Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Plus One Botany Morphology of Flowering Plants One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which plant part is modified into a pitcher in pitcher plants?
(a) stem
(b) leaf
(c) flower
(d) root
Answer:
(b) leaf
Question 2.
Marginal placentation is generally found in the family
(a) Solanaceae
(b) Fabaceae
(c) Liliaceae
(d) Cucurbitaceae
Answer:
(b) Fabaceae
Question 3.
Nonendospermic seeds are found in
(a) pea
(b) groundnut
(c) beans
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 4.
Monocotyledonous seed possess a cotyledon which is represented by
(a) teg men
(b) endosperm
(c) scutellum
(d) aleurone
Answer:
(c) scutellum
Question 5.
Which floral family has (9) + 1 arrangement of anthers in the andoecium
(a) Malvaceae
(b) Fabaceae
(c) Solanaceae
(d) Liliaceae
Answer:
(b) Fabaceae
Question 6.
Based on the relationship, fill in the blanks.
- Prop root: Support
Pneumatophore: ………. - Transpiration: Stomata
Guttation: ……….
Answer:
- breathing /respiration
- Hydathode
Question 7.
The arrangement of petals in the flower is known as
Answer:
Aestivation
Question 8.
When your teacher asked to write a few examples for root modifications, a student wrote Potato. Is it correct? Why?
Answer:
No. Stem modification
Question 9.
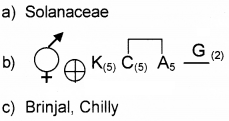
Write the name of the family which has the given floral formula.
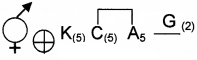
Answer:
Solanaceae
Question 10.
Observe the relationship between first two words and fill up the suitable word in the next place.
- Shoot – plumule: Root …………..
- Outer integument – testa: inner integnment ……….
Answer:
- Radicle
- tegmen
Question 11.
Observe the first pair in a and b and then complete the second pair.
- gourd – Tendril
citrus – ………… - Brinjal – Hypogynous flower
Rose – …………..
Answer:
- Thom
- Epigynous
Question 12.
Identify the family having the given floral formula.
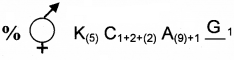
Answer:
Papilionaceae
Question 13.
“Stilt roots are adventitious and give mechanical support’’. How does prop root help the plant?
Answer:
Support the horizontal branches.
Question 14.
“Some flowers are called perigynous”. What do you mean by it?
Answer:
Ovary half inferior or half superior.
Question 15.
From the following terms relating a flower, write its floral formula.
Bisexual; sepals 5 and united petal 5 and united; stamens 5 and epipetalous, carpels 2 and Syncarpous, superior..
Answer:
Solanaceae
Question 16.
Based on morphology pick up the odd one and state reason for your selection (Carrot, Beetroot, Potato, Sweetpotato, radish).
Answer:
Potato- because it is a stem modification.
Question 17.
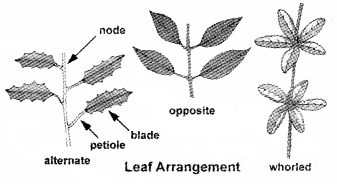
Phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves on the branch. Identify the order of plants showing Alternate, opposite and Whorled phyllotaxy in the following.
(a) China rose, Calotropis, Nerium
(b) Nerium, China rose, Caltropis
(c) Nerium, Caltropis, China rose
(d) China rose, Nerium, Caltropis
Answer:
(a) China rose, Calotropis, Nerium
Plus One Botany Morphology of Flowering Plants Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Identify the types of aestivation in the following diagrams. Justify your answer.
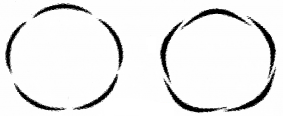
Answer:
- Valvate aestivation – Petals touching each other.
- Imbricate aestivation – petals arranged as one completely in, one completely out & others in and out.
Question 2.
“Potato is a stem and sweet potato is a root”. Justify the statement on the basis of external features only.
Answer:
Potato has distinct nodes and internodes whereas sweet potato does not have nodes and internodes. Potato tuber has scale leaves while sweet potato does not have scale leaves.
Question 3.
Identify the given family. Write the floral formula, mention the economic importance.
- Bisexual, actinomorphic
- Perianth six
- Valvate aestivation
- Ovary superior, Prilocular with many ovules.
Answer:
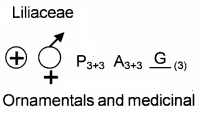
Question 4.
Note the difference between the placenta and thalamus.
Answer:
- Placenta – Region with which ovules are attached to ovary.
- Thalamus – Region where floral parts are attached
Question 5.
Based on the relationship, fill in the blanks.
- Prop root: Support
Pneumatophore: ………… - Transpiration: Stomata
Guttation: …………….
Answer:
- Breathing
- Hydathode
Question 6.
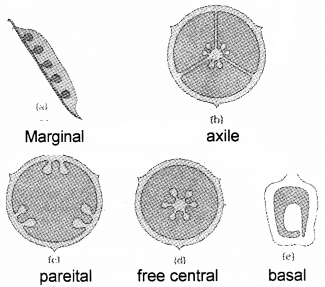
- Identify the type of placentation given below.
- Differentiate between apocarpous and syncarpous condition
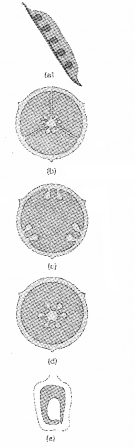
Answer:
- marginal, axile, parietal, freecentral,basal
- apocarpous – free carpels.
Syncarpous – fused carpels
Question 7.
In early morning, on the margins of leaves water drops are seen. Why does it occur?
Answer:
Guttation – The lose of water in the form of water droplets through water stomata seen on the margin on the leaves.
Question 8.
You are provided with the rhizome of a ginger plant.
- Name the part of the plant modified to form this structure.
- Write any three differentiating characters.
Answer:
- Stem
- Presence of Node, internode, terminal bud, axillary buds & scale leaves.
Question 9.
The following diagrams show different types of placentation.
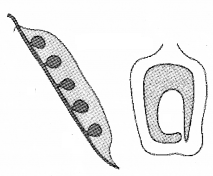
- Name the type of placentations.
- write one example for each placentation.
Answer:
- Marginal, Basal
- Pea & Sunflower
Question 10.
L.S of maize seed is given below.Observe the diagram and label the parts.
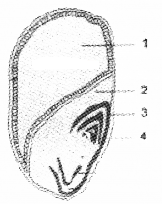
Answer:
- Endosperm
- Scutellum
- Coleoptile
- Plumule
Question 11.
The floral formula of a flower is
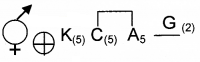
- Identify the family.
- Write the characters of androecium and gynoecium of this family.
Answer:
- Solanaceae
- Androecium – Five stamens epipetalous
Gynoecium – bicarpellary, syncarpous, superior ovary.
Question 12.
Expand the floral formula
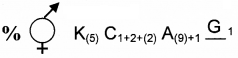
Answer:
zygomorphic bisexual pentamerous gamosepalous papilionaceous corolla diadelphous – Androecium. Gynoecium – superior.
Question 13.
Observe the following diagram and answer to the following Questions.

- Name the part of the plant modified in ‘A’ and ‘B’.
- Mention their functions.
Answer:
- A – Taproot B – Adventitious root
- A – Storage B – Respiration
Question 14.
The rhizome of ginger is found underground. But it is not root. Give reason.
Answer:
It has nodes, internodes, scale, leaves, axillary bud, terminal bud, adventitious root etc.
Question 15.
How is pinnately compound leaf different from palmately compound leaf?
Answer:
When a number of leaflets are present on either sides of a common axis, rachis it is pinnately compound leaf. Rachis represents the midrib of leaf. Eg. Neem When the leaflets are attached at a common point like fingers on palm it is palmately compound leaf. Eg. Bombax or silk cotton.
Question 16.
Identify the phyllotaxy of A and B

Answer:
(a) Alternate
(b) Oppositemedicinal.
Question 17.
Roots obtain oxygen from air in the soil for respiration. In the absence or deficiency of 02, root growth is restricted or completely stopped. How do the plants growing in marshlands or swamps obtain their 02 required for root respiration?
Answer:
In marshy area, the plants get 02 through special roots called pneumatophores or respiratory roots.Such roots are negatively geotropic.
Question 18.
During a feild trip to the coastal areas of Kochi, your team saw many trees growing in swampy areas, when thourdughly observed they found many roots growing upwards above the soil level.
- In your opinion what kind of roots were seen in that trees?
- How do these roots help the trees?
Answer:
- Pneumatophore
- Gaseous exchange
Question 19.
Rhizome of ginger is like the roots of other plants that grows underground. Despite this fact ginger is a stem and not a root. Justify.
Answer:
Because it possess nodes and internodes, buds, scale leaf, and adventitious roots. Hence these are stem characters.
Question 20.
Tendrils are found in the following plants. Identify whether they are stem tendrils or leaf tendrils,
a. Cucumber
b. Peas
c. Pumpkins
d. Watermelons
Answer:
a,c,d – stem tendril b – leaf tendril
Question 21.
You have heard about several insectivorous plants that feed on insects. Nepenthes or the pitcher plant is one such example, which usually grows in shallow water or in marshlands. What part of the plant is modified into a pitcher1? How does this modification help the plant for food even though it can photosynthesize like any other green plant?
Answer:
Lamina, Plant get additional nutrition (nitrogen) from the digested insect body.
Question 22.
Mangrove plants have negatively geotropic roots
- Name the root
- Identify its function
Answer:
- Pneumatophore
- Gaseous exchange
Question 23.
1. Write the floral formula of the flower having following description (Bisexual, Zygomorhic, Calyx 5 gamosepalous, Corolla 5 polysepalous, vexillary aestivation, Androecium 10 (stamens 9 united and1 free), Gynoecium 1 carpel, ovary superior)
2. Identify the family of the flower
Answer:
- K(5)C 1 + 2 + (2) A(9) + 1G1
- Fabaceae
Question 24.
The following diagrams show different types of placentation.
- Name the types of placentations?
- Write one example for each placentations?
Answer:
- Marginal and Basal placentation
- Marginal – pea, Basal – sunflower
Question 25.
Dicot and monocot leaves shows differences on their leaves mostly in the arrangement of veins, explain it.
Answer:
In Dicot, the veins are repeatedly branched to form network. This is called Reticulate venation. In Monocot, the veins run parallel to one another. This is called Parallel venation.
Question 26.
What is placentation? Give two types with example.
Answer:
It is the mode of arrangement of ovules in an Ovary
- Axile placentation – Arrangement of ovules in the axis of ovary having septa.
- Free central placentation – Arrangement of ovules in the central part of ovary without having septa.
Question 27.
Common functions of roots are absorption, fixation and conduction. Besides these, roots perform other functions. Justify this statement with two example.
Answer:
1. In addition to absorption, fixation, and conduction, roots perform mechanical support, eg -prop root and stilt root.
2. Some are Breathing roots eg:- Pneumatophore.
Question 28.
Differentiate between
Hypogynous and Epigynous
Answer:
- In hypogynous flower the position of Gynoecium is superior to all other floral whorls.
- In epigynous flower the position of Gynoecium is inferior to all other floral whorls.
Question 29.
A list of some plant parts are given below. Note the morphological modification in each item.
- Carrot
- Tapioca
- Potato
- Ginger
Answer:
- Carrot – Tap root modification
- Tapioca – Adventitious root modification
- Potato – Underground stem modification
- Ginger – Underground stem modification
Question 30.
Some flowers are called perigynous”. What do you mean by it?
Answer:
In such flowers ovary is half inferior which means position of ovary comes to the same level of other floral whorls lies.
Eg:- plum, rose, and peach
Question 31.
How is pinnately compound leaf different from palmately compound leaf?
Answer:
1. In pinnately compound leaf lamina divided into number of leaflets. It is due to the incisions touch the midrib Eg:- Neem.
2. In palmately compound leaf, lamina is divided into number of leaflets, they are arranged like fingers on the palm Eg:- Silk cotton
Question 32.
When your teacher asked to write a few examples for root modifications, a student wrote Potato. Is it correct? Why ?
Answer:
No, Potato is an example of underground stem modification.
Question 33.
How can you differentiate between free central and axile placentation?
Answer:
In free central placentation, ovules are arranged at central axis of ovary without septa but in axile placentation, ovules are arranged at the central axis of the ovary with septa/ cross walls.
Question 34.
- Name the aestivations given below
- Give an example for each
1. Twisted and imbricate
Hibiscus and cassia
Question 35.
Potato is a stem and sweet potato is a root”. Justify the statement on the basis of external features only.
Answer:
Potato is an underground stem. It possess adventitious bud, nodes and internodes Sweet potato is adventitious root modification. It possess root hairs and stores food.
Question 36.
The floral formula of a family is given below Give two examples for economically important plants
![]()
Answer:
- Indigofera – dye obtained
- Sesbania- Used as Fodder
Question 37.
The mature seeds of plants such as gram and peas possess no Endosperm. Why?
Answer:
Endosperm gets used up by the developing embryo during seed development.
Question 38.
Match the following.
| Group A | Group B |
| A. Aleurone layer B. Parthenocarpic fruit C. Ovule D. Endosperm | i. without fertilization ii. Nutrition iii. Double fertilization iv. Seed |
Answer:
A – iv
B – i
C – iii
D – ii
Question 39.
Mango and coconut are ‘drupe’ type of fruits. In mango fleshy mesocarp is edible.
- What is the edible part of coconut?
- What does milk of tender coconut represent?
Answer:
- Endosperm
- Liquid endosperm (free nuclear endosperm)
Question 40.
The mode of arrangements of sepals or petals in a floral bud is known as aestivation. Draw the various types of aestivation possible for a typical pentamerous flower.
Answer:
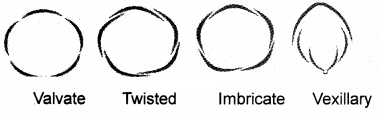
Question 41.
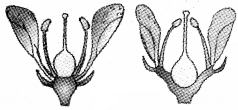
Give the technical term and examples of the flowers given here based on the position of the ovary.
Answer:
Hypogynous- hibiscus and perigynous- plum and rose.
Question 42.
Modified adventitious roots in Banyan tree and Maize plant are known in different names
- Which are they?
- Give its function
Answer:
- Banyan tree – Prop root, Maize plant-Stilt root
- Mechanical support
Question 43.
Thorns and spines are different modified structures in citrus and cactus.
- Which plant part is modified?
- Give its function.
Answer:
- Thorns – stem modification, Spines – Leaf modification
- protective function
Question 44.
Some important family characters are given below flowers are zygomorphic, Hypogynous, monocarpellary ovary, anthers diadelphous, and papilionaceous corolla
- Identify the family
- Give 2 economically important plants
Answer:
- Fabaceae
- dye – Indigofera, fodder yielding – sesbania and Trifolium
Question 45.
Give the technichal term of the following
- Two leaves at each node
- flowers cannot be divided into two equal halves
- position of ovary is higher than other floral whorls
- carpels are fused
Answer:
- opposite phyllotaxy
- asymmetric
- Hypogynous flower
- syncarpous
Question 46.
Mention the statement given below are true or false
- In axile placentation ovules are arranged in axis of a single-chambered ovary
- In Imbricate aestivation floral appendages are in irregular overlapping
- In Alstonia phyllotaxy is whorled
- Floral axis has definite growth in racemose type
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
Plus One Botany Morphology of Flowering Plants Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Justify the following statements on the basis of external features.
- Underground parts of plants are not always roots
- Flower is a modified shoot
Answer:
1. Underground stem get modified for different purposes like food storage, reproduction and perennation. They can be recognized from root in having nodes, internodes,scale leaves, terminal bud &axillary bud eg. Rhizome – ginger, stem tuber- potato.
2. A flower can be considered as a modified shoot because each whorl of a flower represents each node. The leaves at each node is modified to perform functions like protection, attraction and reproduction. The internodes are compressed to form a flower.
Question 2.
- What is meant by modification of root?
- What type of root is found in
- banyan tree
- turnip
- mangrove tree root modification is the change in shape and structure of root for performing functions other than absorption and conduction.
Answer:
- It is modified for performing different functions.
- Modification of root in banyan tree-prop roots- for mechanical support
- Turnip-napiform modification – for food storage
- Mangrove tree-pneumatophores – respiration
Question 3.
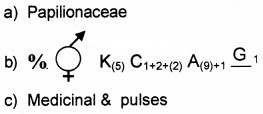
Some characters of a flower is given below. Bisexual, sepals 5 and united, Petals 5 and united, stamens 5 and epipetalous, carpels 2, syncarpous and superior ovary.
- Write its floral formula.
- Identify the family.
- List any two economically important plants belonging to this family.
Answer:
1.
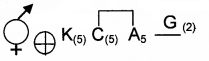
2. Solanaceae
3. Potato – Solanum tuberosum Tomato – Lycopersicum esculentum
Question 4.
A particular flower of a family is characterised by this type of aestivation.
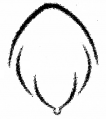
b) Write the floral formula.
c) Mention two economic importance of the family.
Answer:
Question 5.
Observe the relationship between first two words and fill up the suitable word in the fourth place.
- Shoot – plumule: Root ………..
- Nepenthes – pitcher: Utricularia …………
- Outer integument – testa: inner integument …………..
- Ovule – seed: Ovary – …………..
Answer:
- Radicle
- Bladder
- Tegmen
- Fruit
Question 6.
Label the regions of the root tip in the given diagram.
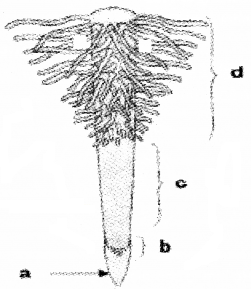
Answer:
- Root cap
- Meristematic
- Region of elongation
- Root hair region
Question 7.
The arrangement of ovules within the ovary is known as placentation.
- What does the term placenta refer to?
- Name and draw various types of placentations in the flower as seen in T.S. or V.S.
Answer:
1. Placenta It is the cushion-like structure in which ovules are arranged.
2.
Question 8.
Define the following terms.
- Aestivation:
- Placentation:
- Actinomorphic:
- Zygomorphic:
- superior ovary:
- Perigynous flower:
- Epigynous
Answer:
- Aestivation: Arrangement of sepals and petals in an unopened flower bud.
- Placentation: The mode of arrangement of ovules within the ovary
- Actinomorphic: When a flower can be divided into two equal radial halves at any radial plane. Eg: Chinarose.
- Zygomorphic: When a flower can be cut into two equal halves only in one vertical plane. Eg: pea.
- Superior ovary: When gynoecium occupies superior or highest position while other parts are situated below it. Eg: Mustard.
- Perigynous flower: If the gynoecium is at the centre and all other, parts arise on the rim of the thalamus. Eg: Rose
Question 9.
Differentiate between
- Racemose and cymose inflorescence.
- Fibrous and adventitious root
- Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary.
Answer:
1. Racemose: The axis or peduncle shows indefinite growth. Flowers are arranged in acropetal succession.
Cymose: the axis or peduncle shows definite growth or ends in a flower. Flowers are arranged in basipetal succession.
2. Fibrous: The primary root stops its growth and lateral roots arise from the base of the stem.
Adventitious: The roots arise from the part of the plant other than the radicle.
3. Apocarpous: When the carpels of the ovary are free.
Syncarpous: When the carpels of the ovary are fused.
Question 10.
Floral characters of a plant are given below: Pentamerous flowers, Polypetalous, Stamens 5, Polyandrous, Bicarpellary Syncarpous, Swollen placenta, Oblique ovary.
a) Name the Family of this plant belongs.
b) Write the floral formula of this family.
c) Give two examples with its importance.
Answer:
Plus One Botany Morphology of Flowering Plants NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How is a pinnately compound leaf different from a plamately compound leaf?
Answer:
1. Pinnately Compound Leaf.
In pinnately compound leaf a number of leaflets are present on a common axis. Example, neem leaves.
2. Palmately Compound Leaf.
In palmately compound leaf number of leaflets are attached at the common point. Example, cotton leaves.

Question 2.
Explain with suitable examples the different types of phyllotaxy.
Answer:
1. Phyllotaxy. Phyllotaxy is the pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch. This is usually of three types – alternate, opposite and whorled.
2. In alternate type of phyllotaxy, a single leaf arises at each node in alternate manner, as in china rose, mustard and sunflower plants.
3. In the Opposite type, a pair of leaves arise at each node and lie opposite to each other as in Calotropis and guava plants.
4. If more than two leaves arise at a node and form a whorl, it is called whorled, as in Alstonia.
Question 3.
What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found to the :
- Banyan tree
- Turnip
- Mangrove trees
Answer:
The Primary function of the root is absorption of water and minerals and giving mechanical support to the plant. Sometimes roots get modified to carry out other functions like storage of food or additional mechanical support.
1. Banyan Tree. In banyan trees long roots develop from branches and they hanging deep down to reach the ground. They are providing additional mechanical support to the huge banyan tree. This modification is called a prop root.
2. Turnip. In turnip the root is modified to store extra food.
3. Mangrove Trees. Mangrove trees are found in marshy area. The roots are modified into pneumatophore providing extra passage to allow additional oxygen to the plant.
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The obliquely growing roots that provides mechanical support to the main stem are
(a) prop root
(b) stilt root
(c) pneumatophore
(d) pillar root
Answer:
(b) stilt root
Question 2.
Lateral branches arise from the base of main stem that grows aerially at first and arch downwards in
(a) pistia
(b) mint
(c) jasmine
(d) both b & C
Answer:
(d) both b & C
Question 3.
Pulvinus is found in the leaf base of
(a) Rosaceae
(b) Leguminosae
(c) Malvaceae
(d) Solanaceae
Answer:
(b) Leguminosae
Question 4.
The appearance of more than one leaf at each node is represented by
(a) china rose
(b) sunflower
(c) Alstonia
(d) guava
Answer:
(c) Alstonia
Question 5.
Roots are significant in the exchange of gases
(a) pneumatophore
(b) stilt root
(c) pillar root
(d) assimilatory root
Answer:
(a) pneumatophore
Question 6.
The type of flower cannot be divided into two similar halves in any vertical plane through centre is
(a) actinomorphic
(b) zygomorphic
(c) asymmetric
(d) both b & c
Answer:
(c) asymmetric
Question 7.
Ovary half inferior is seen in
(a) plum
(b) china rose
(c) peach
(d) both a & c
Answer:
(d) both a & c
Question 8.
Find out the papilionaceous type of corolla from the given figure.
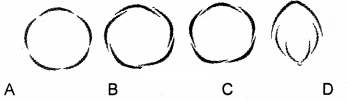
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(d) D
Question 9.
9. Flowers with bisexual, zygomorphic, diadelphous and monocarpellary superior ovary are the characteristic feature of
(a) fabaceae
(b) malvaceae
(c) solanaceae
(d) liliaceae
Answer:
(a) fabaceae
Question 10.
The type of placentation given here is
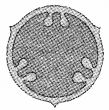
(a) axile
(b) basal
(c) marginal
(d) parietal
Answer:
(d) parietal
Question 11.
Hilum is found in
(a) embryo
(b) seed coat
(c) radicle
(d) chalaza
Answer:
(b) seed coat
Question 12.
Ashwagandha is represented by the family
(a) Fabaceae
(b) papillionaceae
(c) Solanaceae
(d) Liliaceae
Answer:
(c) Solanaceae
Question 13.
The family represented by the floral formula given below is
![]()
(a) fabaceae
(b) papillionaceae
(c) solanaceae
(d) liliaceae
Answer:
(c) solanaceae
Question 14.
Negatively geotropic roots are seen in
(a) zaminkand
(b) Rhizophora
(c) maize
(d) euphorbia
Answer:
(b) Rhizophora
Question 15.
In the following picture, plant part is modified for

(a) storage
(b) respiration
(c) support
(d) protection
Answer:
(a) storage
Question 16.
When the filaments of stamens are attached to the perianth, the condition is
(a) Epiphyllous
(b) epipetalous
(c) adelphous
(d) syngenesious
Answer:
(a) Epiphyllous
Question 17.
In China rose, five carpels are fused at base. This condition is called
(a) Pentacarpellary, syncarpous and pentalocular
(b) Pentacarpellary, apocarpous and pentalocular
(c) polycarpellary, syncarpous and penalocular
(d) Pentacarpellary, syncarpous and multilocular
Answer:
(a) Pentacarpellary, syncarpous and pentalocular
