Kerala Plus One Accountancy Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Bill of Exchange
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The Maker of the bill of exchange is called the ……….
(a) Drawer
(b) Drawee
(c) Payee
Answer:
(a) Drawer.
Question 2.
Bill of exchange before its acceptance is called is ……………
(a) Bill
(b) Promissory Note
(c) Draft
Answer:
(c) Draft.
Question 3.
When a discounted bill is dishonoured, the ………… account is credited in the books of the drawer,
(a) Bank
(b) Drawee
(c) Payee
Answer:
(a) Bank
Question 4.
A bill is noted when it is
(a) Dishonoured
(b) Honoured
(c) Discounted
(d) Accepted
Answer:
(a) Dishonoured
Question 5.
The process of transferring the ownership of the bill is called
(a) Acceptance
(b) Negotiation
(c) Endorsement
Answer:
(c) Endorsement
Question 6.
The credit instrument which contains a promise made by the debtor to pay a certain sum of money for value received is
(a) Bill of Exchange
(b) Debenture
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Equity Share
Answer:
(c) Promissory Note
Question 7.
A bill of exchange is an Instrument.
Answer:
Negotiable
Question 8.
………………. days of grace are allowed in case of time bills for calculating the date of maturity.
Answer:
Three
Question 9.
If the date of maturity of a bill is on a holiday then the bill will mature on ………….. day.
Answer:
The Previous day
Question 10.
When noting charges are paid finally the amount will
be recovered from
Answer:
Drawee.
Question 11.
Complete the following on the basis of hints given
- Dishonour of discounted bill – An entry in the book of drawer.
- ………………………………………………. – No entry in the book of drawer.
Answer:
Honouring of discounted bill.
- Noting charges incurred – When bill is dishonoured.
- Rebate is allowed – …………………….
Answer:
When bill is honoured before due date.
Question 12.
Bill of exchange in Indian languages is called
Answer:
Hundi.
Question 13.
The person to whom the amount mentioned in the promissory note is payable is known as ………………..
Answer:
Promisee.
Question 14.
A person who endorse the promissory note in favour of another is known as ………………..
Answer:
Endorser
Question 15.
In a promissory note, the person who makes the promise to pay is called ……………………
Answer:
Promissor.
Question 16.
Bill of exchange is drawn on the ………….
Answer:
Debtor/Drawee.
Question 17.
The person to whom payment of the bill is to be made is known as ……………….
Answer:
Payee
Question 18.
A promissory note does not require ………..
Answer:
Acceptance.
Question 19.
Making payment of the bill of exchange before the due date is called …………..
Answer:
Retiring of the bill
Question 20.
A bill of exchange accepted without consideration, just to oblige a friend is known as
Answer:
Accommodation Bill
Question 21.
If the proceeds of the bill of exchange is to be paid after a particular period is called …………
Answer:
Time Bill.
Question 22.
Find the odd one and state the reasons.
- Bill of exchange, cheque, promissory note, fixed deposit receipt.
- Drawer, Drawee, Payee, Endorser.
Answer:
- Fixed Deposit Receipt – Others are negotiable instruments
- Drawee – Others may be the same person
Question 23.
On the date of maturity, Arun (acceptor) requested to Santhosh (drawer) to cancel the old bill and draw a new bill upon him for a period of 2 months. Santhosh agrees to this. It is a case of ………………
Answer:
Renewal of bill
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A bill of exchange must contain “an unconditional promise to pay.” Do you agree with a statement?
Answer:
No. The bill of exchange contains an unconditional order to pay a certain amount on an agreed date.
Question 2.
Define Bill of exchange.
Answer:
According to the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 a bill of exchange is “an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of a certain person, or to the bearer of the instrument.”
Question 3.
What are the features of bill of exchange?
Answer:
Following are the essential features of a bill of exchange.
- It must be in writing.
- It must be an order to pay, and not a request to pay.
- No condition should be attached to the order.
- The drawer must sign the bill
- The order must be for the payment of money only.
- It should be properly stamped.
- The amount mentioned in the bill may be made payable either on-demand or after the expiry of a ‘stipulated period.
Question 4.
Who are the parties to a bill of exchange?
Answer:
There are three parties to a bill of exchange:
- Drawer – He is the creditor who draws a bill of exchange upon the debtor.
- Drawee – He is the person upon whom the bill of exchange is drawn. He is the purchaser of the goods on credit and the debtor.
- Payee – He is the person to whom payment of the bill is to be made on the maturity date. The drawer and the payee can be one party when payment is to be made to the drawer.
Question 5.
What are days of grace?
Answer:
Three extra days over the nominal due date legally given to the acceptor of a bill to make payment are called days of grace. Days of grace are allowed only in the case of time bills.
Question 6.
Calculate the maturity date of the following bill.
- Drawn on January 5th for three months.
- Drawn on May 1st for 4 months.
Answer:
1.
- January 5th to February 5th
- February 5th to March 5th
- March 5th to April 5th
- April 5th + 3 days of grace = April 8th
2.
- May 1st – June 1st
- June 1st – July 1st
- July 1st – August 1st
- August 1st – September 1st
- September 1st + 3 days of grace = September 4th
Question 7.
What do you mean by Endorsement?
Answer:
An endorsement is a written order on the back of the instrument by the payee or the holder, for transferring his right to another person. The person who makes the endorsement is called endorser and in whose favour the endorsement is made is called the endorsee.
Question 8.
What is an Accommodation Bill?
Answer:
A bill of exchange and Promissory note may be used for raising funds temporarily. Such a bill is called an ‘accommodation bill’ as it is accepted by the drawee to accommodate the drawer. These are drawn and accepted without consideration with a view to provide funds to one or more parties. There is no trade or debtor-creditor pfifationsip between parties. It is also known as ‘kite bill’ or ‘Wind bill’.
Question 9.
Ram received a bill from Anil on 1/7/2009 for 3 months for Rs. 4,000. Later the bill has been endorsed to Kumar. In this statement identify the parties involved in terms of drawer, drawee endorser and payee.
Answer:
- Drawer – Ram
- Drawee – Anil
- Payee – Kumar
- Endorsee – Kumar
Question 10.
Manu purchased goods on credit from Kumar for Rs. 40,0 on 1st April 2009. On the same date Kumar draws a bill for 2 months and got it accepted by Manu. What are the options available to Kumar in dealing with the bill?
Answer:
The following options are available to deal with the bill.
- He can retain the bill till the date of maturity.
- He can get the bill discounted through the bank.
- He can endorse the bill in favour of his creditor.
- He may sent the bill for collection to the bank.
Question 11.
Mr. Mohan holds a bill of exchange. He approaches a bank to receive the amount of bill before the maturity date. Does he get the money? Write your comments,
Answer:
If the drawer of the bill needs cash immediately or before the maturity date he can discount the bill with the bank. Discounting of the bill means encashing the bill with the banker on the security of the bill before the maturity date. The banker will deduct a certain sum from the bill amount as discount and pays the balance to the holder. The bank will present the bill to the drawee on the due date and get the payment of the bill.
Question 12.
Explain the term “Noting”
Answer:
When a bill of exchange is dishonoured due to nonpayment, it is usual to get it ‘noted’, to establish the matter of dishonour legally. The noting is done by the “Notary public”, who is an officer appointed by the Government for this purpose. Noting authenticates the facts of dishonour.
For providing this service, a number of fees is charged which is called “Noting charges” Noting charges either paid by the holder or any other parties should be borne by the acceptor in the absence of any agreement.
Question 13.
What do you mean by ‘Retiring of Bill’?
Answer:
The acceptor can pay the amount of the bill before its due date. The process of paying the amount of the bills payable before the due date is called retiring the bill. In such case, the holder usually allows some discount to the acceptor of bill. Such a discount is called “rebate on retired bill”. The amount of rebate depends on the period that the bill has yet to run.
Question 14.
What do you mean by Renewal of Bills?
Answer:
process of drawing and accepting a new bill by cancelling the old bill is called renewal of a bill. It is a granting of extension of credit to the acceptor. When this is done the acceptor may have to pay interest for the extended period of credit. It is paid in cash or may be included in the amount of the new bill.
Question 15.
On 1.1.2005 Raju sold goods to Anil for Rs. 20,000/ – and draw upon him a bill for 2 months. Anil accepted the bill and returned it to Raju. Later Raju endorsed the bill to Tom. On the date of maturity the bill was dishonoured.
Give advice to Tom, regarding the steps to be undertaken immediately after the dishonour.
Answer:
1. The holder of the bill, Tom should send a notice of dishonour to the drawer, Raju within a reasonable time. Otherwise, the other parties of the bill may deny their liability.
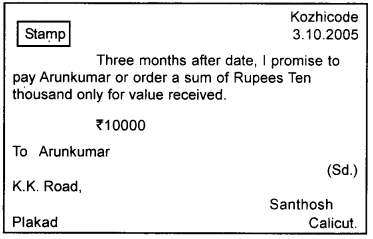
2. When the bill is dishonoured it is better to get the fact noted with a Notary public.
Question 16.
Identify the endorser, endorsee and type of endorsement from the following

Answer:
- Endorser – Santhosh
- Endorsee – Arunkumar
- Type – Conditional Endorsement
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define promissory Note and Point out its Features.
Answer:
According to the Negotiable Instruments Act 1881, a promissory note is “an instrument in writing containing an unconditional undertaking, signed by the maker, to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person, or to the bearer of the instrument.”
The following are the features of the promissory note
- It must be in writing
- It must contain an unconditional promise to pay.
- It must be signed by the maker
- The person to whom payment is to be made must also be certain.
- The amount payable must be certain.
- It should be properly stamped.
Question 2.
Who are the parties to a promissory note:
Answer:
There are two parties to a promissory note.
1. The maker or the promisor:
He is the person who makes or draws the promissory notable is the debtor.
2. The payee or the promisee:
He is a person in whose favour the promissory note is drawn.
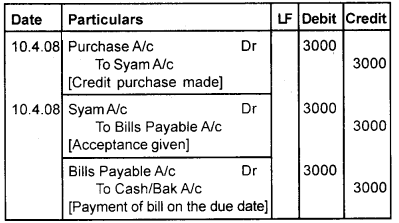
Question 3.
Syam sold goods to Anil on credit for Rs. 3,000, on 10th April 2003. He drew a bill on Anil for the amount at 3 months after date. Anil accepted the same and returned it to syam. At maturity, he met his obligation. Pass journal entries in the books of both parties.
Answer:
Book of Syam (Drawer) Journal
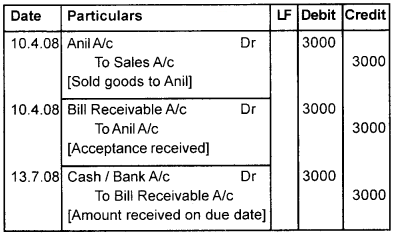
Book of Anil [Drawee] Journal
Question 4.
Haridas discounts a bill for Rs. 10,000 with his banker on 4th February, 2007. The bill was drawn on 1st January for Four months. The discount rate was 12%. p.a. write Journal entries in the book of Haridas.
Answer:
Book of Haridas [Drawer] Journal

Note: Calculation of discount
Discount = 10.000 × 12/100 × 3/12 = 300 It may be noted that discount has been charged for three months and not for 4 months because the bank will have to wait for 3 months to get the payment of bill on the due date.
Question 5.
From the given specimen of a promissory note identify:-
a) Promisor
b) Promisee
c) Consideration
Answer:

Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Four Mark Questions and Answers
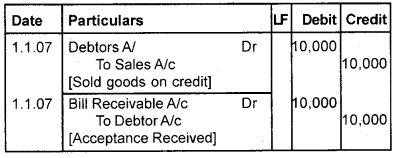
Question 1.
On January 1st, 2006, Ramesh sold goods worth ₹2,000 to Kannan and drew abill for the amount for 3 months. Kannan accepted the bill and returned it to Ramesh. Ramesh endorsed the bill in favour of Jayan, on 6th January. The bill was duly met on maturity. Pass journal entries in the book of Ramesh, Kannan and Jayan.
Answer:
Book of Ramesh [Drawer] Journal
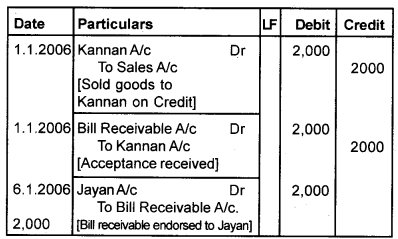
Book of Kannan [Drawee] Journal
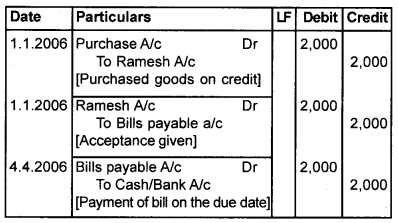
Book of Jayan [Endorser] Journal
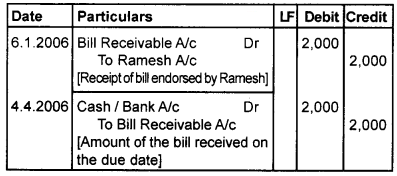
Question 2.
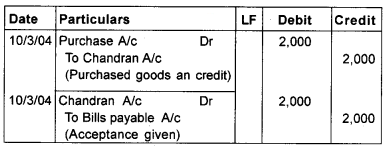
On 10th March 2004, Chandran drew and Devan accepted a 2 monthly bill for Rs. 2000. On April 11 Chandran sends the bill to his bank for collection. On due date the amount is collected. Give journal entries in the book of both the parties.
Answer:
Journal (In the book of Chandran)
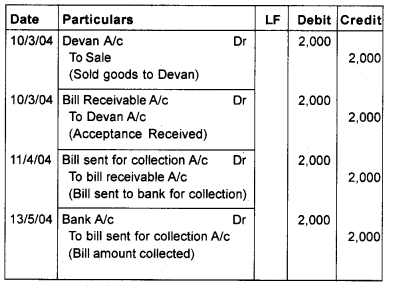
Journal (In the book of Devan)

Question 3.
On 1st June 2005, ‘A’ Sold goods to ‘B’ worth Rs.
20,000 and drew on him a bill for 3 months. ‘B’ accepted the same and returned to ‘A’. On 5th June 2005, ‘A’ discounted the bill with his banker and received Rs. 19,000. On the due date, ‘B’ failed to pay the amount and the bill got dishonoured. Pass journal entries in the books of A and B.
Answer:
Book of A [Drawer] Journal
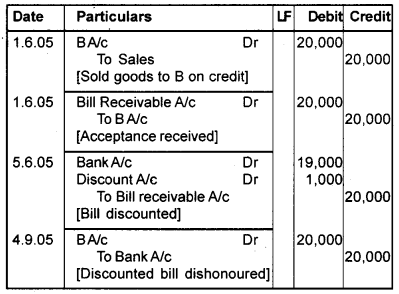
Book of B [Drawee] Journal
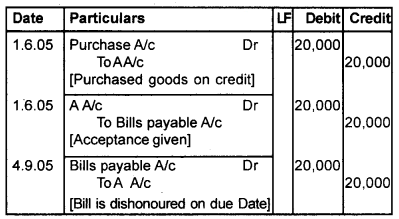
Question 4.
Identify the document shown below and state Any 6 features of the document.
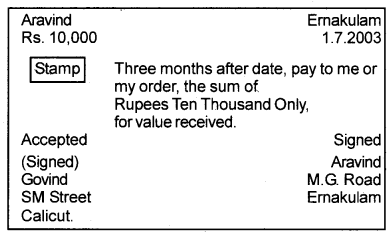
Answer:
Document is a Bill of Exchange.
Features:
- It contains an order to pay money.
- The order shortly be unconditional
- The drawer must sign the bill
- The drawee must be a certain person.
- The order must be for the payment of money only.
- It should be properly stamped.
Question 5.
From the given specimen of Bill of exchange, identify:
- Drawer
- Drawee
- Payee
- Term of bill
- Date of maturity
- Consideration on the bill

Answer:

Question 6.
Complete the following table.
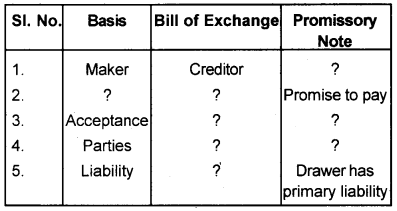
Answer:
- Debtor
- Order or promise, order to make payment
- Needs acceptance by drawee/does not need any acceptance.
- Three – Drawer, Drawee, Payee Two – Drawer and payee
- Drawer has secondary liability.
Question 7.
Complete the journal on the basis of the narration given for a bill of exchange of Rs. 20,000/-
Book of Santhosh Journal
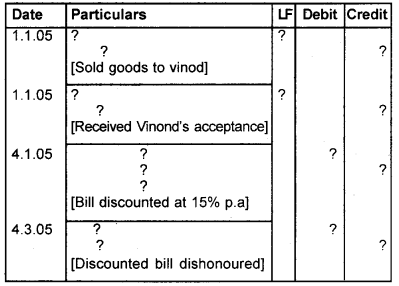
Answer:
Journal Book of Santhosh
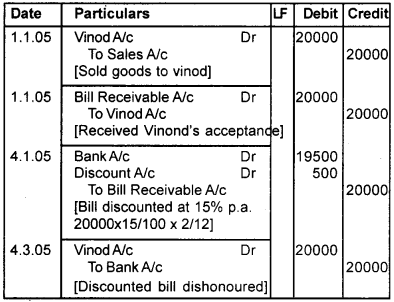
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
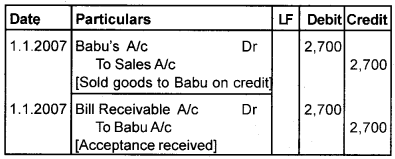
Ajay sold goods to Babu for Rs. 2,700 on 1.1.2007 and immediately drawn a bill for 4 months upon Babu for the same amount Babu accepted the bill and returned it to Ajay. On the 4th February 2007, Babu retires his acceptance under a rebate of 12% p.a. Give journal entries in the books of both the parties.
Answer:
Book of Ajay [Drawer] Journal
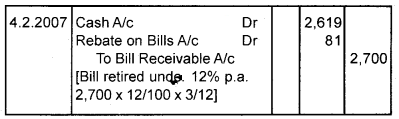
Book of Babu [Drawee] Journal
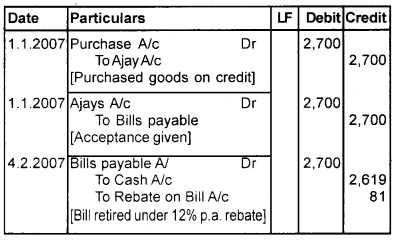
Question 2.
In a classroom debate Mohan argued that a bill of exchange and promissory note are same but syam disagree with him and states that they are different, whose argument is correct? Give reason.
Answer:
The argument of Syam is correct. There are some defference between bill of exchange and promissory note.
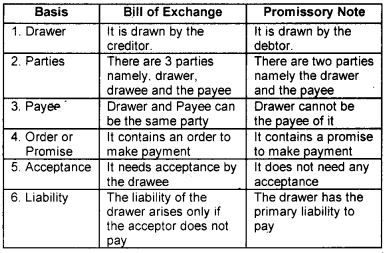
Question 3.
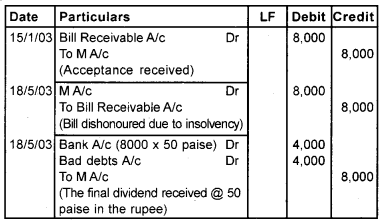
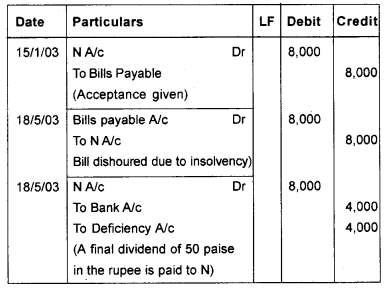
On January 15th, 2003 ‘N’ draw a bill of Rs. 8000 on his debtor ‘M’ for two months. By the due date of the bill, ‘M’ became insolvent and a dividend of 50 paise in the rupee was received from his estate. Pass Journal entries in the books of N and M.
Answer:
Journal (In the book of ‘N’)
Question 4.
Identify the types of endorsement from the given format and write short notes on each type.

Answer:
- Blank Endorsement: The endorser simply puts his signature, without mentioning the name of the endorsee.
- Special Endorsement: The endorser mentions the name of the endorsee along with his signature on the back of the Instrument.
- Restrictive Endorsement: Restrictlnq further endorsement.
- Sans – Recourse Endorsement: If the bill is dishonoured the holder cannot have recourse to the endorser.
- Facultative Endorsement: Endorsement made by waiving some right of the endorser.
Question 5.
The transaction between Rajesh and Murali are journalised below. Identify the drawer, drawee/acceptor, amount and term of bill. Also write appropriate narration to each transaction.
Book of Murali Journal
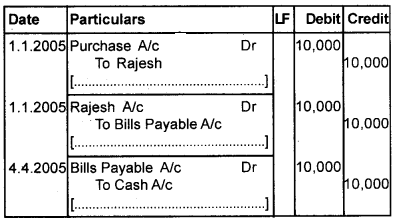
Answer:
- Drawer – Rajesh
- Drawee – Murali
- Amount of bill – 10,000/-
- Term of bill – 3 Months
- Narration:
- Purchased goods on credit
- Acceptance given on bill
- Bill amount paid on the due date
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Six Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
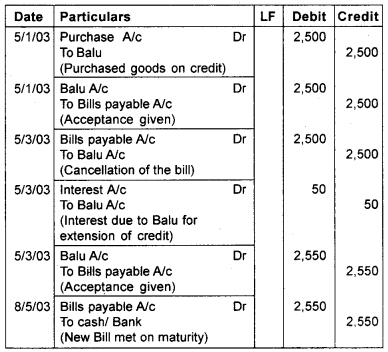
On 5th January 2003, Balu sold goods to Raju for Rs. 2500. Balu drew a 2 months bill on Raju. Raju accepted the bill and returned it to Balu. On 5th March Raju approached Balu with a request to renew the bill for a further period of 2 months. Balu agreed on the proposal for which an interest of Rs. 50 is charged. The second bill is duly accepted and was met on maturity. Give Journal entries in the book of Balu & Raju.
Answer:
Journal (In the book of Balu)
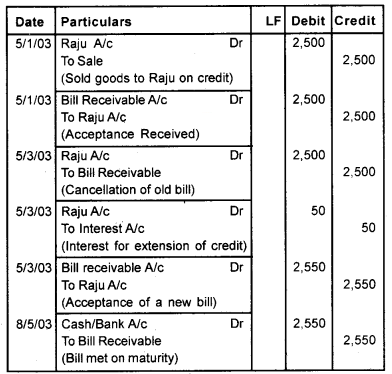
Question 2.
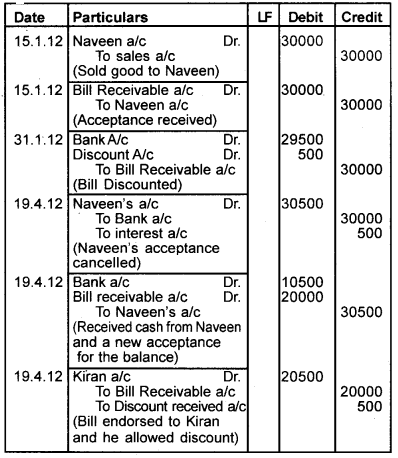
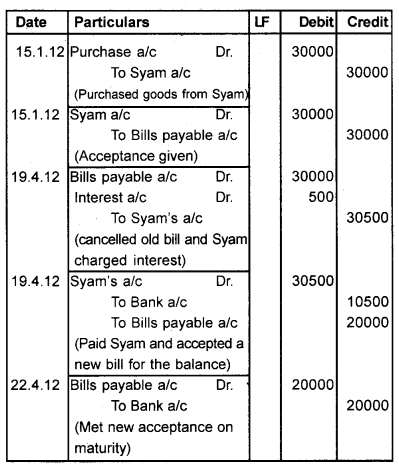
On January 15, 2012, ‘Syam’ sold goods to’ Naveen’ for Rs.30,000 and drew a bill for the same amount payable after 3 months. The bill was accepted by Naveen. The bill was discounted by Syam from his bank for Rs. 29,500 on January 31,2012. On maturity, the bill was dishonoured. He further agreed to pay Rs. 10,500 in cash including Rs.500 interest and accept a new bill for two months for the remaining Rs.20,000. The new bill was endorsed by Syam in favour of his creditor ‘Kiran’ for settling a debt of Rs.20500. The new bill was duly met by Naveen on maturity.
Record the Journal entries in the book of Syam and Naveen.
Answer:
Journal Entries (in the book of Syam)
Journal Entries (in the book of Naveen)
Plus One Accountancy Bill of Exchange Eight Mark Questions and Answers
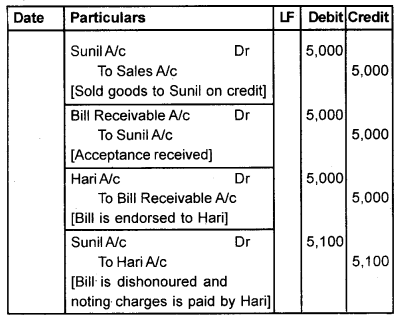
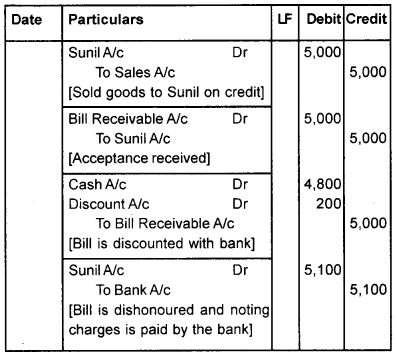
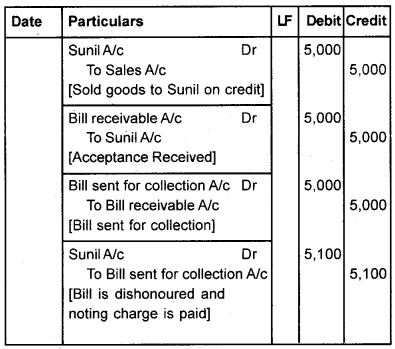
Question 1.
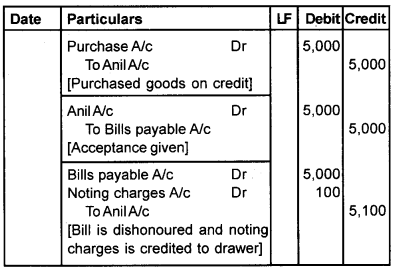
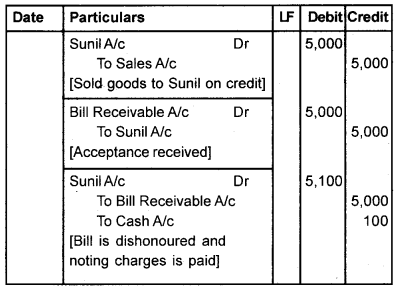
Mr. Anil sold goods to Sunil for Rs. 5,000 on credit and drew a bill for 3 months. Sunil accepted the bill and returned it to Anil. On the due date, the bill was dishonoured, noting charge being Rs. 100. Show journal entries in the books of Anil and Sunil, if
- The bill was retained by Mr. Anil.
- The bill was endorsed to Mr. Hari.
- The bill was discounted with the bank for Rs. 4,800.
- The bill was sent to the bank for collection.
Answer:
Book of Anil [Drawer] Journal
1. If the bill is retained
2. If the bill was endorsed to Mr. Hari.
3. If the bill is discounted with bank.
4. If the bill sent for collection
Book of Sunil [Drawee] Journal