Kerala Plus One Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Identify which of the following is not a social responsibility of business _________
1. Offering goods and services at reasonable price.
2. Keeping environment pollution free
3. Giving reasonable pay to workers
4. Help in nation building activities
Answer:
3. Giving reasonable pay to workers
Question 2.
State Bank of India gives scholarship to bright students each year. This is a part of their __________
1. Sales promotion
2. Social responsibility
3. Charity work
4. Business ethics
Answer:
2. Social responsibility
Question 3.
Application of general ethics and principles in business practice is ____________
Answer:
Business ethics
Question 4.
It is the belief in what is right, proper and just. Identify it.
Answer:
Business ethics
Question 5.
______________ is the code of conduct followed and performed by businessmen.
Answer:
Business ethics
Question 6.
Which among the following is not a case for an ethical activity.
1. child labour
2. equal pay for equal work
3. dumbing of waste in river
4. high usage of preservatives in products.
Answer:
2. Equal pay for equal work
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Roy and Rejitha joined in a factory as peons on the same day. Both of them are doing 8 hrs work a day. Roy is paid ₹100 while Rejitha ₹80 per day. Do you think the owner of the factory is fair to Rejitha? If not, give your opinion. (2)
Answer:
No. The owner of the factory is not fair to Rejitha. It is the social and moral responsibility of the business to offer equal pay for equal work without considering any caste, sex, etc.
Question 2.
Explain the need for pollution control. (2)
Answer:
Need for Pollution Control:
1. Reduction of health hazard:
Pollution control measures can check diseases like cancer, heart attack & lung complications and support a healthy life on earth.
2. Reduced Risk of Liability:
It is a sound business policy to install pollution control devices in its premises to reduce the risk of liability of paying compensation to the affected people.
3. Cost Saving:
An effective pollution control programme is needed to save costs of operating business.
4. Improved Public Image:
A firm that adopts pollution control measures enjoys a good reputation as a socially responsible enterprise.
5. Other social benefits:
Pollution control results in many other benefits like clearer visibility, cleaner buildings, better quality of life, and the availability of natural products in a purer form.
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
George is working in the manufacturing industry. The manager compels him to do 10hrs work continuously without giving any additional benefits. Do you agree with the manager? Give your suggestions. (3)
Answer:
No. We cannot agree with the decision of the manager. It is against the social responsibility of the business. George has to work only 8 hours a day. Compelling to do 10 (without any additional benefits) hours is a violation of human right. Managers cannot ask a worker to do work continuously without giving remuneration. It is also a violation of human rights.
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match column A with columns B and C
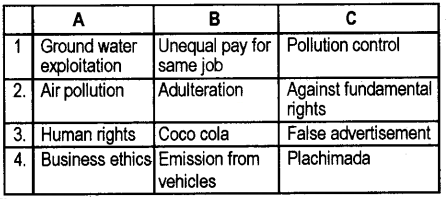
Answer:
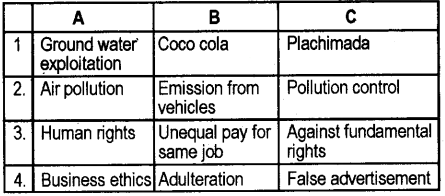
Question 2.
Jaleel, owner of a fish stall, usually sells damaged and decayed fish by pouring chemicals, ice, along with sea sand for creating an impression in the minds of consumers that it is newly caught. Is it justifiable from the point of view of business ethics? How will it affect the reputation of the business? (4)
Answer:
Business ethics refer to the socially determined moral principles which should govern business activities.
A few examples of business ethics are
- charging fair prices from customers
- providing quality products
- using fair weights for measurement of commodities
- giving fair treatment to workers & earning only reasonable profits.
Ethical business behaviour improves public image, earns people’s confidence and trust, and leads to greater success. Selling damaged and decayed fish is unethical.
It will affect the reputation of the business and finally it leads to business loss. He must not goods of low quality for personal gain. No business can make progress without adopting ethical values.
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Anchu, a stationery dealer distributed good quality products at a low price by suffering huge losses, in order to eliminate the competition from Chinju, another stationery dealer, in the same locality. When Chinju stopped her business, Anchu started to supply low-quality products at high prices. (5)
- Can you justify Anchu’s action from point of view of society?
- Give a few undesirable practices which a business follow in a real-life situation.
Answer:
1. No. We cannot justify Anchu’s action. It is against business ethics. Business ethics refers to moral values that should be followed in business activities.
2. Examples of unethical practices are
- Providing low-quality products at high prices.
- Making misleading advertisements.
- Creating artificial scarcity to increase demand.
- Keeping false accounts to avoid paying taxes.
- Acceptance of bribe for personal benefits.
- Manufacture and sale of adulterated goods.
- Polluting the environment.
- Exploiting workers.
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Six Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What steps can an enterprise take to protect the environment from the dangers of pollution? (6)
Answer:
Role of Business in Environmental Protection:
1. A definite commitment by top management to create a work culture for environmental protection
2. Ensuring that commitment of environmental protection is shared throughout the enterprise by all divisions and employees.
3. Developing clear cut policies and programmes for purchasing good quality raw materials, introducing superior technology, using scientific techniques of disposal of waste and developing employee skills for pollution control
4. Complying with the laws and regulations enacted by the Government for prevention of pollution.
5. Participation in government programs relating to management of hazardous substances, cleaning up of polluted rivers, plantation of trees, and checking deforestation.
6. Periodical assessment of pollution control programmes in terms of costs and benefits with a view to improve them.
7. Arranging educational workshops and training materials to share technical information with everyone involved in pollution control.
Question 2.
Explain the elements of business ethics. (6)
Answer:
Business Ethics:
Ethics is concerned with what is right and what is wrong in human behavior. Business ethics refer to the socially determined moral principles which should govern business activities.
Business ethics is the code of conduct followed and performed by every business. Ethical business behavior improves public image earn’s public confidence and leads to greater success.
Examples of Business Ethics:
- Charging fair prices from customers
- Using fair weights for measurement of commodities
- Giving fair treatment to workers
- Earning reasonable profits.
- Avoiding adulteration, hoarding etc.
- Using environmentally friendly products
Elements of Business Ethics:
1. Top management commitment:
The Chief Executive Officer and higher-level managers must give continuous leadership for developing and upholding the moral values of the organisation.
2. Publication of a Code:
‘Code’ refers to a formal written document of the principles, values and standards that guide a firm’s actions. It may cover the areas of fundamental honesty and adherence to laws, product safety and quality, health and safety in the workplace, etc.
3. Establishment of Compliance Mechanism:
A suitable mechanism should be developed to comply with the ethical standards of the enterprise.
4. Employees Involvement:
To make the ethical business a reality, employees at all levels must be involved.
5. Measuring Results:
Ethical results must be verified and audited how far work is being carried according to ethical standards.
Plus One Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Build up arguments for and against social responsibilities. (8)
Answer:
Arguments in favour of Social Responsibility:
1. Justification for Existence and Growth:
The prosperity and growth of business is possible only through continuous service to society.
2. Long term Interest of the firm:
A firm can improve its image and builds goodwill in the long run when its highest goal is to serve the society.
3. Avoidance of government regulations:
Business can avoid the problem of government regulations by voluntarily assuming social responsibilities.
4. Maintenance of society:
Law alone can’t help out people with all the difficulties they face. A socially responsible business can contribute something for social peace and harmony.
5. Availability of resources with business:
Business has valuable financial and human resources which can be effectively used for solving problems of the society.
6. Better environment for doing business:
Social responsibility creates better environment for business operations as it improves quality of life and standard of living of the people.
7. Contribution to social problems:
Some of the social problems have been created by business firms themselves such as pollution, unsafe workplaces, discrimination, etc. Therefore, it is the moral obligation of business to solve such social problems.
Arguments Against Social Responsibility:
1. Violation of profit maximization objective:
According to this argument, business exists only for the maximum profit to its shareholders and do not have a responsibility to society as a whole.
2. Burden on consumers:
Involvement of business in social responsibilities involve a lot of expenditure which will ultimately be borne by the customers.
3. Lack of Social Skills:
The business firms and managers are not expert to tackle social problems like poverty, overpopulation etc.
4. Lack of public support:
Business cannot fulfill social responsibility because of lack of public confidence & cooperation.
Question 2.
Mr. Biju, a readymade garment manufacturer, is of the view that “different interest groups always claim some sort of protection from the business as such. These interest groups, no doubt consist of persons connected with business in one way or other, such as shareholders, employees, society and so on”. Do you agree with this statement? Explain. (8)
OR
“Business is a social institution having responsibilities towards different interest group.” Do you agree. Explain the responsibility towards each group.
Answer:
Social Responsibility towards different interest groups
1. Responsibility towards share holders or owners:
- Provide a fair and regular return on the investment of shareholders.
- Provide regular and accurate information on the financial position of the firm.
- To ensure the safety of their investment.
2. Responsibility Towards the workers:
- Providing fair wages
- Providing good working conditions and welfare amenities.
- Respect democratic rights of workers to form
unions.
3. Responsibility toward consumers:
- Supply right quality and quantity of goods and services at reasonable prices.
- Avoiding unfair trade practices like adulteration, poor quality, misleading advertisement etc.
- Inform them about new products, its features, uses and other matters relating to the products.
- To handle the customers grievance promptly.
4. Responsibility Towards Government:
- Respect the laws of the country
- Pay taxes regularly and honestly.
- act according to the well accepted values of society.
5. Responsibility towards community:
- Make employment opportunities
- Protect the environment from pollution.
- To uplift the weaker sections of society
Question 3.
Prosperity and higher living standards are the hallmarks of industrial development for any nation. But during this course, it equally causes damages to the environment. (8)
- Explain the different types of pollution.
- Substantiate the above statement with regard to various types of pollution.
Answer:
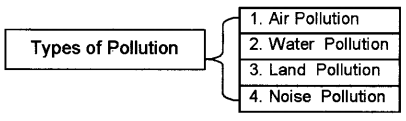
Business & Environmental Protection Causes of Pollution: Many industrial organisations have been responsible for causing air, water, land and noise pollution.
1. Air Pollution:
Air pollution is mainly due to Carbon monoxide emitted by automobiles and smoke and other chemicals from manufacturing plants. It has created a hole in the ozone layer leading to global warming.
2. Water pollution:
Water becomes polluted primarily from chemical and waste dumping. It has led to the death of several animals and posed a serious problem to human life.
3. Land Pollution:
Dumping of toxic wastes reduces the quality of land and making it unfit for agriculture or plantation.
4. Noise Pollution:
Noise caused by the running of factories and vehicles create a serious health hazard such as loss of hearing, malfunctioning of the heart and mental disorders.
Question 4.
Explain the role of business in environmental protection. (8)
Answer:
Role of Business in Environmental Protection:
- A definite commitment by top management to create a work culture for environmental protection
- Ensuring that commitment of environmental protection is shared throughout the enterprise by all divisions and employees.
- Developing clear cut policies and programmes for purchasing good quality raw materials, introducing superior technology, using scientific techniques of disposal of waste and developing employee skills for pollution control
- Complying with the laws and regulations enacted by the Government for prevention of pollution.
- Participation in government programs relating to management of hazardous substances, cleaning up of polluted rivers, plantation of trees, and checking deforestation.
- Periodical assessment of pollution control programmes in terms of costs and benefits with a view to improve them.
- Arranging educational workshops and training materials to share technical information with everyone involved in pollution control.
