Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Plant Kingdom
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Artificial system of classification is mainly based on
(a) vegetative characters
(b) androecium structure
(c) habit and habitat
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 2.
Fusion between morphologically alike gametes is referred to as
(a) anisogamy
(b) isogamy
(c) oogamy
(d) sygamy
Answer:
(b) isogamy
Question 3.
Gametophytic generation is dominant in
(a) bryophytes
(b) pteridophytes
(c) angiosperms
(d) gymnosperms
Answer:
(a) bryophytes
Question 4.
Mycorrhizal roots of _____ are associated with some fungal symbionts
(a) Cedrus
(b) pinus
(c) cycas
(d) lichens
Answer:
(b) pinus
Question 5.
Haplontic life cycle is generally occurs in
(a) algae
(b) pteridophytes
(c) bryophytes
(d) gymnosperms
Answer:
(a) algae
Question 6.
Name the type of cell division which produce four haploid cells with new combination of characters from a diploid cell.
Answer:
Meiosis.
Question 7.
Name the dominating pigment in red algae.
Answer:
Phycoerythrin
Question 8.
Name the algae from which algin is prepared commercially.
Answer:
Laminaria (brown algae)
Question 9.
Name the filamentous structure that appears in the mosses due to the germination of spores.
Answer:
Protonema
Question 10.
Give an example of plant group which produce seed but not fruit.
Answer:
Gymnosperms
Question 11.
What is the genetic constitution of endosperm of angiosperm.
Answer:
Triploid
Question 12.
Fill in the blanks.
- Bryophytes – Haplo-diplontic
Gymnosperms – ________ - Algin – Brown algae
Carrageen – _______
Answer:
- Diplontic
- Red algae
Question 13.
If chlorophyll b is for Chlorophyceae, chlorophyll d is for _______
Answer:
Rhodophyceae
Question 14.
Pick out the correct pairs of plant groups that bearing archegonium.
(a) gymnosperm angiosperm
(b) angiosperm Bryophyta
(c) Bryophyta Pteridophyta
(d) Pteridophyta gymnosperm
Answer:
(d) Pteridophyta gymnosperm
Question. 15
Select the odd one.
(Nitrosomonas, archaebacteria, Nitrococcus, Nitrobacteria)
Answer:
Archaebacteria
Question 16.
The majority of pteridophytes are homosporous ie. they produce similar kind of spores. Give one example of a heterosporous pteridophyte.
Answer:
Selaginella
Question 17.
Archaebacteria, special type of bacteria, which are able to survive in extreme conditions, What is the feature helping them for this?
Answer:
Structure of the cell wall.
Question 18.
Complete the following:
1. Plasmogamy: Fusion of Protoplasms
……………: Fusion of nuclei
Answer:
karyogamy
Question 19.
Laminarin is a stored food in Phaeophyceae, what is the stored food in Rhodophyceae?
Answer:
Floridean starch
Question 20.
The essential element is present in the ring structure of chlorophyll. Which is the element?
Answer:
Mg.
Question 21.
By observing the relationship of the first and fill up the second.
1. Algae and Fungi: Lichen
Roots of higher plants and Fungus:………….
Answer:
Mycorrhiza
Question 22.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill up the blank.
- Moss: Protonema; Fern ………….
- Egg: Zygote; …………; PEN
Answer:
- Prothallus
- Secondary Nucleus
Question 23.
Pick the odd one out from the following and justify your answer.
Chlamydomonas, Volvox, laminaria, Chara.
Answer:
laminaria-brown algae
Question 24.
Choose the correct answer.
- food materials in fungi are stored in the form of (glucose, glycogen, sucrose, starch)
- Membrane covering the vacuole (meninges, tonoplast, pleura).
Answer:
- Glycogen
- Tonoplast
Question 25.
Name the organisms which are not included in any of the kingdoms,
Answer:
Viruses
Question 26.
Name the plant group in which ‘protonema’ is present.
Answer:
Bryophytes
Question 27.
Observe the relationship between the first two pairs and fill up the blanks.
- Sac fungi: Ascomycetes
Imperfect fungi: ………… - Transpiration: Loss of water in the form of water vapour.
……………: Loss of water in the form of liquid
Answer:
- Deuteromycetes
- Guttation
Question 28.
Fusion of two gametes which are dissimilar in size is termed as
(a) Oogamy
(b) Isogamy
(c) Anisogamy
(d) Zoogamy
Answer:
(c) Anisogamy
Question 29.
Holdfast, stipe, and frond constitutes the plant body in case of
(a) Rhodophyceae
(b) Chlorophyceae
(c) Phaeophyceae
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Phaeophyceae
Question 30.
Food is stored as Floridean starch in Rhodophyceae. Mannitol is the reserve food material of which group of algae?
Answer:
Brown algae
Question 31.
A plant shows thallus level of organization. It shows rhizoids and is haploid. It needs water to complete its life cycle because the male gametes are motile. Identify the group to which it belongs to
Answer:
Bryophytes
Question 32.
My body is a gametophyte and I grow under moist and shaded conditions. My group is commonly known as amphibians of the plant kingdom. Name my group.
Answer:
Bryophyta
Question 33.
Name the gametophyte that is free-living structure formed in pteridophytes.
Answer:
Prothallus
Question 34.
The plant body in higher plants is well differentiated and well developed. Roots are the organs used for the purpose of absorption. What is the equivalent of roots in the less developed lower plants?
Answer:
Rhizoids
Question 35.
Plants are generally autotrophic. Can you think of certain plants that are partially heterotrophic?
Answer:
Loranthus – Partial stem parasite
Question 36.
Choose the correct pair.
(a) Spirogyra – Algae
(b) Sphagnum – Gymnosperm
(c) Selaginella – Bryophyte
(d) Funaria – Pteridophyte
Answer:
(a) Spirogyra – Algae
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Diagrams of three bryophytes are given below.
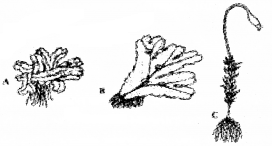
- Observe and give the names of these bryophytes.
- Which of the three bryophytes is the most advanced?
Answer:
1. names of these bryophytes.
- A – Riccia,
- B – Marchantia,
- C – Funaria
2. Funaria
Question 2.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill up the blanks.
- Kingdom fungi – multicellular decomposer
Kingdom Plantae – _____________ - Gymnosperm – Cone
Angiosperm – _____________
Answer:
- Kingdom plantae – multicellular producers
- Angiosperm – flower
Question 3.
Bryophytes are “amphibians of the plant kingdom”. Comment.
Answer:
The vegetative structure are well adapted to live on land but water is essential for fertilization.
Question 4.
Prothallus is the gametophytic stage of Pteridophyte What is protonema?
Answer:
Protonema is the young stage of moss gametophyte
Question 5.
| A | B |
| Chlamydomonas Cycas Selaginella Sphagnum | Moss Pteridophytes Algae gymnosperms |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Chlamydomonas Cycas Selaginella Sphagnum | Algae Gymnosperms Pteridophytes Moss |
Question 6.
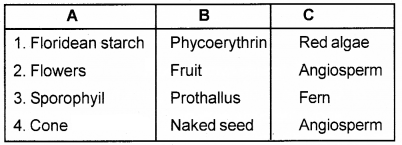
Analyse the table and arrange the matter in an appropriate order.
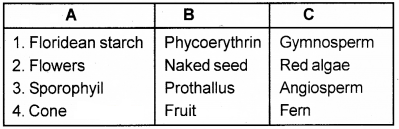
Answer:
Question 7.
Lichens are the symbiotic association between algae and fungi.
- What is symbiosis?
- How both the partners help each other?
Answer:
1. Relationship between 2 organisms, both are benefited.
2. Algae – prepare food
Fungus – Gives shelter to algae
Question 8.
Arrange the following plants in the table given below, (two members from each group)
Riccia, Spirogyra, Adiantum, Chlorella, Funaria, Cycas, Nephrolepis, Pinus.

Answer:
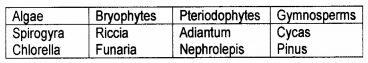
Question 9.
The following is a list of plants. Arrange them in the table given below.
Marchantia, Selaginella, Salvinia, Sunflower, Funaria, Pinus, Maize, Cycas.

Answer:
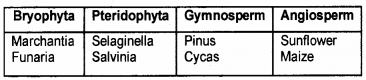
Question 10.
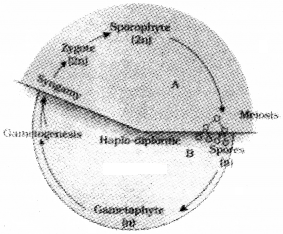
- Identify the life cycle pattern?
- Cite two examples of organisms showing the above life cycle pattern?
Answer:
- Haplo-diplontic.
- Bryophytes and pteridophytes
Question 11.
The classical Taxonomy of organisms is mainly based . on morphological characters. But modern taxonomy gives equal weightage to all characters.
Answer:
- Name this new approach in modern taxonomy.
- Mention any two branches of this taxonomy.
Answer:
- Numerical taxonomy
- Chemo taxonomy, cytotaxonomy
Question 12.
| A | B |
| Sargassum Bryophyte ABA Ribosomes Anabaena | Stomatal movement Palade N2 fixation Brown alga Sphagnum |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Sargassum | Brown alga |
| Bryophyte | Sphagnum |
| ABA | Stomatal movement |
| Ribosomes | Palade |
| Anabaena | N2 fixation |
Question 13.
Pick up the odd one.
- Oscillatoria, Spirulina, Actinomycetes, Nostoc
- Epipetalous, Epiphyllous, Monadelphous, Apocarpous.
Answer:
- Actinomycetes
- Apocarpous
Question 14.
Green algae are considered as the ancestors of angiosperms.
- Is this statement correct?
- Justify your answer.
Answer:
- Yes
- Chloroplast is present
Question 15.
Red algae reach the maximum depth in sea where no other photosynthetic form grow. Justify.
Answer:
The pigment phycoerythrin absorb the blue-green part of the sunlight’s spectrum. The blue-green light has short wavelength and penetrates deep into the water.
Question 16.
During summer you cannot see the growth of Funaria. What is the reason for this?
Answer:
Water is needed for reproduction – amphibians of plant kingdom.
Question 17.
By observing the relationship between the first pair, fill up the blanks.
- Chlorophyceae: Starch: Rhodophyceae: ……………….
- Moss:Protonema; Nephrolepis : ………….
Answer:
- Floridean starch
- Prothallus
Question 18.
Match the following. (Column I with Column II)

Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Chlamydomonas | Algae |
| b) Cycas | Gymnosperm |
| c) Selaginella | Pteridophyte |
| d) Sphagnum | Moss |
Question 19.
Observe the relationship between first two terms and fill up the blanks.
- Phycobiont: Algal partner
……………: Fungal partner - Rhizopus: Phycomycetes
Penicillin: ………….
Answer:
- Mycobiont
- Ascomycetes
Question20.
When & where does reduction division takes place in the life cycle of liverwort, moss, ferns, gymnosperm, and angiosperm?
Answer:
- Liver wort – Reduction division takes place inside the capsule at the time of spore production.
- Moss – Reduction division takes place inside the capsule at the time of spore formation.
- Ferns- Reduction division takes place in sporangium in the leaves at the time of spore formation.
- Gymnosperm – Reduction division takes place in the sporangium born on sporophyte of cone.
- Angiosperm – reduction division takes place at the time of gamete formation in male & female gametophyte during sexual reproduction.
Question 21.
Observe the given table and arrange the matter in an appropriate order.
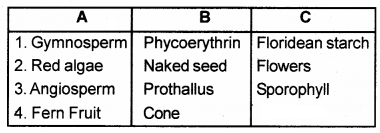
Answer:
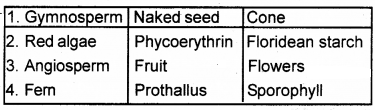
Question 22.
Complete the table using appropriate terms.
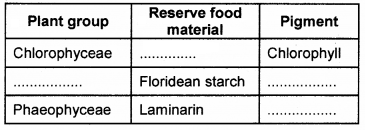
Answer:
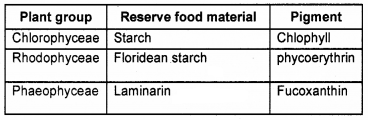
Question 23.
What is the basis of the classification of algae?
Answer:
Algae is classified on the basis of pigment Sreserve food.
Eg:
- Green algae(Chlorophyceae)
- Red algae(Rhodophyceae)
- Brown algae(Phaeophyceae)
Question 24.
Liverworts, mosses and ferns usually grow near water. Comment.
Answer:
External water is required for dehiscence of antheridia, liberation of antherozoids, transfer of antherozoids from antheridia to archegonia, opening of archegonial neck and the movement of antherozoids into the archegonial neck for fertilisation during sexual reproduction.
Question 25.
Both gymnosperm & Angiosperm are seed-bearing plants. Why are they classified separately?
Answer:
Gymnosperm and angiosperm are seed-producing plants. In gymnosperm ovules or seeds are not enclosed by ovary wall after fertilisation. In angiosperm, the seeds are protected by ovary wall after fertilisation.
Question 26.
Some characteristic features of the plant is given below.
- The main plant body posesses rhizoids.
- The nucleus of main plant body have haploid chromosome number.
- Zygote develops into a new plant which is dependant on main plant body.
- The sporophyte has foot, seta, and capsule.
1. Identify the plant.
2. Name the cells where reduction division (meiosis) takes place in the life cycle of the plant.
Answer:
- Moss plant
- Spore mother cells
Question 27.
Differentiate between the following,
- Red algae & Brown algae
- Liverworts & Mosses
- Homosporous & Heterosporous
- Sygamy & Triple fusion
Answer:
1.
| Red Algae | Brown Algae |
| 1. Rhodophycea | 1. Phaeophycea |
| 2. Predominant pigment is phycoerythrin | 2. Predominant pigment is fucoxanthin |
| 3. Stored food is laminarin and mannitol | 3. Stored food is floridean starch |
2.
| Liver worts | Mosses |
| 1. Dorsiventral thallus | 1. The plant is upright bearing leaves, & rhizoids |
| 2. Asexual reproduction by fragmentation & gemma | 2. Asexual reproduction by budding |
| 3. Protonema absent | 3. Protonema stage present |
3.
| Homosporous | Hetero sporous |
| 1. Spores are of same type | 1. Spores produce are 2 types |
| 2. Gametophyte is prothallus & develops male & female sex organs | 2. Female Gemetophyte is retained in the parent sporophyte |
4.
| Sygamy | Triple fusion |
| 1. The fusion between egg & sperm to give rise to diploid zygote egg + sperm = zygoten n 2n | 1. The fusion between the secondary nucleus and male gamete to form the Primary endosperm nucleus. secondary nucleus + sperm =PEN n n 2n |
Question 28.
The following is a list of plants.
Riccia, Chlorella, Selaginella, Adiantum, Chalamydomas, Sugarcane, Funaria, Gnetum, Ficus, Cycas. Categorise these plants into Algae, Bryophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms.
Answer:
- Algae – Chlorella, Chlamydomonas
- Bryophytes – Riccia, Funaria
- Pteridophytes – Selaginella, Adiantum
- Gymnosperms-Gnetum, Cycas
- Angiosperms- Sugarcane, Ficus
Question 29.
Some plants of cycas produce seeds, but not others. Justify.
Answer:
Cycas plants are dioecious. Male plants of cycas produce microsporophylls and female plants produce megasporophyll. So only female cycas produce seeds and not the males.
Question 30.
Complete the table using the following terms.

Primitive vascular plants, Sprogyra, Triploid endosperm, Marchantia, Naked seeded plants, Pteris, Aquatic autotrophs, Wolfie, Amphibians of plant Kingdom, Pinus
Answer:
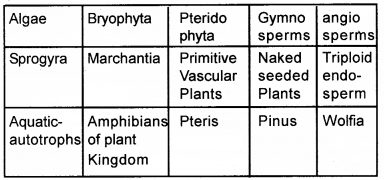
Question 31.
The following is the list of plants Arrange them in the table given below.
Marchantia, Chlorella, Lycopodium, Adiantum, Clamydomonas, Sunflower, Funaria, Gnetum, Cycas, Maize.
Answer:
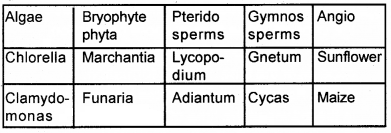
Question 32.
The haplodiplontic life cycle is present in fern plants. Justify your answer.
Answer:
ln fern plants, the haploid phase is alternate with diploid phase in life cycle. Haploid and diploid phases have equal weightage in life cycle.
Question 33.
What is mixotrophic mode of nutrition?
Answer:
It is the type of nutrition found in Euglena that means both autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
Question 34.
Why seed plants are most successful of all land plants?
Answer:
They are most successful of all land plants because external supply of water is not required for fertilization.
Question 35.
How bryophytes are advanced over algae?
Answer:
In higher bryophytes plant body is differentiate into root-like,stem-like and leaf-like structures. They also shows amphibious habit.
Question 36.
Differentite between gametophyte and sporophyte.
Answer:
Gametophyte is haploid and bears gametes. Sporophyte is diploid and bears spores
Question 37.
In which plant will you look for mycorrhiza and corolloid roots? Also explain what these terms mean, pinus and cycas.
Answer:
- Mycorrhiza – association of root and fungus
- Corolloid root – association of root and N2 fixing cyanobacteria.
Question 38.
Why rhizoids are not called roots?
Answer:
Rhizoids are haploid and lack vascular tissue, on the other hand, roots are diploid and bear vascular tissue.
Question 39.
Both gymnosperms and angiosperms bear seeds, then why are they classified separately?
Answer:
Because the gymnosperms are plants that bear ovules that are not covered by any ovary wall i.e the seeds of gymnosperms are not covered( naked). But in the angiosperms the seeds remain enclosed inside the fruits.
Question 40.
Why are some bryophytes called liverworts?
Answer:
Some bryophytes are called liverworts because their gametophyte resembles liver lobes.
Question 41.
Heterospory i.e., formation of two types of spores microspores and megaspores is a characteristic feature in the life cycle of a few members of pteridophytes and all spermatophytes. Do you think heterospory has some evolutionary significance in plant kingdom?
Answer:
It is considered a precursor to seed habit. The microspores of angiosperms develops into male gametophyte and megaspores develops into female gametophyte or embryosac.
Question 42.
Most algal genera show a haplontic lifestyle. Name an alga which is
- Haplo-diplontic
- Diplontic
Answer:
- Ectocarpus, polysiphonia and kelps
- Fucus
Question 43.
What is heterospory? Give its significance?
Answer:
Heterospory is the production of two kinds of spores in pteridophytes. EgfSalvina and Selaginella They produces 2 kind of spores i.e macrospores- these are large in size and microspores-these are small in size.
Question 44.
The spores and gametes produced by some members of algae are nonmotile.
- Do you agree the above statement.
- Give reasons.
Answer:
- Yes
- In members of red algae, the pear-shaped spores and gametes do not possess flagella, hence they are non-motile.
Question 45.
Nature of spore development is different in bryophytes and pteridophytes.
- Give the common name for the structures arise from spores.
- Identify these two.
Answer:
- Gametophyte
- Protonema and Prothallus
Question 46.
- Name the diploid and triploid products formed in Embryosac after fertilisation.
- What will be the fate of haploid structures not participate in fertilisation?
Answer:
- Diploid – Zygote,
Triploid – PEN - Synergids and antipodals degenerate after fertilisation.
Question 47.
- Identify the types of associations in some members of gymnosperms
- Name organisms forms in such associations
Answer:
- Mycorrhiza and corrolloid root
Mycorrhiza – pinus and fungus, - Corrolloid root – N2 fixing cyanobacteria and cycas
Question 48.
- Differentiate the nature of plant body in Bryophytes and gymnosperms.
- Identify the life cycle shown by the above two plant group
Answer:
- Bryophytes – Thallus type (plant body is not differentiated)
Gymnosperms – Plant body is differentiated into root, stem, and leaves - Bryophytes – Haplo-diplontic
Gymnosperms – Diplontic
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mark the statement Ture or False,
- Potato, ginger, turmeric are underground stems. They are modified to store food in them
- Phyllotaxy is the pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch
- A flower having only stamens or carpel is bisexual.
- Calyx and corolla are reproductive organs
- Lamina is the green expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets
- In racemose inflorescence, the main axis terminates in a flower.
- Ovary in epigynous flower is superior
- If the margin of sepals or petals overlap one another but not in a particular direction, the aestivation is called imbricate.
- A sterilse stamen is called staminode
- The seed coat has two layers the outer testa and the inner tegmen.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
Question 2.
What is heterospory. Give a brief account of its significance with examples.
Answer:
Hetrospory is the production of 2 types of spores, Macro (large) and Micro(Small). They give rise to female and male gametophyte respectively. The gamete fused to form zygote which retained in the female gametophyte. This event can be considered as a precursor of seed habit and is an important step in evolution.
Question 3.
Mention the ploidy of the following.
- Protonemal cell of a moss
- Primary endosperm nucleus in dicot.
- Leaf cell of moss.
- Fern Prothalus
- Meristem cell of monocot
- Ovum cell of liverwort
- Zygote of a fern
Answer:
- n – Haploid
- 3n triploid
- n – haploid
- n – haploid
- 2n – diploid
- n – haploid
- 2n)diploid
Question 4.
Explain briefly the following term with suitable examples. Protonejjia, Antheridium, Archegonium, Diplonticand Sporophyll.
Answer:
- Protonema – the 1st gametophytic stage developed by the germination of spores in Bryophytes
- Antheridium – Male sex organs which produce flagellated motile male gamtes. eg: Bryophyte
- Archegonium – Female sex organ which produce nonmotile egg it is a flask shaped. eg: pteridophyte & Gymnosperm
- Diplontic – Diploid sporophytic generation is dominant photosynthetic independent phase of the plant and gametophytic phase is represented by haploid gametophyte eg: gymnosperm & angiosperm
Question. 5
Based on the relationship, fill in the blanks:
- Nephrolepis:Prothallus:: Funaria: ……….
- Penicillium: ………..:: Agaricus Basidiocarp
- …………… Phaeophyceae::Carageen: Rhodophyceae
Answer:
- Protonema
- Conidia
- Mannitol
Question. 6
A few statements regarding algae are given below. Study them carefully and state true or false. If false make them correct.
- Algae are thallophytes.
- Volvox is a red algae.
- Algin is obtained from red algae.
- Floridean starch is found in green algae.
- Green algae are known as Rhodophyte.
- Green algae possess chlorophyll a
Answer:
- True
- False. Green algae 1
- False. Brown algae
- False. Red algae
- False. Chloropyta
- True
Question.7
Write a note on the economic importance of algae & gymnosperm.
Answer:
Algae – increase the level of oxygen in enviomment. They are the chief producers in aquatic ecosystems Some species of brown algae like sargassum, laminaria & Porphyra are used as food. Red algae and brown algae produce hydrocolloids which are water-holding substances. Eg: Gracilaria & gelidium Clorella is used as food supplement by space travelers.
Gymnosperm – Produce alkaloids like terpentine from the stem. They are grown as an ornamental plant. Certain species like ephedra are medicinal.
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How would you distinguish monocots from dicots?
Answer:
- The easiest way is by looking at their seeds. Seeds of monocots have one cotyledon while that of dicots have two cotyledons.
- Dicots have tap root system, while monocots have fibrous root system.
- Dicots show reticulate venation, while monocots show parallel venation.
Question 2.
Match the followings (column I with column II)

Answer:
- a) – iii
- b) – iv
- c) – ii
- d) – i
Question 3.
What is heterospory? Briefly comment on its significance. Give two examples.
Answer:
Certain pteridophytes produce two kinds of spores. This phenomenon is called heterospory.
Question 4.
Both gymnosperms and angiosperms bear seeds, then why are they classified separately?
Answer:
The seeds of gymnosperms are naked, while that of angiosperms are covered by a membrane. That is why they are classified separately.
Question 5.
What is the basis of classification of algae?
Answer:
The main basis of classification of algae is the presence or absence of pigments, which impart an algae
its colour.
1. Chiorophyceae contains chlorophyll a and b, giving it the green colourand the name ‘green algae’.
2. Phaeophyceae contains chlorophyll a and c and fucoxanthin. The fucoxanthin gives it the brown colourand hence the name ‘brown algae’.
3. Rhodophyceae contains chlorophyll a and d and phycoerythrin. The phycoerythrin gives the distinct red colour and hence the name ‘red algae’.
Plus One Botany Plant Kingdom Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The major pigment present in brown algae is
(a) chlorophyll a
(b) fucoxanthin
(c) Floridian starch
(d) phycoerythrin
Answer:
(b) fucoxanthin
Question 2.
Hetrospory is first noticed in
(a) gymnosperm
(b) pteridophytes
(c) gymnosperm
(d) ferns
Answer:
(b) pteridophytes
Question 3.
Mycorrhizal association is found in the root of
(a) ferns
(b) pinus
(c) cycas
(d) potytrichum
Answer:
(b) pinus
Question 4.
Which one of the following belongs to brown algae
(a) polysiphonia
(b) ectocarpus
(c) ulothrix
(d) volvox
Answer:
(b) ectocarpus
Question 5.
Sexual reproduction of bryophytes involves the production of
(a) sperms
(b) biflagellate antherozooids
(c) antheroids
(d) cilliate antherozooids
Answer:
(b) biflagellate antherozooids
Question 6.
The asexual reproductive structures occurs in bryophytes are
(a) zoospores
(b) gemmae
(c) fronds
(d) rhizoids
Answer:
(b) gemmae
Question 7.
Protonema stage occurs when
(a) spore of bryophytes germinate
(b) seed germinates
(c) spore of ferns germinate
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) spore of bryophytes germinate
Question 8.
PEN is formed in
(a) angiosperm
(b) pteridophytes
(c) gymnosperm
(d) ferns
Answer:
(a) angiosperm
Question 9.
The life cycle occurs in ectocarpus is
(a) haplontic
(b) haplodiplontic
(c) diplontic
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) haplodiplontic
Question 10.
Prothallus is
(a) photosynthetic gametophyte
(b) photosynthetic sporophyte
(c) non-photosynthetic gametophyte
(d) non-photosynthetic sporophyte
Answer:
(a) photosynthetic gametophyte
Question 11.
The phylogenetic system of classification is mainly based on
(a) embryological characters
(b) evolutionary characters
(c) morphological Characters
(d) floral characters
Answer:
(b) evolutionary characters
Question 12.
Classification based on cytological information, chromosome number etc. called
(a) chemotaxonomy
(b) cytotaxonomy
(c) numerical taxonomy
(d) cytogenetics
Answer:
(b) cytotaxonomy
Question 13.
In which of the following groups would you place plants having vascular tissue but lacking seeds
(a) pteridophytes
(b) gymnosperms
(c) angiosperms
(d) bryophytes
Answer:
(a) pteridophytes
Question 14.
Life cycle found in pteridophytes
(a) haplontic
(b) diplontic
(c) haplo-diplontic
(d) either haplontic or diplontic
Answer:
(c) haplo-diplontic
Question 15.
Fucoxanthin is the chief pigment in
(a) red algae
(b) brown algae
(c) green algae
(d) blue green algae
Answer:
(b) brown algae
Question 16.
Algae which grow on animals and also occur on shells of molluscs or other invertebrates are called
a) parasitic
b) epiphytic
c) epizoic
d) coenobia
Question 17.
Xylem of gymnosperm lack
(a) tracheids
(b) vessels
(c) both a and b
(d) fibres
Answer:
(b) vessels
Question 18.
Pyrenoids are present in
(a) angiosperms
(b) gymnosperms
(c) algae
(d) pteridophytes
Answer:
(c) algae
Question 19.
The first plants to appear after forest fire are the ferns this is because of the survival of their
(a) fronds
(b) rhizome
(c) spores
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(b) rhizome
Question 20.
The endosperm of gymnosperm is
(a) diploid
(b) triploid
(c) tetraploid
(d) haploid
Answer:
(d) haploid
