Kerala Plus One Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Business
1 Mark Questions and Answers
Plus One Business Studies Malayalam Notes Question 1.
State examples of Analytical industries.
Answer:
Petrol, diesel
Question 2.
Which of the broad categories of industries covers oil refinery and sugar mills?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of them
Answer:
(b) Secondary
Plus One Business Studies Chapter-wise Question Papers Question 3.
Which of the following cannot be classified as an auxiliary to trade?
(a) Mining
(b) Insurance
(c) Warehousing
(d) Transport
Answer:
(a) Mining
Plus One Business Studies Important Questions and Answers Question 4.
The industries which provide support services to
other industries are known as …….
(a) Primary industries
(b) Secondary industries
(c) Commercial industries
(d) Tertiary industries.
Answer:
(d) Tertiary industries
Question 5.
Which of the following cannot be classified as an objective of business?
(a) Investment
(b) Productivity
(c) Innovation
(d) Profit earning
Answer:
(a) Investment
Plus One Business Studies Important Question 6.
Business risk is not likely to arise due to
(a) Changes in government policy
(b) Good management
(c) Employee dishonesty
(d) Power failure
Answer:
(b) Good management
Question 7.
Mr. Abu produces wheat for personal consumption. Will it be a business activity?
Answer:
No. It is not for performed for earning profit.
Question 8.
The human activities that are undertaken with an objective to earn money or livelihood are called ……….
Answer:
Economic Activities.
Question 9.
Activities undertaken to derive mere satisfaction are known as ……..
Answer:
Non-Economic Activities.
Question 10.
The activity is undertaken primarily to satisfy social, religious or cultural requirements of human beings. Which is this activity?
Answer:
Non economic activity
Question 11.
Classify the following activities into Economic and Non-Economic activities ………
- Running a stationery shop
- Conducting a seminar
- Operating a Cine house
- Watching television
Answer:
- Running a stationary shop – Economic activity
- Playing cricket – Non-economic activity
- Operating a cine house – Economic activity
- Watching television – Non-economic activity
Question 12.
Identify the following activities ………..
- A Person visit to the temple for daily prayers.
- Driving a car for rent.
- Running a Hotel.
Answer:
- Non-economic activity
- Economic activity
- Economic activity
Question 13.
Identify the nature of activities of the following persons on the basis of economic and non-economic activities.
- Teacher in a School
- Gardener
- Housewife
- Social Worker
- Businessman
- Doctor
Answer:
- Economic activity
- Economic activity
- Non-economic activity
- Non-economic activity
- Economic activity
- Economic activity
Question 14.
Below are given certain non-economic activities. Convert them into economic activities.
Example: A nurse attending her ailing son. (Non-economic activity)
A nurse attending patients in her hospital. (Economic activity)
- A person working in his own garden.
- A lady preparing food for her husband.
- A man white-washing his own house.
- A teacher teaching his son at home.
- A chartered accountant preparing his own accounts.
Answer:
- A person working in a school garden.
- A lady preparing food in a restaurant.
- A man white-washing the building of a trade centre.
- A teacher teaching students in a school.
- A chartered Accountant preparing accounts of a firm.
Question 15.
Find the odd one
(a) Teaching in a school
(b) Practicing in a court
(c) Praying in a church
(d) Running a hotel
Answer:
(c) Praying in a church
Question 16.
The occupation in which people work for others and get remunerated in return is known as ………..
(a) Business
(b) Employment
(c) Profession
(d) None of them
Answer:
(b) Employment
Question 17.
…… is an economic activity performed for the purpose of earning profit.
Answer:
Business
Question 18.
……. is an occupation involving the provision of personal services of a specialized and expert nature.
Answer:
Profession
Question 19.
……. is an index of performance of the business
Answer:
Profit
Question 20.
Complete the following on the basis of the given hint
Profession: Fee
Business: ………
Employment: ………
Answer:
Business: Profit
Employment: Salary
Question 21.
Which of the following does not characterize business activity?
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Presence of risk
(c) Sale or exchange of goods and services
(d) Salary or wages
Answer:
(d) Salary or wages
Question 22.
Identify the type of activity the following person is doing:-
(a) Alex is an advocate
(b) Balan works in an organization as an Accountant
(c) Chandran buys goods from Banglore and sells in Kerala
(d) David is a doctor and has his own Hospital
Answer:
(a) Profession
(b) Employment
(c) Business
(d) Profession
Question 23.
Identify the following activities and give reason.
(a) A Chartered Account work in a company
(b) A Chartered Account runs a firm
Answer:
(a) Employment
(b) Profession
Question 24.
Identify the type and reward of this activity. Balabhasker, a doctor in a medical college
Answer:
Employment. The reward for employment is salary
Question 25.
Ajith running an internet cafe. Identify the economic activity mentioned here.
Answer:
Business
Question 26.
Mr. Shyam sold his own house for ? 5 lakhs, which is purchased for ? 4 lakhs. Decide whether it is a business activity or not.
Answer:
No. It is not a business activity
Question 27.
Complete the following equation:
Commerce = + Aids to trade
(a) Service
(b) Industry
(c) Business
(d) Trade
Answer:
(d) Trade
Question 28.
……. is the process of buying and selling of goods and services.
Answer:
Trade
Question 29.
Thajudeen, a businessman from Japan purchased goods worth ₹ 5,00,000 from Kumar associates of India. Can you identify which type of trade was conducted between Thajudeen and Kumar associates?
Answer:
Export trade.
Question 30.
Trade between Bombay and Chennai is an example of ……Trade.
Answer:
Home trade
Question 31.
Buying and selling of goods between different countries are called …….
Answer:
Foreign Trade
Question 32.
When trade takes place within the boundaries of a country, it is called ……..
Answer:
Internal trade.
Question 33.
…… is the process of selling goods to a foreign country.
Answer:
Export trade
Question 34.
When goods are purchased from a foreign country, it is known as ……
Answer:
Import trade
Question 35.
……. means importing of foreign goods from some countries to re-export them to other countries.
Answer:
Entrepot trade
Question 36.
When goods are bought in bulk from manufacturers/produces and sold in bulk to retailers is called ……..
Answer:
Wholesale trade
Question 37.
When goods are bought from wholesalers/produces and sold them to consumers is termed as …….
Answer:
Retail trade
Question 38.
Diary farming for milk is an example of ………. industry.
Answer:
Genetic.
Question 39.
Extraction of coal is an example of industries.
(a) Genetic
(b) Construction
(c) Extractive
(d) Manufacturing
Answer:
Extractive industry
Question 40.
Time utility is created by
(a) transport
(b) warehousing
(c) insurance
(d) person
Answer:
(b) warehousing
Question 41.
Complete the following
Removing the hindrance of knowledge: Advertising
Removing the hindrance of time:?
Answer:
Warehousing
Question 42.
Hindrance of knowledge in the exchange of goods are removed by ………
Answer:
Advertisement
Question 43.
……. removes hindrance of person.
Answer:
Trade
Question 44.
……. removes hindrance of place.
Answer:
Transport
Question 45.
……. removes hindrance of risk.
Answer:
Insurance
Question 46.
……… removes hindrance of finance.
Answer:
Banking
2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain any two business activities which are auxiliaries to trade.
Answer:
Auxiliaries to Trade (Aids to trade)
Activities which assist trade are called aids to trade or auxiliaries to trade.

1. Transport & Communication:-
Transport facilitates movement of raw material to the place of production and the finished products from factories to the place of consumption. Communication helps the producers, traders, and consumers to exchange information with one another.
2. Banking & Finance:-
Banking helps business activities to overcome the problem of finance. Commercial banks lend money in the form of overdraft, cash credit, loans, and advances, etc… and they also provide many services required for the business activity.
3. Insurance:-
The goods may be destroyed while in the production process or in transit due to accidents, or in storage due to fire or theft, etc. Insurance provides protection in all such cases.
4. Warehousing:-
The goods should be stored carefully from the time they are produced until the time they are sold. This function is performed by warehouses.
5. Advertising:-
Advertising helps in providing information about available goods and services and create in them a strong desire to buy the product.
Plus one Business Studies Question 2.
Abhijith owns an old car. He sells it and buys a new car. While Ajith purchases a few cars for selling at an assured profit. Do Abhijith and Ajith engage in business activities? Give reason.
Answer:
The activity of Abhjith is not a business activity. But we can say Mr. Ajith engages in business activities. Business is a continuous activity, so there must be regularity in its dealings and its ultimate objective is earning profit. Abhijith’s transaction is casual. So it is not a business activity.
Question 3.
Find the odd one.
- Regularity in service / getting salary/service contract between employer and employee / huge capital investment
- Earning profit / innovation / effective utilization of resources / Appointment letter
Answer:
- Huge capital investment – others are features of employment
- Appointment letter – others are objectives of business
Plus One Business Question 4.
State any two characteristics of ‘business’.
Answer:
Business:-
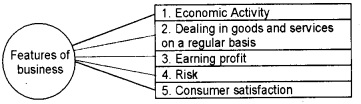
Business may be defined as an economic activity involving the production or purchase and sale of goods and services with the main object of earning profit by satisfying human needs in the society.
Characteristics of business
- Business is an economic activity with the object of earning profit.
- Business includes all the activities concerned with the production or procurement of goods and services.
- There should be a sale or exchange of goods and services for the satisfaction of human needs.
- Business involves dealings in goods or services on a regular basis. Normally, one single transaction of sale or purchase is not treated as a business.
- One of the main objectives of business is to earn maximum profit.
- Business involves risk and uncertainty of income. Risk means the possibility of loss due to change in consumer taste and fashion, strike, lockout competition, fire, theft, etc.
Question 5.
The terms both industry and commerce related to business. As a student how do you correlate these two terms in the business?
Answer:
Business activities can be classified into two. They are Industry and commerce. Industry involves production or processing of goods meant for consumption or for production of other products. Business is a broader term than commerce. Commerce is the sum total of those processes which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of person, place and time in the exchange of commodities. Commerce includes all activities ensuring the free flow of goods and services from the producer to the consumer.
Commerce = Trade + aids to trade.
Question 6.
Define Commerce.
Answer:
Commerce is the sum total of all activities involving the removal of hindrances in the process of exchange of goods and services and facilitates the availability for consumption. So it consists of trade and other support services that facilitate trade.
3 Mark Questions and Answers
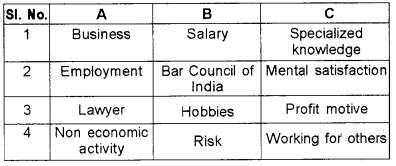
Question 1.
Find the ‘odd one’ and state the reason.
- Teaching in a school, Practising in a court, Praying, Running a hotel.
- Regularity, Body of knowledge, Profit motive, Heavy Risk.
- No capital, Salary, Freedom of work, Service agreement.
Answer:
- Praying – All others are economic activities.
- Body of knowledge – All others are features of Business.
- Freedom of work – All others are features of employment.
Question 2.
Complete the following table with the help of the hints given below.
Question 3.
Identify the following activities and give reason.
- A doctor works in a Government hospital
- A doctor runs his own clinic.
- A doctor treats his own family members.
Answer:
- Employment – Here, the doctor works for others, on a regular basis and gets a salary for his service.
- Profession – Here, the doctor is rendering services for others and gets fees for his service
- Non-economic activity – Here, no monetary benefit is derived but mental satisfaction.
Question 4.
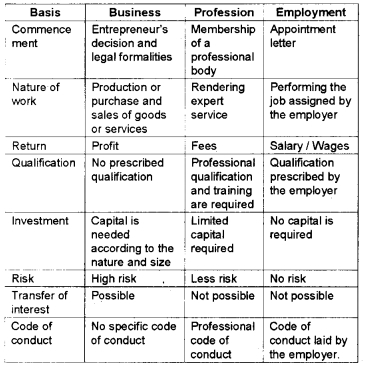
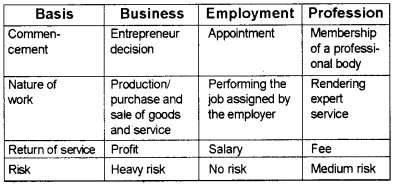
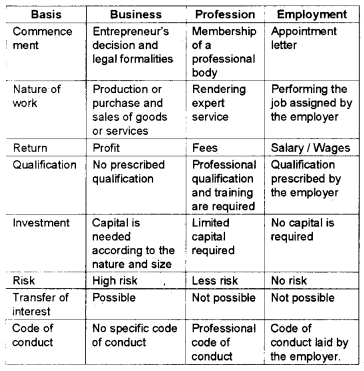
Compare business with profession and employment.
Answer:
Comparison of Business, Profession, and Employment.
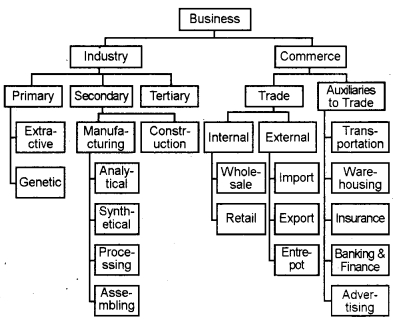
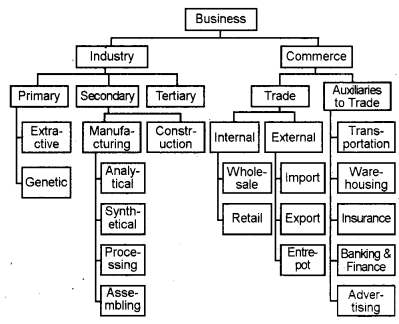
Classification of Business Activities
Business activities may be classified into two categories –
- Industry
- Commerce.
Chart showing business activities
Question 5.
Match column A with column B and column C
| A | B | C |
| Business | Wages / Salary | Qualification |
| Profession | Earn profit | Letter of appointment |
| Employment | Fees | Production and distribution |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Business | Earn profit | Production and distribution |
| Profession | Fees | Qualification |
| Employment | Wages / Salary | Letter of appointment |
Question 6.
Explain the characteristics of business risk.
Answer:
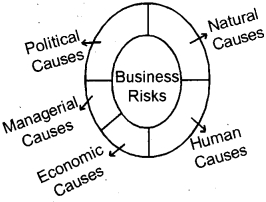
Business Risks
The term ‘business risks’ refers to the possibility of inadequate profits or even losses due to uncertainties or unexpected events.
Business enterprises may face two types of risk,
i.e. speculative risk and pure risk. Speculative risks involve both the possibility of gain as well as the possibility of loss. It a rise due to a change in demand, change in price, etc. Pure risks involve only the possibility of loss or no loss. The chance of fire, theft or strike is examples of pure risks.
Nature of Business Risks
- Business risks arise due to uncertainties.
- Risk can be minimized, but cannot be eliminated. It is an essential part of business.
- Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business:
- Profit is the reward for risk-taking.
Causes of Business Risks
Business risks arise due to a variety of causes. They are:-
1. Natural Causes:-
it includes natural calamities like flood, earthquake, lightning, heavy rains, famine, etc.
2. Human Causes:-
Human causes include dishonesty, carelessness or negligence of employees, strikes, riots, management inefficiency, etc.
3. Economic causes:
These include change in demand, change in price, competition, technological changes, etc.
4. Political Causes:-
Change in Govt, policies, taxation, licensing policy, etc.
4 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match the Following.
Answer:
Question 2.
Following is a list of activities. Classify these activities as Business, Profession or Employment
- Policeman on duty at your local police station.
- Teacher working in an educational institution.
- A driver driving a bus of a State Road Transport Corporation.
- A taxi-driver who runs his own taxi.
- A fisherman selling fish in a village.
- Gopal stitching cloth of the customers regularly at home.
- A daily-wager working in a factory.
- A gardener maintaining the lawns in a college.
- A lawyer practicing in a court.
- An engineer running his consultancy firm.
Answer:
- Employment
- Employment
- Employment
- Business
- Business
- Business
- Employment
- Employment
- Profession
- Profession
Question 3.
Mr. Jagajeevanram, who is running a skin clinic, got his MBBS degree and MD degree from Kerala University. Rahul has been working as an attender in the clinic for the last five years. After having this experience, he started his own clinic for skin diseases.
(a) Is it possible to start a clinic legally in his own name? Why?
(b) What are the essentials to run such an organization?
Answer:
(a) No. Mr. Rahul cannot start legally the clinic in his own name because he has no professional qualification and training,
(b) The essentials to run such an organization are:-
- There must be specialized knowledge and skill, i.e. MBBS degree approved by Medical Council of India.
- Formal training.
- Membership in Indian Medical Association (IMA)
- Follow the code of conduct enforced by IMA
- Charging fee for service.
Question 4.
The following are some examples of industries
Fishing Textile industry
Bridge construction Poultry farming
Limestone mining Animal husbandry
Cement factory Building works
Classify these industries under suitable heads.
Answer:
Extractive industry Fishing, Limestone
Genetic industry Poultry farming, Animal husbandry
Manufacturing industry Textile industry, Cement industry
Construction industry Bridge construction, Building works
Question 5.
Explain the concept of business risk and its causes.
Answer:
Business Risks
The term ‘business risks’ refers to the possibility of inadequate profits or even losses due to uncertainties or unexpected events.
Business enterprises may face two types of risk,
i.e. speculative risk and pure risk. Speculative risks involve both the possibility of gain as well as the possibility of loss. It a rise due to a change in demand, change in price, etc. Pure risks involve only the possibility of loss or no loss. The chance of fire, theft or strike is examples of pure risks.
Nature of Business Risks
- Business risks arise due to uncertainties.
- Risk can be minimized, but cannot be eliminated. It is an essential part of business.
- Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business:
- Profit is the reward for risk-taking.
Causes of Business Risks
Business risks arise due to a variety of causes. They are:-
1. Natural Causes:-
it includes natural calamities like flood, earthquake, lightning, heavy rains, famine, etc.
2. Human Causes:-
Human causes include dishonesty, carelessness or negligence of employees, strikes, riots, management inefficiency, etc.
3. Economic causes:-
These include change in demand, change in price, competition, technological changes, etc.
4. Political Causes:-
Change in Govt, policies, taxation, licensing policy, etc.
5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain different types of manufacturing industries.
Answer:
Industry
Industry refers to economic activities, which are connected with the conversion of resources into useful goods. Industries may be divided into 3 categories. They are
1. Primary industries:-
Primary industries are connected with the extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living organisms, plants, etc. Such industries are further divided into two.
Extractive industries:-
These industries extract products from natural resources. E.g. mining, farming, hunting, fishing, etc.
Genetic industries:-
These industries are engaged in activities like rearing and breeding of animals, birds, and plants. E.g. diary farming, paultry farming, floriculture, pisciculture, etc.
2. Secondary industries:-
Secondary industries deal with materials extracted at the primary stage. Such goods may be used for consumption or for further production. Secondary industries are classified into two. They are:-
(i) Manufacturing industries:-
Manufacturing industries engage in converting raw materials into finished goods. E.g. Conversion of rubber into cotton, timber into furniture rubber into tires, etc. Manufacturing industries may be further divided into four categories. They are,
- Analytical industry which analyses and separates different elements from the same materials. E.g. Oil refinery
- Synthetical industry which combines various ingredients into a new product. E.g. cement
- Processing industry which involves successive stages for manufacturing finished products. Eg. Sugar and paper industry.
- Assembling industry which assembles different component parts to make a new product. E.g. television, car, computer, etc.
(ii) Construction industries:-
These industries are involved in the construction of buildings, dams, bridges, roads, etc.
3. Tertiary industries:-
These are concerned with providing support services to primary and secondary industries. Eg. Transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, communication, advertising, etc.
Question 2.
Mr. Shyam is a leading advocate in Ernakulam. He is also working as a lecturer in a law college. Identify and distinguish with the activities in which Mr. Shyam is engaged.
Answer:
Profession and Employment. Comparison of Business, Profession, and Employment.
Classification of Business Activities
Business activities may be classified into two categories –
- Industry
- Commerce.
Chart showing business activities
Question 3.
The following are some examples of trade. Find the types of trade each of these belongs to.
- Purchase of petroleum products by India from Iraq.
- Purchase of fast-moving consumable goods from Bombay for sale in Kochi.
- Sale of tea leaf to Gulf countries.
- A provision store in a village.
- A shop which deals in tea only in bulk quantity.
Answer:
- Import trade
- Internal trade
- Export trade
- Retail trade
- Wholesale trade
Question 4.
Explain the features of business.
Business:-
Business may be defined as an economic activity involving the production or purchase and sale of goods and services with the main object of earning profit by satisfying human needs in the society.
Characteristics of business
- Business is an economic activity with the object of earning profit.
- Business includes all the activities concerned with the production or procurement of goods and services.
- There should be a sale or exchange of goods and services for the satisfaction of human needs.
- Business involves dealings in goods or services on a regular basis. Normally, one single transaction of sale or purchase is not treated as business.
- One of the main objectives of business is to earn maximum profit.
- Business involves risk and uncertainty of income. Risk means the possibility of loss due to change in consumer taste and fashion, strike, lockout competition, fire, theft, etc.
6 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Study of commerce is the study of Trade and Aids to Trade”. Evaluate this statement.
Answer:
Commerce includes Trade as well as Aids to Trade. Trade means exchange or buying and selling of goods. Classification of Trade 1. Internal 2. External
Activities which assist trade are called aids to trade. Classification of Aids to Trade
- Transport
- Communication
- Insurance
- banking
- Advertising
- Warehousing
- Sales promotion
8 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the factors to be considered before starting a business.
Answer:
Starting a Business – Basic Factors
Factors to be considered for starting a business
1. Selection of line of business:
The first thing to be decided by any entrepreneur of a new business is the nature and type of business to be undertaken.
2. Size of the firm:
If the market conditions are favorable, the entrepreneur can start the business at a large scale. If the market conditions are uncertain and risks are high, a small size business would be a better choice.
3. Choice of form of ownership:
The selection of a suitable form of business enterprise i.e. Sole proprietorship, Partnership or a Joint-stock company is an important management decision. It depends on factors like the nature of business, capital requirements, liability of owners, legal formalities, continuity of business, etc.
4. Location of business enterprise:
Availability of raw materials and labour, power supply and services like banking, transportation, communication, warehousing, etc., are important factors while making a choice of location.
5. Financing:
Proper financial planning must be done to determine (a) the requirement of capital, (b) source from which capital will be raised and (c) the best ways of utilizing the capital in the firm.
6. Physical facilities:
Availability of physical facilities including machines and equipment, building and supportive services is a very important factor to be considered at the start of the business.
7. Plant layout:
Layout means the physical arrangement of machines and equipment needed to manufacture a product.
8. Competent worked force:
Every enterprise needs competent and committed employees to perform various activities so that physical and financial resources are converted into desired outputs.
9. Tax planning:
The promoter must consider in advance the tax liability under various tax laws and its impact on business decision
Question 2.
The main objective of business is to earn profit through service. Explain the objectives of business in the light of this statement.
Answer:
Multiple Objectives of Business
The main objectives of a business are:-
1. Market standing:-
A business firm can succeed only when it has a good market standing. Market standing refers to the position of an enterprise in relation to its competitors.
2. Innovation:-
Innovation means developing new products or services or finding new ideas and new methods of production and distribution. Innovation accelerates the growth of an enterprise.
3. Productivity:-
Productivity is ascertained by comparing the value of output with the value of input. Every enterprise must aim at greater productivity through the best use of available resources.
4. Physical and financial resources:-
The business must aim at maximum utilization of available physical and financial resources, i.e. men, material, money, and machine in the best possible manner.
5. Earning Profit:-
Earning maximum profit is the primary objective of every business. Profit is required for the survival and growth of a business.
6. Manager performance and development:-
Efficient managers are needed to conduct and coordinate business activities. So it is the objective of an enterprise to implement various programs for motivating the managers.
7. Worker performance and attitude:-
Every enterprise must aim at improving its worker’s performance by providing fair salary, incentives, good working conditions, medical and housing facilities.
8. Social responsibility:-
It refers to the obligation of business firms to contribute resources for solving social problems and work in a socially desirable manner.
Question 3.
Explain with the help of a diagram, the different types of industries with suitable examples.
Answer:
Industry
Industry refers to economic activities, which are connected with the conversion of resources into useful goods. Industries may be divided into 3 categories. They are
1. Primary industries:-
Primary industries are connected with the extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living organisms, plants, etc. Such industries are further divided into two.
Extractive industries:-
These industries extract products from natural resources. E.g. mining, farming, hunting, fishing, etc.
Genetic industries:-
These industries are engaged in activities like rearing and breeding of animals, birds, and plants. E.g. diary farming, paultry farming, floriculture, pisciculture, etc.
2. Secondary industries:-
Secondary industries deal with materials extracted at the primary stage. Such goods may be used for consumption or for further production. Secondary industries are classified into two. They are:-
(i) Manufacturing industries:-
Manufacturing industries engage in converting raw materials into finished goods. E.g. Conversion of rubber into cotton, timber into furniture rubber into tires, etc. Manufacturing industries may be further divided into four categories. They are,
- Analytical industry which analyses and separates different elements from the same materials. E.g. Oil refinery
- Synthetical industry which combines various ingredients into a new product. E.g. cement
- Processing industry which involves successive stages for manufacturing finished products. Eg. Sugar and paper industry.
- Assembling industry which assembles different component parts to make a new product. E.g. television, car, computer, etc.
(ii) Construction industries:-
These industries are involved in the construction of buildings, dams, bridges, roads, etc.
3. Tertiary industries:-
These are concerned with providing support services to primary and secondary industries. Eg. Transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, communication, advertising, etc.
