Kerala Plus One Accountancy Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The source documents provide information about the nature of ……………. involved in it.
(a) Transactions
(b) Accounts
(c) Journal
Answer:
(a) Transactions.
Question 2.
Which of the following equation is correct?
a. Assets = Equities
b. Assets = Capital + Liabilities
c. Assets + Expenses = Liabilities + Capital + Income
d. Capital = A – L
(i) a & b
(ii) a, b & c
(iii) a, b, c & d
(iv) d only
Answer:
(iii) All the above four
Question 3.
Journal is the book of ……………
(a) Original entry
(b) Secondary entry
(c) Only cash transaction
Answer:
(a) Original entry.
Question 4.
An ……………. is a formal record of all transactions relating to change in a particular item,
(a) Account
(b) Ledger
(c) Journal
Answer:
(a) Account.
Question 5.
If a firm borrows a sum of money, there will be
(a) Increase in Capital
(b) Decrease in Capital
(c) No effect on Capital
Answer:
(c) No effect on capital
Question 6.
The Purchase day book contains
(a) All Purchases
(b) Cash Purchases
(c) Credit Purchases
Answer:
(c) Credit Purchases
Question 7.
Double column cash book records:-
(a) All transactions
(b) Cash and bank transaction
(c) Only cash transaction
(d) Only Credit transaction
Answer:
(b) Cash and bank transaction.
Question 8.
Goods purchased on cash are recorded in the
(a) Purchase book
(b) Sales book
(c) Cashbook
Answer:
(c) Cashbook
Question 9.
Cashbook does not record transactions of –
(a) Cash nature.
(b) Credit nature.
(c) Cash and credit nature.
Answer:
(b) Credit nature.
Question 10.
Balancing of account means:
(a) Total of debit side
(b) Total of credit side
(c) Difference in total of debit and credit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) The difference in total debit and credit
Question 11.
In sales daybook, all ………… sales of goods are recorded.
Answer:
Credit Sales.
Question 12.
The petty cashier generally works on ……… system.
Answer:
Imprest system.
Question 13.
The cash book serves the dual purposes of …………..
Answer:
a journal and a ledger.
Question 14.
When a transaction is recorded on both sides of the cash book but in different columns, such entry is called ……….
Answer:
Contra Entry.
Question 15.
The source document of purchase return is ………….
Answer:
Debit Note.
Question 16.
Cashbook is a …………. journal.
Answer:
Subsidiary.
Question 17.
Return of goods purchased on credit to the suppliers will be entered in …………. journal.
Answer:
Purchase Return/ Return outward book.
Question 18.
Assets are sold on credit are recorded in ……………….
Answer:
Journal Proper.
Question 19.
Credit balance shown by a bank column in cash book is ………..
Answer:
Overdraft.
Question 20.
A book maintained to record transactions, which do not find a place in a special journal, is known as …………..
Answer:
Journal proper/Journal Residual.
Question 21.
………………… records the page number of the original book of entry on which relevant transaction is recorded.
Answer:
Journal Folio.
Question 22.
Purchased office stationery for Rs. 10,000. The account to be credited is ……….
Answer:
Cash.
Question 23.
The book in which all accounts are maintained is known as ……….
Answer:
Ledger.
Question 24.
Trade discount is allowed by …………….
Answer:
Manufacturer.
Question 25.
…………….. is the process of transferring entries from the book of original entry to the ledger.
Answer:
Posting.
Question 26.
Cash discount is allowed by …………
Answer:
Creditor.
Complete the following on the basis of hints given:
Question 27.
Invoice – Source document of purchases
_____ – Source of sales return
Answer:
Credit Note
Question 28.
Bank Balance – Debit balance in cash book
__________ – Debit balance in pass book
Answer:
Bank overdraft
Question 29.
Pay-in-slip – Used for depositing cash in bank – account
________ – Used for withdrawing money from bank account
Answer:
Cheque
Find the Odd one and State the reason.
Question 30.
Sales Return, Return inward, Credit Note, Debit Note
Answer:
Debit Note, it is related to purchase return but all others are related to sales return.
Question 31.
Journal, Ledger, Purchase Bill, Cash Book
Answer:
Purchase Bill.
Question 32.
…………. discount is allowed by the wholesalers to retailers for bulk purchase.
Answer:
Trade discount.
Question 33.
The process of balancing .of an account involves equalisation of both sides of the account. If the debit side of an account exceeds the credit side, the difference is put on the credit side. The said balance is
(a) A credit balance
(b) A debit balance
(c) None of the above
Answer:
(b) debit balance.
Question 34.
Find out the missing one on the basis of hint given Salary, Electricity Charges, Rent, Telephone Charges = ……..
Answer:
Indirect Expenses
Question 35.
What does the following entry mean?
Drawings A/c Dr 5,000
To Office furniture A/c 5,000
Answer:
The entry stands for withdrawn furniture for personal use of the owner.
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of Double Entry Book-keeping?
Answer:
The recording of the debit aspect and the credit aspect of a transaction in the books of accounts is called double-entry bookkeeping. In this system, every transaction affects at least two accounts or each and every transaction has at least two aspects – a receiving aspect and a giving aspect.
Question 2.
What are the source documents?
Answer:
A voucher or source document is a written document to be used in support of entry made in the accounts. They provide information about the transaction involved and help in verifying the correctness of books of accounts. For example the receipts, bills, cash memos, invoices, salaries bill, wage bills, counterfoils of cheques, registration deeds, etc.
Question 3.
Indicate whether the following accounts will have ‘debit’ or ‘credit’ balances.
- outstanding salaries
- Return outwards
- Sales returns
- Carriage inward
- Bad debts recovered
- Depreciation
- Drawings
Answer:
- Outstanding salaries – Credit
- Return outwards – Credit
- Sales Returns – Debit
- Carriage inward – Debit
- Bad debts recovered – Credit
- Depreciation – Debit
- Drawings – Debit
Question 4.
X Co. Ltd supplied furniture to Mr. Ravi (a trader) on credit. At the time of examining the qualities of the furniture by Mr. Ravi, it was not as per the specification and he returns them to the X Co. Ltd.
- Can you suggest which book shall Mr. Ravi records the return of goods?
- Specify the source document.
Answer:
- Purchase Returns Book/ Purchase Returns Journal
- Debit Note
Question 5.
Pass Journal entry in the books of Saleem Stores during the month of April 2007.
- Commenced business with cash Rs. 6,000/-
- Furniture Rs. 40,000/- and building Rs. 70,000/-
Answer:
- Cash A/c Dr 6,000
- Furniture A/c Dr 40,000
- Building A/cDr 70,000
- To Capital A/c
[Being a Commenced business with cash, furniture, and building]
Question 6.
A cash A/c will never show a credit balance. Why?
Answer:
As a person cannot spend more than his receipts, the receipt side or the debit side of the cash book will always be more than or equal to the credit side. But, it will never be less than the credit side. Hence a cash book always shows a debit balance or nil balance but never credit balance.
Question 7.
Mr. Amal intends to start a computer software unit. He purchased a building for Rs. 3,00,000, for which a sum of Rs. 2,00,000 has been raised by availing a bank loan, and Rs. 75000 has been raised from his friend, Biju Mathew. Show this transaction by developing an accounting equation.
Answer:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital

Question 8.
List out the essential particulars to be contained in a sales bill.
Answer:
- Name and address of the firm.
- Date, Amount, Description of goods.
- Quantity, Signature, Seal, Bill no.
- Name of the Customer.
Question 9.
‘CH’ Ltd makes a purchases of Electrical goods from Arya electronics on credit. Being the goods despatched by Arya electronics is not as per specifications, CH Ltd returns them to the supplier.
- Can you suggest in which book shall CH Ltd. record the return of goods?
- Specify the source document.
Answer:
- Purchase return book or return outward book
- Debit Note
Question 10.
“Cash Book is both a journal and a ledger” Elucidate the statement.
Answer:
Cashbook is basically a journal because all entries relating to cash are first made in the cash book. But in the meantime, it serves the purpose of a ledger since it is drawn in the form of an account.
Question 11.
State any two transactions that increase and decrease capital.
Answer:
- Capital increases by net profit and fresh capital introduced.
- Capital decreases by drawings and net loss.
Question 12
State the three fundamental steps in the accounting process.
Answer:
The three fundamental steps in accounting are. ..
- Identifying financial transactions.
- Recording business transactions.
- Classifying business transactions.
Question 13.
What is a contra entry? Write contra entry transactions.
Answer:
When a transaction is recorded on both sides of the cash book but in different columns, such entry is called contra entry.
eg:
- Cash deposited in bank.
- Withdrawn from bank for office use.
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
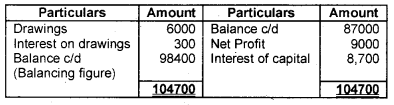
With the following details write up the capital account of Mr. X.
- Opening balance Rs. 87,000
- Drawings Rs. 6,000
- Net Profit Rs. 9,000
- Interest on capital Rs. 8700
- Interest on drawings Rs. 300
Answer:
Capital A/c of Mr.X
Question 2.
State the rules of debit and credit for all types of accounts.
Answer:
The term ‘debit’ is supposed to have derived from ‘debt’ and the term ‘credit’ from ‘creditable’. For convenience ‘Dr1 is used for debit and ‘Cr’ is used for credit. The effects of rules of debit and credit on various types of accounts are given as follows:
- Increase in asset is debit and decrease in asset is credit.
- Increase in liability is credit and decrease in liability is debit.
- Increase in capital is credit and decrease in capital debit.
- Increase in expenses is debit and decrease in expense is credit.
- Increase in revenue is credit and decrease in revenue is debit.
Question 3.
With the help of the given cash book identify the transactions of Sourya stores.
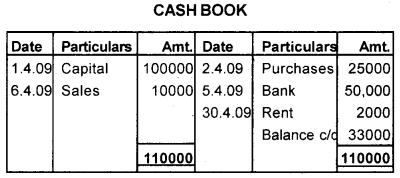
Answer:
- Started business with cash Rs. 1,00,000
- Sold goods for cash Rs. 10,000
- Purchased goods for cash Rs. 25,000
- Cash deposited into bank Rs. 50,000
- Rent paid Rs. 2,000
Question 4.
Enter the following transactions in a simple cash book for November 2014.

Answer:
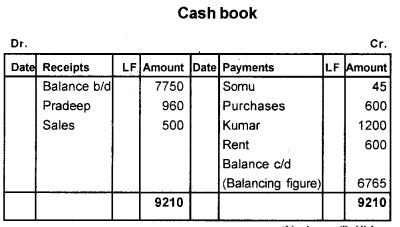
Question 5.
Give journal entries for the following transactions
- Ram started the business with cash Rs. 80,000/- Building Rs. 1,50,000/-Machinery Rs. 1,20,000/ – and stock of goods Rs. 50,000/-
- He purchased goods for Rs. 70,000 of which he paid Rs. 50,000 in cash and balance on credit from Mohan.
Answer:
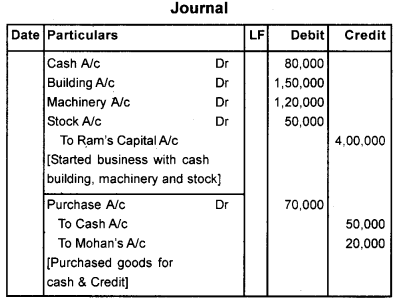
Question 6.
From the following, prepare the purchase return book of Madhamohan Readymade Garments.
- 10/4/09 – Returned to Decent & Co- 4 Shirts @ Rs. 54 per Shirt.
- 15/4/09 – Returned to Kurian & Sons – 2 Shirts @ Rs. 30 per Piece
- 17/4/09 – Returned to Sapna Garments – 1 Churidar @ Rs. 100 per Piece.
Answer:
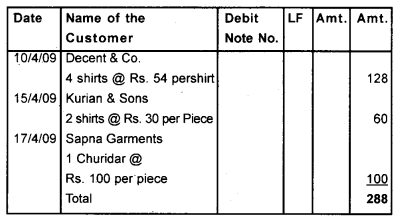
Question 7.
From the following prepare sales daybook of Harihar Furniture Co.
- 1/10/08 – Sold on credit to Tendulkar – 4 tables @ Rs. 2000 and 20 chairs @ Rs. 300
- 10/10/08 – Sold to Ganguly -10 tables@ Rs. 1000 and 3 chairs @ 900,Trade discount 10%.
- 12/10/08 – Sold to sreenath, 2 tables @ Rs. 1000.
Answer:
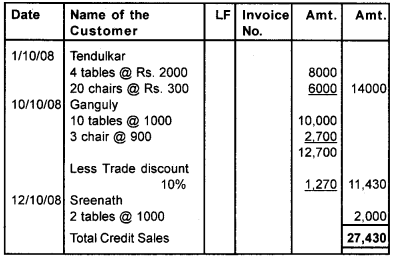
Question 8.
Enter the following transactions in Sales Return Day Book of Cochin furniture.
- 4/10/09 – Mahesh & Co. returned 3 chairs @ 300
- 15/10/09 – Raveendran Traders returned 2 tables @ Rs. 3600
- 16/10/09 – Jayanath Agencies returned 2 chairs @ Rs. 200
Answer:
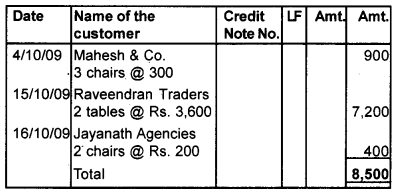
Question 9.
List out the appropriate source documents for recording the following transactions.
- Purchased goods
- Rent paid
- Electricity charges paid
- Salary paid
- Repair charges paid
- Water charges paid
Answer:
- Invoice/Bill
- Receipt from house owner
- Receipt from KSEB
- Payroll
- Payment Voucher
- Receipt from water authority.
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1
Explain the terms:
- Journal
- Narration
- Account
- Ledger
Answer:
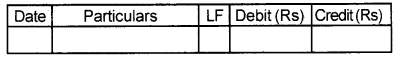
1. Journal:
Journal is the prime book in which transactions are entered first time from a source document. In other words, it is the book used for making primary record of day-to-day transactions chronologically. Recording of transactions in the journal is known as “Journalizing” and the recorded transactions are called journal entries. It is also called “Book of Original Entry or Book of Prime Entry”. A specimen form of a journal is given below.
2. Narration:
After entering each transaction in the journal, a brief explanation is provided below. This is called narration.
3. Account:
An account is a classified summary of transaction relating to a change in a particular item during a particular period.
4. Ledger:
A ledger is a collection of all accounts debited or credited in journals. The ledger is a book of second entry or final entry because transactions first entered in journal are finally incorporated in the ledger. It is also called “the Main or the Principal Book of Account of a business. The process of transferring journal entries into ledger is called “posting”.
Question 2.
What are the difference between books of original entry or journal and ledger?
Answer:
Journal | Ledger |
| 1. Book of primary or initial entry | 1. Book of secondary entry |
| 2. Transactions are entered in the order of their occurrence. | 2. Entries are recorded in an analytical order |
| 3. The process of entering transactions is called journalizing. | 3. The process of recording is called posting. |
| 4. Balancing is not done in the books of original entry. | 4. All ledger accounts are balanced |
Question 3.
What do you understand by petty cash book?
Answer:
The book maintained by the petty cashier to record small payments of repetitive nature (petty payments) ie stationery, postage, carriage, traveling, etc are made by him during a particular period is called the “petty cash book”.
The petty cashier works under the supervision and control of the main cashier who advances a certain amount to the petty cashier in the beginning of a specific period. The petty cashier is permitted to make payments only below a particular limit.
Question 4.
Give an example of a business transaction that causes one asset to increase and another asset to decrease, with no effect on either liabilities or capital.
Answer:
Purchased Machinery for cash Rs. 10,000 or any other similar transaction. Here Machinery increases and cash decreases. Therefore no change happens on the total value of assets.
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Five Mark Questions and Answers
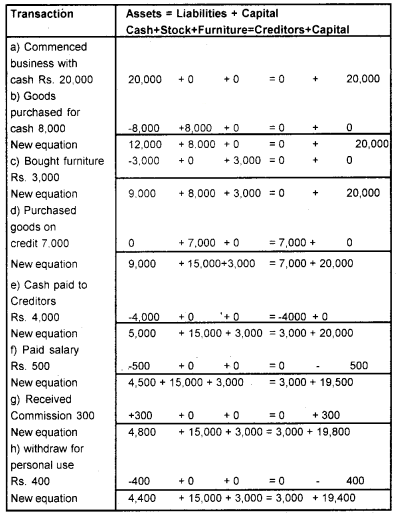
Question 1.
Prove that the accounting equations is satisfied in all the following transaction of Chikku.
- Commenced business with cash Rs. 20,000/-
- Goods purchased for cash Rs. 8,000/-
- Bought furniture Rs. 3,000/-
- Purchased goods on credit Rs. 7,000/-
- Cash paid to creditors Rs. 4,000/-
- Paid salary Rs. 500
- Received commission Rs. 300
- Withdraw for personal purpose Rs. 400.
Answer:
Question 2.
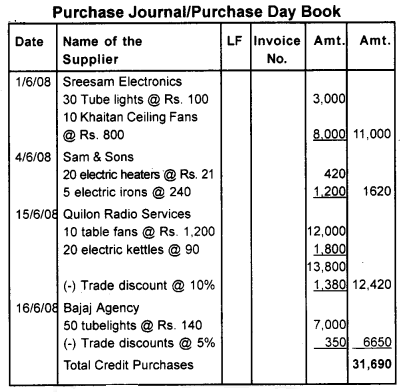
Record the following transactions in the purchase Journal of Suraj Agencies.
- 1/June/2008 -Purchased from sreeman Electronics 30 Philips Tube lights @ Rs. 100 10 Khaitan Ceiling Fans @ Rs. 800
- 4/June/2008 -Purchased from Sam & Sons 20 electric heaters @ Rs. 21 5 electric irons @ 240.
- 15/June/2008 – Purchased from Quilon Radio Services. 10 table fans @ Rs. 1200. 20 electric kettles @ 90. Less Trade discount @ 10%
- 16/June/2008 – Purchased from Bajaj Agency 50 Tii.be lights @ Rs. 140. Less Trade discount @ 5%.
Answer:
Question 3.
What is a special (subsidiary) Journal? Name the important special journals.
Answer:
The journals in which transactions of similar nature only are recorded may be termed as special journals or daybooks. The division of original entry into different Daybook is called the subdivision of the journal. The important special journals are:
- Cash Book – for recording all cash transactions.
- Purchases Day Book – for recording all the credit purchases of goods.
- Sales Day Book – for recording all the credit sale of goods.
- Purchase Return Book – for recording goods returned to suppliers.
- Sales Return Book – for recording goods returned by customers.
- Bill Receivable Book – for recording bill received from customers.
- Bill Payable Book – for recording bills given to suppliers.
- Journal Proper – If specialised journals are kept the journal is used only for recording those transactions that cannot be recorded in other journals. In this case the journal is known as Journal Proper or General Journal.
Question 4.
What is journal proper? Write the transactions recorded in journal proper.
Answer:
A book maintained to record transactions that do not find place in a special journal is known as journal proper or journal residual.
Transactions recorded in journal proper are as follows:
- Opening and closing entry.
- Adjustment entry.
- Rectification entries.
- Transfer entries.
- Sale or purchase of assets on credit.
- Entries for endorsement and dishonor of bills of exchange.
- Goods are withdrawn for personal use.
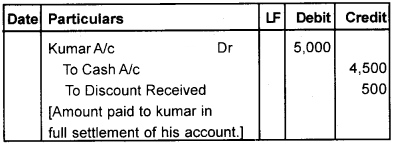
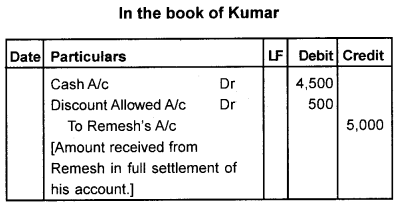
Question 5.
1. Remesh owes Kumar Rs. 5,000. He makes payments of the amount before the due date and Kumar allows him a discount of Rs. 500.
2. Narendran sold to Ravi goods of the catalog price of Rs. 50,000 at a trade discount of 10%. Pass Journal entries in the two cases.
Answer:
Question 6.
What do you understand by petty cash book? Write the advantages of petty cash book.
Answer:
The book maintained by the petty cashier to record small payments of repetitive nature (petty payments) ie stationery, postage, carriage, traveling, etc are made by him during a particular period is called the “petty cash book”.
The petty cashier works under the supervision and control of the main cashier who advances a certain amount to the petty cashier at the beginning of a specific period. The petty cashier is permitted to make payments only below a particular limit.
Advantages of maintaining petty cash book:
- Saving of time and effort of the chief cashier. He can concentrate on cash transactions involving large amounts of cash.
- Effective control over cash disbursement. Cash control becomes easy because of the division of work.
- Convenient recording.
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Six Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
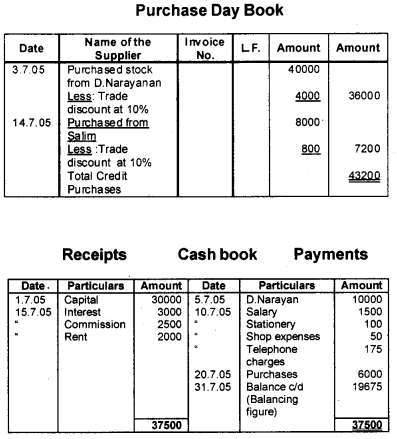
Prepare necessary subsidiary books from the following transactions
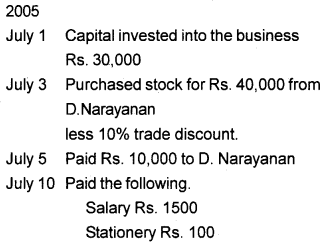

Answer:
Question 2.
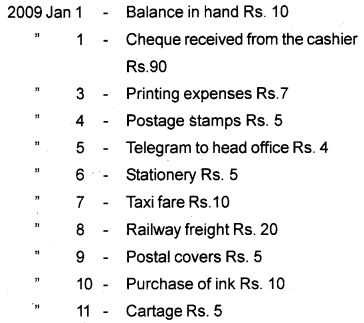
Answer:
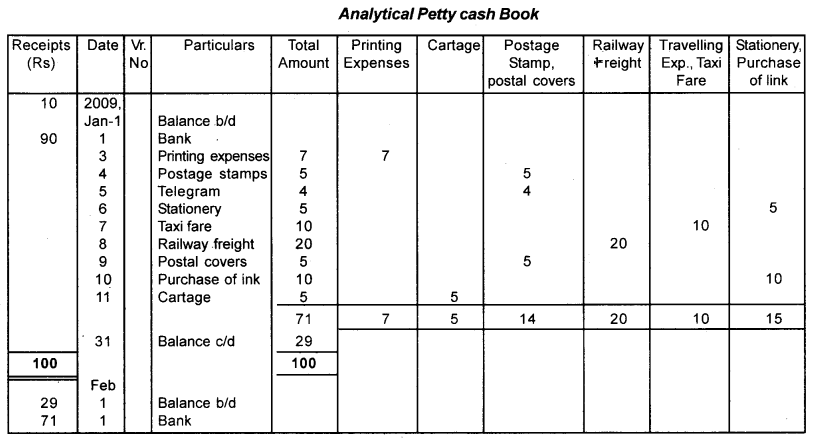
Question 3.
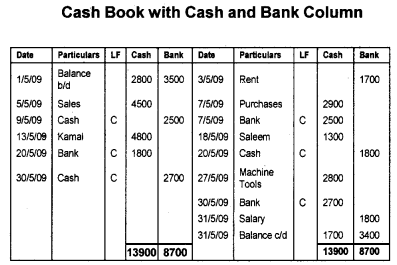
Record the following transactions in a Double column Cash Book.
- 1/5/09 – Opening balance of cash Rs. 2,800 1/5/09 – Opening balance of bank Rs. 3,500 3/5/09 – Rent paid by cheque Rs. 1,700 5/5/09 – Cash sales Rs. 4,500 7/5/09 – Purchases made Rs. 2,900.
- 9/5/09 – Deposited into bank Rs. 2,500.
- 13/5/09 – Received from Kamal Rs. 4,800.
- 18/5/09 – Paid to Saleem Rs, 1,300.
- 20/5/09 – Withdrawal from bank Rs. 1,800.
- 27/5/09 – Paid for purchase of machine tools Rs. 2,800.
- 30/5/09 – Deposited into bank Rs. 2,700.
- 31/5/09 – Salary paid by cheque Rs. 1,800.
Answer:
Plus One Accountancy Recording of Transactions – I & Recording of Transactions – II Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Journalise the following transactions:- 2008 April
- Started business with cash – 30,000
- Opened Bank Account – 12,000
- Purchased Furniture – 2,000
- Purchased goods – 10,000
- Withdrawn from bank for office – 6000
- Goods sold for cash – 8,000
- Cash purchases from John – 5,000
- Cash sales to Rajan – 4,000
- Cash withdrawn for personal use – 500
- Withdrew from bank for personal use 1000
- Goods withdrawn for personal use 3000
- Goods purchased on credit from Jagan 3000
- Goods sold to Dinesh on credit 4000
- Cheques issued to Jagan 4000
- Goods returned to Jagan 1500
- Goods returned by Dinesh 2000
- Received commission 200
- Paid to Alex Rs. 2000, Discount allowed by him Rs.200
- Received from Bonoy Rs.4000, allowed him a discount Rs. 300.
Answer:
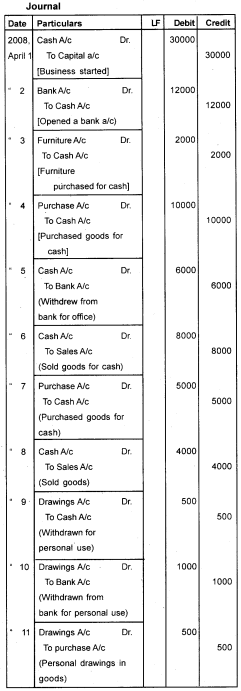
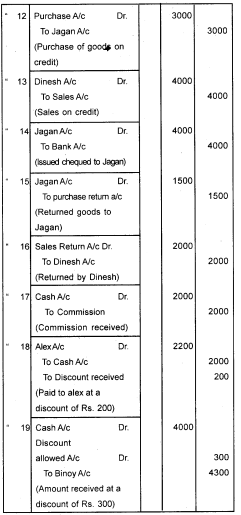
Question 2.
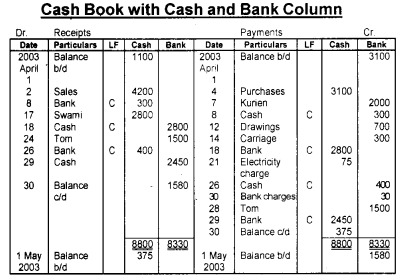
Prepare a cash book with cash and bank column from the following transactions.


Answer: