Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Respiration in Plants
Plus One Botany Respiration in Plants One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis can have many metabolic fates. Under the aerobic condition, it forms
(a) Lactic acid
(b) CO2+H2O
(c) Acetyl CoA + CO2
(d) Ethanol + CO2
Answer:
(b) CO2+ H2O
Question 2.
Electron Transport System (ETS) is located in mitochondrial
(a) Outer membrane
(b) Inter membrane space
(c) Inner membrane
(d) Matrix
Answer:
(c) Inner membrane
Question 3.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) During the conversion of succinyl Co-A to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesized.
(b) Oxygen is vital in respiration for removal of hydrogen.
(c) Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
(d) There is complete breakdown of glucose in fermentation.
Answer:
(a) During the conversion of succinyl Co-A to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesized.
Question 4.
Mitochondria are called powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
(a) Mitochondria have a double membrane
(b) The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
(c) Mitochondria synthesise ATP
(d) Mitochondria are found in almost all plants and animal cells.
Answer:
(c) Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
Question 5.
The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is
(a) NADH
(b) Oxygen
(c) ADP
(d) ATP+H2O
Answer:
(d) ATP+H2O
Question 6.
Fo-F1 particles participate in the synthesis of
Answer:
ATP molecules
Question 7.
The product of aerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle and anaerobic fermentation in yeast are respectively ……… and …….
Answer:
Lactic acid and Ethyl alcohol.
Question 8.
How many NADH2 molecules are produced from molecule of acetyl co A in TCA cycle?
Answer:
Three.
Question 9.
Name the final acceptor of electrons in ETC.
Answer:
Oxygen.
Question 10.
Give the number of ATP molecules produced from 1 glucose molecule in aerobic respiration.
Answer:
38.
Question 11.
The process of oxidation in microorganisms are referred as
(a) Cellular respiration
(b) Aerobic respiration
(c) Fermentation
Answer:
(c) Fermentation
Question 12.
Calculate the RQ of tripalmitin with the help of equation given below.
2(C5H98O6) + 145O2 -»102 CO2 + 98H2O + energy
Answer:
RQ=102CO2145O2=0.7
Question 13.
In the respiration process both in aerobic and anaerobic, the first phase of reactions is the same. Write the name of reaction Answer:
Glycolysis.
Question 14.
A germinating seed released 120 CO2 by utilizing 180 O2 stage. Calculate the RQ. Name the respiratory substrate.
Answer:
The substrate is fat.
Question 15.
Respiratory pathway is an amphibhotic pathway. Comment.
Answer:
It involves both anabolic & catabolic pathways.
Question 16.
Name the unit of oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer:
Oxysomes or Elementary particles.
Question 17.
How many calories are produced by aerobic oxidation of 1 gm mole of glucose?
Answer:
686000 calories.
Question 18.
We commonly call ATP as the energy currency of the cell. Can you think of some other energy carriers present in a cell? Name any two.
Answer:
NADH2 and FADH2.
Question 19.
RQ value changes for wheat and castor oil seeds. Justify.
Answer:
R Q = 1 carbohydrate (wheat)
R Q < 1 fat(castor)
Plus One Botany Respiration in Plants Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Pyruvate, which is formed by the glycolytic catabolism of carbohydrates undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.
- Where does it occur?
- Who first elucidate this?
Answer:
- Cristae of mitochondria
- Hans Kreb
Question 2.
Glycolysis is the first stage in the break down of glucose in all organisms. Do you agree with this statement? Where does it take place? Give the net. gain of ATP molecules in glycolysis?
Answer:
Yes, Cytoplasm, 8ATPs
Question 3
Observe the relation of the first pair and fill up the blanks
- Symport: Molecules cross the membrance in the same direction
…………..: Molecules move in the opposite direction - RQ = 1 : Carbohydrate
RQ > 1: ………..
Answer:
- Antiport
- Organic acids
Question 4.
‘‘Photorespiration is called a wasteful process.” Comment on it.
Answer:
ATP is utilized. There is no production of ATP during this process. It does not produce any beneficial product.
Question 5
Respirometer is an apparatus used to measure R.Q.
- What is R.Q?
- R.Q. of glucose is equal to one. Give the reason.
Answer:
- Amount of CO2 released during respiration / Amount of O2 absorbed during respiration,
- Amount of CO2 released= Amount O2 absorbed
Question 6.
Plant physiologists observed a relationship between respiration and salt absorption. Is absorption of salt increased due to respiration? Explain.
Answer:
Yes. As a result of respiration, the energy is released in the form of ATP. This energy is used for the active absorption of salt.
Question 7.
Glycolysis is the first step of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. During this process glucose undergoes partial oxidation.
- What is the final product of glycolysis?
- What is the total yield of ATP molecules during glycolysis?
Answer:
- Pyruvic acid
- 8 ATP
Question 8.
The RQ value of a respiratory substrate is 1. Find the type of substrate and comment on RQ.
Answer:
Carbohydrate RQ:
It is the ratio of volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed. The value of RQ is different for respiratory substrates eg fat(0.7), protein (0.9)etc.
Question 9.
Oxidative phosphorylation is an important process in cellular respiration. Explain it?
Answer:
Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the inner membrane of mitochondria. In the F1 head the inorganic phosphate combined with ADP to form ATP. It occurs due to the entry of proton pair from intermembrane space to the matrix through proton channel.
Question 10.
Why does anaerobic respiration produce less energy than aerobic respiration?
Answer:
- The regeneration of NAD fails to produce ATP as the electrons are not shifted to oxygen
- The end product of anaerobic respiration can be further oxidized to release energy.
Question 11.
What is fermentation Name any two organic compounds produced in this process?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration also called fermentation involves the production of energy from food nutrients in the absence of oxygen.
Question 12.
“Respiration is an amphibolic pathway”. Justify the statement with reason.
Answer:
Respiration involves both the catabolic and anabolic process. Fatty acid undergoes breackdown to form acetyl. co-A.
Acetyl Co-A is again used for the synthesis of Fat. In respiration cycle the two process are involved.i.e catabolism and anabolism. So it is called a Amphibolic Pathway”.
Question 13.
ADP is converted to ATP as a result of phosphorylation which takes place in photosynthesis and respiration during electron transport system. What is the difference between these two?
Answer:
photophosphorylation, inorganic phosphate combines with ADP to form ATP This process takes place in chloroplast in the presence light. But in oxidative phosphorylation inorganic phosphate combines with ADP to form ATP. It takes place in Mitochondria.
Question 14.
When does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Answer:
In man during streneous exercise O2, inedequecy is experience in Skeletal tissues. In such a case the respiration is anaerobic. In yeast, during fermentation the respiration takes place is anaerobic.
Question 15.
Mention the important series of events of aerobic respiration that occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion as well as ones that take place in inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Answer:
Citric acid cycle,Terminal oxidation and electron transport system.
Question 16.
Name the end products aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis. List the two ways by which molecules of ATP are produced in glycolysis during aerobic respiration in a cell.
Answer:
2 Pyruvic acid, 2ATP and 2 NADH2 Two ways of ATP formation in glycolysis are:
- During dephosphorylation of 1, 3, DPGA called substrate-level phosphorylation
- Reduced NADH2 releases ATP molecules in electron transport chain
Question 17.
Define RQ What is its significance?
Answer:
It is the ratio of volume of CO2 released to volume of O2 taken during respiration. Value of R Q gives the indication of nature of substrate respired by a particular tissue.
Question 18.
Different substrates get oxidized during respiration. How does Respiratory Quotient (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidized?
R Q=A/B
What do A and B stand for?
What type of substrates have R.Q. of 1, < 1 or> 1?
Answer:
A-Volume CO2 evolved B- Volume O2 consumed RQ=1 (Carbohydrate) RQ=< 1 Fat/protein RQ=> 1 (Organic acids).
Question 19.
Which of the following will release more energy on oxidation? Arrange them in ascending order,
a. Moffat
b. 1 gm of protein
c. 1 gm of glucose
d. 0.5 g of protein + 0.5g glucose
Answer:
c → d → b → a
Question 20.
What is the importance of F0-F, particle in ATP production during aerobic respiration?
Answer:
F0 is an integral membrane protein complex and has a proton channel while F1 has enzyme ATP synthase to form ATP. One molecule of NADH produces 3 ATP molecules in ETS.
Question 21.
What is Respiratory Quotient? What is its value for fats?
Answer:
It is the ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2consumed.
So,RQ= Volume of CO2 Evolved Volume of O2 consumed
Question 22.
Give two example for anaerobic respiration occurs in organisms and products.
Answer:
Alcoholic fermentation and Lactic acid fermentation Ethyl alcohol and lactic acid.
Question 23.
The complete oxidation of pyruvic acid that occurs in mitochondria undergoes both oxidation and decarboxylation.
- Which is the first step of oxidative-decarboxylation occurs?
- Where does substrate-level phosphorylation occurs?
Answer:
- Conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA
- Conversion of succinyl CoA to Succinic acid.
Question 24.
Give the name of intermediate compounds having carbon atoms 6,5,4 and 2 of mitochondrial oxidation.
Answer:
- 6C – Citric acid, 5C- Alpha keto glutaric acid,
- 4C- Succinic acid/succinyl coAl malic acid/ OAA,
- 2C- Acetyl CoA.
Plus One Botany Respiration in Plants Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Incomplete oxidation of food material in the absence of oxygen is anaerobic respiration.
(a) Give an example of a microorganism which carry out anaerobic respiration.
(b) Where does anaerobic respiration take place in human beings?
(c) What is the net gain of ATP during this process? Spa) Yeast
(b) Muscle cells
Answer:
(c) 2 ATP
Question 2.
ETS operated in the inner mitochondrial membrane, it involves terminal oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation
- Who discovered chemiosmotic hypothesis in mitochondria
- Name the elementary particle promotes ATP synthesis
- What is chemiosmotic hypothesis
Answer:
- Peter Mitchel
- Fg-F, particle
- Proton gradient leads to ATP production
Question 3.
Yeast cells can respire in the absence of O2
- Name the process
- Write the end product of the process
- Write the net production of ATP during process.
Answer:
- Anaerobic respiration
- CO2 + C2H5OH (Carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol)
- 2 ATPs
Question 4.
Respiration is a breakdown process it involves various steps
- Where does the common step of aerobic and anaerobic process occurs
- Find out the number of carbon atoms of a compound as end product of the above reaction
- Name the 6 C intermedite compound splits and forms another 3 C intermediates.
Answer:
- Cytoplasm
- 3 Carbon (Pyruvic acid)
- Fructose 1, 6 biphosphate
Question 5.
ATP and NADPH2 molecules synthesised in light reaction of photosynthesis are used for the synthesis of glucose in dark reaction.
- Who proposed the dark reaction?
- List out three phases in dark reaction.
- Location of dark reaction in the chloroplast?
- Expense of ATP and NADPH2 for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose in dark reaction?
Answer:
- Melvin Calvin
- Carboxylation
- Reduction
- Regeneration of RUBP
- Stroma
- 12 NADPH2 and 18 ATP molecules.
Question 6.
In the last step of aerobic respiration oxidation of reduced co-enzymes produced in glycolysis and Krebs cycle occur.
- What are the important reduced coenzymes?
- Why is this process called as terminal oxidation?
- Where does terminal oxidation takes place?
Answer:
- FADH2, NADH2.
- It is the formation of metabolic water at the end of electron transport chain by combining protons, electrons, and O2.
- The inner mitochondrial membrane of mitochondria.
Question 7.
An athlete felt muscular pain after a race.
- Explain this in terms of anaerobic respiration?
- Name any two microorganisms in which anaerobic respiration occurs
- Glycolysis is common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In glycolysis, there is a net gain of 8 ATP. But in anaerobic repiration the net gain is only 2 ATP. Give reason.
Answer:
1. Athletes felt muscular pain is due to the inadequecy of 02. In the absence of 02 partial oxidation takes place. It involves the formation of pyruvic acid followed by lactic acid.
2. Yeast & Lactobacillus.
3. After the formation of pyruvic acid, 2 NADPH molecules are utilised for the formation of Lactic acid. So the net gain of ATP in Anaerobic respiration is 2 ATPs.
Question 8.
Mitochondria is called the “Power House’’ of the cell.
- Is the statement correct?
- Write down reasons.
Answer:
- Yes
- Synthesis of ATP takes place in mitochondria,
- Inner membrance acts as electron transport chain.
- Presence of ATP – synthetase enzyme.
- Enzymes for aerobic respiration in mitochondrial matrix
Question 9.
Analyse the diagram and answer the questions.
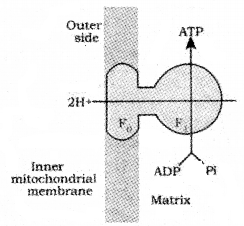
- What does the diagram represent?
- Write the role of F0-F., unit in the process?
- What is oxidative phosphorylation?
- Where does it take place?
Answer:
- ATP synthesis
- Flow of proton
- In the presenceC2, oxidation takes place and ADP combines with inorganic phosphate to form ATP
- Crystal
Question 10.
Respirometer is an apparatus used to measure R.Q.
- What is R.Q?
- R.Q. of glucose is equal to one. Give reason.
- Name the respiratory substrate for which R.Q. is more than one?
Answer:
- Amount of C02 released/Amount of O2 absorbed
- In glucose amount of CO2 released = amount of O2 absorbed
- Organic acids
Question 11.
RuBP carboxylase, PEPcase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactate dehydrogenase. Select/choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Both in photosynthesis and respiration
Answer:
- RuBP carboxylase, PEPcase, ATPase,
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactate dehydrogenase
- ATPase
Question 12.
The following statements are about an important event of cellular respiration. Read them carefully and answer the questions.
It is the last step of cellular respiration It synthesise ATP Water is the end product It accepts oxygen.
- Name the process
- Where does it occur?
- Name any 4 components of ‘it’
Answer:
- Electron transport system/oxidative phosphorylation
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- NADP, FAD, Ubiquinone (Co-Q)
Cyt. b, cyt – a, cty a3 etc.
Question 13.
Respiration is viewed most simply as the oxidative production of ATR Justify the statement.
Answer:
The energy-releasing process by oxidation of organic food materials in the living cell is respiration. During this process, the energy contained in the food is released and is trapped in the ATP molecules. NADH+H+ and FADH2 formed during various steps of respiration are oxidised, and protons (H+) and electrons (e ) are released.
These electrons are transported to the oxygen through a series of electron carries in the electron transport system (ETS), and their energy is stored in ATP molecules. So, respiration is process of oxidative production of ATP. 45% of energy released during the oxidation of 1 glucose molecule is stored in 38 ATP molecules.
Question 14.
The second phase of aerobic respiration takes place within mitochondria. This phase is called TCA cycle. The different steps of this reaction were found out by a British Biochemist who was awarded Nobel Prize in 1953.
- Identify the scientist and name the first product of the reaction.
- Write the first step of this reaction, why it is called TCA cycle?
- From where Acetyl Co. A comes into mitochondria?
- In which step FADHJs formed.
Answer:
- Hans Krebs, citric acid(Tricarboxylic acid)
- oaa+acetylcoA citric acid .since it has three -COOH group
- Cytoplasm
- 5th step (Succinic acid to malic acid)
Question 15.
Glycolysis is common and first phase of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- Who discovered this process?
- What are the substrate and end products in this reaction?
Answer:
- Embeden, Mayerhof & Parnas
- Glucose – Substrate.
The end product – Pyruvic acid.
Plus One Botany Respiration in Plants NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.”
Answer:
Glucose is the favoured substrate for respiration. All carbohydrates are usually first converted into glucose before they are used for respiration. Other substrates can also be respired but then they do not enter the respiratory pathway at the first step.
Since respiration involves breakdown as well as synthesis of substrates, the respiratory process involves both catabolism. That is why respiratory pathway is considered to be an amphibolic pathway rather than as a catabolic one.
Question 2.
What is the significance of step wise release of energy in respiration?
Answer:
If energy will be released at one go then most of it will be most in the form of heat. Cells should be in a position to utilize all the energy to synthesize something. To facilitate proper usage of energy, it is released in a stepwise manner during respiration.
Question 3.
Define RQ. What is its value for fats?
Answer:
The ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration is called the respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio.
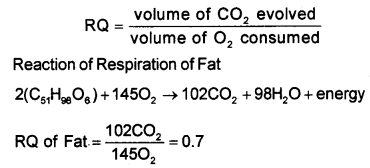
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following:
- Aerobic respiration
- Glycolysis and Fermentation
- Glycolysis and Citric acid Cycle
Answer:
1. There is incomplete oxidation of glucose during anaerobic respiration, while there is complete oxi¬dation during aerobic respiration.
2. The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is first converted to Acetyl coenzyme A, which undergoes citric acid cycle to produce critic acid. At the end of citric acid cycle NADH+H+ is released.
3. In both (b) and (c) glycolysis is the first step cellular respiration. The product of glycolysis is further utilized by either fermentation or critic acid cycle.
Question 5.
What are the assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
Answer:
It is possible to make calculations of the net gain of ATP for every glucose molecule oxidised, but in reality this can remain only a theoretical exercise. These calculations can be made only on certain assumptions that:
1. There is a acquential, orderly pathway functioning, with one substrate forming the next and with glycolysis, TCA cycle and ETS pathway following one after another.
2. The NADH synthesised in glycolysis is transferred into the mitochondria and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.
3. None of the intermediates in the pathway are utilised to synthesise any other compound.
4. Only glucose is being respired – no other alternative substrates are entering in the pathway at any of the intermediary stages.
Plus One Botany Respiration in Plants Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Common phase between aerobic and anaerobic modes of respiration is
(a) Krebs cycle
(b) EMP/glycolysis
(c) oxidative phosphorylation
(d) PPP
Answer:
(b) EMP/glycolysis
Question 2.
Complete oxidation of one gram mol. of Glucose give rise to
(a) 6860,000 cal
(b) 686,000 cal
(c) 68,600 cal
(d) 6860 cal
Answer:
(b) 686,000 cal
Question 3.
When a molecule of pyruvic acid is subjected to anaerobic oxidation and forms Lactic acid there is
(a) loss of 3 ATP molecules
(b) loss of 6ATP molecules
(c) loss of 2 ATP molecules
(d) loss of 4 ATP molecules
Answer:
(b) loss of 6ATP molecules
Question 4.
When one glucose molecule is completely oxidised, it changes
(a) 36 ADP mole into 36 ATP molecules
(b) 32 ADP mole into 32 ATP molecules
(c) 38 ADP mole into 38 ATP molecules
(d) 30 ADP mole into 30 ATP molecules
Answer:
(c) 38 ADP mole into 38 ATP molecules
Question 5.
Substrate phosphorylation occurs during
(a) Fumaric acid → malic acid
(b) Oxalosuccinic acid → alpha-ketoglutaric acid
(c) Succinic acid – fumaric acid
(d) a Ketoglutaric acid – Succinic acid
Answer:
(d) a Ketoglutaric acid – Succinic acid
Question 6.
Glycolysis is significant for energy production in
(a) RBC
(b) fungi
(c) plants
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) RBC
Question 7.
In aerobic respiration
(a) 2 PGAL are formed in Glycolysis and none in kerbs cycle
(b) 6 PGAL in glycolysis, 3 PGAL in kerbs cycle
(c) PGAL formation does not occur in respiration
(d) 8 PGAL in glycolysis, 3 PGAL in krebs cycle
Answer:
(a) 2 PGAL are formed in Glycolysis and none in kerbs cycle
Question 8.
Two enzymes common to EMP pathway and C3 cycle are
(a) Aldolase & triosephosphate isomerase
(b) Aldolase & enolase
(c) Cytochrome oxidase & enolase
(d) phosphoglyceromutase & triosephosphate isomerase
Answer:
(a) Aldolase & triosephosphate isomerase
Question 9.
The RQ value of fat is 0.7, it indicates
(a) volume of CO2 is greater than O2
(b) volume of O2 is greater than CO2
(c) volume of CO2 is greater than volume of O2
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) volume of O2 is greater than CO2
Question 10.
The net gain of ATP in aerobic respiration is
(a) 18
(b) 36
(c) 38
(d) 8
Answer:
(b) 36
Question 11.
Three carboxylic group occurs in
(a) pyruvic acid
(b) citric acid
(c) malic acid
(d) Aspartic acid
Answer:
(b) citric acid
Question 12.
Which is the first 5C carbon compound formed in TCA cycle
(a) succinic acid
(b) oxaloacetic acid
(c) alpha-ketoglutaric acid
(d) fumaric acid
Answer:
(c) alpha-ketoglutaric acid
Question 13.
The concentration of alcohol in fermentation influence the
(a) death of cells
(b) growth of cells
(c) production of succinic acid
(d) production of lactic acid
Answer:
(a) death of cells
Question 14.
Acetyl coA is called
(a) 5C compound
(b) 2C compound
(c) 3C compound
(d) 4C compound
Answer:
(b) 2C compound
Question 15.
Wine and beer are produced directly by fermentation. Brandy and whisky require both fermentation and distillation because
(a) fermentation is inhibited at an alcohol level of 10-18%
(b) distillation prolongs storage
(c) distillation improves quality
(d) distillation purifies the beverage.
Answer:
(a) fermentation is inhibited at an alcohol level of 10-18%
Question 16.
The process by which ATP is produced in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The electron transport system transfers protons from the inner compartment to the outer, as the protons flow back to the inner compartment, the energy of their movement is used to add phosphate to ADP, forming ATP.
(a) Chemiosmosis
(b) Phosphorylation
(c) Glycolysis
(d) Fermentation
Answer:
(a) Chemiosmosis
Question 17.
In which of the following reactions of glycolysis, a molecule of water is removed from the substrate?
(a) Fructose – 6 – phosphate → Fructose -1, 6 – bisphosphate
(b) 3 – phosphate – glyceraldehyde → 1, 3 bisphosphoglyceric acid
(c) PEP → Pyruvic acid
(d) 2 – phosphoglycerate → PEP
Answer:
(d) 2 – phosphoglycerate → PEP
