Kerala Plus One Accountancy Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 60
General Instructions to Candidates
- There is a ‘cool off time of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time of 2 hrs.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and the only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures, and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from 1 to 9. Each carries 1 score. (9 × 1 = 9)
Question 1.
The statement prepared to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
a) Balance Sheet
b) Trial Balance
c) Profit and Loss Account
d) Journal
Answer:
b) Trial Balance
Question 2.
Pick out the WRONG pair.
a) Land, Building
b) Cash, Stock
c) Debtors, Machinery
d) Copyright, Patent
Answer:
c) Debtors, Machinery
Question 3.
Which one of the following is NOT an element of Computer System?
a) IQ
b) Hardware
c) Software
d) People
Answer:
a) IQ
Question 4.
A bill is ‘noted’ when it is ………….
a) Discounted
b) Honoured
c) Dishonoured
d) Endorsed
Answer:
c) Dishonoured
Question 5.
Which one of the following is NOT a contra transaction in Two Column Cash Book?
a) Cash deposited into bank
b) Opened a new account with bank
c) Cash withdrawn from bank for domestic purpose
d) Cash withdrawn from bank for office use
Answer:
c) Cash withdrawn from bank for domestic purpose
Question 6.
Which term refers to writing off the cost of intangible assets like Patents, Copyright, Trade Marks etc.?
a) Amortization
b) Depletion
c) Obsolescence
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Amortization
Question 7.
Fill in the blank with suitable ‘data’ type on the basis of hint given.
a) EmpName : Text/Text (Varchar)
b) Emp Salary : ………….
Answer:
Emp. salary : Number/Currency
Question 8.
‘While preparing final accounts, outstanding wages is added to the wags account’. Identify the accounting principle related with this statement.
Answer:
Matching Principle
Question 9.
Calculate capital at the beginning.
Closing capital – Rs. 6,00,000/-
Profit for the year – Rs. 40,000/-
Drawings during the year – Rs. 58,000/-
Answer:

Answer any 5 questions from 10 to 15, each carries 2 scores. (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 10.
‘Even though computer posses many capabilities it suffers from number of limitations’. Mention any two limitations.
Answer:
- Computer lacks common sense
- Computer have no intelligence
Question 11.
‘Accounting is a post mortem survey’. Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes. Accounting is a post-mortem survey because it records events as they have taken place.
Question 12.
Identify the following symbols used for constructing ER diagrams.
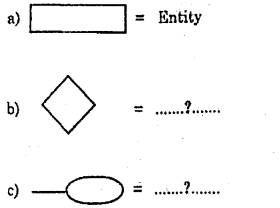
Answer:
b. Relationship
c. Attribute
Question 13.
Write the treatment of return inwards and return out-wards in the financial statements.
Answer:
Return inwards: It is also known as sales return. It is deducted from total sales in the credit side of trading account or debited to trading account.
Return outwards: It is also known as purchase return. It is deducted from total purchases in the debit side of trading account or credited to trading account.
Question 14.
List out any four advantages of computerized accounting system.
Answer:
Advantages of computerized accounting system are as follows:
- Highspeed
- Mass storage
- Real time user interface
- Automated document production
- Quality reports
Question 15.
Complete the following as hint given.
| Transaction | Effect of business |
| a) Purchased good for cash | 1. Increase in assets 2. Decrease in assets |
| b) Bought furniture on credit | 1. ……….. ?……………… 2. ……….. ?……………… |
| c) Bank loan repaid | 1. ……….. ?……………… 2. ……….. ?……………… |
Answer:
| Transaction | Effect of business |
| a) Purchased good for cash | 1. Increase in assets 2. Decrease in assets |
| b) Bought furniture on credit | 1. Increase in asset 2. Increase in liability |
| c) Bank loan repaid | 1. Decrease in assets 2. Decrease in liability |
Answer any two questions from 16 and 18. Each carries three scores. (2 × 3 = 6)
Question 16.
From the following particulars ascertain credit sales.
| Particulars | Rs. |
| Debtors as on 1st April 2017 | 25000 |
| Debtors as on 31st march 2018 | 40000 |
| Cash received from Debtors | 50000 |
| Discount allowed | 7000 |
| Bad debts | 3000 |
Answer:
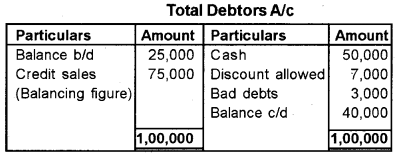
Question 17.
Briefly explain any three components of DBMS.
Answer:
Components of DBMS
a) Tables
b) Queries
c) Forms
d) Reports
e) Pages
f) Macros
Question 18.
Calculate cost of goods sold for the year 2017 with the help of the following information.
| Particulars | Rs. |
| Opening stock | 80,000 |
| Closing stock | 1,30,000 |
| Purchases | 3,75,000 |
| Sales | 6,00,000 |
| Carriage inwards | 7,000 |
| Carriage outwards | 4,000 |
| Wages | 12,000 |
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = (opening stock + net purchases + Direct expense) – Closing stock
= (80,000 + 3,75,000 + 12,000 + 7,000) – 1,30,000
= 4,74,000 – 1,30,000
Cost of goods sold = 3,44,000
Answer any three questions from 19 and 22, each carries four scores. (3 × 4 = 12)
Question 19.
Akhil has the following transactions.
a) Started business with cash Rs. 5,00,000.
b) Purchased goods on credit Rs. 40,000.
c) Sold goods costing Rs. 27,000 on credit for Rs. 30,000.
d) Bank loan received Rs. 80,000.
Prove the accounting equation. (A = L + C)
Answer:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
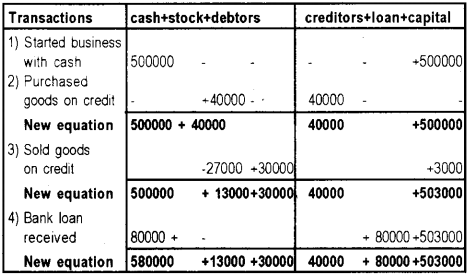
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
6,23,000 = 1,20,000 + 5,03,000
Question 20.
Rectify the following errors.
a) Purchase day book overcast by Rs. 500.
b) Salary paid to Mr.Kumar is debited to his personal account Rs. 26,000.
c) Purchase of goods from Geetha Rs. 2,500 is omitted to record in day book.
d) Sale of office furniture for Rs. 4,000 posted to sales account.
Answer:

Question 21.
On 1st May 2017, Krishna sold goods to Kripa for Rs. 20,000 and drew a bill of exchange for 3 months. Kripa accepted the bill. On 1st June 2017 Krishna discounted the bill with her bank for Rs. 19,500. But on the date of maturity of the bill, Kripa was unable to make the payment. Pass the journal entries in the book of Krishna.
Answer:
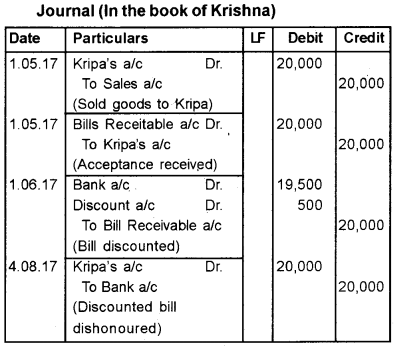
Question 22.
A company purchased a machinery for Rs. 50,000 on 30th June 2015. Depreciation is charged @ 10% under straight line method and accounts closed on 31st December every year.
a) Show the Machinery account upto 31st December 2016.
b) Distinguish between straight line method and written down the value method. Write two points.
Answer:
a)
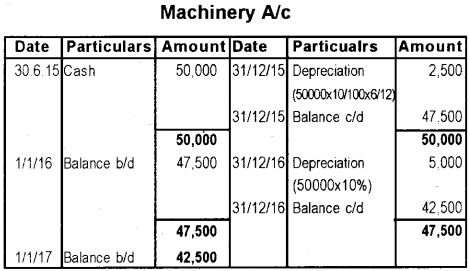
b. i) Under straight line methods, amount of depreciation is same every year but in the case of written down value method, amount goes on reducing year after year.
ii) Under straight line method, depreciation is calculated on original cost. But in written down value method, depreciation is calculated on reducing balance of asset.
Answer question numbers 23, 24 and 25. Each carries five scores. (3 × 5 = 15)
Question 23.
A portion of Trial Balance on 31st December 2016 is as follows:
Sundry debtors – Rs. 62,000
Bad debts – Rs. 4,000
Additional information:
a) Further Bad debts to be written off Rs. 2,000.
b) Create provision for bad debts @5% on debtors.
Give journal entries and show how this items will appear in the final statements of the business.
Answer:
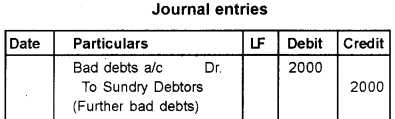
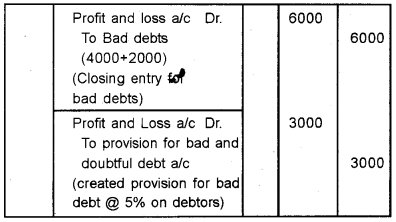
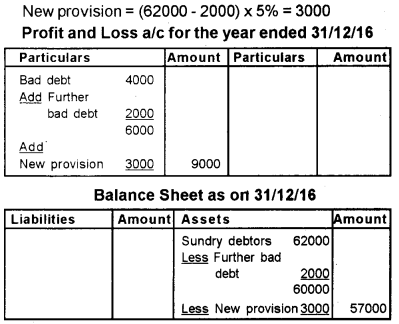
Question 24.
From the following particulars, prepare an analytical petty cash book for the month of November 2018, under the imprest system.
| 2018 November | Rs. | |
| 1 | Balance in hand | 87 |
| 1 | Cheque received from main cashier | 413 |
| 3 | Stamp purchased | 60 |
| 6 | Stationery | 44 |
Answer:
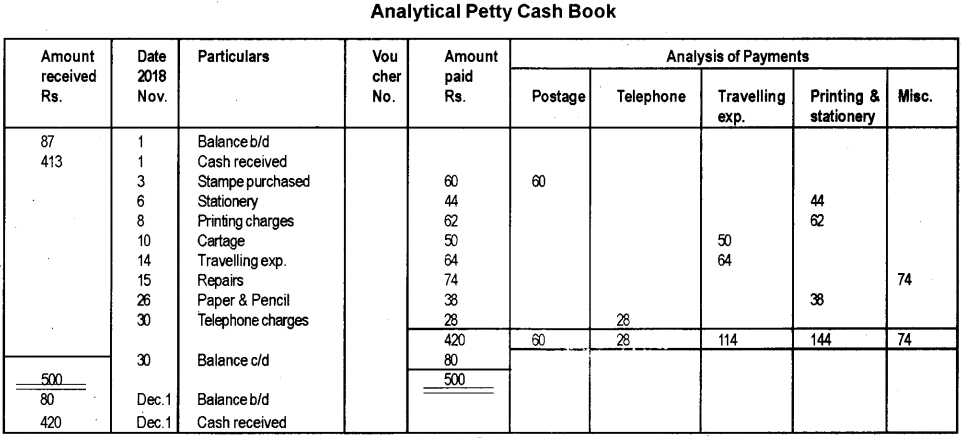
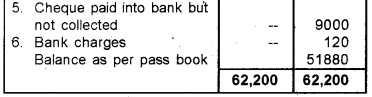
Question 25.
On March 31st 2017 the cash book of Mr. Sreejith, a trader showed a deposit balance of Rs. 48,400. His passbook as on that date was Rs. 51,880. On comparing the cashbook with the passbook, the following differences were observed.
a) Direct payment by three customer to the bank amounted Rs. 7,800
b) Insurance premium paid by bank Rs. 1,200.
c) Bank charges debited in passbook Rs. 120
d) Cheque issued to a customer but not presented for payment Rs. 6,000.
e) Four cheques paid into bank for collection but not collected amounted to Rs. 9,000.
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation statement as on 31st March 2017.
Answer:
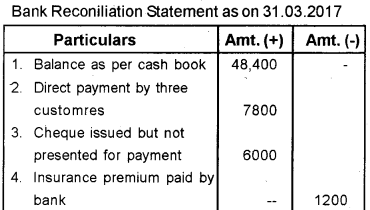
Answer any one question from 26 to 27, which carries eight scores. ( 1 × 8 = 8)
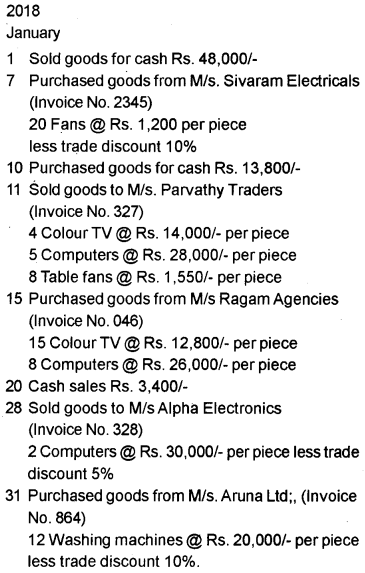
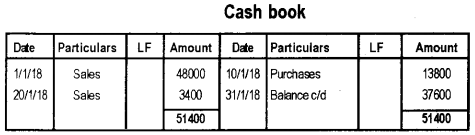
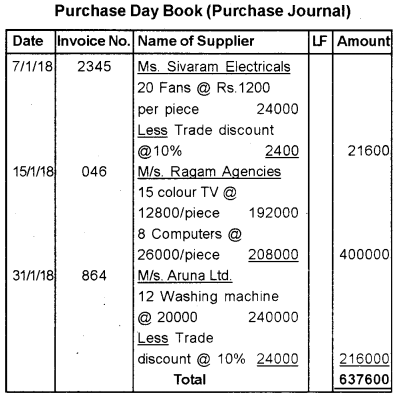
Question 26.
Consider the following transactions and record them into appropriate special journals for the month of January 2018.
Answer:
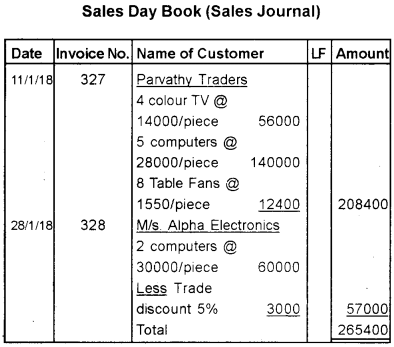
Question 27.
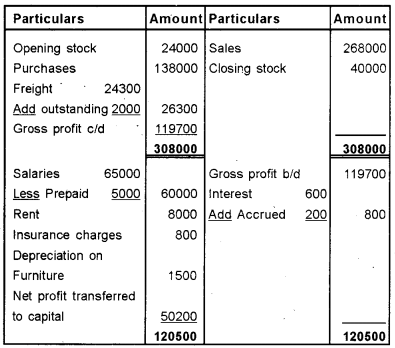
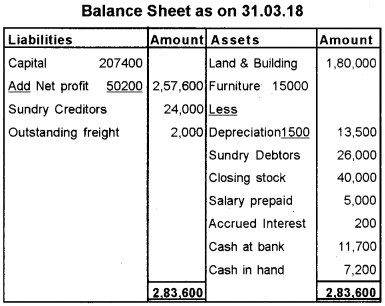
Following is the Trial Balance of Mr. Ajayan as on 31st March 2018.
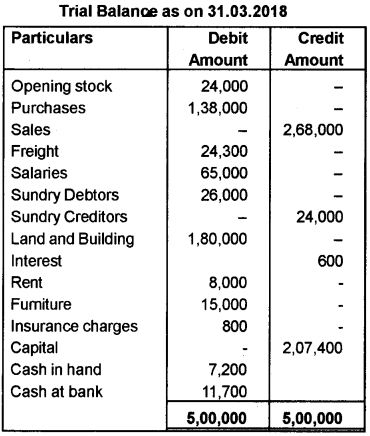
Additional Information:
a) Closing stock was valued at Rs. 40,000/-
b) Freight outstanding Rs. 2,000/-
C) Salaries prepaid Rs. 5,000/-
d) Depreciate furniture by 10%.
e) Internet accrued Rs. 200/-
Prepare Trading, Profit and Loss account for the year ending 31.03.2018 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c for the year ended 31/3/18