Kerala Plus One Accountancy Model Question Paper 1 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 60
General Instructions to Candidates
- There is a ‘cool off time of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time of 2 hrs.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and the only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures, and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from question numbers 1 – 5 which carries score 1 each. (5 × 1 = 5)
Question 1.
Rajeev received an order for 100 Churidars of ₹ 250 per Churidar from Krishna Textiles. But the accountant did not record the item in the books. Point out the accounting concept guided the accountant.
Answer:
Revenue Recognition concept
Question 2.
A loan can be treated as a short loan if the period is
a) Two years
b) More than one year
c) Less than one year
d) More than one year
Answer:
c) Less than one year
Question 3.
Sam sold goods worth ₹ 15,000 on 10.03.2016 to Dinesh and drew a bill for two months. Calculate the maturity date if Dinesh accepted it.
Answer:
Maturity date – 13.05.2016
Question 4.
Identify the key attribute from the following:
a) Name of student
b) Admission number
c) Class
d) Date of birth
Answer:
b) Admission number
Question 5.
SQL stands for
a) Structured Question Language
b) Standard Question Language
c) Structured Query Language
d) Standard Query Language
Answer:
c) Structured Query Language
Answer any five questions from 6 – 12. Every question carry 2 scores. (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 6.
Fill the boxes with suitable example.
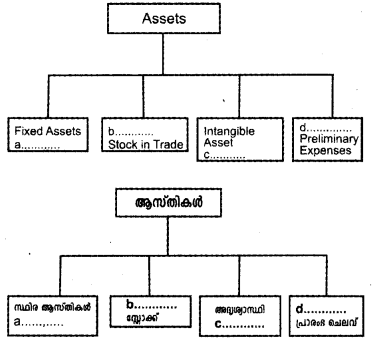
Answer:
a) Land & Building
b) Current Asset
c) Goodwill
d) Fictitious Asset
Question 7.
The following is an error committed in the book of a Car Manufacturing Company
Wages A/c Dr
Cash A/c
(Being wages paid for the construction of Building)
i) Show the rectification entry
ii) Identify the type of error involved
Answer:
i) Building A/c Dr
To wages A/c
ii) Error of principle
Question 8.
Prepare a statement showing the accounting equation on the basis of following transactions.
1) Nihara started business with cash ₹ 5,00,000
2) Purchased goods from Nirmal for ₹ 60,000
3) Paid into Bank ₹ 75,000
4) Sold goods to Abi costing ₹ 80,000 for ₹ 1,00,000
Answer:
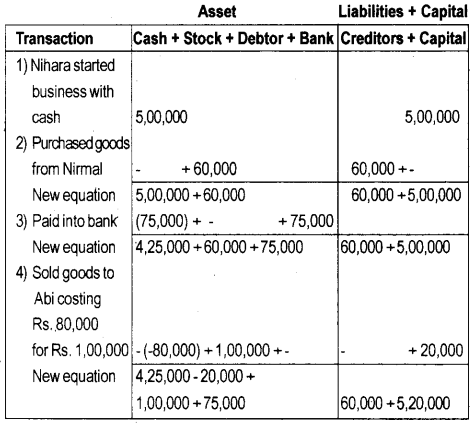
Assets = Liabilities + capital
5,80,000 = 60,000 + 5,20,000
Question 9.
Show the Debit or Credit of the following items.
a) Increase in the value of fixed asset
b) Increase the amount of withdrawals from the business for private affairs
c) Decreasing the value of Debtors
d) Deposting further amount on Investment
Answer:
a) Increase in value of fixed assets – Debit
b) Increase the amount of withdrawals from the business for private affairs – Debit
c) Decreasing the value of debtors – Credit
d) Depositing further amount on investment – Debit
Question 10.
An amount transferred from one account to another account is treated a contra entry. Write two more examples for contra entry.
Answer:
- Cash deposited into bank
- Withdrew from Bank for office use.
Question 11.
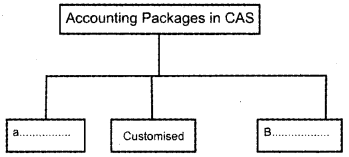
Answer:
a) Ready to use accounting software
b) Tailored software
Question 12.
Briefly explain the following terms:
a) Single Entry
b) Accrual System
Answer:
a) Single Entry:
Accounting records, which are not strictly kept according to double entry system, are known as single entry system or incomplete records.
b) Accrual System:
Under this system, all items of income and expenditure both cash item as well as non-cash items are taken into account. In this system, revenue and costs are recognised in the period in which they occur rather than when they are paid.
Answer any five questions from 13 – 18. Every question carry 3 scores. (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 13.
From the following Transactions of M/s Sujith and Sons for the month of April 2017. Prepare Purchase Day Book.
April 5 2017 Purchased credit from M/s Rahul Mills.
100 pieces of long cloths @ ₹ 90/piece
50 pieces of shirting @ ₹ 150/piece
April 8 2017 Purchased for cash from M/s Niranjan Mills.
50 pieces of suitings @ ₹ 180/piece
April 15 2017 Purchased goods on credit from Sunil Mills.
20 pieces of coatings @ ₹ 1,200/piece
10 pieces of shirtings @ ₹ 150/piece
April 20 2017 Purchased credit from Laneesh Traders
60 Typewriter @ ₹ 500/each
Answer:
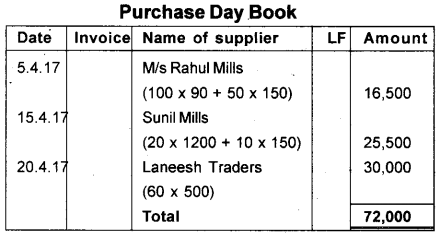
Question 14.
Identify the type of errors on the basis of the following narrations:


Answer:
i) Error of principle
ii) Error of commission
iii) Error of commission
Question 15.
Find out the profit of the business from the given information:
| Capital at the beginning of the year | ₹ 6,50,000 |
| Capital at the end of the year | ₹ 5,00,000 |
| Drawings made during the year | ₹ 2,75,000 |
| Additional Capital introduced | ₹ 50,000 |
Answer:
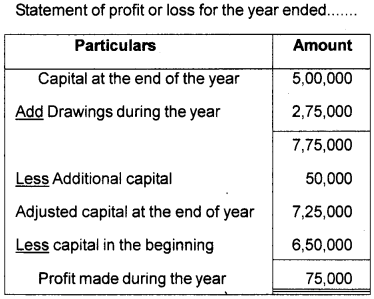
Question 16.
List out three distinctive advantages of computerised accounting over manual accounting.
Answer:
Distinctive advantages of computerised accounting over manual accounting are as follows:
- In manual accounting the recording of financial transactions is through books of original entries. But in the case of computerised accounting, transaction is stored in a well-designed accounting database.
- In computerised accounting data can be easily processed and statement can be prepared with high speed and accuracy. But in manual accounting financial statement cannot be prepared with high speed and accuracy.
- Coding is essential in computerised accounting. It is not essential in manual accounting.
Question 17.
What is Query in computerised accounting?
Answer:
A query is request for data or information from a database table or combination of tables. This data may be generated as results returned by Structured Query Language (SQL) or as pictorials graphs or complex results.
Query language (SQL) allows the user to retrieve report relevant information that is capable of being laid out in pre-designed accounting report.
Question 18.
Balance Sheet differs from statement of affairs. Write three points to support the above statement.
Answer:
Difference between Statement of Affairs and Balance sheet
| Statement of Affairs | Balance Sheet |
| 1. It is prepared on the basis of information from incomplete records | 1. It is prepared purely on the basis of ledger accounts |
| 2. It is prepared to find out capital | 2. It is prepared to show the financial position of the concern |
| 3. Omission of assets or liabilities cannot be discovered easily | 3. Omissions of assets or liabilities can be discovered easily and can be traced from accounting records |
Answer any three questions from 19 – 22. Every question carry 4 scores. (3 × 4 = 12)
Question 19.
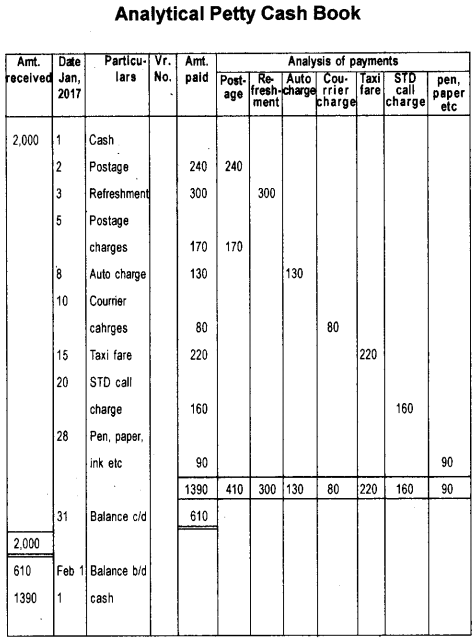
Gopal cashier of Star Traders advanced ₹ 2,000 as imprest amount to Remesh on 1.1.2017 the petty cashier of the firm. Could you help Remesh to record the following items?
| ₹ | |
| 2.1.2017 Postage | 240 |
| 3.1.2017 Refreshments | 300 |
| 5.1.2017 Postage charges | 170 |
| 8.1.2017 Auto charges | 130 |
| 10.1.2017 Courier charges | 80 |
| 15.1.2017 Taxi fare | 220 |
| 20.1.2017 STD Call charge | 160 |
| 28.1.2017 Pen, Paper, Ink etc. | 90 |
Answer:
Question 20.
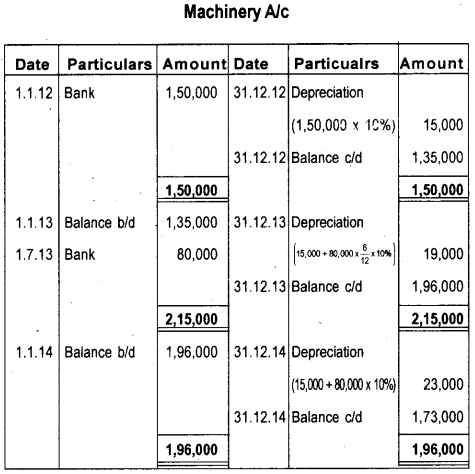
Soorya Traders purchased a Machinery for ₹ 1,50,000 on 1.1.2012. The further purchased machinery on 1.7.2013 for ₹ 80,000. Prepare Machinery Account for three years considering that the firm writes-off depreciation at the rate of 10% on original cost every year.
Answer:
Question 21.
Hari in a discussion agrees that financial statements are the most reliable accounting report to exhibits the profitability of the firm. Do you agree? Why?
Answer:
Yes, The financial statement are the most reliable accounting report to exhibits the profitability of the firm. The following are the main advantages of financial statements:
- It depicts a true and fair view of the financial performance of the business.
- It is relevant to the objective of the organisation.
- It should be prepaid promptly on time.
- All material information should be disclosed in the statement.
Question 22.
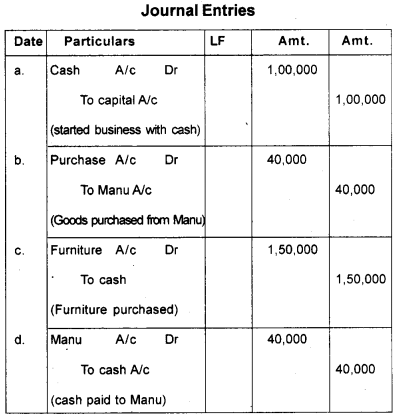
Write journal entries for the following transactions:
a) Business started with cash ₹ 1,00,000
b) Purchased goods from Manu ₹ 40,000
c) Purchased furniture ₹ 1,50,000.
d) Paid cash to Manu in full settlement.
Answer:
Answer any two questions from 23 – 25. Every question carries 5 scores. (2 × 5 = 10)
Question 23.
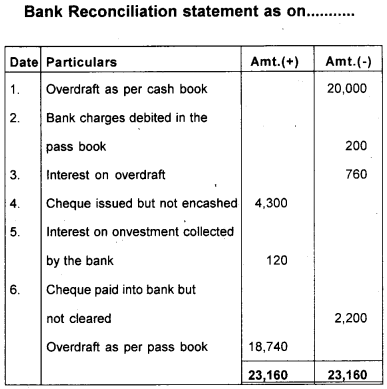
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement.
1) Overdraft shown as per cash book 31.12.2017 ₹ 20,000.
2) Bank charges debited in the passbook ₹ 200.
3) Interest on overdraft ₹ 760.
4) Cheque issued but not encashed ₹ 4,300.
5) Interest on Investment collected by the bank and credited in the passbook ₹ 120.
6) Cheque paid into bank but not cleared before 31.12.2017 ₹ 2,200.
Answer:
Question 24.
Sojan sold goods for ₹ 50,000 to Sreejith on 1.4.2017. Sojan drew a bill of exchange upon Sreejith for the same amount for three months. Sreejith accepted the bill and returned it to Sojan. Sojan endorsed the bill to George. The bill is dishonored on the due date. Show the journal entries in the books of Sojan.
Answer:
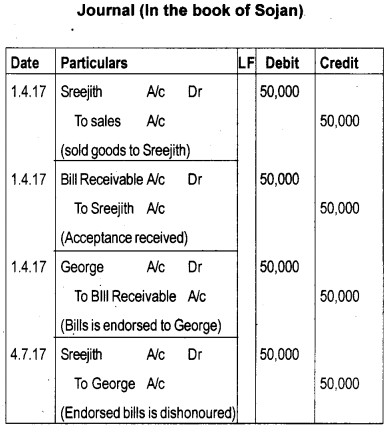
Question 25.
List out five situations which leads discrepancies in passbook balance and cash book balance.
Answer:
The difference between the cash book balance and the passbook balance is caused by the following reasons:
- Cheques issued by the bank but not yet presented for payment.
- Cheques paid into the bank but not yet collected.
- Direct payment made by a customer to the bank.
- Direct payment made by the bank on behalf of the customer.
- Interest and dividends collected by the bank on behalf of the customer.
Answer the following questions which carry 8 scores. (1 × 8 = 8)
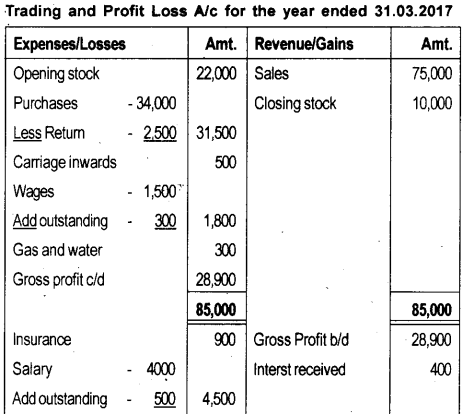
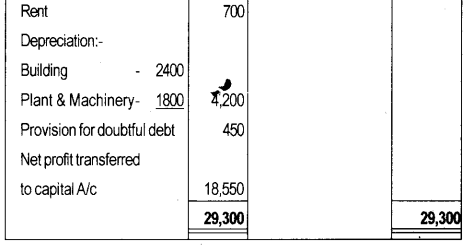
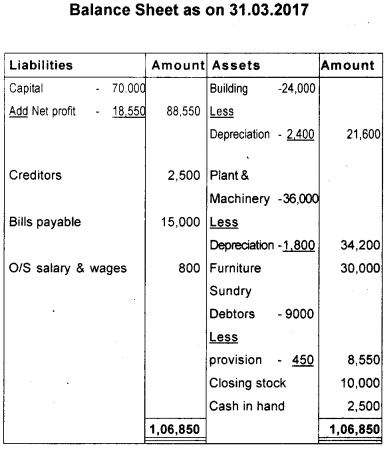
Question 26.
The following balances are extracted from the Trial Balance of R.K. Bros. Prepare Trading and Profit and Loss A/c on the year ending 31st March 2017.
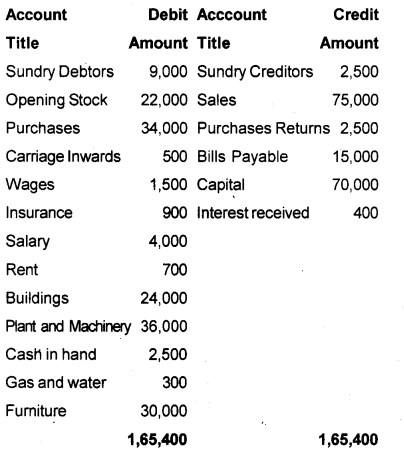
1) Closing Stock ₹ 10,000.
2) Provide 5% provision on doubtful debts.
3) Wages ₹ 300 and salary ₹ 500 are outstanding.
4) Depreciation on plant and Machinery 5%, Building @10%.
Answer: