Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 9 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Plus One Botany Photosynthesis in Higher Plants One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which metal ion is a constituent of chlorophyll?
(a) Iron
(b) Copper
(c) Magnesium
(d) Zinc
Answer:
(c) Magnesium
Question 2.
Which pigment acts directly to convert light energy to chemical energy?
(a) Chlorophyll a
(b) Chlorophyll b
(c) Xanthophyll
(d) Carotenoid
Answer:
(a) Chlorophyll a
Question 3.
Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
(a) 100 – 390
(b) 390 – 430
(c) 400 – 700
(d) 760 – 100,00
Answer:
(c) 400-700
Question 4.
Which light range is most effective in photosynthesis?
(a) Blue
(b) Green
(c) Red
(d) Violet
Answer:
(c) Red
Question 5.
Chemosynthetic bacteria obtain energy from
(a) Sun
(b) Infra red rays
(c) Organic substances
(d) Inorganic chemicals
Answer:
(d) Inorganic chemicals
Question 6.
What is the name given to the process of splitting of water during light reaction?
Answer:
Photolysis
Question 7.
What tissues and cells of a leaf contain the chloroplast
Answer:
Mesophyll
Question 8.
What colour of visible spectrum is least effective in the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Green
Question 9.
How many molecules of ATP and how many molecules of NADPH are spent to fix three molecules of CO2 in Calvin cycle?
Answer:
ATP and 6 NADPH
Question 10.
Name the two photosynthetic pigments belonging to carotenoides.
Answer:
Carotene and xanthophylls
Question 11
The most abundant enzyme in the world plays a dual role in rice, tomato etc. Identify the enzyme.
Answer:
RUBISCO
Question 12
Which products formed during the light reaction of photosynthesis are used to drive the dark reaction?
Answer:
ATP and NADPH2
Question 13
By looking at which internal structure of a plant can you fill whether a plant is C3 or C4. Explain.
Answer:
C4 – Plants shows kranz anatomy -chloroplast dimorphism
Question 14
Why does the rate of photosynthesis decrease at higher temperatures?
Answer:
Enzymes present in stroma undergoes denaturation in the presence of high temperatures.
Question 15
Name the only natural process by which oxygen is liberated for the use of respiration.
Answer:
By photolysis of water during photosynthesis
Plus One Botany Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
If we study vertical sections of leaves of C3 plant and C4 plant, there are some anatomical differences.
- What are the anatomical peculiarities of a C4 plant?
- Explain C4 pathway by listing the main steps.
Answer:
1. C4 plants show kranz anatomy – Chloroplast dimorphism
2.
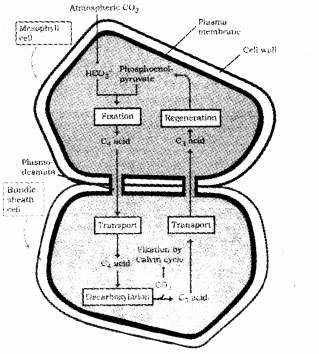
Question 2.
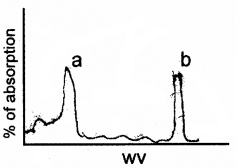
The above graph indicates absorption spectrum related to chlorophyll pigments. On the basis of. this graph answer the following.
- The peak a & b represents for what?
- Which pigments shows a & b peak of absorption?
Answer:
- Absorption maxima
- Chlorophyll
Question 3.
C4 cycle is called so because of the presence of a C4 acid in this cycle.
- Name that C4 acid.
- How does it form?
Answer:
- Oxalic acetic acid.
- It is formed by combining CO2 with PEP in the presence of PEP case enzyme.
Question 4
The response of plant towards periods of day/night is termed as photo peroidism’.
- Mention three plant groups based on photoperiodism.
- Would a defoliated plant respond to the photoperiodic cycle? Why?
Answer:
- Long day plants, short-day plants, day-neutral plants.
- No. Photo periodic receptors are located in leaves.
Question 5
Melvin Calvin was awarded the nobel prize in 1961 for the discovery of one of the most important biological process in nature.
- Name the process.
- Name site for photosynthesis.
Answer:
- C3 cycle
- Chloroplast
Question 6
Analysis the given and write down the photosynthetic response of the C3 and C4 plant in terms of CO2 concentration.
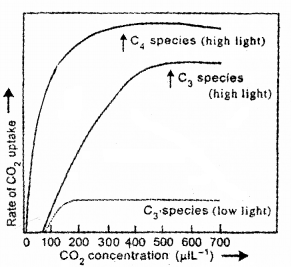
Answer:
High light intensity induces the opening of stoma. When stoma opens CO2 uptake increases. At high CO2 concentration, the rate of photosynthesis becomes high under high light in both C3 and C4 plants.
Question 7.
C4 plants have a special type of anatomy in leaves to avoid photorespiration.
- What is the special anatomy called?
- Name any two plants having this anatomy.
Answer:
- Kranz
- Wheat, Sugarcane
Question 8.
Fill up the blanks:
- Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from …………
- Inhibition of lateral buds growth by terminal bud is known as …………
Answer:
- Water
- Apical dominance
Question 9.
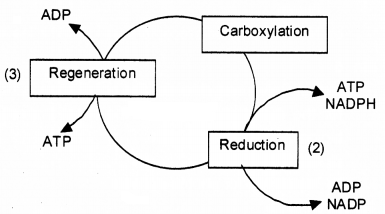
Based on the above diagram answer the following questions.
i) Write the steps of
a) Carboxylation
b) Reduction
c) regeneration
ii) Name the major enzyme involved in C3 pathway.
Answer:
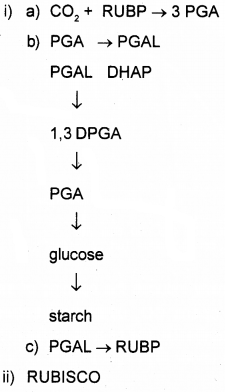
Question 10.
Give the diagram of a chloroplast and label the following parts.
- thylakoids
- grana
- stroma
- fret
Answer:
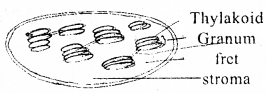
Question 11.
Certain distinguishing characters of C3 and C4 plants are given below. Arrange them in the correct table provided.
- The primary CO2 acceptor is a PEP, RuBP;
- The first stable product is PGA, OAA;
- Kranz anatomy is seen not seen;
- Carboxylase enzyme in RuBisCo, PEP carboxylase, and RubisCo.
Answer:
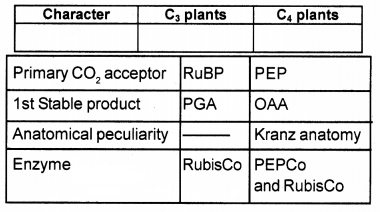
Question 12.
Given below is the schematic diagram of calvin cycle, which completes in three stages.
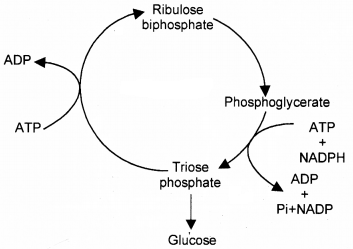
- Where does this cycle takes place?
- State the three stages of calvin cycle?
- Calculate the energy budget for each stage to synthesise one molecule of glucose during the process.
Answer:
- Stroma
- Carboxylation
- Carbon reduction
- Regeneration
- 18 ATP
- 12NADPH2
Question 13.
ADP is converted into ATP as a result of phosphorylation which takes place in photosynthesis and respiration during electron transport system. What is the difference between these two.
Answer:
Photophosphorylation in the case of photosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation in respiration.
Question 14.
Rubisco is an enzyme that catalyse two different processes in plants.
- What are those reactions?
- Name the full form of Rubisco.
- What are the site of reaction that takesplace in high oxygen concentration?
Answer:
- Carboxylation in C3 cycle. Oxygenation in photorespiration
- Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase.
- Chloroplast, peroxisomes & mitochondria
Question 15.
Some plants are called C3 and some others are called C4.
- Why they are called so?
- Explain with examples.
Answer:
- C3 plants – First stable product is a 3 carbon compound – PGA
- C4 plants – First stable product is a 4 carbon compound – OAA
Question 16.
Do reactions of photosynthesis called, as ‘Dark Reaction’ need light? Explain.
Answer:
photosynthesis is a two-step process which involves light and dark reaction. CO2 fixation takes place in dark reaction.
Question 17.
Where is NADP reductase enzyme located in the chloroplast? What is the role of this enzyme in proton gradient development?
Answer:
- The NADP reductase enzyme is located on the stroma side of the membrane.
- Oxidation of NADPH2 is involved in the accumulation of more proton concentration inside the thylakoid than outside.
Question 18.
What conditions enable RUBISCO to function as an oxygenase? Explain.
Answer:
Under high O2 concentration and low CO2 concentration, RUBISCO to function as an oxygenase and doing photorespiration.
Question 19.
Chlorophyll ‘a’ is the primary pigment for light reaction. What are accessory pigments? What is their role in photosynthesis?
Answer:
Clorophyll b,c ,d and carotenoides. These pigments harvest light energy and hand over to chlorophylla.
Question 20.
2H2O → 2H+ + O2 + 4e –
Based on above equation, answer the following questions:
- Where does this reaction take place in plants?
- What is the significance of this reaction?
Answer:
- Lumen of the thylakoids.
- O2 is evolved during this reaction, moreover, electrons are made available to PS-II continuously.
Question 21.
What is the basis for designating C3 and C4 pathways of photosynthesis?
Answer:
The first stable product formed in some plants are 3 carbon compound but in others 4 carbon compound, therefore such plants designated as C3 and C4 respectively.
Question 22.
Chlorophyll b and carotenoids are known as accessory pigments. Give reason?
Answer:
Chlorophyll b and carotenoids harvest light energy and hand over to chlorophyll a (reaction centre)
Question 23.
C4 plants show high rate of photosynthesis than C3 plants. Are you agree with the statement? Give reason?
Answer:
Yes. In C4 plants photorespiration does not occur. It is a wastage process that occur in C3 plants only, because RUBISCO present in C3 plants can act as carboxylase and oxygenase.
Question 24.
How many ATP molecules are required for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose in
- C3 pathway
- C4 pathway
Answer:
- C3 pathway – 18 ATPs
- C4 pathway – 30 ATPs
Question 25.
Cyanobacteria and some other photosynthetic bacteria don’t have chloroplasts. How do they conduct photosynthesis?
Answer:
Cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic bacteria have thylakoids suspended freely in the cytoplasm (i.e., they are not enclosed in membrane), and they have bacteriochlorophyll.
Question 26.
What would happen to the rate of photosynthesis in C3 plants if CO2 concentration level almost doubles from the present level in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The rate of photosynthesis in C3 plants increases with increase in CO2 concentration
Question 27.
Does photorespiration pose threat to plants yet it occurs in angiosperms why?
Answer:
Any angiospermic plants bear only one type of chloroplast and CO2 acceptor is RUBP in these cases. Thus there is no other possibility except to undergo C3 pathway which may ultimately lead to photorespiration.
Question 28.
Secondary CO2 fixation is inevitable for C4 plants. Do you agree? Give justification of your answer.
Answer:
Yes. This type of CO2 fixation takes place in bundle sheath chloroplast and carbohydrate is formed.
Question 29.
Carboxylation of C3 plants are interrupted in changed environmental conditions. Why?
Answer:
Normally carboxylation takes place in C3 plants but in high O2 and low CO2 concentration, the energy wasteful process (photorespiration ) occur.
Question 30.
RuBisco is an enzyme that acts both as a carboxylase and oxygenase. Why do you think RuBisco carries out more carboxylationin in C4 plants.
Answer:
1. The C4 plants have dimorophic chloroplasts. In mesophyll cells chloroplast are granal but in bundle sheath cells the chloroplasts are agranal.
2. So in the these plants when CO2 is fixed in bundle sheath cells, the intracellular CO2 concentration is increased that is why RuBisco enzyme carries out more carboxylation in C4 plants.
Question 31.
Succulents are known to keep their stomata closed during the day to check transpiration. How do they meet their photosynthetic CO2 requirements?
Answer:
1. Succulent (water-storing) plants such as cacti, euphorbias fix CO2 into organic compound using. PEP carboxylase at night, when the stomata are open.
2. PEP + CO2 → OAA → Malic acid
The organic compound (malic acid) accumulates throughout the night and is decarboxylated during the day to produce CO2.
Question 32
In C4 plants RUBISCO is present but photorespiration does not occur. Why?
Answer:
Because intracellular CO2 concentration is high. Hence RUBISCO do not show oxygenase activity.
Question 33
The statements are given below. Identify true and false
- Carbohydrate (glucose) is formed in mesophyll chloroplast of C4 pathway
- Calvin cycle involves 3 steps
- The absorption peak of PS I is 680nm
- Calvin cycle takes place in Temperate plants
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- True
Plus One Botany Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
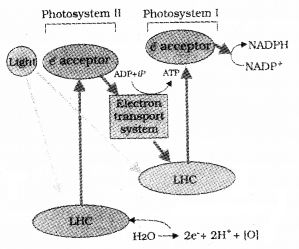
A plant physiologist while studying the light reaction step of photosynthesis using Chlorella, could detect the following facts.
- Name the reaction
- What is meant by photolysis?
- Draw the electron transport schematically.
Answer:
- Noncyclic photophosphorylation
- Splitting of water
Question 2.
The enzyme catalysing C4 and C3 pathway is different but they are coming under dark reaction.
- Name the enzyme shows CO2 fixation in such plants
- Where is the second CO2 fixation occurs in C4 plants
- Which is the primary CO2 acceptor and stable product of C3 pathway
Answer:
- C4 pathway – PEPCO, C3 pathway-RUBISCO
- Bundle sheath chloroplast
- CO2acceptor-RUBP, Stable product— 3- phosphoglycerate
Question 3.
CO2 fixation is associated with wasteful process and efficiency is decreased
- Name the wasteful process.
- Identify the enzyme catalysing the above process
- Which is the chief organelle responsible for this?
Answer:
- Photorespiration
- Oxygenase activity of RUBISCO
- peroxisome
Question 4.
Answer the following questions based on carbon fixation by plants.
- which is the key enzyme involved in carbon fixation of photosynthesis in C3 plants?.
- Rubisco has a dual role. Comment.
- Give the name of two cell organells other than chloroplast involved in the process that catalysed by Rubisco.
Answer:
- Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase
- Carboxylation & oxygenation
- Peroxisome & mitochondria
Question 5.
The type of CO2 fixation in tropical plants is different from temperate plants
- Identify the plants in which efficient CO2 fixation occurs.
- Tropical plants do not show the wasteful process why?
- Give two examples for such plants
Answer:
- C4 plants (Tropical plants)
- Because intracellular CO2 concentration is very high
- Sugarcane and Maize.
Question 6.
Cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation is associated with the light reaction of photosynthesis.
- Where does photolysis occur?
- Give two difference between cyclic and noncyclic
Answer:
- Inside thylakoid
- Cyclic – It involves PSI (P700)
- Only ATP is formed
- Noncyclic – It involves PSI and PSII (P680)
- ATP and NADPH2 are produced
Question 7.
Do you think that synthesis of glucose occur during light reaction?
- If not what is the function of light reaction?
- name the CO2 acceptor in C3 cycle and C4 cycle
Answer:
- In light reaction, energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH2 are produced. These are used in Dark reaction for Glucose synthesis,
- RUBP – CO2 acceptor in C3 cycle
- PEP – CO2 acceptor in C4 cycle
Question 8.
Sugar cane has a special leaf anatomy which make the plant photosynthetically more efficient.
- Name the leaf anatomy
- Write a note on carbon dioxide fixation in sugarcane.
Answer:
1. Kranz anatomy
2. In sugarcane CO2 fixation tapseplace in mesophyll chloroplast. Initially CO2 is accepted by PEP and by using Pepco it is converted into OAA. It is then transported to bundle sheath chloroplast.
After the transport, decarboxylation occurs and forms pyruvic acid which is transported to mesophyll chloroplast and converted into PEP. The CO2 released during decarboxylation enters into calvin cycle for the synthesis of Glucose.
Question 9.
C4 plants have special leaf anatomy in which C3 cycle also take place.
- Name the primary acceptor of CO2 and first stable product in C4 cycle.
- Why is photorespiration absent in C4 plants?
- Name the special type of leaf anatomy and explain.
Answer:
1. CO2 acceptor in C4 is PEP and the stable product is OAA.
2. Because in C4 plants, the primary CO2 acceptor is PEP but in C3 plants the primary CO2 acceptor is RUBP. The enzyme RUBISCO present C3 plants have dual function ie, carboxylase and oxygenase activity. Oxygenase activity promotes photorespiration.
3. Kranz anatomy in C4 plants. In this bundle sheath chloroplast are arranged in the form of a ring or wreath.
Question 10.
Explain how during light reaction of photosynthesis, ATP synthesis is a chemiosmotic phenomenon.
Answer:
The conditions helpful in chemiosmotic ATP synthesis are:
1. The splitting of the water molecule takes place on the inner side of the membrane, it causes the accumulation of protons or hydrogen ions within the lumen of the thylakoids.
2. As electrons move through the photosystems, protons are transported across the membrane, and proton is released into the inner side or the lumen side of the membrane.
3. The NADP reductase enzyme is located on the stroma side of the membrane. Along with electrons that come from the accepter of electrons of PS I, protons are necessary for the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH+ H+. These protons are also removed from the stroma.
Question 11.
Chemiosmotic hypothesis explains the mechanism of ATP synthesis during respiration and photosynthesis.
- Write the difference in the accumulation of proton during the above process.
- What causes the proton gradience across the thylakoid membrane within the chloroplast?
OR
C3 plants complete the Biosynthetic phase through 3 stages and sometimes they are affected by high concentration of O2.
- Name the 3 stages of Biosynthetic phase.
- Name the assimilatory powers used during this phase and specify the number.
- Write the process carried out by C3 plants during high concentration of O2.
- How does the high O2 concentration affect RUBISCO?
Answer:
1.
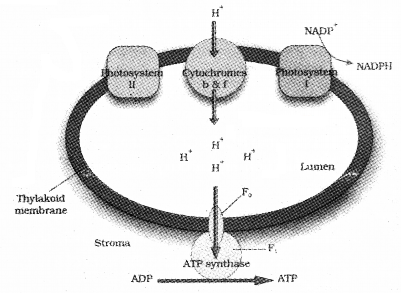
2. Movement of electrones through electron carrier
OR
- Carboxylation, carbon reduction and regeneration
- ATP & NAD PH2
- Photorespiration
- RUBISCO – undergoes oxygenase activity
Question 12.
ATP and NADPH2 molecules synthesized in Light reaction of Photosynthesis are used for the synthesis glucose in Dark reaction.
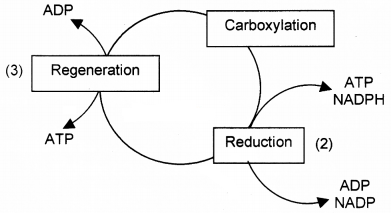
- Who proposed the Dark reaction?
- List out three phases in Dark reaction.
- Location of dark reaction in the chloroplast.
- Expense of ATP and NADPH2 for the synthesis of one molecule of Glucose in Dark reaction.
Answer:
- Melvin Calvin
- Carboxylation, carbon reduction and regeneration
- Stroma
- 18 ATP and 12 NADPH2
Question 13.
Observe the labeled and write down the following :
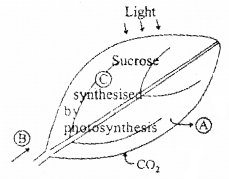
- Which gas is passed out into the atmosphere at A?
- What raw material required for photosynthesis, enters the leaf at B?
- Describe the major steps involved at C in the synthesis of sugar.
Answer:
- O2
- H2O
- CO2 is reduced to sugar (glucose or fructose), by the biochemical reaction of photosynthesis (Calvin cycle). It has 3 major steps.
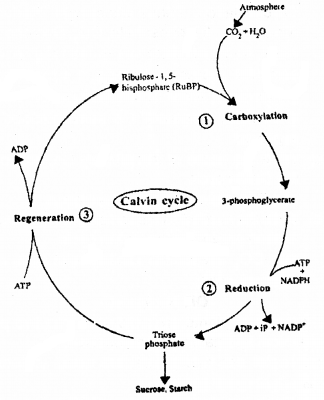
- Carboxylation – During which CO2 combines with RuBP.
- Reduction – During which carbohydrate is formed at the expense of the photochemically made ATP and NADPH.
- Regeneration – During which is the CO2 acceptor (RuBP) is formed again so that the cycle continues.
Plus One Botany Photosynthesis in Higher Plants NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
By looking at a plant externally can you tell whether a plant is C3 or C4? Why and how?
Answer:
Usually plants growing in dry conditions use ( pathways. It cannot be said conclusively if the plant is a C3 or C4 by looking at fleshy leaf structure of C4 plants.
Question 2.
By looking at which internal structure of a plant can you tell whether a plant is C3 or C4? Explain.
Answer:
The particularly large cells around the vascular bundles of the C4 pathway plants are called bundle sheath cells, and the leaves which have such anatomy are said to have ‘Kranz’ anatomy. ‘Kranz’ means ‘wreath’ and is a reflection of the arrangement of cells.
The bundle sheath cells may form several layers around the vascular bundles; they are characterised by having a large number of chloroplasts, thick walls impervious to gaseous exchange and no intercellular spaces.
Plus One Botany Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The ATP production in photosynthesis is called
(a) Phototropism
(b) phosphorylation
(c) Photo-oxidation
(d) photophosphorylation
Answer:
(d) photophosphorylation
Question 2.
Conditions helpful in photorespiration are
(a) more oxygen and less carbon dioxide
(b) less oxygen and more carbon dioxide
(c) more temperature and less oxygen
(d) more humidity and less temperature
Answer:
(a) more oxygen and less carbon dioxide
Question 3.
What is common between chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts?
(a) Presence of pigments
(b) Possession of thylakoids and grana
(c) Storage of starch, proteins, and lipids
(d) Ability to multiply by a fission-like process
Answer:
(d) Ability to multiply by a fission-like process
Question 4.
A student set up an experiment on photosynthesis as follow: He takes soda water in a glass tumbler and keeps the tumbler exposed sunlight hoping that he has provided necessary ingredient for photosynthesis to proceed (viz, CO2 H2O chlorophyll and light)
What do you think what will happen after, say few hours of exposure of light?
(a) Photosynthesis will take place and glucose will produced
(b) Photosynthesis will take place and starch will be produced which will turn the mixture turbid
(c) Photosynthesis will not take place because CO2 dissolved in soda water escapes into the atmosphere
(d) Photosynthesis will not take place because intact chloroplasts are needed for the process
Answer:
(a) Photosynthesis will take place and glucose will produced
Question 5.
Photochemical reactions in the chloroplasts are directly involved in
(a) Fixation of carbon dioxide
(b) synthesis of glucose and starch
(c) formation of Phosphoglyceric acid
(d) photolysis of water and phosphorylation of ADP
Answer:
(d) photolysis of water and phosphorylation of ADP
Question 6.
Match the following with correct combination
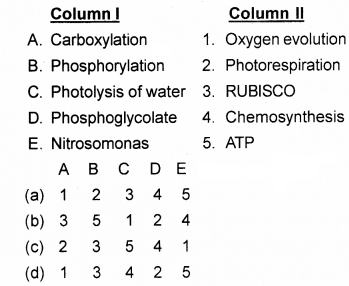
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
Choose the correct statement.
(a) The C4 – plants do not have RUBISCO
(b) Carboxylation of RuBP leds to the formation of PGA and phosphoglycolate
(c) Carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate results in the formation of C4 – acids
(d) Decarboxylation of C4 – acids occurs in the mesophyll cells
Answer:
(c) Carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate results in the formation of C4 – acids
Question 8.
In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, there are photolysis of 12 water molecules, How many H+ are formed?
(a) 24 H+
(b) 36 H+
(c) 12 H+
(d) 32 H+
Answer:
(a) 24 H+
Question 9.
In Hatch and Slack pathway.
(a) chloroplasts are of same type
(b) occurs in Kranz anatomy where mesphyll have small Chloroplasts whereas bundle sheath have granal chloroplasts
(c) occurs in Kranz anatomy where mesphyll have small Chloroplasts whereas bundle sheath have larger agranal chloroplasts
(d) Kranz anatomy where mesphyll cells are diffused
Answer:
(c) occurs in Kranz anatomy where mesphyll have small Chloroplasts whereas bundle sheath have larger agranal chloroplasts
Question 10.
To form one molecule of glucose in Calvin cycle
(a) 9ATP and 36 NADPH are required
(b) 6 ATP and 6 NADPH are required
(c) 3 ATP and 2 NADPH are required
(d) 18ATPand12 NADPH are required
Answer:
(d) 18ATPand12 NADPH are required
Question 11.
Photosynthesis is correctly explained by the equation
(a) 6 CO2 + 12H2 O → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
(b) 6 CO2 + 6H2 O → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 + 6H2
(c) 6CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12 O6+ 6O2
(d) 2CO2+ 12H2O → C6H12 O6+ 2CO2
Answer:
(a) 6 CO2 + 12H2 O C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Question 12.
In sugarcane plant, CO2is fixed into malic acid, in which the enzyme that fixes carbon dioxide is
(a) ribulose phosphate kinase
(b) fructose phosphatase
(c) ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase
(d) phosphoenol pyruvate carboxlase
Answer:
(d) phosphoenol pyruvate carboxlase
Question 13.
Which fractions of the visible spectrum of solar radiations are primarily absorbed by carotenoids of higher plants?
(a) Red and violet
(b) Violet and blue
(c) Blue and green
(d) Green and red
Answer:
(b) Violet and blue
Question 14.
Which factor is not limiting in normal condition for photosynthesis?
(a) Air
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Water
(d) Chlorophyll
Answer:
(a) Air
Question 15.
Which of the following is used during discovery of Calvin cycle?
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Volvox
(c) Chlamydomonas
(d) Chlorella
Answer:
(d) Chlorella
Question 16.
Photosynthesis in C4 plants is relatively less limited by atmospheric carbon dioxide levels because
(a) Four carbon acids are the primary initial carbon dioxide fixation products
(b) the primary Fixation of carbon dioxide is mediated via PEP caroxylase
(c) effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells.
(d) Rubisco in C4_ plants has higher affinity for CO2
Answer:
(b) the primary Fixation of carbon dioxide is mediated via PEP caroxylase
Question 17.
NADP is converted into NADPH2 in
(a) photosystem I
(b) photosystem II
(c) calvin cycle
(d) non cyclic photophosphorylation
Answer:
(d) noncyclic photophosphorylation
