CO2+ + Ni
b) In the reats
Pb0(s) + Pb+4 O2(s) + 2H2 SO4(aq) → 2 Pb+2 SO4(aq) + 2H2 O(i)
i) Substance oxidised → Pb
ii) Substance reduced → PbO2
iii) Oxidising agent → PbO2
iv) reducing agent → Pb
Question 9.
a) Calculate the oxidation number of Cr in Cr2O3 and S in H2SO4. (Say – 2013)
b) In disproportionation reaction an element in one oxidation state is simultaneously oxidised and reduced. Identify the element undergoing disproportionation in the following reaction
P4 + 3O + 3H2O → PH3 + 3H2PO2
Answer:
a) Oxidation number of Cr in Cr2O3:
2 x + 3(-2) = 0
2 x – 6 = 0 2x = 6
x = 3
Oxidation number of S in H2SO4:
2(+1) + x + 4(-2) = 0
2 + x – 8 = 0
x = 6
b) Phosphorus is simultaneously is oxidised and reduced. Hence, the element undergoing disproportionation is P.
Question 10.
a) Write the formula of the following compounds. (March – 2014)
i) Nickel Sulphate
ii) Tin Oxide
b) Fluorine reacts with ice as given below:
H2O(s) + F2(g) → HF(g) + HOF(g)
Justify that this is a redox reaction.
Answer:
a) i) NiSO4
ii) SnO2
![]()
In this reaction oxidation number of F2 changes from zero to -1 in HF and HOF whereas oxidation number of oxygen changes from -2 in H2O to zero in HOF. Thus, F2 is reduced, whereas oxygen is oxidised and, therefore, it is a redox reaction.
Question 11.
a) Using stock notation, represent the following compounds: (August – 2014)
i) HAUCI4
ii) MnO2
b) i) Define the electronic concept of oxidation and reduction.
ii) Find out the oxidizer and reducer in the following reaction on the basis of the electronic concept. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) 2NaCI(s)
Answer:
a) i) HAU(III)CI4
ii) Mn(IV)O2
b) i) Oxidation – Loss of electron(s) by any species. Reduction – Gain of electron(s) by any species,
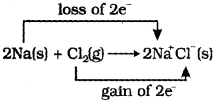
Oxidiser – Cl2, since it is the acceptor of electrons. Reducer – Na, since it is donor of electrons.
Question 12.
a) Given the redox reaction : (March – 2015)
![]()
i) Identify the species which undergo reduction and which undergo oxidation.
ii) Identify the reductant and oxidant in the above reaction.
b) Among the following reactions, identify the one which is NOT a redox reaction.
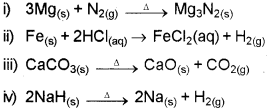
Answer:
![]()
Species undergoing reduction – CuO
Species undergoing reduction – H2
ii) Reductant – H2
Oxidant – CuO
![]()
Question 13.
Identify the oxidant and reduction in the following ionic equation and balance it using oxidation number method.
![]() (March – 2015)
(March – 2015)
Answer:

Question 14.
Redox reactions can be considered as electron transfer reactions. In an experiment a copper rod is dipped in Ag NO3 solution. (March – 2016)
a) What happens to the colour of the solution and why?
b) Identify the oxidizing and reducing agent in this reaction.
c) Calculate the oxidation number of Cr in K2 Cr2 O7 and P in H2P2O5.
Answer:
a) The solution develops blue colour due to the formation of Cu2+ ions on account of the reaction: Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
b) Here Ag+(aq) is the oxidising agent and Cu(s) is the reducing agent.
c) Oxidation number of Cr in K2 Cr2 O7 is +6
Oxidation number of P in H4P2O5 is +4
(Actually, the compound is H4P2O5 in which oxidation state of P is +3)
Question 15.
In a redox reaction, reduction and oxidation takes place simultaneously. (Say – 2016)
a) Write the reclox reaction ¡n Daniefl cell.
b) When CuSO4 solution stored in iron vessel, the blue colour changes to pale green. Do you agree with it? Justify.
Answer:
a) Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
b) Yes.
Since Fe is more reactive than Cu it displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution to form pale green coloured FeSO4.
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq)
Question 16.
Permanganate ion reacts with bromide ion in basic medium to give manganese dioxide and bromate ion., Write the balanced equation for the reaction using oxidation number method. Skeletal equation is MnO4 + Br → MnO2 + BrO3. (March – 2017)
Answer:
Step 1: The skeletal equation is: MnO4(aq) + Br(aq) → MnO2(s) + BrO3(aq)
Step 2: Assign oxidation numbers for Mn and Br
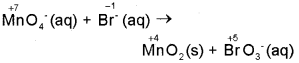
Step 3: Calculate the increase and decrease of oxidation number, and make the increase equal to the decrease by multiplying with a suitable number.
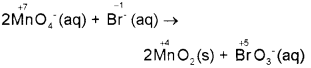
Step 4: As the reaction occurs in the basic medium, and the ionic charges are not equal on both sides, add 20H- ions on the right to make ionic charges equal.
![]()
Step 5:Count the hydrogen atoms and add an appropriate number of water molecules (i.e., one H20 molecule) on the left side to achieve a balanced redox change.
![]()
We hope the Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
