Kerala Plus One Business Studies Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 12 International Business – II
Question 1.
When goods are delivered on the ship, the captain of that ship issues a document called ………….. (March – 2009)
a) Mate’s receipt
b) Bill of lading
c) Shipping order
d) Charter party
Answer:
Mates receipt
Question 2.
“There are the specially delineated duty-free enclaves treated as foreign territory for trade purposes”. (March – 2009)
a) Identify the area.
b) Write its important features.
Answer:
a) Special Economic Zones. (SEZ)
b) Features of SEZ
- Creation of duty-free enclave, which is. treated as foreign territory for trade operations
- Exemption from a routine examination of import and export of cargo by customs authorities.
- Units in SEZ can engage in manufacturing, trading, and service activities
- Units are permitted to import capital goods and raw materials duty-free.
- The sale of goods in the domestic market is permitted on payment of duty.
- It provides an internationally competitive environment for the production of export goods.
- Duty-free goods are allowed to be utilized within the approval period of 5 years.
- 100% FDI is permitted
Question 3.
It is through this document that the shipping company intimates the exporter about the reservation of space on board. (March – 2010)
a) Bill of Entry
b) Bill of Lading
c) Mates Receipt
d) Shipping Order
Answer:
Shipping Order
Question 4.
The newly appointed manager of a company is assigned to clear some imported goods. The importer has to submit a document to the customs office in the form of a declaration containing the particulars of the goods imported. But the manager miserably failed to remember the name of the document. Can you make him competent by reminding him of the name of the document with any three of its characteristics? (March – 2011)
Answer:
Bill of Entry:- Bill of entry is a document stating that goods of the stated value and quantity are entering into the country from abroad. It is filled up by the importer and submitted to the customs office for assessing the duty payable.
Features
- It is a declaration about goods imported.
- It is prepared in triplicate.
- It contains the particulars about the imported goods, shipping company, exporter, etc.
Question 5.
Mathew is a planter and trader of spices in Wayanad. In the global spices meet held at Kochi, he got an order to export spices to Germany. But he is not aware of the export formalities. Support Mathew by briefly explaining the export procedure. (March – 2011)
Answer:
Export Procedure
1. Receipt of enquiry and sending quotations: The prospective buyer of a product sends an enquiry to different exporters requesting them to send information about price, quality, terms of payment, etc. The exporter sends a reply to the enquiry in the form of a quotation referred to as a proforma invoice.
2. Receipt of order or indent: If the buyer is satisfied with the export price and other terms and conditions, he places the order or indent for the goods.
3. Assessing importer’s creditworthiness and securing a guarantee for payments: After receipt of the indent, the exporter makes the necessary enquiry about the creditworthiness of the importer. To minimize the risk, most exporters demand a letter of credit from the importer.
4. Obtaining export license: The exporter must apply for an export license to the appropriate authority. The following procedure is followed for obtaining the export license.
- ]Opening a bank account in any bank authorized by the Reserve Bank of India
- Obtaining Import Export Code (IEC) number
- Registration cum Membership Certificate (RCMC) from appropriate export promotion council
- Registering with Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) in order to safeguard against risks of non-payments.
5. Obtaining pre-shipment finance: After obtaining the export license, the exporter approaches his banker in order to obtain pre-shipment finance for carrying out production.
6. Production or procurement of goods: Exporter, after obtaining the pre-shipment finance from the bank, proceeds to get the goods ready as per the orders of the importer.
7. Pre-shipment inspection: Quality control and pre-shipment inspection are compulsory in India as per Quality Control and Inspection Act. An inspection certificate is provided by the Export Inspection Council. The customs authority permits the shipment of goods only if there is an inspection certificate.
8. Excise clearance: According to the Central Excise Tariff Act, excise duty on the material used in manufacturing goods is to be paid. For this purpose, the exporter applies to the concerned Excise Commissioner in the region with an invoice. But in many cases, the government exempts payment of excise duty or later on refunds it if the goods so manufactured are meant for exports. The refund of excise duty is known as a duty drawback.
9. Obtaining certificate of origin: In order to obtain Tariff concessions or other exemptions, the importer may ask the exporter to send the certificate of origin.
10. Reservation of shipping space: The exporting firm applies to the shipping company for the provision of shipping space. Then the shipping company issues a shipping order. A shipping order is an instruction to the captain of the ship that the specified goods after their customs clearance at a designated port be received on board.
11. Packing and forwarding: The goods are then properly packed and marked with necessary details such as the name and address of the importer, gross and net weight, the port of shipment and destination, country of origin, etc. The exporter then makes the necessary arrangement for the transportation of goods to the port
12.Insurance of goods: In order to protect the goods against the risk of loss or damage the exporter gets the goods insured with an insurance company.
13.Customs clearance: The goods must be cleared from the customs before these can be loaded on the ship. For obtaining customs clearance, the exporter prepares the shipping bill. Shipping bill contains particulars of the goods being exported, the name of the ship, the port at which goods are to be discharged, exporter’s name and address, etc. Five copies of the shipping bill along with the following documents are then submitted to the Customs Appraiser at the Customs House:
- Export Contract or Export Order
- Letter of Credit
- Commercial Invoice
- Certificate of Origin
- Certificate of Inspection, where necessary
- Marine Insurance Policy
14.Obtaining mates receipt: A mate receipt is a receipt issued by the commanding officer of the
ship when the cargo is loaded on board and contains the information about the name of the vessel, berth, date of shipment, description of packages, condition of the cargo at the time of receipt on board the ship, etc.
15. Payment of freight and issuance of bill of lading: The clearing & forwarding agent (C&F agent) hands over the mate s receipt to the shipping company for the computation of freight. After receipt of the freight, the shipping company issues a bill of lading which serves as evidence that the shipping company has accepted the goods for carrying to the designated destination.
16. Preparation of invoice: The exporter prepares an invoice for the dispatched goods. The invoice contains information regarding the number of goods sent & the amount to be paid by the importer. It is duly attested by the customs.
17. Securing payment: After the shipment of goods, the exporter informs the importer about the shipment of goods. Various documents like a certified copy of the invoice, bill of lading, packing list, insurance policy, certificate of origin, and letter of credit are sent by the exporter through his bank. These documents are required by the importer for getting the goods cleared from customs. The exporter gets payment from his bank on the submission of necessary documents called negotiations of the documents.
Question 6.
Mr. Rajesh steals a bill of lading from somewhere and endorses it to Suresh. He receives it in good faith and for valuable consideration. Does Suresh get a better title than Rajesh? Substantiate your answer. (March – 2012)
Answer:
Bill of lading is a document issued by the shipping company after the cargo is loaded in the ship. It is an acknowledgment of the receipt of goods by the shipping company. It is a document which shows the title of the goods.
Question 7.
An engineering graduate likes to set up an export-oriented industrial unit based on nanotechnology. He wants to import heavy machinery from Japan without involving import duty. He needs a place with sound infrastructural facilities. (March – 2012)
a) Where should he locate this business?
b) Explain the benefits available to him by starting his venture at this location.
Answer:
EPZ
Advantages of EPZ
- Mr. Murukan can locate his business in Economic Processing Zone (EPZ).
- EPZs are established as special enclaves separated from the domestic tariff area.
- It provides an internationally competitive and duty-free environment for the production of export goods.
- They are usually located near seaports or airports.
- The units located in EPZ can import capital goods and raw materials for the production of export goods without a license and without payment of customs duty.
The important benefits of EPZ are:
- It helps to earn maximum foreign exchange
- It generates more employment opportunities for domestic people
- It helps to acquire the latest technology and advanced skills.
- It diversifies in exports.
Question 8.
“Through the process of liberalization, Indian companies are free to access global capital markets for raising finance”.Do you agree? (October – 2013)
Answer:
Yes.
Global Depository Receipt (GDR):
GDR is issued by an Indian company to an intermediary abroad called an Overseas Depository Bank. They are issued and traded in the European Market.
American Depository Receipts (ADR):
The depository receipts issued by a company in the USA are known as ADR. They issued and traded in the USA.
Question 9.
Complete the diagram (October – 2013)
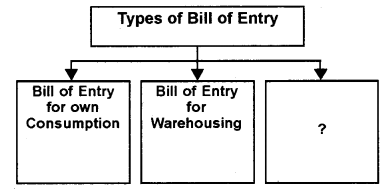
Answer:
Ex – Bond bill of entry.
Question 10.
Mr. George is a planter and trader of spices in Idukki. In the global spices meet held at Kochi, he got an order to export spices to the UK. But he is not aware of the export formalities. Support Mr. George by listing any eight steps of the export procedures. (March – 2014)
Answer:
Export Procedures:
- Receipt of enquiry and sending quotations
- Receipt of order or indent
- Assessing importer’s creditworthiness and securing a guarantee for payments
- Obtaining an export license
- Obtaining pre-shipment finance
- Production or procurement of goods
- Pre-shipment inspection
- Excise clearance
Question 11.
Name the document which was issued by a shipping company as an acknowledgment of goods received for export. (August – 2014)
Answer:
Bill of Lading
Question 12.
Briefly explain any three organizations that have been constituted in the country by the Government of India for promoting foreign trade in the nation. (March – 2015)
Answer:
Department of Commerce
1. Department of Commerce in the Ministry of Commerce, Govt, of India is the apex body responsible for the country’s external trade and all matters concerned with it.
2. Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)
They are non-profit organizations registered under the Companies Act or Societies Registration Act. Their main objectives are to ‘ promote and develop the country’s export of particular products falling under their Jurisdiction.
3. Commodity Boards
These are the boards that have been specially established by the Govt, of India for the development of the production of traditional commodities and their exports.
Question 13.
I Briefly explain any three organizations that have been constituted in India by the Government for promoting foreign trade in the nation. (Say – 2015)
Answer:
Department of Commerce
1. Department of Commerce in the Ministry of Commerce, Govt, of India is the apex body responsible for the country’s external trade and all matters concerned with it.
2. Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)
They are non-profit organizations registered under the Companies Act or Societies Registration Act. Their main objectives are to promote and develop the country’s export of particular products falling under their Jurisdiction.
Commodity Boards
These are the boards that have been specially established by the Govt, of India for the development of the production of traditional commodities and their exports.
Question 14.
Match the following. (March – 2017)
| A | B | C |
| WTO | World bank | 1992 |
| IBRD | New Delhi | GATT |
| ITPO | Janeeva | Washington DC |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| WTO | Janeeva | GATT |
| IBRD | World bank | Washington DC |
| ITPO | New Delhi | 1992 |
Question 15
State the procedures for getting an export license. (Hint: Minimum three procedures) (September – 2016)
Answer:
1. Receipt of enquiry and sending quotations: The prospective buyer of a product sends an enquiry to different exporters requesting them to send information about price, quality, terms of payment, etc. The exporter sends a reply to the enquiry in the form of a quotation referred to as a proforma invoice.
2. Receipt of order or indent: If the buyer is satisfied with the export price and other terms and conditions, he places the order or indent for the goods.
3. Assessing importer’s creditworthiness and securing a guarantee for payments: After receipt of the indent, the exporter makes the necessary enquiry about the creditworthiness of the importer. To minimize the risk, most exporters demand a letter of credit from the importer.
Question 16.
A receipt issued by the commanding officer of the ship when the cargo is loaded on the ship is known as ……….. (March – 2017)
a) shipping receipt
b) mates receipt
c) cargo receipt
d) charter receipt
Answer:
b) mates receipt
Question 17.
What do you mean by Export Promotion Zones (EPZ)? (March – 2017)
Answer:
Export Processing Zones (EPZs): They are industrial estates, which form special enclaves separated from the domestic tariff areas. These are usually situated near seaports or airports. They are intended to provide an internationally competitive duty-free environment for export production at a low cost. They can import capital goods and raw materials for the production of export goods without a license.
