Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Plus One Botany Cell Cycle and Cell Division One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Meiosis results in
(a) Production of gametes
(b) Reduction in the number of chromosomes
(c) Introduction of variation
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 2.
At which stage of meiosis does the genetic constitution of gametes is finally decided
(a) Metaphase I
(b) Anaphase II
(c) Metaphase II
(d) Anaphase I
Answer:
(d) Anaphase I
Question 3.
Meiosis occurs in organisms during
(a) Sexual reproduction
(b) Vegetative reproduction
(c) Both sexual and vegetative reproduction
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Sexual reproduction
Question 4.
During anaphase-l of meiosis
(a) Homologous chromosomes separate
(b) Non-homologous autosomes separate
(c) Sister chromatids separate
(d) non-sister chromatids separate
Answer:
(a) Homologous chromosomes separate
Question 5.
Mitosis is characterised by
(a) Reduction division
(b) Equal division
(c) Both reduction and equal division
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Equal division
Question 6.
A bivalent of meiosis-l consists of
(a) Two chromatids and one centromere
(b) Two chromatids and two centromere
(c) Four chromatids and two centromere
(d) Four chromatids and four centromere
Answer:
(c) Four chromatids and two centromere
Question 7.
Cells which are not dividing are likely to be at
(a) G1
(b) G2
(c) Go
(d) S phase
Answer:
(c) Go
Question 8.
Which type cell divisions occur in meristematic cell of root apex?
Answer:
Mitosis
Question 9.
In which stage the actual reduction of chromosome number occurs in meiosis.
Answer:
Anaphase 1
Question 10.
Give the term for the failure of separation of homologous chromosomes.
Answer:
Non-disjunction
Question 11.
Name the cell divisions which help in growth and recombination of genes.
Answer:
Mitosis and meiosis
Question 12.
It is observed that heart cells do not exhibit cell division. Such cells do not divide further and exit ____ phase to enter an inactive stage called ____ of cell cycle. Fill in the blanks.
Answer:
G1 and G0
Question 13.
In the case of plant cells, the formation of new cell wall begins with a simple precursor. What is this precursor?
Answer:
Middle lamella
Question 14.
It is said that the one cycle of cell division in human cells (eukaryotic cells) takes 24 hours. Which phase of the cycle, do you think occupies the maximum part of cell cycle?
Answer:
Interphase.
Question 15.
At what stage of cell cycle does DNA synthesis take place?
Answer:
substage of Interphase
Question 16.
If the failure of division of cytoplasm occurs after nuclear division, What will happen to the cell?
Answer:
Free nucleii are formed
Question 17.
An anther has 1200 pollen grains. How many pollen mother cells must have been there to produce them?
Answer:
300 pollen mother cells
Question 18.
What is the peculiarity of zygotene?
Answer:
The pairing of the homologous chromosome called synapsis
Question 19.
It is the inactive stage of cell division but cell differentiation occurs. Name it.
Answer:
G0 Phase /Quiscent stage.
Plus One Botany Cell Cycle and Cell Division Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Meiosis is the type of cell division which maintain the race. Discuss.
Answer:
Reduces the chromosome number to half, so that chromosome number is maintained in the next generation.
Question 2.
Interphase in cell cycle is sometimes referred to as resting phase. Do you consider this statement true? Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
No.
- Nucleus and cytoplasm are metabolically very active.
- Amount of DNA becomes doubled.
Question 3.
A diagram of typical cell cycle of a higher plant is shown here. Identify each stage of the cycle and explain what happens during these stages.
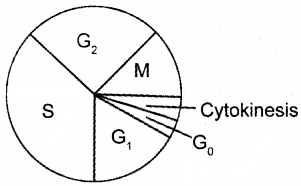
Answer:
- G1 – pre mitotic gap -synthesis of RNA &Proteins
- S – phase of synthesis – DNA replication
- G2 – Post mitotic Gap phase synthesis of RNA &Proteins continues
- M – Mitotic phase
- G0 – Inactive phase
Question 4.
Cytokinesis differs in plant and animal cell. Substantiate this statement.
Answer:
- Plant cell – formation of cell plate.
- Animal cell – Invagination of cell membrane.
Question 5.
Analyse column A and B arrange the matter is an appropriate order.
| A | B |
| 1) Pachytene 2) S phase 3) Dyad 4) M phase | a) Interphase b) Telophase I c) Mitotic phase d) Prophase I |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1) Pachytene 2) S phase 3) Dyad 4) M phase | Prophase I Interphase Telophase I Mitotic phase |
Question 6.
Identify the stages of Mitosis in which the following events take place:
- Synapsis
- Terminalisation of chiasmata.
Answer:
- Zygotene
- Diakinesis
Question 7.
Different stages of Prophase I of Meiosis are given in column A, arrange them in correct order and match them with the events in column B.
| A | B |
| i) Diplotene | a) Chromosomes become gradually visible under the light microscope |
| ii) Pachytene | b) The pairing of Homologous chromosomes |
| iii) Leptotene | c) The appearance of recombination nodules and crossing over takes place |
| iv) Zygotene | d) Dissolution of synaptonemal complex and separation of bivalents. |
| e) Terminalisation of Chiasmata |
Answer:
- (i) – d
- (ii) – c
- (iii) – a
- (iv) – b
Question 8.
The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis.
- Name each pair of homologous chromosomes.
- Name the stage of prophase at which it takes place.
Answer:
- Bivalent
- Zygotene
Question 9.
Specific chromosome number of each species is conserved across generations in sexually reproducing organisms. What is the reason for this? Write the different steps of this process.
Answer:
- Meiosis (meiosis I & II)
- Prophase Metaphase Ana phase Telophase
Question 10.
The life cycle of a cell is called cell cycle. It consists of four stages such as Gv S, G2, and M.
- Construct a pie diagram showing the different stages indicated above.
- State the major events occurring in G, S, and G2 phases.
Answer:
1. Pie diagram of cell cycle.
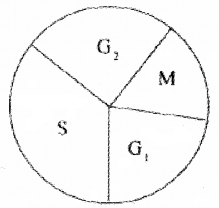
2. G1 Phase -1, Cell grows in size and prepares the machinery needed for the DNA replication. RNA and proteins are synthesized. S phase – DNA replication. G2 phase – Synthesis of RNA and proteins.
Question 11.
Arrange the following stages of cell cycle in correct sequence S, G2, G1, M.
Answer:
S, M, G1, S, G2
Question 12.
X’ shaped structure called ‘chiasmata occurs during a particular stage of cell division.
- Name the stage?
- What is the significance of this type of cell division?
Answer:
- Pachytene
- The exchange of genes takes place between homologous chromosomes.
Question 13.
Given below are the five phases of prophase I of Meiosis I. Arrange them in correct order.
Zygotene, diakinesis, diplotene, leptotene, pachytene
Answer:
Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis
Question 14.
Give the scientific term of the following.
- Interchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of the homologues chromosomes
- The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase
Answer:
- Crossing over
- Equatorial
Question 15.
Identify the diagram and label a, b,c and write the events during this.
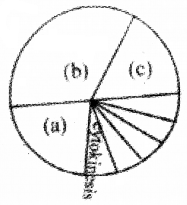
Answer:
(a) G1
(b) S
(c) G2
- G1 – Interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication.
- S – DNA synthesis or replication of DNA occurs.
- G2 – In this phase proteins are synthesised for mitosis.
Question 16.
You have supplied I set of glass slides showing gametogenesis or garnets formation in an animal In one of the slide you observed the following features. Four cells with haploid number of chromosomes. Your friend told you that this is a meiotic division. (Hint: The diploid number of chromosome is 16.)
Are you agree with this statement. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes. Meiosis takes place in diploid cell or meiocyte to form four haploid cells. These cells contain 8 chromosomes each.
Question 17.
Differentiate reduction division from equational division.
Answer:
1. Reduction division:
It occurs in diploid cells to form 4 haploid cells, ie, the Chromosome number reduced to half in Meiosis I and results 2 daughter cells, which again divides to form 4 daughter cells. All cells formed in meiosis are haploid.
2. Equational division:
It is the mitotic division results 2 daughter cells carrying same set of chromosomes as that of parent cell. No genetic variation occurs.
Question 18.
Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in S phase?
Answer:
There cannot be mitosis without DNA replication in 5 phase of interphase because the trigger for mitosis is disturbance of nucleocytoplasmic ratio caused by DNA replication in S phase. Mitosis restores the quantity of genetic material to the species-specific level.
Question 19.
How does anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis differ from each other?
Answer:
In anaphase of mitosis chromatids separate while in anaphase 1 of meiosis homologous chromosomes separate.
Question 20.
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer:
1. In an animal cell a furrow in the plasma membrane.lt joins in the centre and dividing the cell cytoplasm into two.
2. In-plant cells, wall formation starts in the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls. Then Cell division occurs.
Question 21.
How cytokinesis is different in an animal and a plant cell?
Answer:
In-plant cell cytokinesis occurs by cell plate formation while in the animal cell it occurs by cell furrow formation.
Question 22.
Why mitosis is called equational division ? Give the occurrence of mitosis.
Answer:
It keeps the chromosome number constant. It occurs in somatic cells.
Question 23.
What is the feature of a metacentric chromosome?
Answer:
The metacentric chromosome has a centromere in the middle region with two equal arms of the chromosome.
Question 24.
What is kinetochore? Give its function.
Answer:
It is a disc-like area in each chromatid and is site of attachment of spindle microtubule.
Question 25.
Why is meiosis essentially in sexually reproducing organisms?
Answer:
Meiosis reduces the chromosome number to half as it is followed by fertilization which restores diploidy.
Question 26.
Name the stage of cells cycle at which one of the following events occurs.
- Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator
- Centromere splits and chromatids separate
- Pairing between homologous chromosomes. takes place
- Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Answer:
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
Question 27.
Downs syndrome and Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs due to mistake in cell division. What does it indicate?
Answer:
It is due to the failure of separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Question 28.
The events occur in prophase and telophase are one opposite to other,
- Name the cell structures shown the above events
- How many daughter nuclei are formed at the end of mitotic and meiotic prophase?
Answer:
- Nuclear membrane, nucleolus and spindle fibres
- Two
Question 29.
Mangolism or Trisomy is due to the failure of one event in cell division.
- Which is the improperly functioning stage?
- What is the event that not occurs?
Answer:
- Anaphase I of meiosis
- Separation of homologous chromosomes
Question 30.
- What will be the ploidy level of dyad and tetrad of cells in meiosis?
- How is it occurs?
Answer:
- Dyad – haploid, Tetrad – Haploid
- It occurs in meiosis due to separation of homologous chromosomes and chromosome number reduced to half.
Plus One Botany Cell Cycle and Cell Division Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In which phase of meiosis is the following formed? Choose the answers from hint points given below.
- Synaptonemal complex ______
- Recombination nodules ______
- Appearance/activation of enzyme recombinase _____
- Termination of chiasmata _______
- Interkinesis ________
- Formation of dyad of cells ________
Answer:
- Zygotene
- pachytene
- pachytene
- diakinesis
- After Meiosis-I before meiosis II
- after first cytokinesis
Question 2.
The interphase stage is significant in mitotic and meiotic cell division
- Give one specific event
- Name the stage of interphase this event occurs
- How will you differentiate interphase from interkinesis?
Answer:
- DNA replication
- S – phase
- Interphase – cell prepares for cell division Interkinesis – short interval between meiosis I and meiosis II
Question 3.
The following events occur during the various phases of the cell cycle, Write the phase against each of the events.
- Appearance of nucleolus
- Division of centromere
- Replication of DNA
Answer:
- Telophase
- Anaphase
- Interphase
Question 4.
Life cycle of a cell is called cell cycle. ‘S’ phase is an important phase of cell cycle.
- Justify your answer.
- Name the stages of cell cycle at which the following events occur.
- Crossing over of homologous chromosome.
- Pairingof homologous chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are arranged at the equatorial plane.
Answer:
- phase of DNA synthesis
- stages of the cell cycle
- Pachytene
- Zygotene
- Metaphase
Question 5.
Name the stages of cell division in which the following events occur?
- Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
- Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
- Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Answer:
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Pachytene
Question 6.
Match the words listed in column I with suitable words from column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Diplontic cycle b) Karyokinesis c) Haplontic cycle d) Cytokinesis e) Meiosis f) Cell plate | i) Meiocytes ii) Gametic meiosis iii) Plant cells iv) Nuclear division v) Zygotic meiosis vi) Cytoplasmic division |
Answer:
- a) – Gametic meiosis
- b) – Nuclear division
- c) – Zygotic meiosis
- d) – Cytoplasmic division
- e) – Meiocytes
- f) – Plant cells
Plus One Botany Cell Cycle and Cell Division NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Answer:
The division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis, while the division of the nucleus is called Karyokinesis.
Question 2.
What is G0 (quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Answer:
Some cells in the adult animals do not appear to exhibit division (e.g., heart cells and many other cells divide only occasionally, as needed to replace cells that have been lost because of injury or cell death.
These cells do not divide further exit G1 phase to enter an inactive stage called quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle. Cells in this stage remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism.
Question 3.
Describe the event taking place during interphase.
Answer:
The interphase is divided into three further phases:
1. G1 phase (Gap 1). G1 phase corresponds to the interval between mitosis initiation of DNA replication. During G, phase the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
2. S phase (Synthesis). S or synthesis phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place.
3. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles. If the initial amount of DNA is denoted as 2C then it increases to 4C. However, there is no increase in the chromosome number, if the cell had diploid or 2n number of chromosomes at G1, even after S phase the number of chromosomes remains the same, i.e., 2n.
4. G2 phase (Gap 2). In animal cells, during the S phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus, and the centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm during the G2 phase, proteins are synthesised in preparation for mitosis White cell growth continues.
Question 4.
Why is mitosis called equational division?
Answer:
Since the number of chromosomes remains same in parent and daughter cells so mitosis is also called a equational division.
Question 5.
Name the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur.
- Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
- Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
- Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
- Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Answer:
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Metaphase I of meiosis
- Prophase I of meiosis
Question 6.
What is the significance of meiosis?
Answer:
Significance of Meiosis:
- Maintaining genetic identity by maintaining number of chromosomes.
- Bringing variations to ensure better species.
- Facilitates sexual reproduction.
Question 7.
Discuss with your teacher about.
- haploid insects and lower plants where cell division occurs, and
- Some haploid cells in higher plants where cell division does not occur.
Answer:
- Male bees, wasps and ants are haploid organisms because they are produced from unfertilized eggs.
- Synergids and antipodal cells in the ovule don’t undergo cell division.
Question 8.
Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase?
Answer:
DNA replication is necessary for cell division, and cell division cannot happen without DNA replication.
Question 9.
Can there be DNA replication without cell division?
Answer:
DNA replication takes place in order to prepare for cell division. Cell division is the next logical step after DNA replication.
Question 10.
Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and notice how the following two parameters change
- number of chromosomes (N) per cell
- amount of DNA content (C) per cell
Answer:
- Number of chromosomes remains same after mitotic cell division and becomes half after meiotic cell division.
- During S phase the DNA content doubles, but number of chromosomes remains the same.
Plus One Botany Cell Cycle and Cell Division Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Cleavage is a unique form of mitotic cell division in which
(a) there is no growth of cells
(b) the nucleus does not participate
(c) no spindle develops to guide the cells
(d) the plasma membranes of daughter cells do not separate.
Answer:
(a) there is no growth of cells
Question 2.
In animal cells, cytokinesis involves
(a) the separation of sister chromatids
(b) contraction of the contractile ring of microfilament
(c) depolymerisation of kinetochore microtubules
(d) a protein kinase that phosphorylates other enzymes
Answer:
(b) contraction of the contractile ring of microfilament
Question 3.
During mitosis, the number of chromosomes gets
(a) change
(b) no change
(c) maybe change if cell is mature
(d) maybe change if cell is immature
Answer:
(b) no change
Question 4.
A diploid living organism develops from zygote by which type of the following repeated cell divisions?
(a) Meiosis
(b) Amitosis
(c) fragmentation
(d) Mitosis
Answer:
(d) Mitosis
Question 5.
If you are provided with root-tips of onion in your class and are asked to count the chromosomes, which of the following stages can you most conveniently look into?
(a) Metaphase
(b) Telophase
(c) Anaphase
(d) Prophase
Answer:
(a) Metaphase
Question 6.
At which stage of mitosis, chromatids separated and passes to different poles
(a) prophase
(b) Metaphase
(c) anaphase
(d) Telophase
Answer:
(c) anaphase
Question 7.
The two chromatids of a metaphase chromosome represent
(a) replicated chromosomes to be separated at anaphase
(b) homologous chromosomes of a diploid set
(c) non-homologous chromosomes joined at the centromere
(d) maternal and paternal chromosomes joined at the centromere
Answer:
(a) replicated chromosomes to be separated at anaphase
Question 8.
The process of cytokinesis refers to the division of
(a) nucleus
(b) chromosomes
(c) cytoplasm
(d) nucleus and cytoplasm
Answer:
(c) cytoplasm
Question 9.
Which of the following serves as mitotic spindle poison?
(a) Ca2
(b) azide
(c) Tubulin
(d) Colchicine
Answer:
(d) Colchicine
Question 10.
Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs at which stage?
(a) Zygotene
(b) Leptotene
(c) Metaphase
(d) Pachytene
Answer:
(a) Zygotene
Question 11.
In meiosis, division is
(a) I reductional and II equational
(b) I equational and II reductional
(c) Both reductional
(d) Both equational
Answer:
(a) I reductional and II equational
Question 12.
Which type of chromosomes segregate when a cell undergoes meiosis?
(a) Homologous chromosomes
(b) Non-homologous chromosomes
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) centric and acentric chromosomes
Answer:
(a) Homologous chromosomes
Question 13.
Chiasmata are most appropriately observed in meiosis during
(a) diakinesis
(b) diplotene
(c) metaphase-ll
(d) pachytene
Answer:
(b) diplotene
Question 14.
During cell division, sometimes there will be failure of separation of homologous chromosomes. This event is called
(a) interference
(b) complementation
(c) non-disjunction
(d) coincidence
Answer:
(c) non-disjunction
Question 15.
The second meiotic division leads to
(a) separation of sex chromosomes
(b) fresh DNA synthesis
(c) separation of chromatids and centromere
(d) separation of homologous chromosomes.
Answer:
(c) separation of chromatids and centromere
Question 16.
Term meiosis was proposed by
(a) Farmer and Moore
(b) Flemming
(c) Strasburger
(d) Darlington
Answer:
(a) Farmer and Moore
Question 17.
Synapsis occurs in the phase of meiosis.
(a) zygotene
(b) diplotene
(c) pachytene
(d) leptotene
Answer:
(a) zygotene
Question 18.
When the number of chromosomes is already reduced to half in the first reductional division of meiosis, where is the necessity of second meiotic division
(a) The division is required for the formation of four gametes
(b) Division ensures equal distribution of haploid chromosomes
(c) Division ensures equal distribution of genes on chromosomes
(d) Division is required for segregation of replicated chromosomes
Answer:
(d) Division is required for segregation of replicated chromosomes
