Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 9 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Question 1.
Label the marked parts in the given diagram of a chloroplast. (MARCH-2010)
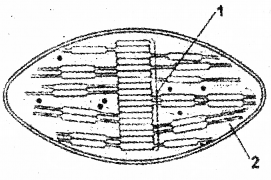
Answer:
1) Grana
2) Stroma thylakoid
Question 2.
Comment on the speciality of carbon fixation in some plants adapted to dry tropical regions. What are the anatomical peculiarities of the leaves of these plants? (MARCH-2010)
OR
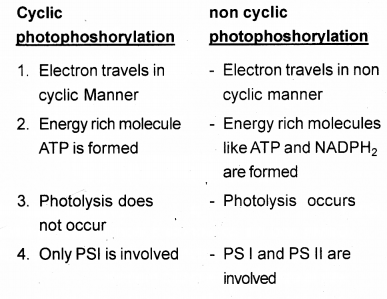
Comment on the differences between cycle photophosphorylation and noncyclic photophosphorylation. Which among the two is responsible for the production of oxygen in photosynthesis.
Answer:
These plants (C4) show efficient photosynthesis due to the absence of photorespiration.
In this type primary C02 fixation takes place in mesophyll chloroplast and secondary C02 fixation takes place in bundle sheath chloroplast. The latter C02 fixation results carbohydrate (glucose)
They shows special type of leaf anatomy called Kranz anatomy.
OR
Question 3.
As a part of experiment to study the influence of light on carbohydrates synthesis, a potted plant was kept in light for some time and then it was transferred to dark room. (SAY-2010)
a) It was observed that carbohydrate production continued for some time and came to a halt. Suggest reason for this phenomenon.
b) What would happen to carbohydrate production if the same plant is again transferred back to light?
Answer:
a) ATP & NADPH2 are used for synthesis of sugar.
b) Starts the synthesis of carbohydrate.
Question 4.
Calvin, Benson and others found that during photosynthesis the first stable product in sugar formation is 3- phosphoglyceric acid, while Hatch and slack showed that it is oxaloacetic acid. Comment on these contradicting observation. (SAY-2010)
Answer:
Calvin and others – 3 PGA is the first stable compound in 3 plants
Hatch & slack – OAA is the first stable compound in C4 plants.
Question 5.
Given below are the scientific terms related to photosynthesis. Classify them in appropriate manner in the given table. (SAY-2010)
RUBISCO, Rice plant , C02, Maize plant, Oxalo acetic acid, 3 -PGA,PEP case.
Answer:
| SI. No. | C3 plant | C4 plant |
| 1. . | RUBISCO | RUBISCO/ PEP case |
| 2. | C02 | C02 |
| 3. | 3 – PGA | Oxaloacetic acid (OAA) |
| 4. | Rice plant | Maize plant |
Question 6.
Calvin and his co-worksers worked out the whole pathway of C02 fixation and showed that the pathway is operated in a cyclic manner (MARCH-2011)
a) Draw this cycle using the given terms in the correct order. 3 phosphoglycerate, Regeneration,Carboxylation, Triose phosphate, Reduction, Ribulose, 1,5 biphosphate, C02, Sucrose.
b) Write the name of the primary Co2 acceptor in the Calvin cycle.
c) Write the number of carbon atoms in the first C02 fixation product in the Calvin cycle.
OR
Pigments in plants are organized into two photo-chemical light harvesting complexes.
a) Name the reaction center of PS-1 and write its absorption peak.
b) Name the reaction center of PS-11 amd wrote ots absorption peak.
c) Explain noncyclic photophosphorylation giving reasons for the naming of the phenomenon, with the help of a diagram
Answer:
a)
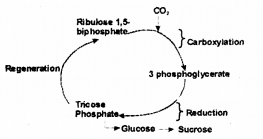
b) RUBP (Ribulose Biphosphate)
c) 3-phosphoglycerate (3 carbon)
OR
a) P700 – Peak is 700nm
b) P680 – Peak is 680nm
c)
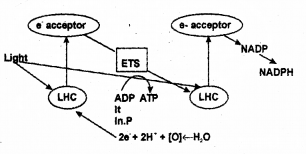
The schematic representation showing z-scheme.
Question 7.
During photosynthetic C02 fixation certain plants, produce PGA as first stable product. Name such plants. Who reported the pathway? What is the enzyme for carboxylation? Name the molecule which accepts C02 in such plants. (SAY-2011)
Answer:
C3 plant, Melvin Calvin, RUBISCO, RUBP
Question 8.
Given diagram is the chemiosmotic hypothesis of ATP formation during light reaction. Complete the numbered places. (SAY-2011)
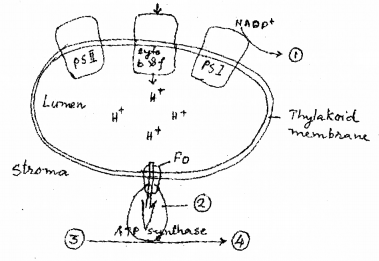
Answer:
1) NADPH
2) F1
3) ADP
4) ATP
Question 9.
An anatomist observed a peculiar type of large spherical bundle sheath cells in sugarcane leaf and a physiologist identified the presence of PEP carboxylase in that leaf mesophyll. (MARCH-2012)
a) Name the peculiar leaf anatomy.
b) Explain the physiological advantages of such type of plants.
Answer:
a) Kranz anatomy
b) 1. Tolerate high temperature.
2. Response to high light intensities.
3. Photorespiration does not occure
4. Greater productivity and yield
Question 10.
Photorespiration is a curse to plants’. (MARCH-2012)
a) Evaluate this statement.
b) Find the reason for this event to take place.
Answer:
a) In photo respiration neither synthesis of sugar nor ATP takes place. But release of Co2 with the utilization of ATP occurs. Photosynthetically fixed carbon is lost, no synthesis of ATP or NADPH. It is a wasteful process.
b) In C3 plants, Oxygen bind to RuBisco and hence Co2 fixation is decreased. Here, Kranz anatomy is noy present
Question 11.
Light reaction and dark reaction are the two stages of photosynthesis. (SAY-2012)
a) Where does light reaction occurs?
b) What are its end products?
c) Comment on their roles in dark reaction.
Answer:
a) Thylakoid or Grana
b) NADPH2, ATP & 02
c) NADPH2 – used in reduction of 3 PGA or conversion of Co2 to sugar or glucose or food.
Question 12.
C4 plants are adapted to overcome a wasteful process found in C3 plants and hence productivity and yields are better in these plants. (MARCH-2013)
a) Name the wasteful process found in C3 plants.
b) Identify the cells involved in the C4 pathway.
c) Write any two differences between C4 plants and C4 plants.
Answer:
pa) photorespiration
b) Mesophyll and bundle sheath chloroplast
c) In C3 plants the primary C02 acceptor is RUBP and the first stable product formed is 3PGA
In C4 plants the primary C02 acceptor is PEP and the first stable product formed is OAA
Question 13.
Light reaction is otherwise called photophosphorylation. (MARCH-2013)
a) Justify the statement.
b) Locate the site of this reaction.
c) Write any two differences between cyclic photophosphorylation and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer:
a) It is the addition of inorganic phosphate with ADP and forms ATP in the presence of light
b) It occurs in the grana of chloroplast
c) In cyclic photophosphorylation PSI is functional and electron flow is cyclic but in non-cyclic photophosphorylation PSI and PSII are functional and electron flow is in noncyclic manner.
Question 14.
Chlorophyll contain a metallic element. (SAY-2013)
a) Name the metallic element.
b) Mention any one deficiency symptom of that element.
Answer:
a) Magnesium
b)Chlorosis
Question 15.
Light reaction of photosynthensis is divided into two processes. In one process the electrons emitted will return to the place from where it is emitted. (SAY-2013)
a) What are the names of these two processes?
b) What happens to the electrons in the second phase?
c) Explain it with schematic representation.
Answer:
a) cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation
b) Electrons starts from a point but never return back. Hence such transport is non cyclic.
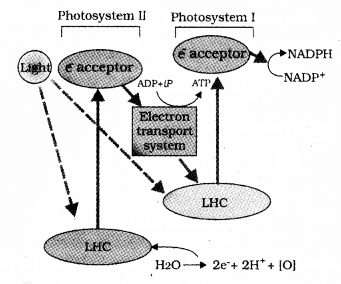
The Z-scheme associated with photolysis of water release electrons and protons. Electrons reaches PS II and it is emitted from PS II. Then electrons accepted by electron acceptor. Then passes through series of electron acceptors and finally reaches PSI. Electron emitted from PSI and proton coming from water combines with NADP and forms reduced coenzyme NADPH2
Question 16.
Ru Bis Co is an enxyme that catalysis two entirely different processes. (SAY-2013)
a) Which are the processes?
b) In which process chloroplast alone is used as cell organelle?
c) Label the parts A, B, C, D of the given diagram.
Answer:
a) C3 pathway and photorespiration
b) C3 pathway
c)
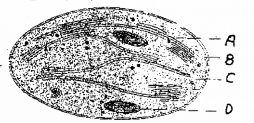
B – Grana
C – Stroma
D – Starch Granul
Question 17.
Plants that are adapted to dry tropical regions have a special type of C02 fixation in addition to the C3 cycle. (MARCH-2014)
a) Name this pathway.
b) Can you identify any speciality in the leaf anatomy of such plants? If so, what is this anatomy called?
c) Which is the primary C02 acceptor in this pathway?
d) Write any one advantage of such plants over C3 plants.
Answer:
a) C4 pathway
b) yes, Kranz anatomy
c) Phospho enol pyruvic acid (PEP)
d) They are photosynthetically efficient than C3 plants
Question 18.
The use of radioactive C14 by Melvin Calvin in algal photosynthesis studies led to the discovery of C02 fixation in greenplants. (MARCH-2014)
a) Identify the first stable product in this C02 fixation cycle.
b) Which are the three main stages of this cycle?
c) Name the enzyme which catalyzes the first stage of this cycle.
d) Work out how many ATP and NADPH molecules will be required to make one molecule of glucose.
Answer:
a) 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
b) Carboxylation, Reduction and Regeneration of RUBP
c) RUBISCO
d) 12NADPH2,18ATPs
Question 19.
C4 cycle is so called because of the presence of a C4 acid. (SAY-2014)
a) Name the C4 acid
b) Name the leaf anatomy present in C4 plants.
Answer:
a) Oxalo acetic acid
b) Kranz anatomy
Question 20.
The light reaction of photosynthesis is divided into two reactions. They are cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation. Mention any three differences between cyclic and noncyclic reactions (SAY-2014)
Answer:
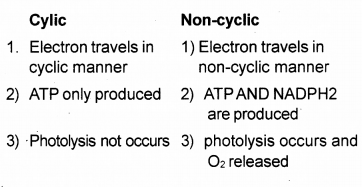
Question 21.
There is a clear division of labour within the chloroplast. Substantiate the given statement with an explanation stating two points. (MARCH-2015)
OR
Photosynthesis can be considered as the most significant physicochemical process on earth. Evaluate this statement citing any two significances.
Answer:
In grana ATP and NADPH2 are produced.
In stroma dark reaction leads to carbohydrate formation
OR
Photsynthesis helps in the preparation of food Light energy is converted into chemical energy and stored in carbohydrate molecules
Question 22.
C4 plants have special features. List out any four specialities of C4 plants compared to C3 plants. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
- C4 plants
- Plants can tolerate high temperature
- They lack photorespiration
- They shows specialised leaf anatomy/ Kranz anatomy
- Greater productivity of biomass / yield
Question 23.
Write any four peculiarities of ‘Z scheme’ electron transport in light reaction. (SAY-2015)
Answer:
a) splitting of water occurs
b) ATP &NADPH2 are produced
c) two photosystems are involved
d) 02 evolution takesplace
Question 24.
The reaction center of photosystems in green plants during light reaction is (MARCH-2016)
a) Xanthophyll
b) Carotenoids
c) Chlorophyll b
d) Chlorophgyll a
Answer:
chlorophyll a
Question 25.
a) Name the special type of leaf anatomy shown by C4 plants. (MARCH-2016)
b) Illustrate the major advantages of C4 plants over C3 plants.
Answer:
a) Kranz anatomy
b) C4 plants are photo synthetically efficient than C3 plants because energy wasteful process photorespiration occur in C3.
C4 plants can tolerate high temperature conditions than C3 plants.
Question 26.
Light reaction involve cyclic and monocyclic electron transport. Classify the features given below under the above stages of light reaction. (SAY-2016)
a) Only pigment system I is involved
b) ATP and NADPH are formed
c) Splitting of water occurs
d) Only ATP is formed
| Cyclic electron transport | Noncyclic electron transport |
Answer:
| Cyclic electron transport | Noncyclic electron transport |
| Only pigment system I is involved Only ATP is formed | Splitting of water occurs ATP & NADH are formed |
Question 27.
Chemiosmosis theory of photosynthesis requires a protein gradient for ATP synthesis to occur. Explain any two events that causes protein gradient. (SAY-2016)
Answer:
- Splitting of water molecules and accumulation of protons within the thylakoid lumen..
- During electron transport, protons are removed from stroma and released into the lumen of thylakoid
Question 28.
An important difference between C3 and C4 plants is photorespiration. Explain how photorespiration occurs in C3 plants. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
- In C3 plants 02 binds with RuBisCO and converted to 2 molecules of PGA and phosphoglycolate .It takes place in high 02 and low C02 concentration.
- In the photorespiratory pathway neither synthesis of sugars nor of ATP. So it is a wastefull process.
Question 29.
Write any four agricultural applications of ethylene. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
- Ripening of fruits, breaks seed and bud dormancy
- It initiates germination in peanut seeds,sprouting of potato tubers
- It promotes rapid internode/petiole elongation in deep water rice plants
- It promotes root growth and root hair formation, helping the plants to increase their absorption surface
- It promote senescence and abscission of leaves flowers, and fruits.
