Kerala Plus One Business Studies Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Business
Question 1.
Your friend Sreekumar intends to start a garment making unit. But he is not aware of the possible risks that he may have to face in his new venture. Advise him about the causes of business risks with examples. (June 2008)
Answer:
The possible cause that Sree Kumar may face in his new venture are:
- Natural causes: Rain, earthquake, flood, drought etc.
- Human causes: Theft, strikes, riots, carelessness etc.
- Economic causes: Change in demand, change in price, trade depression, competition, technological changes, market conditions etc.
- Political causes: Change in Govt, policies, taxation, licensing policy etc
- Managerial causes: Mismanagement, poor planning, lack of supervision etc.
Question 2.
Among the following terms, which is used to denote income from the business? (June 2008)
a) salaries
b) profit
c) donation
d) fees
Answer:
b) Profit
Question 3.
Find the odd one out and give justification. (June 2008)
- a) Doctor/Engineer/Chartered Accountant/Clerk
- b) Agriculture/Poultry/Business/Social work
Answer:
- a) Clerk – All others are professionals
- b) Social work – Others are economic activities
Question 4.
Match column A with column B. (March 2009)
| A | B |
| Extractive industry | Building work |
| Genetic industry | Cement |
| Constructive industry | Animal husbandry |
| Manufacturing industry | Fishing |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Extractive industry | Fishing |
| Genetic industry | Animal husbandry |
| Constructive industry | Building work |
| Manufacturing industry | Cement |
Question 5.
Smt. Drisya is a leading advocate in Ernakulam. She is also working as a lecturer in a law college. Identify and distinguish the activities in which Smt. Drisya is engaged. (March 2009)
Answer:
- Smt. Drisya is a leading advocate in Ernakulam – it is a profession
- She also works as a lecturer in a law college – it is an employment
Differences between profession and employment are
| Basis | Profession | Employment |
| Nature of work | Rendering of personalized expert services. | Performing work according to the instruction of the employer |
| Qualification | Professional qualification and training is required. | Qualification prescribed by the employer is required |
| Reward | Fees | Salary/Wages |
| Risk | Low risk | No risk |
| Code of conduct | Professional code of conduct to be followed | Code of conduct laid down by the employer is to be followed. |
| Transfer of ownership | Not possible | Not possible |
| Capital | Limited capital is required | No capital is required |
Question 6.
Identify the persons who are conducting a non-economic activity. (March 2009)
Answer:
a) Abhiram, a doctor, in a medical college.
b) Athira, a computer expert, running an Internet cafe.
c) Meera, a teacher, conducting free tuitions for poor students.
d) Pavithra, a lawyer, practicing in a court.
Answer:
c) Meera, a teacher, conducting free tuition for poor students
Question 7.
Place utility is created by _________ (March 2009)
a) Warehousing
b) Transport
c) Insurance
d) Person
Answer:
a) Warehousing
Question 8.
Nishad is desirous of starting a readymade shop exclusively for men in the city. He is not aware of the hindrances he may face in his trading activities. Point out any four hindrances and their possible remedies. (March 2009)
Answer:
The various hindrances (Functions of commerce) are
1. Hindrance of person: There is a wide gap between producers and consumers. Traders help the exchange of goods by acting as a link between producers and consumers. Trade removes the hindrance of a person.
2. Hindrance of place: Goods are produced in one place and they are consumed in various parts of the world. So goods must be moved from the production centre to the consumption centre. This is made with the help of transportation. Transport removes the hindrance of place.
3. Hindrance of time: Goods are produced at one time and they are consumed at another time. Goods must be stored till they are consumed by the consumers. This function is performed by warehouses. Warehousing removes the hindrance of time.
4. Hindrance of risk: There may be chances of loss in trade due to fire, theft, accident, etc. Insurance removes the hindrance of risk.
Question 9.
Yohannan and Zachariah were classmates in Law Academy. After completing a law degree Yohannan joined as a legal advisor in Parvathy Mills on a full-time basis. While Zachariah started practice as an advocate in Kerala High Court. Identify the type of economic activities performed by them and state any three differences between their economic activities. (August 2009)
Answer:
The economic activity of Yohannan is Employment and the Zacharia is a profession. The differences between employment and profession are:
| Basis | Employment | Profession |
| Nature of work | Performing work according to the instruction of the employer | Rendering expert service. |
| Return of service | Salary/Wages | Fee |
| Qualification | The qualification prescribed by the employer | Professional qualification and training. |
| Commencement | Appointment letter | Membership of professional body |
| Code of conduct | Code of conduct laid down by the employer | Professional code of conduct to be followed. |
Question 10.
Match column A with column B and column C. (August 2009)
| A | B | C |
| E-Commerce | Roads | Re-export |
| Entrepot | Electronic media | Labour intensive |
| Construction industry | Import | Website |
| Transport | Mining | Petroleum |
| Extractive industry | Place utility | Hindrance of trade |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| E-Commerce | Electronic media | Website |
| Entraport | Import | Re-export |
| Construction industry | Roads | Labour intensive |
| Transport | Place utility | Hindrance of trade |
| Extractive industry | Mining | Petroleum |
Question 11.
During a study tour, Asok purchased a raincoat from Chennai for ₹ 250 for his use. But when he went back home his friend Benoy offered ₹ 300 for the raincoat and Asok sold it to him. State whether this is a business activity or a non-business activity. (August 2009)
Answer:
Non-business activity
Question 12.
A textile dealer Sooraj wants to know the non-insurable risk from the following: (August 2009)
a) fire
b) theft
c) marine perils
d) change in fashion
Can you help him to identify it?
Answer:
d) Change in fashion
Question 13.
Dr. Abhiram is working as a lecturer in the Medical College. Identify the activity he is engaged in and explain its features. (March 2010)
Answer:
Employment.
Features of employment:
- There exist a contract of agreement between the employer and employee.
- The remuneration for the service is wages or salary
- There should be regularity in service
- There must exist an employer-employee relationship.
Question 14.
‘Trade is the nucleus of commerce.’ In light of the statement, explain the different types of trade. (March 2010)
Answer:
Types of Trade
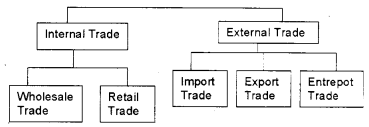
Trade refers to the sale, transfer, or exchange of goods.
Trade may be classified into two broad categories
They are:
- Internal trade
- External trade
1. Internal, domestic or dome trade Is concerned with the buying and selling of goods and services within the geographical boundaries of a country. This may further be divided into two. They are:
- Wholesale trade: Under wholesale trade, the trader purchases goods in large quantities from the producers, and sells them in smaller quantities to the retailers.
- Retail trade: Under the retail trade, the trader buys in comparatively smaller quantities from the wholesalers or producers and sells them to ultimate consumers.
2. External or Foreign trade: Foreign trade consists of an exchange of goods and services between two or more countries. Foreign trade may be divided into three.
- Import Trade: If goods are purchased from a foreign country, it is called import trade.
- Export Trade: When goods are sold to a foreign country, it is known as export trade.
- Entrepot Trade: When goods are imported for export to other countries, it is known as entrepot trade.
Question 15.
The primary objective behind an economic activity is __________ (March 2010)
a) service
b) sympathy
c) welfare
d) wealth creation
Answer:
d) Wealth creation
Question 16.
Importing foreign goods with the object of reexporting them to other countries is known as __________ (March 2010)
a) Import trade
b) Export trade
c) Entrepot trade
d) Extra pot trade
Answer:
c) Entrepot trade
Question 17.
Find the odd one out: ___________ (March 2010)
a) Offering goods at a reasonable price.
b) Giving fair wages to workers.
c) Keeping the environment pollution-free.
d) Expecting a high profit from the business.
Answer:
d) Expecting a high profit from the business
Question 18.
While on a study tour, Krishnaraj purchased a helmet for ₹ 500 from Chennai. When he returned home, his friend Ganesh offered ₹ 750 and he sold it to him. (March 2011)
- Is it a business activity or not?
- Give the reason.
Answer:
- It is not a business activity
- Business is a continuous activity, so there must be regularity in its dealings.
Question 19.
Usman Sait and Shahul Hameed were classmates in a Law College. After completing their law degrees, Usman Saif joined the Malabar Spinning Mill as a law officer on a full-time basis with a monthly salary of ₹ 20,000. However, Shahul Hameed started practice as an advocate in the High court. According to their neighbor Raju, both of them earn money. But he does not know the differences between their economic activities. Can you make the neighbour aware of the names of the two different economic activities and any three differences between them? (March 2011)
Answer:
Usman Sait: Employment
Shahul Hameed: Profession
Differences between Employment and Profession
| Basis | Employment | Profession |
| Nature of work | Performing work according to the instruction of the employer | Rendering expert service. |
| Return of service | Salary/Wages | Fee |
| Qualification | The qualification prescribed by the employer | Professional qualification and training. |
| Commencement | Appointment letter | Membership of professional body |
| Code of conduct | Code of conduct laid down by the employer | Professional code of conduct to be followed. |
Question 20.
According to Jyothis, a textile shop owner, all the business risks are not insurable. Which one among the following is not insurable? (March 2011)
a) Fire
b) Change in fashion
c) theft
d) Death of an individual
Answer:
b) Change in fashion
Question 21.
Mr. Biju Luckose is a Chartered Accountant, who runs an accounting firm for preparing the financial statement and auditing the books of accounts of traders. (March 2012)
- Identify the economic activity he is engaged in.
- State any two distinguishing features of this occupation.
Answer:
- Profession.
- Features of Profession.
- A profession requires specialized knowledge, training, and skill
- Membership of a professional body is a must
- Charging fee for service.
- Obedience of code of conduct
Question 22.
“The success of a business depends not only on his efforts but also a number of uncontrollable factors”. Do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer by specifying the major causes of such unexpected events happening in a business. (March 2012)
Answer:
Yes.
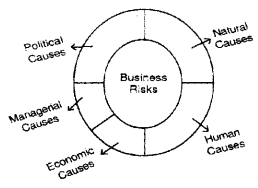
Business risk is the chance of loss which are beyond the control of a businessman. Every business has an element of risk. Risk arises because of the uncertainties of future events.
The important causes of business risk are:
- Natural causes
- Human causes
- Economic causes
- Political causes
- Managerial causes
Natural causes: Rain, earthquake, flood, storm, draught etc.
Human causes: Theft, strikes, lockouts, riots, carelessness, dishonesty of employees etc.
Economic causes: Change in demand, change in price, trade depression, competition, technological changes, market conditions etc.
Political causes: Change in Govt, policies, taxation, licensing policy etc.
Managerial causes: Mismanagement, poor planning, lack of supervision etc.
Question 23.
Profit acts as a powerful motivator for every businessman. Identify which among the following is the role of profit in a business: (March 2012)
a) Source of funds for growth.
b) Livelihood for a businessman.
c) Reward for risk-taking.
d) All of these.
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 24.
Which among the following is an example of a ‘Genetic Industry’? (March 2012)
a) Dairy farming
b) Building roads
c) Mining of coal
d) Furniture making
Answer:
a) Dairy Faming
Question 25.
Complete the series, based on the given hint: (March 2012)
Hint: Hindrance of place → transportation
- Hindrance of time → ______ ? __________
- Hindrance of knowledge → _______ ? ________
Answer:
- Hindrance of time, Warehousing
- Hindrance of Knowledge, Advertisement
Question 26.
Mr. Venu, a Chartered Accountant, is now working as a finance manager, in a private limited company. Mention the category of economic activity to which Mr. Venu belongs. Also, state the features of that category. (March 2013)
Answer:
Employment. Features of employment are
- Exists employer-employee relationship
- Service contract
- Get salary or wages
- Regularity in service
Question 27.
Dr. Soorya runs a clinic. Mr. Sooraj is running a bakery. Identify the types of economic activities performed by both of them and state any four differences between them. (March 2013)
Answer:
Soorya – Profession
Suraj – Business
Differences between Profession and Business are:
| Basis | Business | Profession | Employment |
| Commencement | Entrepreneur’s decision and legal formalities | Membership of a professional body | Appointment letter |
| Nature of work | Production or purchase and sales of goods or services | Rendering expert service | Performing the job assigned by the employer |
| Return | Profit | Fees | Salary/Wages |
| Qualification | No prescribed qualification | Professional qualification and training are required | Qualification prescribed by the employer |
| Investment | Capital is needed according to the nature and size | Limited capital required | No capital is required |
| Risk | High risk | Less risk | No risk |
| Transfer of interest | Possible | Not possible | Not possible |
| Code of conduct | No specific code of conduct | Professional code of conduct | Code of conduct laid by the employer. |
Question 28.
In any type of business, there is a possibility of occurring loss. Give any three reasons for this. (October 2013)
Answer:
- Natural Causes: It includes natural calamities like floods, earthquakes, lightning, heavy rains, famine, etc.
- Human Causes: Human causes include dishonesty, carelessness, or negligence of employees, strikes, riots, management inefficiency, etc.
- Economic causes: These include the change in demand, change in price, competition, technological changes etc.
Question 29.
Dr. Rahul is running a skin clinic. Smt. Sumathy had been working as a nurse in this clinic for the last 7 years. On the basis of this experience, she started a clinic in her own name. (October 2013)
a) Is it legally possible for Sumathy to work as a skin specialist.
b) Explain the feature of economic activity performed by Dr. Rahul.
Answer:
No. Features of profession
a) A profession requires specialized knowledge, training, and skill
b) The membership of a professional body is a must
c) Professionals have a code of conduct
d) They charge a fee in return for their service.
Question 30.
Mr. Shyam is a leading advocate in Ernakulam. He is also working as a lecturer in a Law College. Identify and distinguish the activities in which Mr. Shyam is engaged. Give at least two distinctions. (March 2014)
Answer:
Employment and Profession.
Differences between Employment and Profession:
| Employment | Profession |
| Membership of a professional body | Appointment letter |
| Rendering expert service | Performing the job assigned by the employer |
Question 31.
Match column ‘A’ with columns ‘B’ and ‘C’. (March 2014)
| A | B | C |
| a) Economic causes of risk | means of livelihood | new products |
| b) Profit | Terrorism | trade depression |
| c) Business | latest technology | World Trade Center |
| d) Human causes of risk | profit motive | Goodwill |
| e) Innovation | change in demand | Risk |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Economic causes of risk | Change in demand | Trade depression |
| Profit | Means of livelihood | Goodwill |
| Business | Profit motive | Risk |
| Human causes of risk | Terrorism | World Trade Centre |
| Innovation | Latest technology | New products |
Question 32.
The most important function of Commerce is _______ (August 2014)
Answer:
Trade
Question 33.
Match column ‘A’ with columns ‘B’ and ‘C’. (August 2014)
| A | B | C |
| a) Employment | personal satisfaction | personalized service |
| b) Business | Fees | research and development |
| c) Innovation | service contract | gardening at home |
| d) Profession | Profit | Salary |
| e) Noneconomic activity | Creativity | high risk |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Employment | Service contract | Salary |
| Business | Profit | High risk |
| Innovation | Creativity | Research and development |
| Profession | Fees | Personalised service |
| Non-economic activity | Personal satisfaction | Gardening at home |
Question 34.
Profit is the most important aspect of a business. Explain the role of profit in a business. (August 2014)
Answer:
- It is a means of livelihood for the business
- Profit is the reward for risk-bearing
- It is required for the survival of the business.
- It is required for the growth, expansion, and diversification of business activities.
- It helps to increase the goodwill of the business firm.
- Profit is essential for the payment of reasonable salaries to the employees.
Question 35.
Mrs. Sneha is a doctor, working in a private hospital and she also runs her own clinic. (March 2015)
a) Identify these activities on the basis of the type of economic activity.
b) State any two differences between these two activities.
Answer:
a) Employment and Profession
b)
| Employment | Profession |
| Appointment letter | Membership of a professional body |
| Performing the job assigned by the employer | Rendering expert service |
Question 36.
The industries which provide support service to other industries are known as ________ (Say 2016)
a) Primary industries
b) Secondary industries
b) tertiary industries
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Tertiary industries
Question 37.
Classify the following industries under suitable heads. (Say 2016)
- Mining
- Textile industry
- Building works
- Animal husbandry
Answer:
- Mining – Extractive industry
- Textile industry – Manufacturing industry
- Building works – Construction industry
- Animal husbandry – Genetic industry
Question 38.
Explain the multiple objectives of the business. (Say 2016)
Answer:
Multiple Objectives of Business
The main objectives of a business are:
a) Market standing: A business firm can succeed only when it has a good market standing. Market standing refers to the position of an enterprise in relation to its competitors.
b) Innovation: Innovation means developing new products or services or finding new ideas and new methods of production and distribution. Innovation accelerates the growth of an enterprise.
c) Productivity: Productivity is ascertained by comparing the value of output with the value of the input. Every enterprise must aim at greater productivity through the best use of available resources.
d) Physical and financial resources: The business must aim at maximum utilization of available physical and financial resources, i.e. men, material, money, and machine in the best possible manner.
e) Earning Profit: Earning maximum profit is the primary objective of every business. Profit is required for the survival and growth of a business.
f) Manager performance and development: Efficient managers are needed to conduct and coordinate business activities. So it is the objective of an enterprise to implement various programs for motivating the managers.
g) Worker performance and attitude: Every enterprise must aim at improving its worker’s performance by providing fair salary, incentives, good working conditions, medical and housing facilities.
h) Social responsibility: It refers to the obligation of a business firm to contribute resources for solving social problems and work in a socially desirable manner.
Question 39.
Mr. Sudheer a businessman incurred some financial loss due to the dishonesty of his workers. This loss is caused due to __________ (March 2016)
a) natural cause
b) financial cause
c) human cause
d) economic cause
Answer:
c) Human cause
Question 40.
Banking is ________ (March 2016)
a) Primary industry
b) secondary industry
c) tertiary industry
d) not an industry
Answer:
c) Tertiary industry
Question 41.
Adv. Praful is practicing in the High Court. Adv. Rajeev Menon is working as the legal advisor of Karthika Consultancy Ltd., in which economic activities these two are engaged in. Explain both activities with the help of one example each. (March 2016)
Answer:
Adv. Praful – Profession.
Adv. Rajeev Menon – Employment
Employment: Employment refers to that type of economic activity in which people engage in some work for others regularly and get salary or wages in return for their services.
Eg. a Teacher teaching in a School.
Profession: Profession refers to an occupation which requires specialized knowledge, skill, and training. Its objective is to provide service to society.
Eg. A doctor runs his own clinic.
Question 42.
Which among the following is NOT a characteristic of business? (September 2016)
a) Dealing with goods and services
b) Profit motive
c) Noneconomic activity
d) Uncertainty of return
Answer:
c) Non-economic activity
Question 43.
Explain any three objectives of the business. (September 2016)
Answer:
The main objectives of a business are:
a) Market standing: A business firm can succeed only when it has a good market standing. Market standing refers to the position of an enterprise in relation to its competitors.
b) Innovation: Innovation means developing new products or services or finding new ideas and new methods of production and distribution. Innovation accelerates the growth of an enterprise.
c) Productivity: Productivity is ascertained by comparing the value of output with the value of the input. Every enterprise must aim at greater productivity through the best use of available resources.
Question 44.
Which one of the following is NOT related to the general objectives of the business? (March 2017)
a) Innovation
b) Physical and financial resources
c) Warehousing
d) Productivity
Answer:
c) Warehousing
Question 45.
Transportation removes the hindrance of __________ in trading activities. (March 2017)
a) place
b) time
c) risk
d) finance
Answer:
a) Place
Question 46.
“People work for others and get remuneration”. (March 2017)
- Identify the economic activity involved in the above statement.
- Write any two features of that economic activity.
Answer:
- Employment
- Employment refers to that type of economic activity in which people engage in some work for others regularly and get salary or wages in return for their services.
Characteristics of Employment
- There must exist the employer-employee relationship
- There must be a service contract between the employer and employee
- Employees get salary or wages for their services
- Regularity in service.
Question 47.
Explain the causes of business risks. (March 2017)
Answer:
Business risks arise due to a variety of causes. They are:
- Natural Causes: It includes natural calamities like floods, earthquakes, lightning, heavy rains, famine, etc.
- Human Causes: Human causes include dishonesty, carelessness, or negligence of employees, strikes, riots, management inefficiency, etc.
- Economic causes: These include a change in demand, change in price, competition, technological changes, etc.
- Political Causes: Change in Govt, policies, taxation, licensing policy, etc.
Question 48.
Which among the following is not a feature of business? (SCERT Sample Question Paper-I)
a) Dealing in goods and service.
b) Certainty of return
c) Profit motive
d) Regularity in dealings
Answer:
b) Certainty of return
Question 49.
Cochin refineries Ltd. imports crude oil and separates different products like petrol, Diesel, etc. Name the type of manufacturing industry. (SCERT Sample Question Paper-I)
Answer:
a) Synthetical
b) Analytical
c) Processing
d) Assembling
Answer:
b) Analytical
