Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Plant Growth and Development
Plus One Botany Plant Growth and Development One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Ethylene is used for
(a) Retarding ripening of tomatoes
(b) Hastening of ripening of fruits
(c) Slowing down ripening of apples
(d) Both b and c
Answer:
(b) Hastening of ripening of fruits.
Question 2.
Coconut milk contains
(a) ABA
(b) Auxin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Gibberellin
Answer:
(c) Cytokinin
Question 3.
The affect of apical dominance can be overcome by which of the following hormone:
(a) IAA
(b) Ethylene
(c) Gibberellin
(d) Cytokinin
Answer:
(d) Cytokinin.
Question 4.
Growth can be measured in various ways. Which of these can be used as parameters to measure growth
(a) Increase in cell number
(b) Increase in cell size
(c) Increase in length and weight
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 5.
ABA acts antagonistic to
(a) Ethylene
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Gibberlic acid
(d) IAA
Answer:
(c) Gibberlic acid.
Question 6.
Name the growth regulator which was isolated from the endosperm of maize.
Answer:
Cytokinin(Zeatin).
Question 7.
What can induce bolting cabbage plant?
Answer:
Gibberellins
Question 8.
Certain plants flower only when they are exposed to low temperature for a few weeks . What do you call for this requirement?
Answer:
Vernalisation.
Question 9.
Some volatile substance from the ripened oranges that hastens the ripening of stored unripened bananas. Name the hormone which induces ripening.
Answer:
Ethylene
Question 10.
In a wheat field, some broad-leaved weeds were found by a farmer. Which phytohormone can be used to eradicate them.
Answer:
2, 4 – D (Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid).
Question 11.
Name the phytohormone that can cause the development of seedless fruits.
Answer:
Gibberellic acid.
Plus One Botany Plant Growth and Development Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match the following. (Column I with Column II)
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Cytokinin | i) Promote senescence |
| b) IAA | ii) Delay senescence |
| c) ABA | iii) Initiate rooting |
| d) Ethylene | iv) lateral shoot growth |
| v) Plant growth inhibitor |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Cytokinin | Delay senescence |
| b) IAA | Initiate rooting |
| c) ABA | Plant growth inhibitor |
| d) Ethylene | Promote senescence |
Question 2.
Match the following.
| A | B |
| 1. Ethylene | Zeatin |
| 2. Abscisic acid | Overcome apical dominance |
| 3. Cytokinins | Fruit ripening |
| 4. Gibberellins | Stomatal closure |
| Herbicide |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Ethylene | Fruit ripening |
| 2. Abscisic acid | Stomatal closure |
| 3. Cytokinins | Zeatin |
| 4. Gibberellins | Overcome apical dominance |
Question 3.
In plants, the adverse environmental conditions such as severe drought can be overcome by the production of a hormone.
- Name the hormone.
- Write the role of the hormone.
Answer:
- ABA
- Stress hormone – Closure of stomata.
Question 4.
Auxin is a growth-promoting phytohormone. Write any two functions of auxin,
Answer:
- Production of Seedless fruit
- Used as Weedicide
Question 5.
Growth pattern of a plant is displayed in graph. Observe the figure.
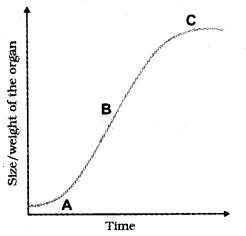
- What kind of growth form is this?
- Why does the graph show a decline to a near-constant level?
Answer:
- Sigmoid curve
- Stationary phase
Question 6.
Some important functions of a Phytohormone are given below:
Production of Parthenocarpic Fruits Eradication of weeds
- Identify the hormone.
- Mention any other two important functions of this hormone.
Answer:
- Auxin
- Root initiation, Apical dominance
Question 7.
In Plants, adverse environmental conditions such as severe drought can be overcome by the use of a hormone.
- Name the hormone
- Write the role of this hormone.
Answer:
- ABA (Abscisic Acid)
- It causes the Closure of stomata. This reduces the rate of transpiration.
Question 8.
- A farmer is going to plant Tapioca cuttings. Which hormone you will suggest for early rooting of tapioca cuttings?
- A defoliated short day plant is kept under short-day conditions for 15 days and another short-day plant with single leaf is kept under short-day conditions for 1 day. Which plant will possibly flower first and give reasons?
Answer:
- Auxin
- A short day plant with single leaf will flower first Leaf recives the light stimulus and produce Florigen, It is then transported to the vegetative apex. As a result vegetative apex is converted into reproductive apex and bears floral leaves.
Question 9.
Synthetic auxins are of much importance in agriculture. Name any two synthetic auxins.
Answer:
- 2, 4 – D (2,4 – Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid)
- 2, 4, 5 – T. ( 2,4,5 – Trichlorophenoxy acetic acid).
Question 10.
Which hormone will add, if you are asked to help a farmer to
- Quickly ripens fruit
- Bolt a resette plant
- Initiate rooting in a twig
- Induce stomatal closure in leaves.
Answer:
- a) Ethylene
- Gibberelline
- Auxin
- Abscisic acid (ABA)
Question 11.
A gardener finds some broad-leaved dicot weeds growing in his lawns. What can be done to get rid of the weeds efficiently?
Answer:
The dicotyledonous plant grow by their apical shoot meristems while grasses (which make lawns) possess intercalary meristem. Certain auxins, such as synthetic 2, 4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4- D) when applied in excess can damage the shoot apical meristems but they do not cause any damage to the intercalary meristems. Thus, when 2, 4-D is sprayed on lawns, only the dicots get killed and the lawns become free of weeds.
Question 12.
What is the mechanism underlying the phenomenon by which the terminal/apical bud suppresses the growth of lateral buds? Suggest measures to overcome this phenomenon.
Answer:
The phenomenon by which the terminal apical bud suppresses the growth of lateral buds is referred to as apical dominance. This js because of the hormone auxin synthesised in the apical bud that inhibits lateral bud development.
This can be overcome by removing the apical bud (decapitating) and young leaves which will increase branching. It may also be possible to overcome this phenomenon by application of cytokinin and antiauxins like ethylene chlorohydrin, DCA (trichloroanisole), etc.
Question 13.
Ethylene is otherwise known as a fruiting hormone. So this is widely used in agricultural fields. Which compound is used as a source of ethylene and what are its merits?
Answer:
Ehephone-Merits:
- It promotes female flowers in cucumbers.
- It hastens fruit ripening in tomatoes and apples.
- It promotes abscission of flowers and fruits.
Question 14.
Plant hormones are organic compounds influencing growth and development. One of the hormones was first isolated from human urine and other is a gaseous hormone.
a) Name the two hormones.
b) Write any two functions of these hormones.
Answer:

Question 15.
How will you induce lateral branching in a plant which normally does not produce them ? Give reason in support of your answer.
Answer:
When apical bud is removed, it promotes lateral branching. It is due to the removal the auxin from the tip and growth of apical bud is inhibited.
Question 16.
Describe how auxins are related with the bending of shoot towards the source of light.
Answer:
When unilateral light is given, auxin from the illuminated side shifted towards the shaded side and more growth occurs on that side. This causes the bending of the shoot.
Question 17.
How does abscisic acid act antagonistically to auxins and gibberellins?
Answer:
Gibberellin causes the breaking of bud dormancy but auxin check the fruit fall and leaf fall. These two physiological functions are inhibited by ABA.
Question 18.
What is meant by abscission? Name the phytohormone involved in it.
Answer:
It is the shedding of leaves, flowers, fruits, and bark. Abscisic acid(ABA)
Question 19.
What does a stationary phase of sigmoid growth curve indicate?
Answer:
It is otherwise called a declining phase because growth slows down.
Question 20.
What is the full form of I BA? Also, mention its one use in agriculture.
Answer:
Indole – 3 -butyric acid
It initiates root formation on stem cuttings by activating root primordia
Question 21
Fill in the places with appropriate word/words.
- A phase of growth which is the maximum and fastest is _____.
- Apical dominance as expressed in dicotyledonous plants is due to the presence of more _____ in the apical bud than in the lateral ones.
- In addition to auxin, _____ must be supplied to culture medium to obtain a good callus in plant tissue culture.
- ______ of vegetative plants are the sites of photoperiodic perception.
Answer:
- exponential/log phase of an S – curve.
- auxin/IAA
- cytokinin/Kinetin/6 BAP/Zeatin/etc.
- leaves.
Question 22.
Why is abscisic acid called stress hormone?
Answer:
Abscisic acid is also called stress hormone because the synthesis of abscisic acid is stimulated by drought, waterlogging and other adverse environmental conditions. It causes the closure of stomata.
Question 23.
Root and shoot elongation takes place at constant rate in one type of growth but in others zygote develops into embryo. What are the types of growth in both?
Answer:
In the former growth is arithematic type while in the latter initial geometric then arithematic type.
Question 24.
Give the term for the process given below.
- formation of vascular cambium and cork cambium
- Formation of secondary tissues in dicot stem
Answer:
- Dedifferentiation
- Redifferentiation
Question 25.
- Name the phenomenon of the influence of day length on the flowering of long day and short-day plants
- Which is the part of plant shows response to such phenomenon
Answer:
- Photoperiodism
- Leaf.
Question 26.
Identify the true or false statements from the following.
- ABA is known as Anti- gibberellin
- Auxin promotes flowering in pineapple
- Low-temperature treatment not promote flowering in varieties of wheat
- Bakane disease associated with ethylene
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
Plus One Botany Plant Growth and Development Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Identify the hormone have important role from the statement given below
- In Tea plantation and hedge making
- Increase stem length of sugar cane
- ripening of fruits
Answer:
- Auxin
- Gibberellin
- Ethylene
Question 2.
Which one of the plant growth regulators would you use if you are asked to:
- Induce rooting in a twig
- Quickly ripen a fruit
- Delay leaf senescence
- ‘bolt’ a rosette plant
- Induce immediate stomatal closure in leaves.
Answer:
- auxin
- ethylene
- cytokinin
- gibberellins
- ABA
Question 3.
The S-shaped growth curve is shown in the diagram. Label ‘a’ to ‘c’ and also write short notes on ‘a’ and ‘b’.
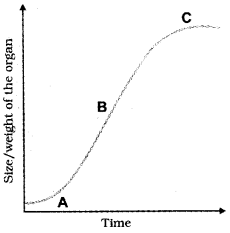
Answer:
- a – lag phase (slow phase)
- b – exponential phase (rapid phase)
- c – stationary phase (stagnant phase)
Question 4.
Plant growth substances (PGS) have innumerable practical Applications. Name the PGS you should use to
- Increase yield of sugar cane
- Promote lateral shoot growth
- Inhibit seed germination
Answer:
- GA3/gibberellinfgibberellic acid
- Cytokinin zeatin/kinetin
- ABA/Abscissic acid.
Plus One Botany Plant Growth and Development NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why is abscisic acid also known as stress hormone?
Answer:
Abscisic acid increases the tolerance of plants to various kinds of stresses. Therefore, it is also called the stress hormone.
Question 2.
‘Both growth and differentiation in higher plants are open’. Comment.
Answer:
Theoretically, growth and differentiation in higher plants are open. This means that there is no limit to the ‘extent a plant part can grow. But it is more correct to say that development and differentiation is open in higher plants. Once a cell loses its capacity to divide then it differentiates Differentiation is the process by which a particular plant starts doing the job it is meant to do.
For example, the job of a leaf is to make food for plant. Sometimes environment or a particular phase of growth can dictate a particular part to behave differently. This is the phase when redifferentiation occurs and the plant part takes on a new role. Thus, it can be said that development and differentiation are open to change under the given environmental conditions and demands of those conditions.
Question 3.
Which one of the plant growth regulators would you use if you are asked to:
- induce rooting in a twig
- quickly ripen a fruit
- delay leaf senescence
- induce growth in axillary buds
- ‘bolt’ a rosette plant
- induce immediate stomatal closure in leaves
Answer:
- Auxins
- Ethylene
- Cytokinins
- Auxins
- Gibberellins
- Abscisic Acid
Question 4.
Would a defoliated plant respond to the photoperiodic cycle? Why?
Answer:
The hormone responsible for photoperiodism is found in leaves. So a defoliated plant will be devoid of such hormones and will not respond to the photoperiodic cycle.
Question 5.
What would be expected to happen if:
- GA is applied to rice seedlings
- dividing cells stop differentiating
- a rotten fruit gets mixed with unripe fruits
- you forget to add cytokinin to the culture medium
Answer:
1. GAj increases the length of axis. This property will help increase the length of axis so that yield of rice can be increased.
2. When dividing cells stop differentiating then it is the maturity stage of that part of the plant. Further growth of that particular region will be stopped.
3. The ethylene present in rotten fruit will hasten the ripening process of unripe fruit and may lead to premature ripening.
4. There will be lesser cell division and culture will not grow as per the target.
Question 6.
Why is not anyone parameter good enough to demonstrate growth throughout the life of a flowering plant?
Answer:
Like most of the organisms plants also go through various phases of growth. When a seed is germinating then the parameters of growth will be different compared to growth of a mature plant. Moreover, plants can be of huge variety, right from perennial plants to plants living hundreds of years. Because of sheer diversity in size and life span any single parameter to define and measure the growth of a plant can never be sufficient.
Plus One Botany Plant Growth and Development Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The ripening of fruits can be fastened by treatment with
(a) gibberellins
(b) cytokinins
(c) ethylene gas
(d) auxin
Answer:
(c) ethylene gas
Question 2.
Which of the following is the effect of a plant hormone, which is synthesized more in the absence of light?
(a) Inhibits the development of seedless fruits
(b) Responsible for closing of stomata
(c) Induces the dormancy of seeds
(d) Length of intemodes increases
Answer:
(d) Length of intemodes increases
Question 3.
Leaf abscission is caused by
(a) ABA
(b) cytokinin
(c) auxin
(d) gibberellin
Answer:
(a) ABA
Question 4.
A hormone delaying senescence is
(a) auxin
(b) cytokinins
(c) ethylene
(d) gibberellin
Answer:
(b) cytokinins
Question 5.
Which of the following induces bolting in rosette plants?
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Auxins
(d) Ethylene
Answer:
(a) Gibberellins
Question 6.
Sprouting of potato under storage condition can be prevented by
(a) auxin
(b) gibberellin
(c) ethylene
(d) cytokinin
Answer:
(a) auxin
Question 7.
The plant hormone produced by Rhizobium for nodulation is
(a) IBA
(b) NAA
(c) 2, 4-D
(d) IAA
Answer:
(d) IAA
Question 8.
Cell elongation in internodal regions of the green plants takes place due to
(a) indole acetic acid
(b) cytokinins
(c) gibberellins
(d) ethylene
Answer:
(c) gibberellins
Question 9.
How does pruning help in making the hedge dense?
(a) It induces the differentiation of new shoots from the rootstock
(b) It frees axillary buds from apical dominance
(c) it promotes adventitious root growth
(d) it promotes the growth of apical buds
Answer:
(b) It frees axillary buds from apical dominance
Question 10.
Name of a gaseous plant hormone is
(a) IAA
(b) gibberellin
(c) ethylene
(d) abscisic acid
Answer:
(c) ethylene
Question 11.
The maximum growth rate occurs in
(a) stationary phase
(b) senescent phase
(c) lag phase
(d) exponential phase
Answer:
(d) exponential phase
Question 12.
Growth promoting hormone is
(a) gibberellins
(b) ABA
(c) auxins
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(d) both a and c
Question 13.
The discovery of gibberellins is related with one of the following
(a) blast disease of rice
(b) foolish seedling disese
(c) bakane disease of rice
(d) early blight disease of potato
Answer:
(c) bakane disease of rice
Question 14.
Which of the following movements in plants is due the increased concentration of auxin?
(a) Movement of shoot towards the source of light
(b) Nyctinasty
(c) Movement of sunflower towards sun
(d) root differentiation
Answer:
(a) Movement of shoot towards the source of light
Question 15.
The problem of necrosis and gradual senescence, while performing tissue culture can be overcome by
(a) spraying auxins
(b) spraying cytokinins
(c) suspension culture
(d) subculture
Answer:
(b) spraying cytokinins
Question 16.
The following statements are given about plant growth hormones
I. Cytokinins especially help in delaying senescence
II. Auxins are involved in regulating apical dominance
III. Ethylene is especially useful in enhancing seed germination
IV. Gibberellins are responsible for immature falling of leaves
Which of the above statements are correct
(a) I and II only
(b) I and III only
(c) II and III only
(d) II, III, and IV only
Answer:
(a) I and II only
Question 17.
Which plant hormone promotes seed dormancy, bud dormancy and causes stomatal closure?
(a) auxin
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) GA
(d) CH2=CH2
Answer:
(b) Abscisic acid
Question 18.
Abscisic acid is primarily synthesized in
(a) lysosomes
(b) Golgi complex
(c) chloroplast
(d) ribosomes
Answer:
(c) chloroplast
Question 19.
Auxin in plant means for
(a) cell elongation
(b) fruit ripening
(c) cell division
(d) cell differentiation
Answer:
(c) cell division
Question 20.
The hormone present in the liquid endosperm of coconut is
(a) cytokinin
(b) gibberellin
(c) ethylene
(d) auxin
Answer:
(a) cytokinin
