Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Transport in Plants
Plus One Botany Transport in Plants One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?
(a) it is used for water purification.
(b) In this technique, a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure is applied to the system
(c) It is a passive process
(d) It is an active process
Answer:
(c) It is a passive process
Question 2.
Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
(a) Light
(b) wind speed
(c) temperature
(d) chlorophyll content of leaves
Answer:
(d) chlorophyll content of leaves
Question 3.
The lower surface of leaf will have a number of stomata in a
(a) isobilateral leaf
(b) dorsiventral leaf
(c) both a and b
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) dorsiventral leaf
Question 4.
The form of sugar transported through phloem is
(a) Fructose
(b) Sucrose
(c) glucose
(d) ribose
Answer:
(b) sucrose
Question 5.
The process of guttation takes place
(a) when the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low
(b) when the root pressure is low and the rate of transpiration is high
(c) when the root pressure equals the rate of transpiration
(d) when the root pressure, as well as rate of transpiration, are high.
Answer:
(a) when the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low
Question 6.
Which of the following is an example of imbibition
(a) uptake of water by root hair
(b) exchange of gases in stomata
(c) swelling of seed when putting in the soil
(d) opening of stomata
Answer:
(c) swelling of seed when putting in the soil
Question 7.
What will happen to a plant cell when kept in hypotonic solution?
Answer:
Cell become turgid
Question 8.
How are protoplasm of adjacent cells connected to each other?
Answer:
Plasmodesmata
Question 9.
Name the process in which water drops ooze out from margins of leaves.
Answer:
Guttation
Question 10.
The C4 plants are twice as efficient as C3 plants in terms of fixing C02 but lose only as much water as C3 plants for the same amount of C02 fixed.
Answer:
Half
Question 11.
Plants could be grown in a nutrient solution in the complete absence of soil. Name the technique.
Answer:
Hydroponics
Question 12.
Name the hormone which signals the closure of stomata during severe drought or severe solar radiation.
Answer:
Abscisic acid (ABA)
Question 13.
Name the physical phenomena associated with the first step of seed germination.
Answer:
Imbibition
Question 14.
What causes the leaves of grasses to roll in dry weather?
Answer:
Presence of bulliform cells or motor cells
Question 15.
The diagram below shows the cells placed in hypertonic solution and hypotonic solution. If the diagram ‘B’ is ‘turgid’ what will be diagram ‘A’?
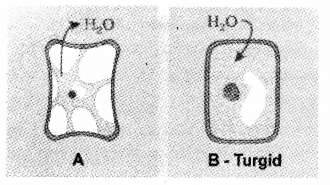
Answer:
A – Flaccid
Question 16.
The excess of one element may inhibit the uptake of another element. What is this effect called?
Answer:
Toxicity of micronutrients
Question 17.
Name the type of obligatory association found in pinus seeds that promote germination.
Answer:
Mycorrhiza
Question 18.
A plant cell when kept in a certain solution got plasmolysed. What was the nature of this solution?
Answer:
Hypertonic solution
Question 19.
Why turgidity of the cell essential for plants?
Answer:
It helps to maintain plant organs in normal shape
Question 20.
Absorption of water from the soil by dry seeds increases the, thus helping seedlings to come out of the soil.
Answer:
Pressure
Question 21.
A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant dies. Give reason.
Answer:
It is due to exosmosis.
Question. 22
Identify a type of molecular movement which is highly selective and requires special membrane proteins, but does not require energy.
Answer:
Facilitated diffusion
Question 23.
Smaller, lipid-soluble molecules diffuse faster through cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances are facilitated by certain biomolecules. Name it.
Answer:
Protein
Question. 24
The bending of wooden doors during rainy reasons is due to physiological phenomenon. Name it.
Answer:
Imbibition
Plus One Botany Transport in Plants Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give below is a diagram, where hypotonic solution is separated by a semipermeable membrane from a hypertonic solution and kept for a few hours.
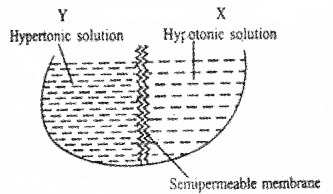
- In which direction will the solvent move? From X to Y or Y to X.
- Name the process of movement of the solvent.
Answer:
- X to Y
- Osmosis
Question 2.
Differences between the following.
Diffusion and Osmosis
Answer:
1. Diffusion:
It is the movement of solute from the region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration.
2. Osmosis:
It is the movement of solvent from the region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
Question 3.
Differences between Guttation and transpiration
Answer:
1. Guttation:
Loss of water in the form of water droplets from the margin of leaves through hydathode.
2. Transpiration:
It is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the surface of leaves through stomata.
Question 4.
Both the xylem and phloem are tubular structures. One is unidirectional and the other is bi-directional. Comment on it.
Answer:
Phloem is bidirectional in order to transport prepared food from leaves to different parts of the plant and translocates stored food from downward to upward for the growth of buds.
Question 5.
Ramu while observing the root nodules of pea plant, noticed the pink colour. Sita said that it is due to the presence of a substance. Can you name the substance and write its role.
Answer:
Leg hemoglobin. It is an O2 scavenger. It creates the anaerobic condition for enzyme Nitrogenase during N2 Fixation
Question 6.
Match the following :
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Imbibition 2) Exosmosis 3) Diffusion 4) Transpiration | a) Leaves b) Perfumes c) Dried grapes d) Pickles |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Imbibition 2) Exosmosis 3) Diffusion 4) Transpiration | Dried grapes Pickles Perfumes Leaves |
Question 7.
Water is absorbed by the root hairs, It can move deeper into root layers by two distinct pathways.
- Write the name of the pathways.
- Which substance controls water transport in the endodermal region?
Answer:
- Apoplast pathway & Symplast pathway
- Suberin
Question 8.
“Root pressure is inadequate to lift the water molecules in taller plants like Eucalyptus”.
- Which theory is successfully explaining the Ascent of sap in plants like Eucalyptus?
- Who proposed this theory?
Answer:
- Transpiration pull – cohesion tension theory
- Dixon & Jolly
Question 9.
Fresh mangoes can survive fora prolonged period of time when they are placed in highly concentrated salt solution. Some physiological changes take place in the cell. Comment on the changes.
Answer:
- Exosmosis.
- Bacteria can not survive in hypertonic solutions.
Question 10.
Pure Honey checks the growth of microorganisms. Justify based on your knowledge in osmosis.
Answer:
Pure honey is hypertonic .bacterial cells shrink and die due to plasmolysis.
Question 11.
A fesh mango pieces is placed in water containing high concentration of sodium chloride.
Exosmosis, Plasmolysis, Deplasmolysis, Imbibition
- Select and write down the appropriate terms given above to represent the sequence of events leading to shrinking.
- What is plasmolysis?
Answer:
- Exosmosis – Plasmolysis
- The withdrawal of the protoplast from the cell wall due to exosmosis.
Question 12.
Ψw =Ψs + Ψp
- Expand the equation.
- Why solute potential is always negative?
Answer:
1.
- Ψw – Water potential
- Ψs – Solute potential,
- Ψp – pressure potential
2. Since adding solute reduces water potential, it is always negative.
Question 13.
Observe the given figure showing the pathways of water movement in the plant body and answer the questions.
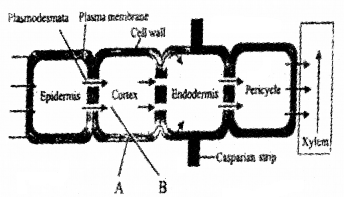
- Identify A and B pathways.
- In which of the above pathways does water move beyond endodermis?
Answer:
- A – Apoplast pathway
B – Symplast pathway - Apoplast pathway
Question 14.
Apoplast and symplast pathways are the two distinct pathways of water to move deeper into the root layers. Which is the only pathway through which water can enter the vascular cylinder and why?
Answer:
Symplast – Because endodermal wall is suberised.
Question 15.
When a freshly collected Spirogyra filament is kept in 10% potassium nitrate solution, it is observed that the protoplasm shrinks in size:
- What is this phenomenon called?
- What will happen if the filament is replaced in distilled water?
Answer:
1. This phenomenon is called plasmolysis. (The shrinkage of protoplast from the cell wall under the influence of a strong solution/ hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis.
2. If filaments are replaced in water the protoplast starts swelling. It comes in contact with the cell wall and cell regains its original size.
The swelling up of plasmolyzed protoplast under the influence of a weak solution or water is called deplasmolysis.
Question 16.
1. In an experiment, Deepa put a piece of raw mango in 0.5M salt solution and another piece in 1M salt solution. Which mango piece will get plasmolyzed fast?
2. Water potential of solution A is -0.3 bar and that of solution B is -0.1 bar. If solution A is separated from solution B by a semi-permeable membrane water molecules will flow from to
Answer:
- Mango piece put in 1 M salt solution get plasmolysed rapidly than. 0.5M solution.
- B (-1.1) to A (-0.3)
Question 17.
An unavoidable waste mechanism is found in higher plants during high temperature.
- Name the process.
- Why is it said so?
Answer:
- Transpiration
- It has merits and demerits. Since water and minerals are absorbed and translocated to distant sites by this process but 99% of water absorbed is transpired out.
Question 18.
Water moves up against gravity and even for a tree of 20 m height, the tip receives water within two hours. Which is the most important physiological phenomenon responsible for the upward movement of water is
Answer:
Transpirational pull.
Question 19.
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. What are the factors influence rate and direction of osmosis?
Answer:
Pressure and concentration gradient.
Question 20.
When a tea bag is placed in a cup of water, which phenomenon is observed? Explain the phenomenon.
Answer:
Diffusion. It is the movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Question 21.
Phloem transport is bidirectional while xylem transport is unidirectional. Give a reason?
Answer:
Phloem transport is bidirectional because prepared food materials translocated to storage regions. These storage food materials are again transported to growing regions for the growth of buds. So, through phloem downward and upward transport takes place. Xylem transport is unidirectional because water and minerals are absorbed and conducted upwards.
Question 22.
Write a suitable term in each pair
- apoplast: through cell wall; ………: through the cytoplasm
- endosmosis: turgid; exosmosis: ………..
- ………..: unidirectional; phloem transport: bidirectional
- Mg : macroelement: …………: microelement
Answer:
- Symplast
- Flaccid
- Xylem
- Mn
Question 23.
‘Ψw = Ψs + Ψp Expand the equation
Answer:
- Ψw = Water potential is the sum of
- Ψs = Solute potential solute potential
- Ψp = pressure potential and pressure potential.
Question 24.
Bacteria cannot live in highly salted pickle. Why?
Answer:
The bacterial cell undergoes plasmolysis in saltwater. This results shrinking of protoplast. Hence, Bacteria cannot live in saltwater.
Question 25.
Observe the following diagram showing the movement of water in plant cells. Identify 1 & 2.
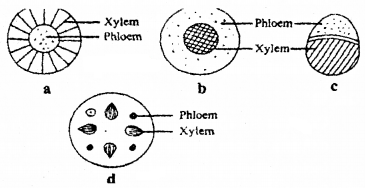
Answer:
- Apoplastic pathway
- Sym plastic pathway
Question 26.
A few Pieces of potato were weighed and kept in saltwater overnight. In the morning they are weighed again.
- What will be the change in weight?
- Name the process responsible for the change.
Answer:
- The weight of potatoes is decreased.
- Exosmosis results in the loss of water from the potato, it leads to plasmolysis.
Question 27.
Before eating Grapes, it is advised to wash them well by keeping them in water for some time to wash off the pesticides on them. However, it is more advisable to keep the Grapes in salt water than in fresh water to make them safer for consumption. Suggest an explanation for this.
Answer:
The grapes put in saltwater are safer for consumption because poisonous chemicals present in grapes are come out by the process of exosmosis.
Question 28.
The cytoplasm in a plant cell is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane. Give reason.
Answer:
The cell wall is freely permeable to water and substances in solutions but membrane is selectively permeable.
Question 29.
In a girdled plant, when water is supplied to the leaves above the girdle, leaves may remain green for sometime then wilt and ultimately die. What does it indicate?
Answer:
Girdling removes phloem and hence phloem transport is blocked.
Question 30.
Movement of substances in xylem is unidirectional while in phloem it is bidirectional. Why?
Answer:
Xylem conducts”Water and minerals in upward direction only but phloem conducts food in downward direction and in spring season stored food is again transported to upward for bud growth. Hence movement of substances in xylem is unidirectional while in phloem it is bidirectional.
Question 31.
Plants absorb water from the soil through root hairs by two pathways?
- Name the pathways
- Explain any one of them
Answer:
- Apoplastic pathway and symplastic pathway
- In apoplastic pathway, water transport takes place through the nonliving part of the cell (cell wall).
Question 32.
What is the water potential of pure water at atmospheric pressure? What happens to it when solutes are added to it?
Answer:
Zero, Water potential is decreased and comes to more negative values.
Question 33.
Transport of hydrophilic substances through cell membrane is difficult. Do you agree ? Give reason.
Answer:
Yes, because the cell membrane contains lipids.
Question 34.
What is meant loading and unloading of phloem?
Answer:
The entering of sugar into sieve tube is called loading and movement of sugar out of sieve tube into storage tissues is called unloading.
Question 35.
Root pressure theory is not adequate for explaining water movement up a long day plant. Why?
Answer:
It is used for explaining water movement up in herbaceous plants but in long plants, it is explained by the transpiration pull theory.
Question 36.
Why is energy required to develop root pressure?
Answer:
Every activity requires energy. Root pressure develops due to activity of living cells of the root.
Question 37.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Answer:
When a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution, its water potential is increased.
Question 38.
How is mycoorrhizal association helpful in absorption of water and mineral in plants?
Answer:
Mycorrhizal association help in water and mineral absorption. Fungal hyphae have a very large surface area that absorbs mineral ions and water from a much larger volume of soil.
Question 39.
Give an example for obligate mycorrhizal asociation.
Answer:
Mycorrhizal association is found in pinus seeds i.e Pinus seeds do not germinate and establish without mycorrhiza.
Question 40.
Downhill and uphill movement are used in transport of molecules through membrane.
- Which is the above process that requires energy?
- Which is the above process not dependent on concentration gradient. Why?
Answer:
- uphill transport is active transport requires energy.
- Downhill transport, because molecules move from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration.
Question 41.
Two pathways of water movement into the deeper layers of root ie; from epidermis to xylem vessels
- Name the two pathways
- Which is the substance present in the endodermis block one pathway?
Answer:
- Apoplastic pathway and symplastic pathway
- suberin in casperian strips
Question 42.
In plants translocation of photosynthates occur in 2 ways but water and mineral transport in one way.
- Which is the two way suggested?
- Name the conducting channel for both.
Answer:
1. Food translocated from leaves to storage regions called downward transport. During spring season food again transported upward for bud growth. So such type of transport is bidirectional.
2. Food transported through phloem and water and mineral transported through the xylem.
Question 43.
In plants stomata opens during day time and close during night time.
How is decreasing water potential of guard cell affect the opening and closing of stomata?
Answer:
If decreasing the water potential of guard cell, water enters into guard cell from the subsidiary and it becomes turgid, stomata open.
Plus One Botany Transport in Plants Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“Water is transient in plants. Less than 1% of water reaching the leaves is used in photosynthesis and plant growth’’. What is the fate of remaining percentage of water? Specify the phenomenon? Give its significance in plants?
Answer:
99% of water absorbed is lost through transpiration.
- It provides cooling effect to leaves and other organs.
- It promotes mineral absorption.
- It helps to maintain the shape and structure of plants by keeping up its turgidity.
Question 2.
What are the factors responsible for ascent of xylem sap in plants?
Answer:
- Cohesion: The mutual attraction between water molecules
- Adhesion: The attraction of molecules to polar surface e g., the surface of tracheary elements
- Surface Tension: The water molecules are attracted to each other in liquid phase more than to water in gas phase.
All these properties provide water high tensile strength (an ability to resist a pulling force) as well as high capillarity (ability to rise in a thin tube).
In plants, capillarity is aided by the small diameter of both tracheids and vessels.
Question 3.
The solution taken in the beaker have lower solute concentration than thistle funel, osmosis starts and continues
- What will hapen if more solute is added in the thistle funel ?
- Which is the solution mentioned above have higher water potential?
- Which is the method possible to change flow of solvent molecules?
Answer:
- Diffusion takes place faster
- solution was taken in the beaker
- apply greater pressure than atmospheric pressure in solution of thistle funel.
Question 4.
Look at the following figure in which two chambers, A and B, containing solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Answer the following questions.
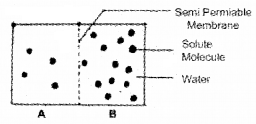
- Solution of which chamber has a lower water potential
- In which direction will osmosis occur?
- Which solution has a higher solute potential?
- If one chamber has a Ψ of -2000KPa and the other -1000 KPa, which is the chamber that has the higher Ψ?
Answer:
- Solution in B chamber has lower water potential.
- Osmosis occurs from a to b.
- A solution has higher solute potential.
- The chamber having -ve 1000K Pa has the higher psi
Question 5.
Identify the following.
- Stress hormone
- The shrinking of protoplasm due to continuous exosmosis
- The positive pressure develops within the xylem of roots due to the absorption of water and minerals.
Answer:
- Abscisic acid
- Plasmolysis
- Root pressure
Plus One Botany Transport in Plants NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
Answer:
- Factors affecting the rate of diffusion:
- Gradient of Concentration
- Permeability of membrane
- Temperature
- Pressure
Question 2.
What are porins? What role do they play in diffusion?
Answer:
The porins are proteins that form huge pores in the outer membranes of the plastids, mitochondria and some bacteria allowing molecules up to the size of small proteins to pass through. Thus porins faciliate diffusion.
Question 3.
Decribe the role played by protein pumps during active transport in plants.
Answer:
Active transport uses energy to pump molecules against a concentration gradient. Active transport is carried out by membrane – proteins.
Question 4.
Explain why pure water has maximum water potential?
Answer:
Water molecules possess kinetic energy. In liquid and gaseous form they are in random motion that is both rapid and constant. The greater the concentration of water in a system, the greater is its kinetic energy or ‘water potential’.
Hence, it is obvious that pure water will have the greatest water potential if two systems containing water are in contact, random movement of water molecules will result in net movement of water molecules from the system with higher energy to the one with lower energy. Thus water will move from the system containing water at higher water potential to having low wate potential.
This process of movement of substances down a gradient of free energy is called diffusion. Water. potential is denoted by the Greek symbol Psi and is expressed in pressure units such as pascals(Pa). By convention, the water potential of pure water at standard temperatures, which is not under any pressure, is taken to be zero.
Question 5.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Answer:
Under constant temerature the volume of liquid varies inversely to pressure. Moreover, if greater pressure is applied then it will change the state of the matter from liquid to solid at a given temperature. Any liquid will abide by these laws.
Question 6.
Discuss the factors responsible for ascent of xylem sap in plants.
Answer:
The transpiration driven ascent of xylem sap depends mainly on the following physical properties of water:
- Cohesion – the mutual attraction between water molecules.
- Adhesion – the attraction of water molecules to polar surfaces (such as the surface of tracheary elements).
- Surface Tension – water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than to water in the gas phase.
These properties give water high tensile strength, i.e., an ability to resist a pulling force, and high capillarity, I ‘.e., the ability to rise in thin tubes. In plants capillarity is aided by the small diameter of the tracheary elements – the tracheids and vessel elements.
Plus One Botany Transport in Plants Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Closure of stomata due to water stress is brought about by
(A) Auxin
(B) Ethylene
(C) Abscisic acid
(D) Cytokinin
Answer:
(C) Abscisic acid
Question 2.
The most common type of transpiration is
(A) Stomatal
(B) Cuticular
(C) Lenticular
(D) Foliar
Answer:
(A) Stomatal
Question 3.
All the following include osmosis except
(A) Passage of water from root hair to adjacent cells
(B) Passage of water from lower xylem to upper xylem
(C) Passage of water from xylem vessel to mesophyll cell
(D) The entry of water into root hair from soil solution
Answer:
(B) Passage of water from lower xylem to upper xylem
Question 4.
Stomatal opening and closure are due to
(A) Presence of gases inside leaves
(B) Gene action
(C) Pressure offered by guard cells
(D) Pressure offered by subsidiary cells
Answer:
(C) Pressure offered by guard cells
Question 5.
Translocation of sugars is correlated by
(A) Boron
(B) Iron
(C) Molybdenum
(E) Calcium
Answer:
(A) Boron
Question 6.
Identify the wrong statement of the following
(A) Root pressure is a positive pressure that develops in the xylem sap of the root of some plants.
(B) Water molecules remain attached to one another by a strong mutual force called cohesion force
(C) Guttation is frequently seen in herbaceous plants growing under the conditions of low soil moisture and low atmospheric humidity
(D) In monocot leaves, guard cells remain dumbbell-shaped and their cell walls are thickened only in the middle
Answer:
(C) Guttation is frequently seen in herbaceous plants growing under the conditions of low soil moisture and low atmospheric humidity
Question 7.
In which of the following plants, will there be no transpiration?
(A) Plants living in deserts
(B) Plants growing in hilly regions
(C) Aquatic submerged plants
(D) Aquatic plants with floating leaves
Answer:
(C) Aquatic submerged plants
Question 8.
When a cell is placed in hypertonic solution
(A) Exosmois occurs and the cell becomes turgid
(B) Endosmosis occurs and the cell becomes turgid
(C) Exosmosis occurs and the cell becomes plasmolysed
(D) Endosmosis occurs and the cell becomes plasmolysed
Answer:
(C) Exosmosis occurs and the cell becomes plasmolysed
Question 9.
The thin film of water covering soil particles and held strongly by attractive forces is called
(A) Hygroscopic water
(B) Runaway water
(C) Gravitational water
(D) Capillary water
Answer:
(A) Hygroscopic water
Question 10.
Plants die when over-fertilized because of the fertilizer
(A) Damages the wall of delicate root hairs
(B) Blocks absorption of nitrogenous ions
(C) Causes dehydration of plants by exosmosis
(D) Upsets soil environment by poisoning
Answer:
(C) Causes dehydration of plants by exosmosis
Question 11.
Movement of individual molecules of substance from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration is called
(A) Osmosis
(B) Turgor pressure
(C) Diffusion
(D) Osmotic potential
Answer:
(A) Osmosis
Question 12.
The proteins that form large pores in the outer membranes of the plastids, mitochondria, etc are
(A) Porins
(B) Aquaporins
(C) Symporins
(D) Both A & B
Answer:
(A) Porins
Question 13.
Transport of molecules across the membrane in the same direction is
(A) Antiport
(B) Symport
(C) Permeability
(D) Uniport
Answer:
(B) Symport
Question 14.
Rate of osmosis depends on
(A) Diffusion
(B) Pressure gradient
(C) Concentration gradient
(D) BothB&C
Answer:
(D) BothB&C
Question 15.
One of the following is selectively permeable
(A) Tonoplast
(B) Suberised cell wall
(C) Copperferrocyanide membrane
(D) Cellulosic cell wall
Answer:
(A) Tonoplast
Question 16.
What will happen if a flaccid cell is placed in hypotonic solution?
(A) Plasmolysis
(B) Exosmosis
(C) Endosmosis
(D) None of these
Answer:
(C) Endosmosis
Question 17.
Pressure that occurs in a cell due to osmotic diffusion of water inside is called
(A) Osmotic pressure
(B) Turgor pressure
(C) Water pressure
(D) Diffusion pressure
Answer:
(A) Osmotic pressure
Question 18.
Movement of water through the cell wall without crossing any membrane is
(A) Apoplastic
(B) Symplastic
(C) Tonoplastic
(D) Cytoplastic
Answer:
(A) Apoplastic
Question 19.
Cytoplasmic strands that connects two neighbouring cells through
(A) Pits
(B) Semipermiable membrane
(C) Plasmodesmata
(D) Root hair
Answer:
(C) Plasmodesmata
Question 20.
Guttation occurs in leaves through
(A) Stomata
(B) Epithelium
(C) Hydathode
(D) Leaf margin
Answer:
(C) Hydathode
Question 21.
Dry seeds swells when they are placed in water due to
(A) Imbibition
(B) Plasmolysis
(C) Diffusion
(D) Osmosis
Answer:
(A) Imbibition
Question 22.
Transpiration in plants helps to
(A) The supply of water for photosynthesis
(B) Maintains cells turgidity
(C) Transport minerals from the soil to all parts of the plant
(D) All the above
Answer:
(D) All the above
