Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Question 1.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions. Which character of a flower is indicated by the diagram? Give an example for a plant having flowers with this character. (MARCH-2010)
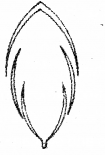
Answer:
Papillionaceous corolla with vexillary aestivation Pea flower of Fabaceae.
It consists of one standard petal, two wing petal and two fused keel petal.
Question 2.
Name the parts of a monocot embryo in the given diagram. (MARCH-2010)
1 …………
2 ………….
3 …………
4 ……………
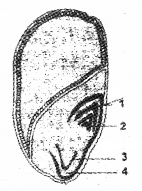
Answer:
1) coleoptile
2) plumule
3) radical
4)coleorhiza
Question 3.
Use the appropriate terms for the following description. (SAY-2010)
a) Axiliary buds of stem modified as slender & spirally coiled structure for helping plants to climb.
b) Axilary buds of stem modified as woody straight and pointed structure to protect plants from browsing animals.
Answer:
a) Tendril
b) Thorns
Question 4.
Given below is the floral diagram drawn by anil based on the floral bud of plant. (SAY-2010)
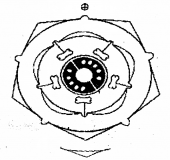
a) Help him to complete the floral formula.
b) Name the family to which this plant belongs.
Answer:
a)
![]()
b) Solanaceae
Potato family / Solanum family
Question 5.
L.S. of two flowers shows two types of ovaries. One is superior and the other is inferior. Name the type of flower based on this. (MARCH-2011)
Answer:
Flowers with superior ovary – Hypogyneous
Flowers with Inferior ovary – Epigyneous
Question 6.
Floral formula of a pea plant is given below: (MARCH-2011)
![]()
Give the important floral characters of the plant using the floral formula.
Answer:
Flowers are bisexual, complete, dichlamydeous, Pentamerous
Caly x – sepals 5, gamosepalous
Corolla – petals 5, polypetalous, papilionaceous
Androecium – stamens 10, diadelphous (9+1)
Gynoecium – Monocarpellary, half inferior (Perigyneous)
Question 7.
Teacher showed the chart of astivation to students and asked them to name the types of aestivation. What is aestivation? Explain any two types of aestivation. (SAY-2011)
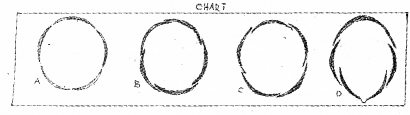
Answer:
The mode of arrangement of sepals or petals in floral bud known as aestivation
Valvate – When sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin, without overlapping bud known as aestivation
Eg- Calotropis.
Twisted – One margin of the appendage overlaps that of the next one and so on.
Eg-china rose, lady’s finger and cotton.
Question 8.
Observe the given relation and fill in the blanks. (MARCH-2012)
Cucumber: Tendril::
Citrus : ……….
Answer:
Thom
Question 9.
Given below is the floral diagram of a family you have studies. (MARCH-2012)
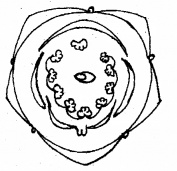
a) Identify the family and aestivation of corolla.
b) Describe three other floral characters from the floral diagram using technical terms.
Answer:
a) Fabaceae – Vexillary aestivation
b) 1) Bisexual, Zygomorphic
2) Sepals – 5 – gamosepalous – valvate
3) Petals – 5 – Polypetalous – Papilionaceous corolla.
4) Vexillary aestivation
5) Stamens -10 – diadelphous
6) Superior ovary – monocarpellary, with marginal placentation
Question 10.
Observe the following diagrams “a and b” and identify the placentation. (SAY-2012)
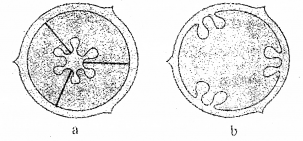
Answer:
a) Axile
b) Parietal
Question 11.
In cactus both leaves and stem are modified to perform different functions. Name the modifications and identify their functions. (SAY-2012)
Answer:
Spine – Protection
Phylloclade or stem modification Photosynthesis
Question 12.
Observe the given relation and fill in the blanks. (MARCH-2013)
Plumule : Coleoptile : :
Radicle : ……………
Answer:
coleorhiza
Question 13.
The diagram given below shows parts of a true fruit. (MARCH-2013)
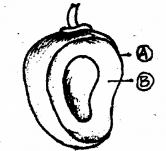
a) Write the technical name of this fruit developed from a monocarpellary superior ovary.
b) Label the parts A and B.
c) Can you distinguish a parthenocarpic fruit from the given fruit?
Answer:
a) drupe
b) A- Epicarp B- Mesocarp
c) The given fruit is a true fruit but parthenocarpic fruit is developed from un fertilized ovary (seedless fruit)
Question 14.
Observe the floral diagram and answer the following questions: (SAY-2013)
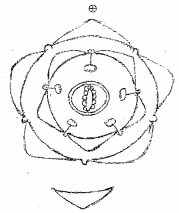
a) Name the family.
b) Write the nature of stamen.
Answer:
a) Solanaceae
b) Epipetalous type
Question 15.
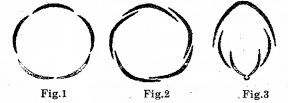
The following figures show two types of aestivation. Answer the following questions: (SAY-2013)
a) Identify the types A and B.
b) How will you distinguish A and B?
Answer:
a) A – Valvate, B – Twisted
b) A-margin of sepal/petal just touch with one another B-margin of sepal/petal overlap the next one & so on.
Question 16.
Normally, roots grow into the soil. But in some plants like Rhizophora, many roots come out of the ground and grow vertically upwards. What are these roots called? Give their function. (MARCH-2014)
Answer:
Breathing roots/respiratory roots/pneumatophores. It is involved in the exchange of gases.
Question 17.
The following diagram represents five petal of a flower in a plant belonging to a major family. (MARCH-2014)
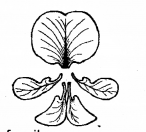
a) Identify the family.
b) Write the floral formula of the flower.
Answer:
![]()
Question 18.
The arrangement of ovules in the ovary is known as placentation. Given below are different types of placentations. (SAY-2014)
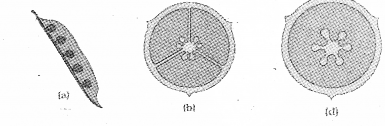
Identify (a), (b), and (c).
Briefly explain a,b,c in one or two sentences.
Answer:
a) a) Marginal placentation
b) axile placentation
c) free central placentation
b) Marginal placentation – Placenta forms the ridge along ventral suture of ovary in which ovules are arranged
Axile placentation – Ovules are arranged in the central axis of multi chambered ovary
Free central placentation – Ovules are arranged in the central axis of single chambered ovary
Question 19.
In most of the plants, roots are meant for absorption and fixation. But there are exceptions to these functions. Justify the statements citing at least three examples. (MARCH-2015)
OR
The main function of most of the stems is spreading out branches, bearing leaves, flowers and fruits and the conduction of materials.
But there are exceptions to this. Justify the statement citing at least three examples.
Answer:
In some plants adventitious roots are modified for special functions
1) Prop root – They hanging from upper part of banyan tree and act as pillar. So they have mechanical supporting function.
2) Stilt root – It arise from the basal nodal portions of the main stem of sugar cane and maize, responsible for mechanical support.
3) Respiratory root- It is otherwise called pneumatophore or breathing root responsible for exchange of gases .
OR
In some plants stem is modified for special functions they are
1) Climbing – In watermelon, cucumber and pumkin etc axillary bud is modified into tendril for climbing
2) Protection – In citrus and bougainvillea axillary bud is modified into thorns for protection from grazing animals
3) Food storage – In ginger, colocasia etc. Underground stem is modified for food storage.
Question 20.
Four stem modifications are given below. Three of them are underground stem modifications. Pick the odd one out as your answer. (SAY-2015)
(Potato, Opuntia, Ginger, Colocasia)
Answer:
opuntia
Question 21.
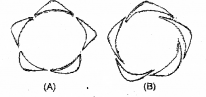
Write the names of aestivations in figures 1,2 and 3. Identify aestivation of petals in pea flowers from the above three aestivations.
Answer:
a- valavate, b-imbricate c-vexillary
Pea flowers petals in vexillary aestivation
Question 22.
Observe the given floral diagram (MARCH-2016)
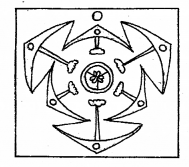
Write any four floral characters of the identified family.
Answer:
a) Lilliacea
b) tepal six (3+3), often united into tube; valvate aestivation, stamen six, (3+3), tricarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, trilocularwith many ovules; axile placentation.
Question 23.
By examining the four match pairs given below, find the correct matched pair from the alternatives given below. (SAY-2016)
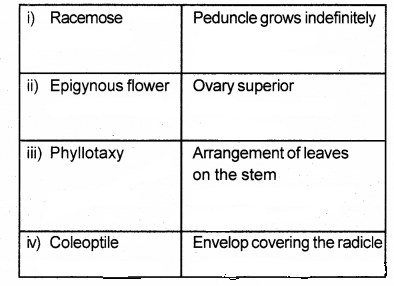
a) (i) and (ii)
b) (ii) and (iv)
c) (ii) and (iii)
d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
d) i) Racemose-peduncle grows indefinitely
iii) Phyllotaxy-Arrangement of leaves on stem
Question 24.
Identify the diagram and label the parts shown as (SAY-2016)
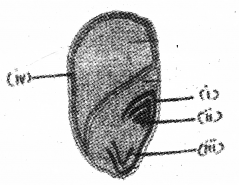
Answer:
i) Coleoptile
ii) Plumule
iii) Radicle
iv) Aleurone layer
Question 26.
a) The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is called …………. (MARCH-2017)
i) Aestivation
ii) Phyllotaxy
iii) Placentation
iv) Inflorescence
b) How can you differentiate an actinomorphic flower from a zygomorphic flower?
a) iv) inflorescence
Answer:
b) Actinomorphic: Flower can be divided into two equal halves in any radial plane passing through the centre
eg – china rose.
Zygomorphic: Flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane
eg – pea
