Kerala Plus One Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Business Services
Plus One Business Services One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the type of account opened in a bank with an overdraft facility
Answer:
Current Account
Question 2.
DTH services are provided by
Answer:
Cellular companies
Question 3.
CWC Stands for
Answer:
Central warehousing corporation
Question 4.
Mr. James running a software development business, incur heavy expenditure for replacement of computers due to updation in technology. To avoid this expenditure he may opt for
(a) Factoring
(b) Venture capital
(c) Leasing
(d) Merchant banking
Answer:
(c) Leasing
Question 5.
Name the type of account opened in the bank with overdraft facility
Answer:
Current account
Question 6.
Classify the following into appropriate categories SBI, Federal Bank, American Express Bank.
Answer:
- SBI – Public Bank
- Federal Bank – Private bank
- American Express bank – Foreign bank
Question 7.
Which among the following helps in issue management of shares,
(a) Mutual fund
(b) Merchant banks
(c) Venture Capital
(d) Factoring
Answer:
(b) Merchant banks
Question 8.
Classify the following bank into Appropriate Categories,
- IDBI
- HDFC
- Axis Bank
- Canara Bank
- HSFC
- CITI Bank
Answer:
- IDBI – Private Bank
- HDFC – Private Bank
- Axis Bank – Public Bank
- Canara Bank – Public Bank
- HSFC – Private Bank
- CITI Bank – Foreign Bank
Question 9.
Which facility allows a current account holder to withdraw more amount than his deposit?
Answer:
Overdraft
Question 10.
Which of the following is not applicable in life insurance contract?
(a) Conditional contact
(b) Unilateral contract
(c) Indemnity contract
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Indemnity contract
Question 11.
When the same subject matter is insured with more than one insurer, it is called
Answer:
Double insurance
Question 12.
________ is a contract of insurance entered into by the insurer with another insurer to reduce the risk.
Answer:
Reinsurance
Question 13.
Rajiv insures his shop for ₹5,00,000 against fire. His shop is completely damaged by a mob attack. Rajiv claims ₹5,00,000/- from the insurance company.
- Will the company admit the claim of Rajiv?
- Which principle of insurance is applicable here?
Answer:
- No.
- Causa Proxima
Question 14.
Principle of indemnity does not apply to __________
(a) Life insurance
(b) Health insurance
(c) Fire insurance
(d) Marine insurance
Answer:
(a) Life insurance
Question. 15
I will give security against fraudulent practices of employees who deal with cash or other variables. Can you identify me? Explain its features?
Answer:
Fidelity insurance
Question 16.
Govind insures his shop for ₹6,00,000. in a fire accident. The shop incurred a loss of ₹3,00,000. But he claimed for the assured sum. Will the insurance co admit the claim in full? Identify the principle of insurance which is applicable here.
Answer:
No. Principle of indemnity
Question 17.
Life insurance is a contract of ________
Answer:
Guarantee
Question 18.
_______ principle states, the insurer step into the shoes of insured.
Answer:
Subrogation.
Question 19.
Jacob purchased a new car for ₹15,00,000 and insured it with National insurance company and Oriental Insurance Company for ₹15,00,000 each. On an accident, the car was damaged completely and he claimed compensation from both companies.
- Can he get compensation from both companies?
- Identify relevant principle of insurance.
Answer:
- No
- Principle of Contribution
Question 20.
According to _________ principle, the insured is not allowed to make any profit out of his loss.
Answer:
Indemnity
Question 21.
Rajan wants to take an insurance policy covering the risk arising from the dishonesty of employees. Which type to policy close he have to take?
Answer:
Fidelity insurance
Question 22.
__________ is a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of premium, undertakes to compensate the insured for the loss or damage suffered due to fire.
Answer:
Fire insurance
Plus One Business Services Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define service and goods. (2)
Answer:
Services are those identifiable and intangible activities that provide satisfaction of wants. Goods is a physical product which can be delivered to a purchaser and involves the transfer of ownership from the seller to customer.
Question 2.
Explain various telecom services available for enhancing business. (2)
Answer:
The various types of telecom services are:
1. Cellular mobile services:
Mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
2. Radio paging services:
It means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed line services:
It includes voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkage for long distance traffic.
4. Cable services:
Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially one way entertainment related services.
5. VSAT services (Very small Aperture Terminal):
It is a Satellite-based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH services (Direct to Home):
It is a Satellite based media services provided by cellular companies with the help of small dish antenna and a set up box.
Question 3.
Mr. Dino is running a textile shop. He insured the shop for ₹1,00,000 against natural calamities. After this the shop was completely destroyed by fire due to electrics short circuit. He claimed for compensation. But the insurance company refused to admit the claim on the ground that the shop was insured against natural calamities. (2)
- Can you justify the decision of insurance company.
- Which principle of insurance is applicable here.
Answer:
- Yes.
- Causa proxima. It states that insurance company will admit the claim only if mishap has resulted directly by an event covered by under insurance.
Question 4.
Mr. Sabu is running a provision store. He insured the shop for ₹ 50,000 against fire. One day during course of business the shop caught fire and Mr. Sabu purposefully did not take any efforts to minimize the loss. He claimed for compensation. In this situation. (2)
- What will be your decision assuming that you are the officer in charge of admitting the claims for insurance company?
- Which principle is applicable here?
Answer:
- The claim can not be admitted because the insurer did not take any reasonable steps to minimize the loss.
- Principle of mitigation of loss
Question 5.
Why do we say that the principle of indemnity is not applicable to life insurance. Illustrate your answer. (2)
Answer:
The loss due to death of the insured cannot be measured in terms of money. So principle of indemnity is not applicable to Life insurance.
Question 6.
Mr. Sibi purchased a new car and it was completely damaged in an accident. Subsequently, he lodged a claim with the insurance company and the same was admitted. Later, the insurance company recovered the destroyed property. (2)
- Why did the company take ownership of the car?
- State the relevant principle. Explain.
Answer:
- Ownership of the damaged car is vested with the insurance company.
- According to the principle of subrogation, once the claim of the insured has been settled, the right of ownership of such property passes to .the insurer.
Question 7.
Mr. Anand your friend has started a new business. He decided to open a bank account with SBI. He has only a vague idea about the type of accounts available to the business people. So he seeks your help to choose the most favourable account for him. Give reason. (2)
Answer:
Mr. Anand can open current account. There is no restriction on the frequency and volume of deposits or withdrawals of money.
Question 8.
Match the following
| A | B |
| Warehousing | Mutual Funds |
| Unit Trust Of India | Hindrance Of Time |
| Insurance | External Comunication |
| Telecom | Causa proxima |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Warehousing | Hindrance Of Time |
| Unit Trust Of India | Mutual Funds |
| Insurance | Causa proxima |
| Telecom | External Comunication |
Plus One Business Services Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mr. Janardhanan, a business man, has a current a/c of ₹1,00,000 in the S.B.I. He is in need of another ₹50,000 for the purpose of expansion of his business. By availing which facility, can he have money from the bank? Explain its features. (3)
Answer:
Overdraft: Overdraft is an arrangement where customers are allowed to withdraw up to a level over and above their deposits in the current account. Interest is to be paid only on the actual amount of overdraft availed by him. OD is granted to businessmen against their current account.
Question 2.
Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department. (3)
Answer:
1. Postal services:
Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services across India. Various facilities provided by postal department are
(a) Financial facilities:
They provide postal banking facilities to the general public and mobilise their savings through the saving schemes like public provident fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, National Saving Certificate, Recurring Deposit Scheme and Money Order facility
(b) Mail facilities:
1. Mail services consist of
- Parcel facilities that is trans-mission of articles from one place to another
- Registration facility to provide security of the transmitted articles
- Insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post.
2. Allied Postal Services
- Greetings Post: Greetings card can be sent through post offices.
- Media Post: Corporate can advertise their brands through post cards, envelops etc.
- Speed Post: It allows speedy transmission of articles to people in specified cities.
- e-bill post: The post offices collect payment of telephone, electricity, and water bills from the consumers.
- Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service.
(2) Telecom Services:
The various types of telecom services are:
1. Cellular mobile services:
Mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
2. Radio paging services:
It means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed line services:
It includes voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkage for long distance traffic.
4. Cable services:
Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially one way entertainment related services.
5. VSAT services (Very Small Aperture Terminal):
It is a Satellite-based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH services (Direct to Home):
It is a Satellite based media service provided by cellular companies with the help of a small dish antenna and a setup box.
Question 3.
What is e-banking? What are the advantages of e-banking? (3)
Answer:]
e-banking is a service provided by many banks, that allows a customer to conduct banking transactions, such as managing savings, checking accounts, applying for loans or paying bills over the internet using a personal computer, mobile telephone. Eg. Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT), ATM etc.
Question 4.
Babu insures his shop for ₹3,00,000. In a fire accident the shop burned and incurred a loss of ₹1,50,000. Babu claimed for the assured sum i.e, ₹3,00,000. (3)
- Will the insurance company admit the claim in full. Why?
- Which principle of insurance is applicable here.
Answer:
- No. According to the principle of indemnity, in the event of occurrence of loss, the insured will be indemnified to the extent of actual value of his loss or the sum insured which ever is less,
- Principle of Indemnity
Question 5.
Mrs. Anjali has a medical shop and it is insured with two insurers for ₹50,000 each against natural calamities. During the rainy season, the subject matter was partly destroyed by flood. The total amount of loss was estimated at ? 30,000. She claimed compensation from both insurance companies for ₹30,000 each. (3)
- Can she get the claim from both the insurers?
- Justify your answer with regard to the relevant principle of insurance.
Answer:
- No. She cannot get claim from both the insurance.
- According to the principle of contribution, the insured is eligible to receive a claim only up to the amount of actual loss suffered by her.
Question 6.
Mr. Joy keep stock of inflammable materials in his shop premises, takes an insurance policy for the shop against fire. But he did not disclose anything about the inflammable materials to the insurance company. Later, the inflammable goods caught fire and the shop was completely destroyed by fire. The insurance company refused to admit the claim of Mr. Joy on the ground that he did not disclose information about the inflammable goods. (3)
- Can you justify the decision of the insurance company?
- What principle of insurance is applicable here ?
Answer:
- Yes.
- Principle of utmost good faith. The insured must disclose all material facts about the subject matter to the insurer. Otherwise, the insurer can cancel the contract. The insurer must disclose all the terms and conditions in the insurance contract to the insured.
Plus One Business Services Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mr. Surendran is running an electrical shop which is insured against fire for ₹50,000. Due to heavy rainfall his stock was fully damaged and he claimed for compensation. The insurance company refused to admit the claim as goods were not insured against natural calamities. Can you justify the decision of the insurance company? Which principle of insurance is applicable here? (4)
Answer:
Yes. The decision taken by the insurance company is correct. Mr. Surendran has no right to claim compensation from the insurance company. The principle of insurance applicable here is causa proxima. It states that insurance company will admit the claim only if the mishap has resulted directly by an event covered under the insurance. An event covered under the insurance.
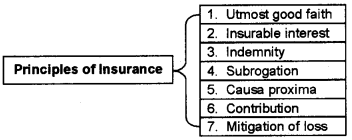
Question 2.
Draw a chart showing types of insurance. (4)
Answer:
Question 3.
Explain the functions of Transport. (4)
Answer:
Functions of Transport:
- Helps in the movement of goods and materials from one place to another
- Helps in the stabilisation of prices.
- Helps in the social, economic and cultural development of the country
- Helps in national and international trade
- Facilitates large scale production
- Generates employment opportunities
- Increases growth of towns and cities
- Connects all part of the world
Plus One Business Services Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the functions of warehousing. (5)
Answer:
Functions of Warehousing:
- Warehouse helps in supplying the goods to the customers when it is needed.
- By maintaining a balance of supply of goods warehousing leads to price stabilization.
- By keeping the goods in the warehouse, the trader can relieve himself of the responsibility of keeping of goods.
- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods into smaller quantities.
- Warehousing helps in the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses.
- The functions of grading, branding, and packing of goods can be done in warehouses.
- The warehousing receipt can be used as collateral security for obtaining loans.
Question 2.
Name the principle of insurance violated in the following cases. (5)
1. ‘A’does not own the building but is trying to get it insured as a party to the insurance policy.
2. ‘A’ enters into life insurance contract with LIC of India. ‘A’ was ailing with heart decease but he did not reveal this at the time of entering the contract.
3. ‘B’ enters into insurance contract with two companies ‘C’ and ‘D’. The subject matter is a building worth ₹ 5 lakh. The building caught fire and properties worth ₹3 lakhs were damaged. ‘C’ paid the entire claim and asked ‘D’ to share the claim. ‘D’ denies.
4. Goods worth ₹50,000 are damaged and the insurance company pays the claim to ‘Z’ for the loss. ‘Z’ not only took compensation for loss but also claims the damaged goods.
5. ‘P’ takes an insurance policy for ₹1 lakh with ‘Q’ company. The goods of ‘P’ are damaged due to fire the loss incurred is ₹25,000. ‘Q’ shall restore the actual loss but ‘P’ claims full amount of the policy.
Answer:
- Principle of insurable interest
- Principle of utmost good faith
- Principle of contribution
- Principle of subrogation
- Principle of Indemnity
Question 3.
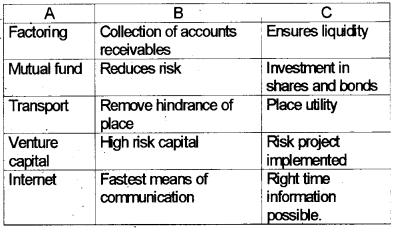
Match A with B and C.
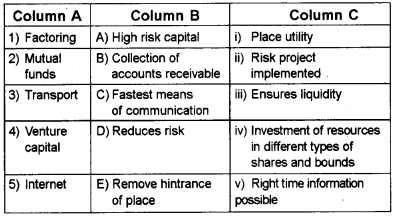
Answer:
Plus One Business Services Six Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Distinguish between life insurance and general insurance. (6)
Answer:
| Life Insurance | Fire insurance | Marine Insurance |
| The subject matter of insurance is human life | The subject matter is any asset. | The subject matter is a ship, cargo or freight. |
| it has the elements of protection and investment | It has only the element of Protection | It has only the element of Protection. |
| insurable interest exists at the time of contract alone. | Insurable interest exists at the time of contract and at the time of loss. | Insurable interest exists at the time of contract |
| Period of coverage is long period | Period of coverage is up to one year | Marine insurance policy is for one or period of voyage or mixed. |
| Life insurance is not a contract of indemnity | Fie insurance is a contract of indemnity. | Marine insurance is a contract of indemnity |
| Loss Is not measurable. | Loss is measurabie. | Loss is measurable. |
| Surrender of policy is possible | Surrender of policy is not possible | Surrender of policy is not possible |
| One can insure for any amount in life insurance. | The amount of the policy cannot be more than the value of the subject matter. | The amount of the policy can be the market value of the ship or cargo. |
| It is contract of assurance | It is contract of insurance | It is contract of insurance |
Question 2.
I will give security against fraudulent practices of employees who deal with cash or other valuables
- Can you identify me?
- Explain my features. (6)
Answer:
1. Fidelity insurance.
2. This type of policy is taken by the employer of a fire to cover the risk arising out of fraud or dishonesty of his employees. Banks, Financial institutions and other business firms commonly use such insurance policies.
Question 3.
What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics? (6)
Answer:
Nature of Services
1. Intangibility:
Services are intangible, i.e., they cannot be touched. They are experiential in nature, e.g. Treatment by a doctor.
2. Inconsistency:
Since there is no tangible product, services have to be performed according to the demand and expectations of the different customers, e.g. Mobile services/Beauty parlour.
3. Inseparability:
Another important characteristic of services is the simultaneous activity of production and consumption being performed, i.e. They are inseparable, e.g. ATM may replace clerk but presence of customer is a must.
4. Less Inventory:
Services cannot be stored for future use.
5. Involvement:
Participation of the customer in the service delivery is a must.
Plus One Business Services Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Suppose you have visited a commercial bank in your locality. Then what information you have collected from there with regard to. (8)
- Deposit schemes
- Lending scheme
- Other services
Answer:
Functions of Commercial Banks:
a. Acceptance of deposits:
A commercial bank accepts following types of deposits. They are
1. Current deposit:
This type of account is usually opened by business men.lt carries no interest. There are no restrictions on number of deposits or withdrawals.
2. Savings deposit:
Savings accounts are for encouraging savings by individuals. Banks pay rate of interest as decided by RBI on these deposits. Withdrawal from these accounts has some restrictions.
3. Fixed deposit:
Fixed accounts are time deposits with higher rate of interest. They cannot be withdrawn before the maturity period.
b. Lending of funds:
The second important function of a commercial bank is to grant loans and advances out of the money received through deposits. These advances can be made in the form of overdrafts, cash credits, discounting trade bills, term loans, consumer credits and other miscellaneous advances.
1. Cash Credit:
Under this arrangement, the bank advances loan up to a specified limit against current assets. The bank opens an account in the name of the borrower and allows him to withdraw the money up to the sanctioned limit. Interest is charged on the amount actually withdraw.
2. Bank Overdraft:
Overdraft is an arrangement where customers are allowed to withdraw up to a level over and above their deposits in the current account. Interest is to be paid only on the actual amount of overdraft availed by him. OD is granted to businessmen against their current account.
3. Discounting of bill of exchange:
Under this, a bank gives money to its customers on the security of a bill of exchange before the expiry of the bill after deducting a small amount of discount.
4. Term Loans:
These loans are provided by the banks to their customers for a fixed period. Interest will be charged to the entire amount of loan.
c. Secondary Functions:
The secondary functions of commercial banks are as under:
1. Agency Functions:
- Cheque facility: Bank collects customers cheque drawn on other bank. There are two types of cheques mainly
Bearer cheques, which are encashable immediately at bank counters Crossed cheques which are to be deposited only in the payees account. - Payment of insurance premium, telephone charges, collection of dividend etc
- Purchase and sale of shares and debentures
- Acting as trustees or executors
- Providing credit information
2. General utility services:
- Providing lockers for safe custody of jewellery and others valuables of customers
- Issuing letter of credit, pay orders, bank draft, credit cards, traveller’s cheques to customers.
- Underwriting issues of shares and debentures
- Providing foreign exchange to importers and traveller’s going abroad.
Bank Draft:
It is a financial instrument with the help of which money can be remitted from one place to another. The payee can present the draft on the drawee bank at his place and collect the money. Bank charges some commission for issuing a bank draft.
Pay Order:
It is almost like a bank draft. Banks issue pay order for local purpose and issue bank draft for outstations.
Question 2.
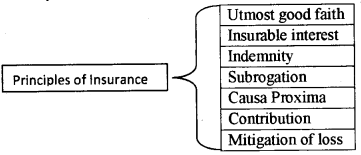
“For the smooth conducting of insurance, the insurer and Insured should know the relevant factors underlying the insurance contracts.” In light of this statement, can you state the principles of Insurance?
Answer:
1. Utmost good faith:
The insured must disclose all material facts about the subject matter to the insured. Otherwise, the insurer can cancel the contract. The insurer must disclose all the terms and conditions in the insurance contract to the insured.
2. Insurable interest:
The insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest means the interest shown by the insured in the continued existence of the subject matter or the financial loss he is subjected to on the happening of an event against which it has been insured.
3. Indemnity:
All insurance contracts, except life insurance are contracts of indemnity. According to the principle of indemnity, in the event of occurrence of loss, the insured will be indemnified to the extent of the actual value of his loss or the sum insured which ever is less. The objective behind this principle is nobody should treat insurance contract as the source of profit.
4. Subrogation:
According to this principle, after the insured is compensated for the loss to the property insured by him the right of ownership of such property passes on to the insurer. This is because the insured should not be allowed to make any profit, by selling the damaged property.
5. Causa proxima:
When the loss is the result of two or more causes, the proximate cause for the loss alone will be considered by the insurance company for admitting the claim.
6. Contribution:
In certain cases, the same subject matter is insured with one or more insurer. In case there is a loss, the insured is eligible to receive a claim only up to the amount of actual loss suffered by him.
7. Mitigation of loss:
This principle states that it is the duty of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize the loss or damage to the insured property. If reasonable care is not taken then the claim from the insurance company may be rejected.
Question 3.
Prepare a seminar paper on Types of warehouses. (8)
Answer:
Warehousing:
Warehousing means holding or preserving goods in huge quantities from the time of their purchase or production till their consumption. Warehousing is one of the important auxiliaries to trade. It creates time utility by bridging the time gap between production and consumption of goods.
Functions of Warehousing:
- Warehouse helps in supplying the goods to the customers when it is needed.
- By maintaining a balance of supply of goods warehousing leads to price stabilization.
- By keeping the goods in the warehouse, the trader can relieve himself of the responsibility of keeping of goods.
- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods into smaller quantities.
- Warehousing helps in the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses.
- The functions of grading, branding and packing of goods can be done in warehouses.
- The warehousing receipt can be used as a collateral security for obtaining loans.
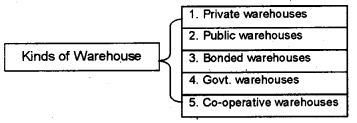
Types of Warehouses:
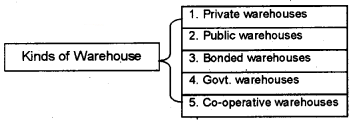
1. Private warehouses:
Private warehouses are owned by big business concerns or wholesalers for keeping their own products.
2. Public warehouses:
They are owned by some agencies, offer storage facilities to the public after charging certain fees. The working of public warehouses is subject to some govt, regulations. They are also known as Duty paid warehouses.
3. Bonded warehouses:
These warehouses are used to keep imported goods before the payment of import duties. It offers many advantages to the importer, i.e. The importer can releases the goods in part by paying the proportionate amount of duty. The goods can be branded, blended, and packed in the warehouse itself.
4. Government warehouses:
These warehouses are fully owned and managed by the government. For example, the Food Corporation of India, State Trading Corporation, and Central Warehousing Corporation.
5. Co-operative warehouses:
Marketing co-operative societies and agricultural oo operative societies have set up their own warehouses for members of their cooperative society.
