Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons is part of Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer . Here we have given Plus One Chemistry Previous Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons.
Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
Question 1.
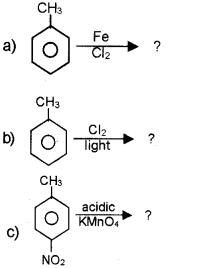
Answer:
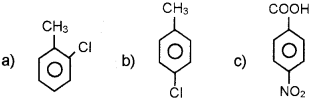
Question 2.
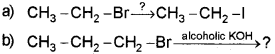
c) Freons are known with respect to ozone layer depletion.
i) WhatareFreons?
ii) Howcan you prepare a Freon from CCI4?
Answer:
a) Kl
b) CH3 – CH = CH2
e) Chioroflurocarbon
Question 3.
a) How will you prepare ethane by Kolbe’s electrolytic method? (March – 2009)
b) Explain Markownikoff’s rule for the addition reaction using a suitable example.
Answer:
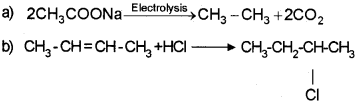
Addition of an hydrohalogen into an alkene takes place in such a way that its -ve part will go to the region having lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Question 4.
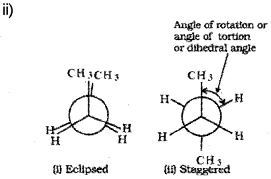
a) A spatial arrangement of atoms that can be converted into one another by rotation around a C-C single bond are called conformations. (March – 2010)
C-C single bond are called conformations.
i) Represent Sawhorse and Newman projection formulae of staggered and eclipsed conformation of ethane.
ii) Compare the stabilities of staggered and eclipsed conformations.
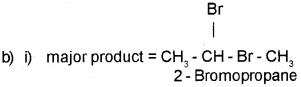
b) Consider the reaction given below:
![]()
i) Identify the major product obtained.
ii) Name the rule governing the formation of the major product.
Answer:
a) Sawhorse method
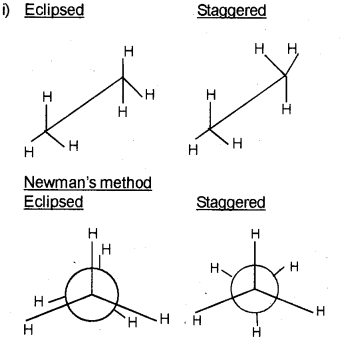
b) In staggered form, minimum repulsive force, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule. In eclipsed method increase in electron cloud re-pulsions. Due to this molecule has more energy and it has lesser stability.
Question 5.
In a special condition addition of HBrto unsymmetrical alkene takes place contrary to Markovnikov’s rule. (Say – 2010)
a) What is the special condition?
b) Give the mechanism of anti-Markovnikov’s addition of HBr to propene.
Answer:
a) In the presence of organic peroxide.
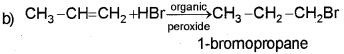
The mechanism of Antimarkovnikov’s rule involves the following steps.
1) Initiation
2) Propagation
3) Termination
Question 6.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds: (March – 2011)
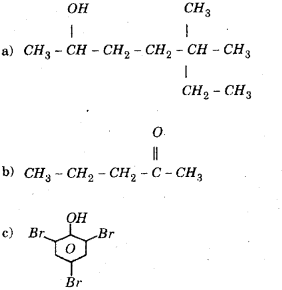
Answer:
a) 5, 5 -Dimethylheptan – 2-01.
b) 2-Pentanone
c) 2, 4, 6- tnbromo phenol
Question 7.
a) Complete the following reactions:
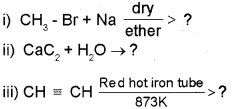
b) llustrate Markovnikov’s rule taking the example of propene.
Answer:
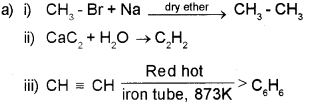
b) When a hydrogen halide is added to an ansymmetrical alkene, the halogen atom will goes to the doubley bonded carbon containing lesser no. of hydrogen atom.
Question 8.
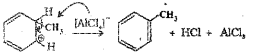
The higher homologue of benzene can be prepared by the following reaction. (Say – 2011)
![]()
a) Identify the reagent A.
b) Which named reaction is this?
c) Writethe reaction mechanism of this reaction.
Answer:
a) CH3CI
b) Friedei-Craft’s alkylation
c) Step I: Generation of the electrophile, CH3+
![]()
Step II: Attack of the electrophile CH3+ on benzene ring to form a sigma complex in which one of the carbon is sp3 hybridized.
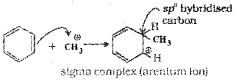
Step III: Removal of proton – The sigma complex releases a proton from the sp3 hybrid carbon by the attack of AICI4.
Qn. 9.
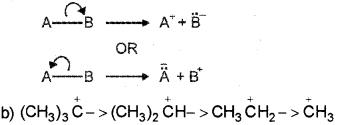
Carbocations are formed by the heterolytic cleavage of a covalent bond. (March – 2012)
a) What is heterolytic bond fission?
b) Arrange the following carbocations in the increasrig order of stability:
(CH3)2 CH3, CH3+, (CH3)3C, CH4CH2+
Answer:
a) When the bond between two atoms A-B breaks in such a way that the shared pair of electrons stays on any one of the atoms. The proces is called hetrolytic fission.
Qn. 10.
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only.
a) Complete the following chemical reactions:
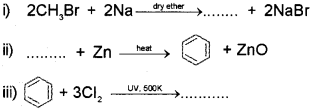
OR
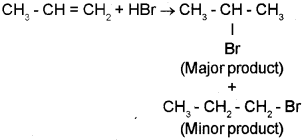
b) Analyze the following reaction:
CH3-CH = CH2 + H- Br → ’A’ + ‘B’
If ‘A’ is the major product and ‘B’ is the minor product, identify ‘A’ and ‘B’. Also name the related rule.
Answer:
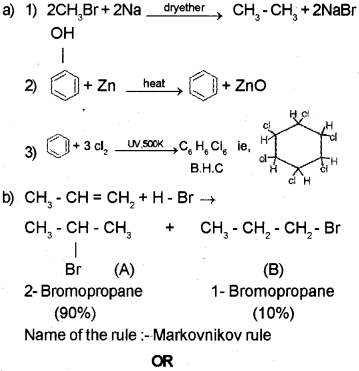
a) Steam distillation
b) Prussian blue – Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
c) Kjeldahl’s method for estimation of nitrogen. Organic compound containing nitrogen is heated with con. H2SO4 in presence of K2SO4 and CuSO4, the nitrogen present in it is quantitatively converted to ammonium sulphate. The re-saltant liquid is then treated with excess of alkali and the liberated ammonic gas is absorbed in a known volume of excess of standard acid. The amount of ammonia is estimated by determining the amount of acid neutralised by back titration with some standard alkali.
Let the weight of organic compound be Wg. Let VmLof N1 HCI be required to completely neutralise alt the ammonic gas evolved from back titration.

Qn. 11
a) Name the following reaction. (Say – 2012)
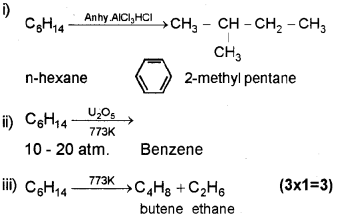
b) Naphthalene is an aromatic compound. Explain its aromaticity using Huckel’s rule.
Answer:
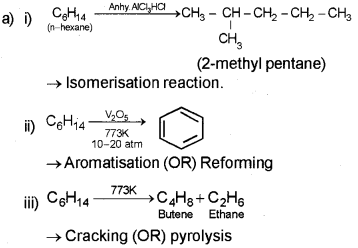
b) According to Huckel – Cychc, conjugated, planar systems having (4n + 2) π electrons where ‘n’ may be 0, 1, 2, 3 will behave as an aromatic compound.
![]()
because it is cyclic, conjugated(ie. alternate single and double bond), planar systems having (4n + 2) π electrons (ie. 10 ir electron (n = 2)
Qn. 12.
Free rotation is possible with respect to a C-C bond in the case of alkanes. (March – 2013)
a) The repulsive interaction between the adjacent bonds in a conformation is called ……………….
b) Draw Newman’s projections of the two conformers of ethane. Which among these is more stable? Justify.
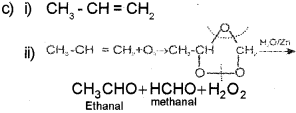
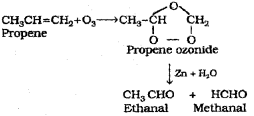
c) An alkene on ozonolysis followed by reduction of the ozonide formed with zinc and water gave a mixture of ethanal and methanal.
i) Identify the alkene.
ii) Illustrate the above mentioned the above mentioned reaction using the chemical equation.
Answer:
a) Torsional strain
b) New man’s projection of the conformers of ethene
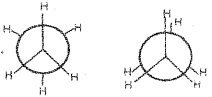
The staggered form is more stable due to
1) Hydrogens of both carbon atoms are visible
2) H-atoms are as far apart from each other
3) There is a minimum repulsion or torsional strain.
Qn. 13.
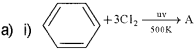
500K Name the products. (Say – 2013)
ii) Draw the Newman projections of the eclipsed and staggered conformations of n-butane.
b) What ¡s Baeyers reagent? Write the chemical equation of its reaction with ethylene (CH2 = CH2).
Answer:
a) i) Benzene Hexachioride (BHC)
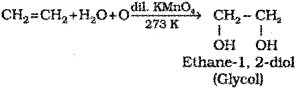
b) Dilute aqueous solution of potassium permanganate ¡s called Baeyer’s reagent.
Qn. 14.
a) Write the products of the following chemical reactions and also name them. (March – 2014)
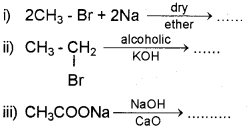
b) An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gave two molecules of formaldehyde. Write the name of ‘A’ and the chemical equation of ozonolysis.
Answer:
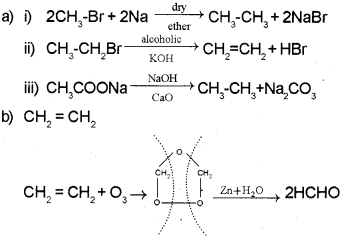
Qn. 15.
a) Draw the cis-and tía nsisom ers of the following compound: (August – 2014)
C2 H5CCH2 CCH3C2H5
b) Complete the following reactions.
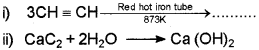
c) Draw the sawhorse projections for eclipsed and staggered forms of a ethane molecule.
OR
a) How is alkane prepared by Kolbe’s electrolytic method?
b) Select the activating groups from the following:
i) -NH2
ii) -SO3H
iii) -CH3
iv) -COOH
c) What is ozonolysis? Wnte the names of the producs obtained when propene undergoes ozonolysis.
Answer:
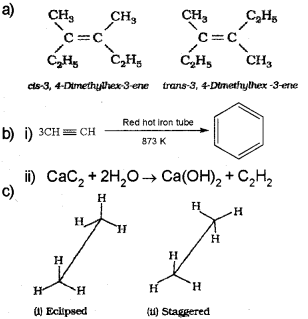
OR
a) An aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salt of a carboxylic acid on electrolysis gives alkane containing even number of carbon atoms at the anode.
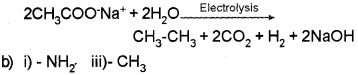
c) Ozonolysis of alkenes involves the addition of ozone molecule to alkene to form ozonide, and then clevage of the ozonide, and then cleavage of the ozonide by Zn – H2O to smaller molecules. When propene ¡s subjected to ozonolysis a mixture of ethanal and methanal are formed.
Qn. 16.
a) Complete the following chemical equations: (March – 2015)
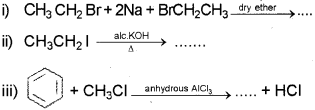
b) Explain geometrical isomerism taking 2-Butene asanexample.
Answer:
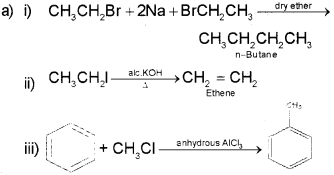
b) Geometrical isomerism is a type of stereo isomerism caused by the restricted rotation of atoms or groups around the doubly bonded carbon atoms. This gives se to different geometries of such compounds. Stereo isomers of this type are called geometrical isomers. The isomer in which two identical atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond is called cis isomer and the other isomer in which identical atoms or groups lie on the opposite sides of the double bond is called transisomer.
2-Butene has two geometrical isomers namely, cis-But-2-ene and trans-But-2-ene as shown below:
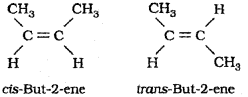
Question 17.
Controlled oxidation of alkanes in the presence of suitable catalysts give a variety of products, (Say – 2015)
a) Complete the following reaction
![]()
Free rotation about a carbon-carbon single bond is permitted in an alkane molecule.
What are conformers? Draw the structure of the eclipsed and staggered conformers of ethane in Sawhorse and Newman projections and explain their relative stability.
Answer:
a) HCHO
b) Conformers are the different spatial arrangements of atoms in a molecule which can be converted to one another by rotation around a C-C single bond.
Sawhorse projections:
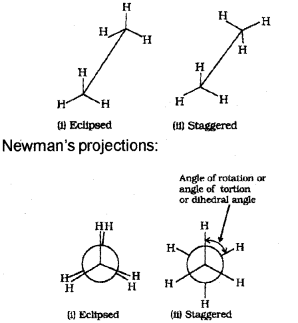
The staggered form has least torsional strain and the eclipsed form has maximum torsional strain. Hence, staggered form is more stable than the eclipsed form.
Question 18.
a) 1-alkynes are weakly acidic in nature. Give any two reactions to show the acidic character of ethyne. (March – 2016)
b) From the following, select the one in which Markownikoffs rule is best applicable.
i) C2H4 + HCI
ii) C3H6 + Br2
iii) C3H6 + HBr
iv) C3H8 + CI2
c) Hydrocarbons exhibit isomerism.
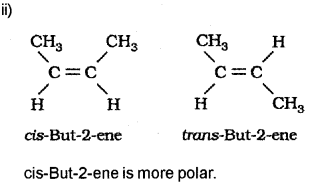
i) Name the type of isomerism exhibited by 2-Butene.
ii) Draw the structure of the isomers of 2-Butene and select the one which is more polar.
Answer:
a) 1) Ethyne reacts with sodium to form monosodium ethynide and disodium ethynide with the liberation of dihydrogen gas.
2) Ethyne reacts with sodamide (NaNH2) sodium ethynide with the liberation of ammonia gas.
b) iii) C3H6 + HBr
c) I) Geometrical ¡somerism or cis-trans isomerism (Or any other type of isomerism shown by 2-Butene such as position isomerism, chain isomerism or ring-chain isomerism)
Qn. 19.
a) i) Complete the following reactions: (Say – 2016)
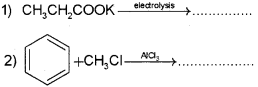
ii) Write the names of the above reactions.
b) Baeyer’s reagent is used to find whether the compound is unsaturated or not. What is Baeyer’s reagent?
c) What is the product formed 4ien ethylene ¡s treated, the Baeyer’s reagent?
Answer:
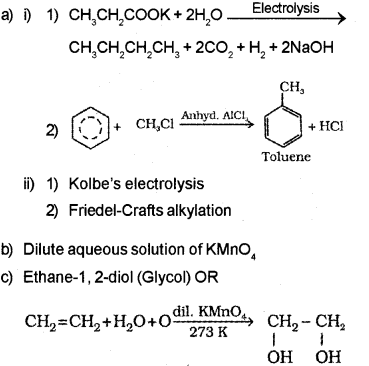
ii) 1) Kolbe’s electrolysis
2) Friedel-Crafts alkylation
b) Dilute aqueous solution of KMnO4
c) 1,2-dio I (Glycol) OR
Question 20.
Benzene and benzenoid compounds show aromatic character. (March – 2017)
a) Selectthearomaticcompoundsfromthefollowing:
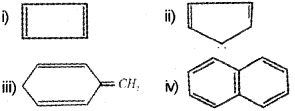
b) Suggest a method to convert Ethyne to benzene.
c) Give the products formed when benzene reacts with
i) CH3CI /AlCl3
ii) Cl2/hu
Answer:
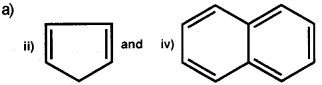
b) Ethyne (acetylene) on passing through red hot iron tube at 873K undergoes cyclic polymerization to form benzene.
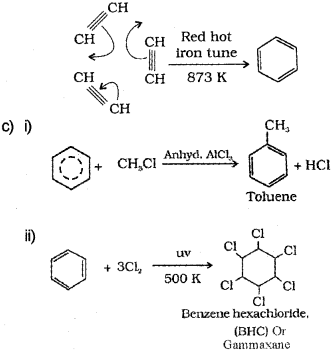
We hope the Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
