Kerala Plus One Accountancy Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting
Plus One Accountancy Introduction to Accounting One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Who among the following are not a user of accounting information?
(a) Management
(b) Investors
(c) Advertisers
(d) Lenders
Answer:
(c) Advertisers
Question 2.
Spot the odd one out and state reason
(a) Loose Tools
(b) Copy Write
(c) Patent
(d) Goodwill
Answer:
(a) Loose Tools, is a Fixed assed, all others are intangible assets.
Question 3.
A Person who owes money to the business is a
(a) Debtor
(b) Investor
(c) Creditor
(d) Borrower
Answer:
(a) Debtor
Question 4.
Book-keeping is concerned with
(a) Analysis of transaction
(b) Recording of transaction
(c) Classification of transaction
Answer:
(b) Recording of transaction
Question 5.
Amount spent for purchasing fixed asset is a
(a) Revenue Expenditure
(b) Capital Expenditure
(c) Deferred Revenue Expenditure
Answer:
(b) Capital Expenditure.
Question 6.
Which quantitative characteristics of accounting in-formation is reflected when accounting information is clearly presented?
(a) Understandability
(b) Relevance
(c) Comparability
(d) Reliability
Answer:
(a) Understandability.
Question 7.
Which of the following is an example of a business transaction?
(a) Appointed Mr.Ram as the Manager of the business with a salary of Rs. 15,000.
(b) Obtain a loan of Rs. 1,00,000 to the business from Bank of India.
(c) Sent a quotation to Matha Traders worth Rs. 20,000.
Answer:
(b) Obtained a loan of Rs. 1,00,000 from Bank of India. Loan is taken meant for business. So it is a business transaction.
Question 8.
Find the odd one out and state the reasons,
(a) share capital
(b) Debentures
(c) Sundry creditors
(d) Long-term loans.
Answer:
(c) Sundry creditors, all others are long term liabilities.
Question 9.
Value of goods remaining unsold at the end of an accounting period is termed as …………
Answer:
Closing Stocks
Question 10.
Arun, a sole trader, draw Rs. 500 from the business for paying tuition fees to his child. This amount is termed as ……….
Answer:
Drawings.
Question 11.
Assets minus liabilities are called ……….
Answer:
Capital.
Question 12.
………….. assets are those assets, which do not have any real value.
Answer:
Fictitious Assets.
Question 13.
The amount earned by a business concern through sale of its products or providing services to customers is called ……
Answer:
Revenues.
Question 14.
The assets bought for long-term use in the business are termed as …………….. assets
Answer:
Fixed.
Question 15.
Analysis of recorded data to bring entries of similar nature to one plane is called …………..
Answer:
Classifying.
Question 16.
A Person who is entitled to get money from the business is termed as …………
Answer:
Creditor
Question 17.
Information in financial reports is based on …………….. transaction.
Answer:
Economic.
Question 18.
All claims against the business are called ………………..
Answer:
Equity
Question 19.
The transaction is one wherein payment or receipt of money is postponed for a future date.
Answer:
Credit transaction.
Question 20.
Mr. Ismail, who is the owner of a Provision shop, took 50 kg. of rice worth Rs. 600 for his house-hold use. He should record this as
Answer:
Drawings.
Question 21.
Ravi, a trader purchased 100 notebooks from ‘Shyni stores’ on credit. How is Shyni stores related to Ravi?
Answer:
Shyni stores is the creditor of Ravi.
Question 22.
Who was the inventor of double-entry bookkeeping?
Answer:
Luca Pacioli
Question 23.
Expand AICPA
Answer:
The American Institute of Certified Public Accounts.
Question 24.
Identify the events not used to the accounting treatment.
(a) Commenced business with cash
(b) Bought Machinery for cash
(c) Cash Purchase of goods.
(d) The firm appointed an efficient Manger.
Answer:
(d) The firm appointed an efficient Manger.
Plus One Accountancy Introduction to Accounting Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define Accounting.
Answer:
According to American Institute of certified Public Accountants, “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are in part, at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.”
Question 2.
‘Accounting is the language of the business’. Why?
Answer:
Accounting is the language of the business:
The performance of the business in terms of profit or losses is conveyed to users of accounting information in a systematic manner. The financial position of the business concerned is revealed through accounting information.
Question 3.
“Raju sold goods to Rahim on credit”. What relation exists between them? What are the accounting terms involved in it?
Answer:
- Rahim – Debtor
- Raju – Creditor
Question 4.
You are the accountant of a firm. What are the functions to be performed by you?
Answer:
Accounting provides information regarding the financial status of a business and results of its operations. The following are the important functions of accountant of a firm.
- Recording transactions by referring source documents.
- Preparing journal, subdivision of journal.
- Preparing ledger accounts.
- Summarising.
- Making statements of interpretation 0 Reporting to Management.
Question5.
Users of accounting are classified as under:
- Internal users – Management, Investor, Creditor, Bank, Employees, Stock exchange.
- External Users – Customers, Government, Researchers, Lenders.
Do you agree with this classification, if not correct it?
Answer:
No,
1. Internal Users:
- Management
- Employees
2. External Users:
- Investors
- Creditors
- Bank
- Stock Exchange
- Government
- Customers
- Lenders
- Researchers
Question 6.
All business transactions are events. But all events are not business transactions. Comment.
Answer:
Events can be anything, some events can be expressed in monetary terms while others are not. Only those events which can be expressed in money, terms are business transactions. Transaction is an event or economic activity of a businessman in his business having exchange of money or money’s worth. While events are part of the business transaction.
Question 7.
Classify the following expenses into capital expenditure and revenue expenditure.
- Machinery purchased
- Rent paid
- Interest paid
- Purchased building
- The amount for repair of the building
Answer:
1. Capital Expenditure:
- Machinery Purchase
- Purchased building
2. Revenue Expenditure:
- Rent paid
- Interest
- paid Amount for the repair of the building
Question 8.
How will you define Revenue and Expenses?
Answer:
1. Revenue:
These are the amounts earned by a business concern through the sale of its products or providing services to customers. The common items of revenues are sales, the commission received, rent received, interest received, etc.
2. Expenses:
The amount spent in the process of earning revenue is termed as expenses. Examples are Wages, Salaries, rent, Interest paid, electricity charges, etc.
Question 9.
What is a capital expenditure? Give some examples?
Answer:
Capital expenditure represents the amount spent for the acquisition of assets, the benefit from which is derived over a period that extends beyond the accounting year. It is long term in nature.
Examples: Furniture purchased, Land Purchased, Building purchased, etc.
Question 10.
Explain the meaning of Gain and Profit.
Answer:
1. Profit: The excess of revenues of a period over its related expenses during an accounting year is profit. Profit increases the investment of the owners.
2. Gain: A profit that arises from events or transactions which are incidental to business such as the sale of fixed assets, winning a court case, receipt of interest and dividend, etc. Gain is irregular in nature. Gains are part of a capital receipt. Gains are also known as “non-operating income.”
Question 11.
Match the following.

Answer:

Question 12.
Name the branches of accounting.
Answer:
- Financial Accounting
- Cost Accounting
- Management Accounting
Plus One Accountancy Introduction to Accounting Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following assets into suitable head Goodwill, Building, Land, Patent, Cash, Oilwell, Copy-write, Debtors, Stock, mines, Bill receivable, Preliminary expenses.
Answer:
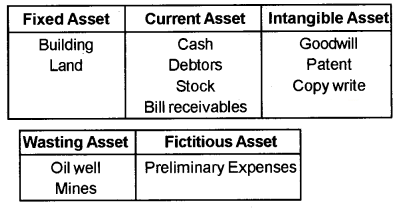
Question 2.
Define assets, Liabilities, and capital.
Answer:
1. Assets:
Assets are properties and things of value owned by the business which can be expressed in monetary terms. Examples of Machinery, Buildings, Stock, Debtors, Furniture, etc.
2. Liabilities:
Liabilities are the obligations that an enterprise owes. These represent the amount payable by the business in the future. They represent the claim against the asset of the business. Examples Loans, Creditors, Bills payable, etc.
3. Capital:
Capital is the investment made by the owners for use in the business. It is the owner’s claim on the total assets of the business and is also called “owners equity”.
Question 3.
Distinguish between:
- Goods and Assets
- Expense and Loss
Answer:
1. Goods and Assets:
- Goods refer to things in which the trader deals. But assets refers to things with which the trader deals.
- Goods are meant for resale, while assets are kept in the business permanently with the help of which the business is carried on.
2. Expense and Loss:
- Costs incurred by a business in the process of earning revenue are known as expense.
- The excess of expenses of a period over its related revenues is termed as loss. It decreases in owner’s equity.
Plus One Accountancy Introduction to Accounting Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Accounting has certain objectives to business Explain.
Answer:
The following are the important objectives of accounting.
- Keeping of records of business transactions.
- Ascertainment of Profit or Loss.
- Ascertainment of financial position of business enterprises.
- Providing meaningful information to different groups of people having interest in the business.
1. Keeping of records of business transaction:
The main purpose of accounting is to identify business transactions of financial nature and enter into appropriate books of accounts. The accounting records should be made properly and systematically, so that requisite information may be obtained at a glance.
2. Ascertainment of Profit or Loss:
The result of business (Profit or Loss) is available from the statement prepared for ascertaining it, called the Profit and Loss Account.
3. Ascertainment of financial position:
At the end of an accounting year, a position statement is known as the ‘Balance Sheet’ is prepared. The value of assets and liabilities are depicted in the Balance Sheet. The Balance sheet gives a true and fair view of the state of affairs of the concern.
4. Providing meaningful information to different groups of people having an interest in the business:
Accounting records provide meaningful information to different groups of people having an interest in the business.
Question 2.
Accounting information must possess certain qualitative characteristics. What are they?
Answer:
The following are the qualitative characteristic of accounting information.
- Reliability: Accounting information will be reliable if it is free from error and faithfully represents what it seeks to represent.
- Relevance: Information should be relevant and must be available on time.
- Understandability: Accounting information that is relevant must be capable of being understood by all its users.
- Timeliness: Information must be available timely. If not, it loses its ability to influence decisions.
- Comparability: Accounting information should facilitate inter-firm comparison as well as interfirm comparison.
Maximum Cputtishers
Question3.
Accounting and Book-keeping are viewed as distinct functions. Mention any four differences between Accounting and Book Keeping.
Answer:
| Book-Keeping | Accounting |
| 1. It is concerned with the presentation of primary books of accounting. | 1. It deals with the recording, analysis, and final Interpretation of data. |
| 2. It has limited scope | 2. It has a wider scope. |
| 3. In book-keeping, the level of work is less. This work is done by junior staff. | 3. The level of work is high. |
| 4. It does not show the net result and financial position of the business. | 4. It shows the profit of the business and the net worth of the business. |
Question 4.
“Accounting gives number of advantages to the business”. What are the important advantages of accounting?
Answer:
The following are the advantages of accounting
1. Provide Quantitative information:
Accounting helps in gathering quantitative information on profits earned by the business or loss sustained by them.
2. Helps in ascertaining financial position of the business that is, total assets owned and total liabilities owed.
3. Helps in making a systematic record of transactions, which can be used for future reference and appropriate retrieval.
4. Acts as an information system:
It provides adequate information to the interested users in a processed form.
5. Beneficial to different interested users of accounting information.
Question 5.
Accounting has certain ‘Limitations’. Explain.
The following are the limitations of accounting.
Answer:
1. It records only transactions which can be recorded in monetary terms:
Qualitative aspects like managerial skill, Services of experts, etc. are not recorded.
2. Accounting is a post mortem survey:
It records events as they have taken place. For example, expenses are recorded as incurred, assets are recorded at their cost of purchase. There is no scope for ascertaining what the appropriate expenditure or cost of acquisition should have been.
3. Effect of price level changes are not considered:
Transactions are always recorded in the books at cost price and not at market price.
4. Inexactness:
Accounting transactions are not exact. Different firms have their own different methods, so the results of the business will change in the practice.
Plus One Accountancy Introduction to Accounting Six Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the different types of assets? Explain briefly.
Assets are things of value owned. They may be subdivided into the following.
Answer:
1. Fixed Assets:
Fixed Assets are assets held on long term basis, such as land, buildings, machinery, plant, furniture, etc. These assets are used for the normal operations of the business.
2. Current Assets:
These are assets held on a short-term basis such as debtors, bills receivables, stock, cash in hand, cash at bank, etc. It is also known as “Floating asset.”
3. Fictitious Assets:
These are those assets, which do not have a physical form. They do not have any real value. Actually, they are not the real assets but they are called assets on legal and technical grounds. Examples are preliminary expenses, discount on issue of shares or debentures, etc.
4. Tangible Assets:
Assets having physical existence which can be seen, touched are known as tangible assets. These assets are land, building, plant, equipment, etc.
5. Intangible Assets:
These assets have no physical existence which cannot be touched, seen or felt. Examples are Goodwill, trademark, patent, copyright.
6. Wasting Assets:
Assets, whose value goes on declining with the passage of time, are known as wasting assets. Mines, oilwells, quarries are its examples.
7. Liquid Assets:
Liquid assets are those assets, which can be converted into cash at short notice. Examples of liquid assets are cash in hand, cash at bank, debtors, bills receivable, etc. Liquid assets = Current Assets – (Stock + Prepaid Expenses)
Question 2.
“Accounting provides information to various users.” Discuss accounting as an information system.
Answer:
Accounting plays a significant role in society by providing information to management at all levels (internal users) and to those having a direct financial interest in the enterprise (external users), such as present and potential investors, creditors. Accounting information is also important to those having an indirect financial interest, such as regulatory agencies, tax authorities, customers, labour unions, stock exchange, and others.
Internal users, mainly management, need timely information on cost of sales, profitability, etc. for planning, controlling and decision making. External users who have limited authority, ability and resources to obtain the necessary information have to rely on financial statements. The external users are interested in the following.
1. Investors and Potential investors:
Information on the risks and returns on investments.
2. Suppliers and Creditors:
Information on whether amounts owed will be repaid when due and on the continued existence of the business.
3. Customers:
Information on the continued existence of the business and thus the profitability of a continued supply of products, parts, and after-sales services.
4. Employees:
They are interested in getting their salary, welfare measures, bonus, working conditions, etc. which are all related to financial performance of the business.
5. Lenders:
Information on the creditworthiness of the business and its ability to repay loans and pay interest.
6. Government and other regulators:
Information on the allocation of resources and the compliance to regulators.
