Kerala Plus One Accountancy Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
Question 1.
Depreciation of a fixed asset is an example of ________ (March 2010)
a) revenue expenditure
b) capital expenditure
c) deferred revenue expenditure
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Revenue expenditure
Question 2.
Under the ______ method, depreciation remains the same from year to year. (March 2010)
Answer:
Straight-line method
Question 3.
Fixed instalment method is also called _________ (March 2010)
a) Straight-line method
b) Re-evaluation method
c) Depletion method
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Straight-line method
Question 4.
Depletion method of depreciation is used for _________ (March 2010)
a) cattle, loose tools, etc.
b) mines, quarries, etc.
c) machinery, building, etc.
Answer:
b) mines, quarries, etc.
Question 5.
Under the ______ method, depreciation goes on reducing from year to year. (March 2010)
Answer:
Reducing Balance/Diminishing/Written down value method
Question 6.
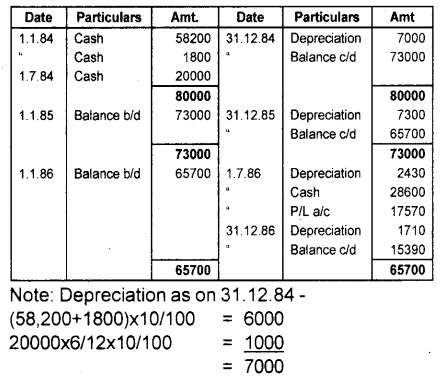
A firm purchased machinery for ₹ 58,200 on 1st January 1984 and spent ₹ 1,800 on its erection. On 1st July 1984, additional machinery costing ₹ 20,000 were purchased. On 1st July 1986, the machinery purchased on 1st January 1984 was sold for ₹ 28,600. Provide depreciation at the rate of 10% on the written down value. Give the machinery account for 1984 to 1986. (March 2010)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Question 7.
Reserves can be classified into _______ reserves and revenue reserves. (March 2011)
a) revenue
b) asset
c) capital
d) liability
Answer:
c) Capital Reserve
Question 8.
Under the _____ method, depreciation goes on decreasing from year to year. (March 2011)
Answer:
Diminishing balance/Reducing balance/written down value method
Question 9.
While calculating depreciation, _______ is deducted from the total cost. (March 2011)
Answer:
a) additional purchases of assets
b) scrap value
c) provision for depreciation
Answer:
b) Scrap value
Question 10.
Reserve is a _______ of profit. (March 2011)
Answer:
Appropriation/Adjustment of profit
Question 11.
Machinery was purchased for ₹ 10,000 and ₹ 1,000 spent on its installation. The market value of the machinery is ₹ 15,000. The cost that should be recorded is ₹ _________ (March 2011)
Answer:
₹ 11,000
Question 12.
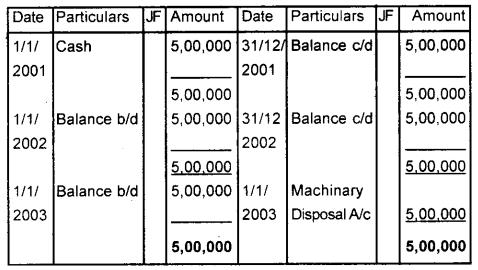
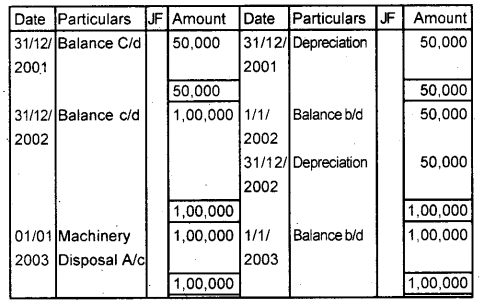
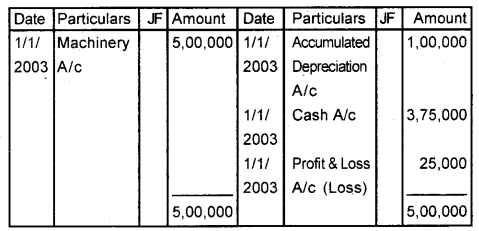
A firm purchased machinery for ₹ 5,00,000 by cash on 1st January 2001. Depreciation is charged at 10% of the original cost and depreciation transferred to the Depreciation Provision account On 1st January 2003, the machinery was sold for ₹ 3,75,000. Show the Machinery account, Accumulated Provision for Depreciation account, and Machinery Disposal account. (March 2011)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Accumulated Depreciation A/c
Machinery Disposal A/c
Question 13.
Profit on sale of machinery is __________ (March 2012)
a) capital profit
b) revenue profit
c) deferred revenue expenditure
d) capital reserve
Answer:
a) Capital profit
Question 14.
The amount of depreciation should be accurately estimated and accounted for _________ (March 2012)
a) to present a true Balance Sheet
b) to avoid excess payment of Income Tax
c) to fulfill legal requirements
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 15.
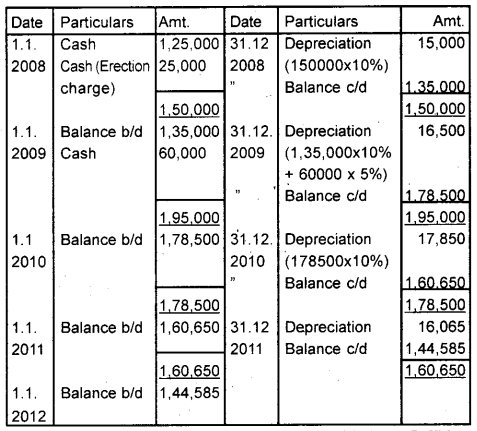
A company purchased machinery costing ₹ 1,25,000 on 1st January 2008 and spent ₹ 25,000 on its erection. On 1st July 2009, additional machinery was purchased for the value of ₹ 60,000. The company decided to write off depreciation at 10% p.a. Prepare the machinery account for the first 4 years under the diminishing balance method. (March 2012)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Question 16.
Under the diminishing balance method, depreciation provided in the initial years will be higher. True/False. (September 2012)
Answer:
True
Question 17.
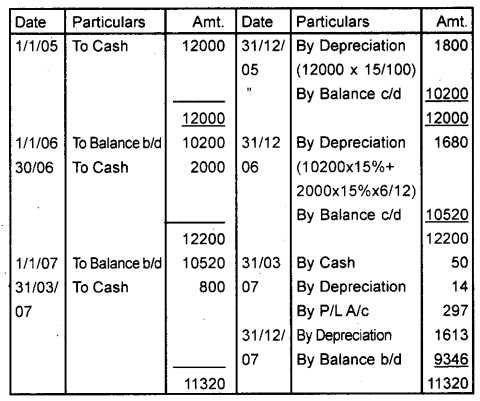
On 1 st January 2005 a limited company purchased machinery for ₹ 12,000, and on 30th June 2006, it acquired additional machinery at a cost of ₹ 2,000. On 31st March 2007, one of the original machines which had cost ₹ 500 was found to have become obsolete and was sold as scrap for ₹ 50. It was replaced on that date by a new machine costing Rs. 800. Depreciation is to be provided @ 15% p.a. on the written down value. Show the Machinery A/c for the first 3 years. (September 2012)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Question 18.
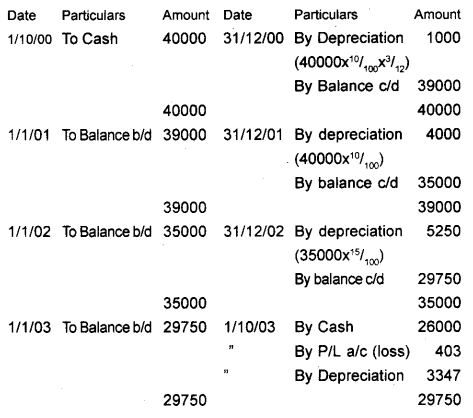
On 1 st October 2000 a firm purchased machinery for ₹ 40,000. Depreciation was provided at 10% per annum on the straight-line method and accounts were closed on 31 st December every year. With effect from 1st January 2002, the firm decided to change the method of depreciation to diminishing balance method @ 15% p.a. On 1st October 2003, the machinery was sold for ₹ 26,000. Prepare Machinery Account from 2000 to 2003. (September 2012)
Answer:
Machinery A/c

Question 19.
Granite quarry is an example of ________ assets. (March 2013)
a) Intangible
b) Wasting
c) Fictitious
d) Tangible
Answer:
b) Wasting
Question 20.
A company bought machinery at a cost of ₹ 8200 and spent ₹ 800 on erection charges. It is estimated that its working life is 4 years and the value of scrap is ₹ 1000. Calculate the amount of annual depreciation. (March 2013)
Answer:
Depreciation = \(\frac{(8200+800)-1000}{4}\) = 2000
Question 21.
On 1st January 2001, Saraswathy Traders purchased a machine at a cost of ₹ 46,000. The erection charges of ₹ 4,000 were paid separately. It was decided to charge depreciation @ 10% on a straight line. On 30th June 2005, the machinery was sold for ₹ 30,000. Write up the machinery account. (March 2013)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
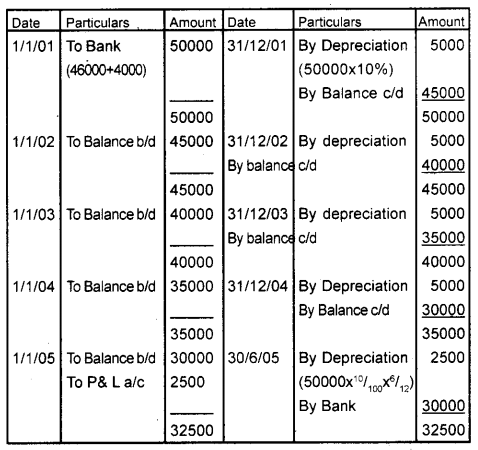
Note: Selling price = 30000
Value of machinery on the date of sale = (30000 – 2500) = 27500
Profit on sale of machinery = 2500
Question 22.
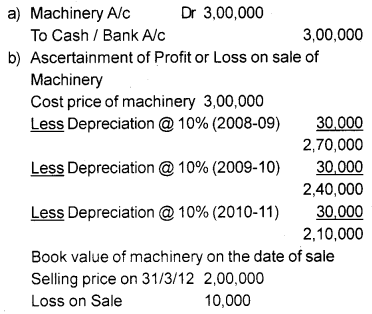
Star Ltd. purchased machinery for ₹ 2,90,000 and spent ₹ 10,000 on its installation on 1st April 2008. After using it for 3 years, it was sold for ₹ 2,00,000 on March 31, 2011. Depreciation is to be provided at 10% on the fixed installment method.
a) Pass a journal entry for recording the purchase of machinery.
b) Find the amount of profit/loss on the sale of machinery assuming that the accounting year closes on 31 st March every year. (March 2013)
Answer:
Question 23.
Erection charges of machinery are debited to the _______ (March 2014)
a) Profit and Loss A/c
b) Sundry Expenses A/c
c) Machinery A/c
d) Trading account
Answer:
c) Machinery a/c
Question 24.
Introduction of the latest technologies may be one of the causes for _______ (March 2014)
a) depletion
b) amortization
c) appreciation
d) depreciation
Answer:
Obsolescence
Question 25.
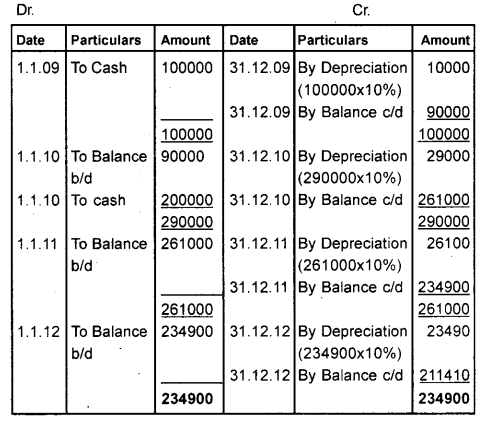
Mr.Noel, a sole trader bought a building for ₹ 1,00,000 on 01.01.2009. Further, he constructed another building which was completed on 01.01.2010. He spent ₹ 2,00,000 for this. Depreciation was charged at the end of every year on 31 st December on the diminishing balance method @ 10%. Draw the building account till 2012. (March 2014)
Answer:
Building A/c
Question 26.
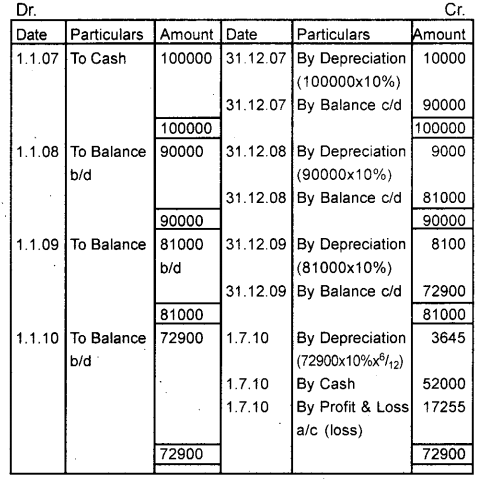
Mahesh Enterprises purchased machinery for ₹ 1,00,000 on 1 st January 2007. Depreciation is to be charged @ 10% per annum under the diminishing balance method. On 1st July 2010, the machinery was sold for ₹ 52,000. Show the machinery account. (March 2014)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Question 27.
John and Co. purchased machinery for ₹ 42,000 on 1.1.2010. The estimated life of machinery is 10 years and its scrap value is ₹ 2,000. On 1.7.2012, the machinery was sold for ₹ 38,000.
Depreciation is charged under the straight-line method. (March 2015)
a) Calculate the actual amount of depreciation.
b) Prepare the Machinery account from 2010 to 2012.
Answer:
a) Depreciation = \(\frac{42000-2000}{10}\) = 4000
b) Machinery A/c
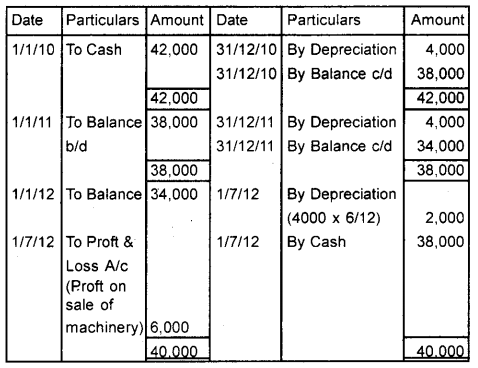
Note:
Proft on sale of machinery Cost of machinery as on 1/7/12
(34000 – 2000) = 32,000
The selling price of machinery = 38,000
Proft on Sale = 6,000
Question 28.
On 1st July 2012, a firm purchased a plant worth ₹ 40,000. The firm writes-off depreciation @ 10% on the original cost. The accounts are closed on 31st December every year. If the plant is sold for ₹ 35,000 on 1st July 2013, prepare the Plant account upto this date. (March 2015)
Answer:
Plant Account
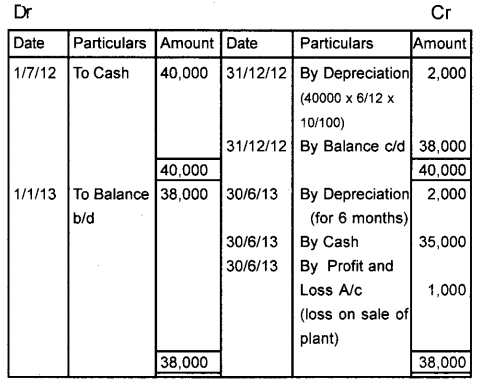
Note:
Loss on Sale of plant
Value of plant as on 30/6/2013 = 38000 – 2000 = 36000
Selling Price = 35000
Loss on sale = 1000 (35000 – 36000)
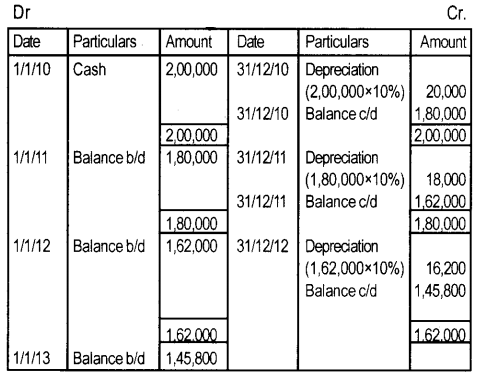
Question 29.
Given below is the transaction relating to the purchase and sale of vehicles by the tour operators for the purpose. 01-01-2010 Purchase of vehicles ₹ 2,00,000. The firm has employed a written down value method for calculating depreciation. The rate being 10% and the accounting year ends on 31st December every year. Prepare vehicles to account for three years. (September 2015)
Answer:
Vehicle A/c
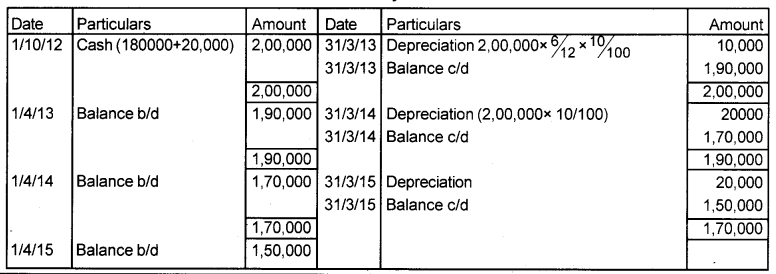
Question 30.
Kannan and Sons acquired a machine for ₹ 1,80,000 on 10th October 2012, and spend ₹ 20,000 on its installation. The firm write-off depreciation at the rate of 10% p.a. on original cost every year. Draw up machinery account for the first 3 years given that the books of accounts close on March 31st, every year. (March 2016)
Answer:
Machinery A/c
Question 31.
SK associates purchased secondhand machinery on 1st October 2009 for ₹ 60,000 and spent ₹ 10,000 for its repairs. They also spent ₹ 5,000 on its installation. Another machinery was purchased for ₹ 20,000 on 1st April 2010. Depreciation is charged @ 10% on a written down value basis.
a) Prepare Machine A/c upto 31st March 2012 assuming the accounts are closed on 31st March every year.
b) Find the profit if the machinery purchased on 1st October 2009 were sold on 31st March 2011 for ₹ 68,000. (March 2016)
Answer:
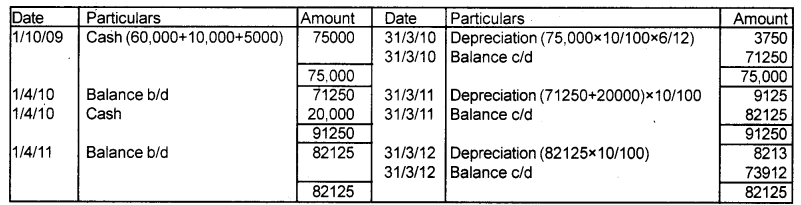
b) Cost of machinery (Purchased on 1/10/09) = 75,000
Less depreciation (3750 + 7125) = 10875
Valueof machinery on 31/11/11 = 64125
Sales value of machinery = 68,000
Profit on sale of machinery = +3875
Question 32.
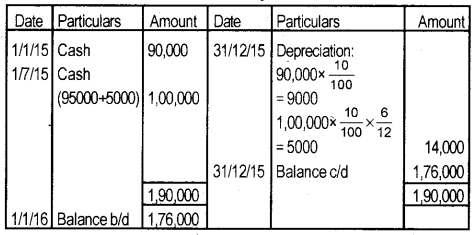
A company purchased machinery costing ₹ 90,000 on 01/01/2015. On 01/07/2015 another machinery was purchased for ₹ 95,000. The installation cost was ₹ 5,000. Provide depreciation at the rate of 10% per annum. Show the machinery account for the year 2015. Assume that book is closed on 31/12/2015. (September 2016)
Answer:
Machine A/c
Question 33.
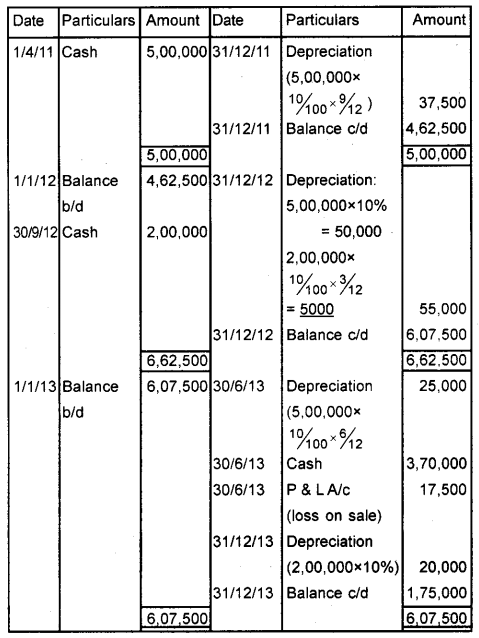
Machinery was purchased by Kefcon Ltd., for ₹ 5,00,000 on 1st April 2011. It purchased additional machinery for ₹ 2,00,000 on 30th September 2012. The machinery purchased on 1 st April 2011 was sold for ₹ 3,70,000 on 30th June 2013. Depreciation is to be charged at 10% p.a. under the straight-line method. (March 2017)
a) Prepare machinery account upto 31 st December 2013 books are closed on 31st December each year.
b) Make correct pairs form the following on the basis of the hint given.
(Hint: Current Assets: Fluctuation)
i) Depreciation
ii) Depletion
iii) Wasting Assets
iv) Fixed Assets
Answer:
Machinery A/c
b) Depreciation – Fixed Assets
Depletion – Wasting Assets
Question 34.
Writing off the cost of intangible assets is termed as _______ (March 2017)
a) depreciation
b) depletion
c) amortization
d) obsolescence
Answer:
c) amortization
Question 35.
a) Mention the name of the reserve that is created out of revenue profits.
b) How does it differ from capital reserve? (March 2017)
Answer:
a) Revenue Reserve/General Reserve
b) Difference between Revenue Reserve and Capital Reserve
| Revenue Reserve | Capital Reserve |
| i) It is created out of business profits. | i) It is created out of capital profits. |
| ii) It can be utilised for distribution of dividend | ii) It cannot be utilised for distribution of dividend |
| iii) It is created to strengthen the financial position | iii) It is created for compliance with legal requirements or accounting practices |
