Kerala Plus One Accountancy Notes Chapter 7 Bill of Exchange
Summary:
Bill of Exchange:
A bill of exchange is an acknowledgment of debt given by one person to another, incorporating all the terms and conditions of payment.
Features and advantages of a bill:
A bill is a written unconditional order, it is signed by the creditor and accepted by the debtor, the amount of the bill is payable either on-demand or at a fixed period.
Parties to a bill of Exchange:
There are three parties, ie., drawer, drawee and payee.
Promissory Note:
A promissory note is an undertaking in writting given by the debtor to the creditor to pay the latter a certain sum of money in accordance with the conditions stated therein. There are two parties to a promissory note, the promissor and the promisee.
Maturity of Bill:
The term maturity refers to the date on which a bill or promissory note becomes due for payment. In arriving at the maturity date three days known as “days of grace” must be added to the date on which the period of credit expires instrument is payable.
Endorsement:
An endorsement is a written order on the back of the instrument by the payee or the holder for transferring his right to another person.
Accounting treatment:
A bill can be treated in the following four ways by its receiver.
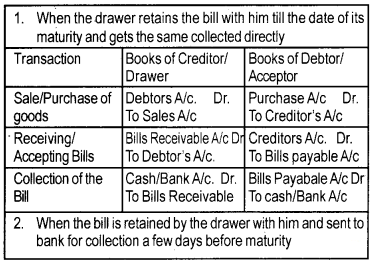
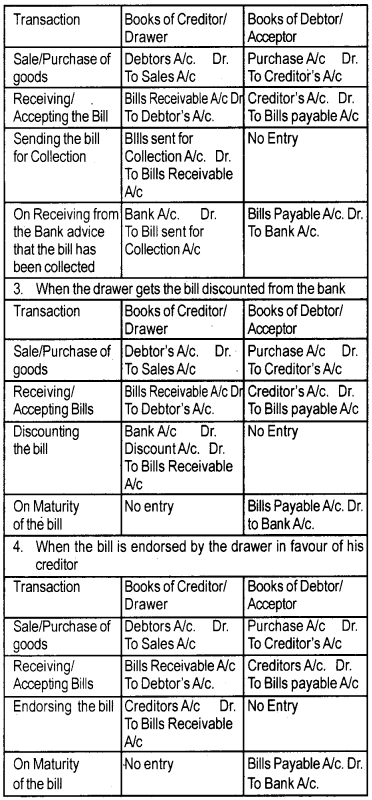
Dishonour of a bill:
A bill is said to have been dishonoured when the drawee fails to make the payment on the date of maturity. In this situation, liability of the acceptor is restored. Therefore, the entries made on the receipt of the bill should be reserved. The entries of dishonour of bill as follows
(i) When the bill was kept by drawer till maturity.
![]()

Noting Charges:
When a bill is dishonoured due to non-payment, it is usual to get it ‘noted’, to establish the matter of dishonour. The noting is done by “Notary Public.” Noting authenticates the fact of dishonour. For providing this service, a fees is charged by the Notary Public which is called Noting Charges. The following facts are generally noted by the Notary;
- Date, fact and reasons of dishonour;
- If the bill is not expressly dishonoured, the reasons why he treats it as dishonoured and;
- The amount of noting charges.
The entries recorded for noting charges in the drawers book are as follows:
When Drawer himself pays:
![]()
Where endorsee pays:
![]()
When the bank pays on discounted bill:
![]()
When the bank pays in the event of sending the bill for collection to the bank:
![]()
The entry recorded for noting charges in the book of drawee as follows:
For recording noting charges the drawee opens “Noting ChargesAccount”.
![]()
Renewal of the bill:
Sometimes the acceptor of the bill foresees that it may be difficult to meet the obligation of the bill on maturity and may, therefore approach the drawer with the request for extension of time for payment.
If it is so, the old bill is cancelled and . the fresh bill with new terms of payment is drawn and duly accepted and delivered. This is called renewal of the bill. The drawee may have to pay interest to the drawer for the extended period of credit.
Following journal entries are recorded in the case of renewal of the bill.
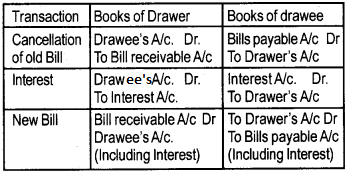
Retiring of the Bill:
Making payment of the bill of exchange before the due date is called retiring of the bill. To encourage the retirement of the bill, the holder allows some discount called “Rebate on bill” for the period between date of retirement and maturity. The rebate is calculated at a certain rate of interest.
The following journal entries are recorded:
(i) In the book of drawer:
On retiring the acceptance, rebate allowed.

(ii) In the book of drawee:

