Kerala Plus One Business Studies Notes Chapter 4 Business Services
Contents
- Meaning – Nature of Service – Differences between Services and Goods – Types of services
- Banks – Types of banks – Commercial bank – Functions of Commercial bank – e-Banking – Benefits of e-banking
- Insurance – Functions of insurance – Principles of insurance
- Types of insurance – Life insurance – Fire insurance – Marine insurance
- Communication services – Postal services Telecom services
- Transportation – Functions of Transportation
- Warehouse – Functions – Types of warehouses Services are those identifiable, essentially intangible activities that provides satisfaction of wants. For example, consulting a doctor for medical help, getting legal opinion from an advocate etc.
Nature of Services:
1. Intangibility:
Services are intangible, i.e., they cannot be touched. They are experiential in nature, eg: Treatment by a doctor.
2. Inconsistency:
Since there is no tangible product, services have to be performed according to the demand and expectations of the different customers, eg: Mobile services/Beauty parlour.
3. Inseparability:
Another important characteristic of services is the simultaneous activity of production and consumption being performed, i.e. They are inseparable, eg: ATM may replace clerk but presence of customer is a must.
4. Less Inventory:
Services cannot be stored for future use.
5. Involvement:
Participation of the customer in the service delivery is a must.
Difference between Services and Good:
| Service | Goods |
| An activity or process. e.g., watching a movie in a cinema hall | A physical object, e.g., a video cassette of movie |
| Heterogeneous | Homogenous |
| Intangible e.g., doctor treatment | Tangible e.g., medicines |
| Different customers having different Demands, e.g. mobile services | Different customers getting standardised demands fulfilled. |
| Simultaneous production and consumption, eating an ice-cream in a restaurant | Separation of production and consumption, e.g., purchasing ice cream from a store |
| Cannot be kept in stock. | Can be kept in stock |
| participation of customers at the time of service delivery | Involvement at the time of delivery not possible |
Types of service:
1. Business Services:
Business services are those services which are used by business enterprises for the conduct of their activities. For example, banking, insurance etc.
2. Social Services: Social services are generally provided voluntarily in pursuit of certain social goals. Eg. improve the standard of living for weaker sections of society, to provide educational services to their children etc.
3. Personal Services: Personal services are those services which are experienced differently by different customers, eg: tourism, restaurants, etc. Banking.
According to Banking Regulation Act 1949, banking means “accepting, for the purpose of lending and investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheques, draft, order or otherwise”. Banks can be classified into the following:
- Commercial banks
- Cooperative banks
- Specialised banks
- Central bank
1. Commercial Banks:
Commercial Banks are banking institutions that accept deposits and grant short-term loans and advances to their customers. There are two types of commercial banks, public sector and private sector banks.
(a) Public Sector Bank:
Public sector banks are those banks, which are owned and managed by the Government. eg. SBI, PNB, IOB etc. Presently there are 28 public sector banks in India
(b) Private Sector Bank:
Private sector banks are owned and managed by private parties. Eg. HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank and Jammu and Kashmir Bank etc. ICICI bank is the largest private sector bank in India.
2. Cooperative Banks:
Cooperative Banks are governed by the provisions of State Cooperative Societies Act. They managed on the principles of co-operation, self help and mutual help.
3. Specialised Banks:
Specialised banks are foreign exchange banks, industrial banks, development banks, export-import banks which provide financial aid to industries, joint venture projects and foreign trade.
4. Central Bank:
The Central bank supervises, controls and regulates the activities of all the commercial banks of that country. It also acts as a government banker. It controls and coordinates currency and credit policies of any country. The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of our country.
Insurance:
Insurance is an agreement between two parties whereby one party undertakes, in exchange for a consideration, to pay the other party an agreed sum of money to compensate the loss, damage or injury caused as a result of some unforeseen events.
- Policy: The agreement or contract entered into by the insured and insurer is known as a ‘policy’.
- Insurer: The firm which insures the risk of loss is known as ‘insurer’.
- Insured: The person whose risk is insured is called ‘insured’.
- Premium: The consideration in return for which the insurer agrees to compensate the insured is known as ‘Premium’.
Functions of Insurance:
1. Providing certainty:
Insurance provides certainty of payment for the risk of loss. The insurer charges premium for providing the certainty
2. Protection:
Insurance provides protection from probable chances of loss.
3. Risk sharing:
Insurance helps in sharing of risk. The premium collected from a large number of people are used for compensating the loss of a few.
4. Assist in capital formation:
The accumulated funds of the insurer received by way of premium are invested in various income generating schemes.
Principles of Insurance:
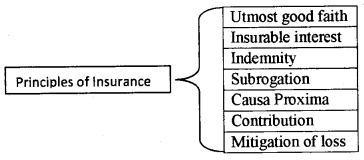
1. Utmost good faith:
The insured must disclose all material facts about the subject matter to the insured. Otherwise the insurer can cancel the contract. The insurer must disclose all the terms and conditions jn the insurance contract to the insured.
2. Insurable interest:
The insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest means the interest shown by the insured in the continued existence of the subject matter or the financial loss he is subjected to on the happening of an event against which it has been insured.
3. Indemnity:
All insurance contracts, except life insurance are contracts of indemnity. According to the principle of indemnity, in the event of occurrence of loss, the insured will be indemnified to the extent of the actual value of his loss or the sum insured which ever is less. The objective behind this principle is nobody should treat insurance contract as the source of profit.
4. Subrogation:
According to this principle, after the insured is compensated for the loss to the property insured by him the right of ownership of such property passes on to the insurer. This is because the insured should not be allowed to make any profit, by selling the damaged property.
5. Causa proxima:
When the loss is the result of two or more causes, the proximate cause for the loss alone will be considered by the insurance company for admitting the claim.
6. Contribution:
In certain cases, the same subject matter is insured with one or more insurer. In case there is a loss, the insured is eligible to receive a claim only up to the amount of actual loss suffered by him.
7. Mitigation of loss:
This principle states that it is the duty of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize the loss or damage to the insured property. If reasonable care is not taken then the claim from the insurance company may be rejected.
Types of Insurance:
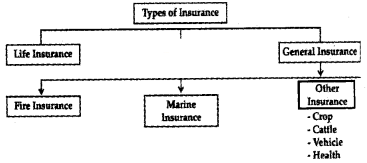
Life Insurance:
It is a contract whereby the insurer undertakes to pay a certain sum of money either on the death of the insured or on the expiry of a specified period of time in consideration of a certain amount (premium) paid by the insured either in lump sum or in installments.
Elements of Life insurance contract:
- The life insurance contract must have all the essentials of a valid contract
- Life insurance is a contract of utmost good faith
- The insured must have insurable interest in the life assured
- Life insurance is not a contract of indemnity
Types of life insurance policies:
1. Whole Life Policy:
In this kind of policy, the sum assured becomes payable only on the death of the policy holder.
2. Endowment Life Policy:
Here, the sum assured becomes payable either at the end of the stipulated period or on the premature death of the policyholder which ever is earlier.
3. Joint Life Policy:
Under this policy, the lives of two or more persons are insured jointly. The sum assured becomes payable on the death of any one, to the survivor. Usually, this policy is taken up by husband and wife jointly or by two partners of the firm.
4. Annuity Policy:
Under this policy, the assured sum or policy money is payable after the assured attains a certain age in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual installments.
5. Children’s Endowment Policy:
This policy is taken by a person for his/ her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age.
Fire Insurance:
Fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of premium, undertakes to compensate the insured for the loss or damage suffered due to fire. The premium is payable in single installment.
A claim for loss by fire must satisfy the two following conditions:
- There must be actual loss;
- Fire must be accidental and non intentional.
Elements of Fire insurance contract:
- The insured must have insurable interest in the subject matter.
- Fire insurance is a contract of utmost good faith.
- It is a contract of indemnity.
- Fire must be the proximate cause of damage or loss.
Marine Insurance:
Marine insurance is an agreement by which the insurance company agrees to indemnify the owner of a ship or cargo against risks which are incidental to marine adventures. eg: collision with other ship, collision of ship with the rocks, fire, storm etc. Marine insurance insures ship hull, cargo and freight.
Elements of Marine insurance contract:
- Marine insurance is a contract of indemnity
- It is a contract of utmost good faith
- Insurable interest must exist at the time of loss
- The principle of causa proxima will apply to it.
There are three types of Marine insurance. They are:
Ship or hull insurance:
when the owner of a ship is insured against loss on account of perils of the sea, it is known as Ship or Hull insurance.
Cargo insurance:
Marine insurance that covers the risk of loss of cargo is known as Cargo Insurance.
Freight insurance:
The shipping company may seek insurance of the risk of loss of freight. Such a marine insurance is known as freight insurance.
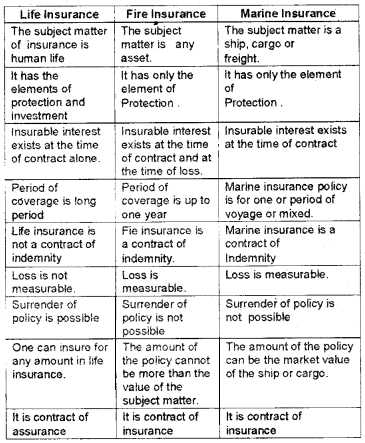
Differences between Life, Fire and Marine insurance:
Communication services:
Communication services are helpful to business for establishing links with the outside world viz., suppliers, customers, competitors etc. The main services which help business can be classified into postal and telecom.
1. Postal services:
Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services across India. Various facilities provided by postal department are:
(a) Financial facilities:
They provide postal banking facilities to the general public and mobilise their savings through the saving schemes like public provident fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, National Saving Certificate, Recurring Deposit Scheme and Money Order facility.
(i) Mail facilities: Mail services consist of
- Parcel facilities that is transmission of articles from one place to another
- Registration facility to provide security of the transmitted articles
- Insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post.
(b) Allied Postal Services
- Greetings Post: Greetings card can be sent through post offices.
- Media Post: Corporate can advertise their brands through postcards, envelopes etc.
- Speed Post: It allows speedy transmission of articles to people in specified cities.
- e-bill post: The post offices collect payment of telephone, electricity, and water bills from the consumers.
- Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service.
2. Telecom Services:
The various types of telecom services are
1. Cellular mobile services:
Mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
2. Radio paging services:
It means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed line services:
It includes voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkage for long distance traffic.
4. Cable services:
Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially one way entertainment related services.
5. VSAT services (Very small Aperture Terminal):
It is a Satellite based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH services (Direct to Home):
It is a Satellite based media services provided by cellular companies with the help of small dish antenna and a set up box.
Transportation:
Transport refers to the activity that facilitates physical movement of goods and individuals from one place to another transportation removes the hindrance of place, i.e., it makes goods available to the consumer from the place of production.
Functions of Transport:
- Helps in the movement of goods and materials from one place to another
- Helps in the stabilisation of prices.
- Helps in the social, economic and cultural development of the country
- Helps in national and international trade
- Facilitates large scale production
- Generates employment opportunities
- Increases growth of towns and cities
- Connects all part of the world
Types of Transport:
- Land Transport
- Road Transport
- Rail Transport
- Pipeline Transport
- Water Transport
- Inland water Transport
- Ocean Transport
- Air Transport.
Warehousing:
Warehousing means holding or preserving goods in huge quantities from the time of their purchase or production till their consumption. Warehousing is one of the important auxiliaries to trade. It creates time utility by bridging the time gap between production and consumption of goods.
Functions of Warehousing
- Warehouse helps in supplying the goods to the customers when it is needed.
- By maintaining a balance of supply of goods warehousing leads to price stabilization.
- By keeping the goods in the warehouse, the trader can relieve himself of the responsibility of keeping of goods.
- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulkquantity of goods into smaller quantities.
- Warehousing helps in the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses.
- The functions of grading, branding and packing of goods can be done in warehouses.
- The warehousing receipt can be used as a collateral security for obtaining loans.
Types of Warehouses:
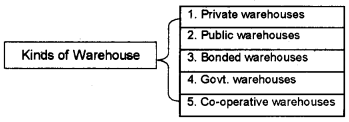
(a) Private warehouses: Private warehouses are owned by big business concerns or wholesalers for keeping their own products.
(b) Public warehouses:
They are owned by some agencies, offer storage facilities to the public after charging certain fees. The working of public warehouses is subject to some govt, regulations. They are also known as Duty paid warehouses.
(c) Bonded warehouses:
These warehouses are used to keep imported goods before the payment of import duties. It offers many advantages to the importer, i.e. The importer can releases the goods in part by paying the proportionate amount of duty. The goods can be branded, blended and packed in the warehouse itself.
(d) Government warehouses:
These warehouses are fully owned and managed by the government. For example, Food Corporation of India, State Trading Corporation, and Central Warehousing Corporation.
(e) Co-operative warehouses:
Marketing co-operative societies and agricultural oo operative societies have set up their own warehouses for members of their cooperative society.
